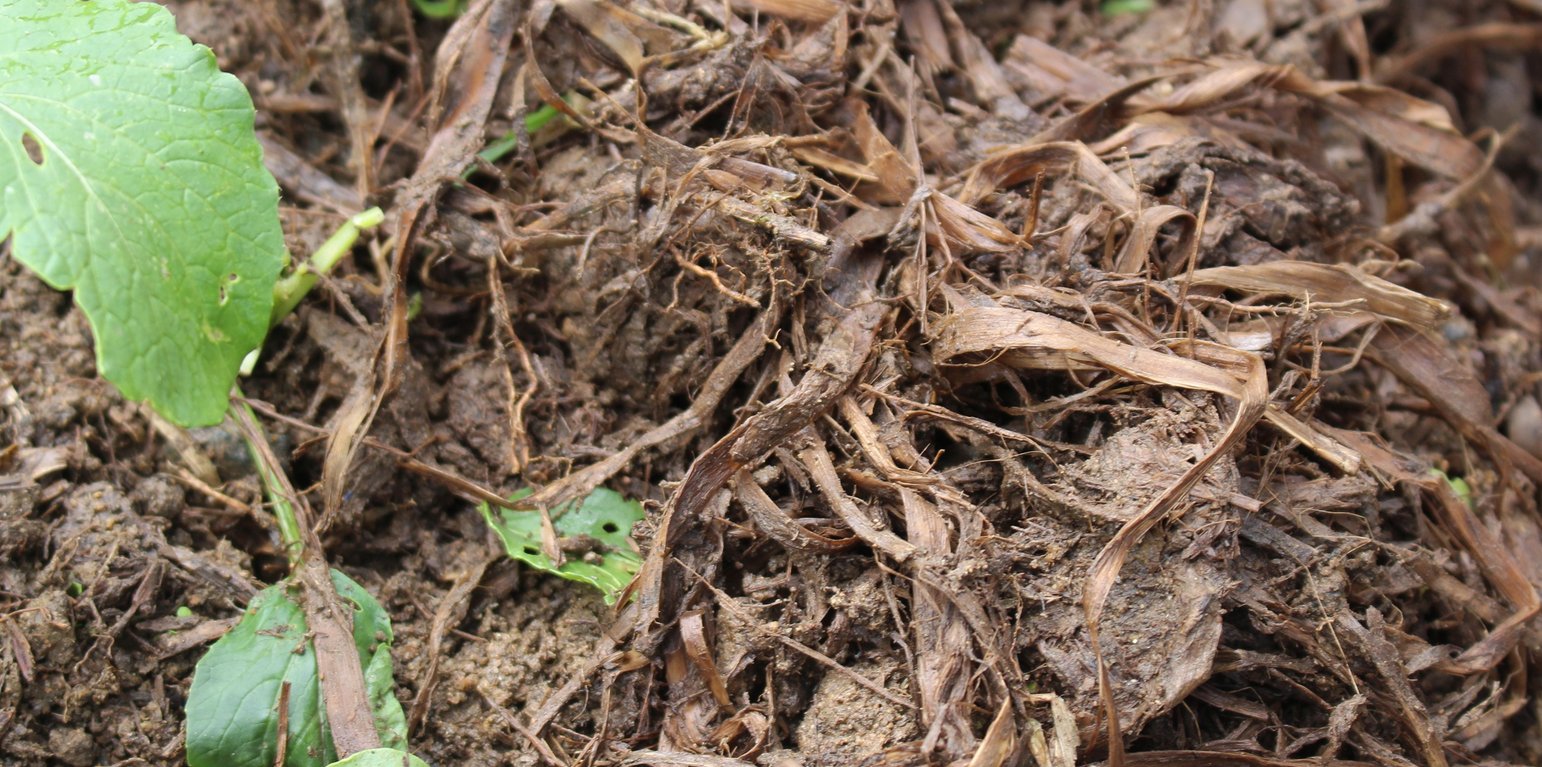




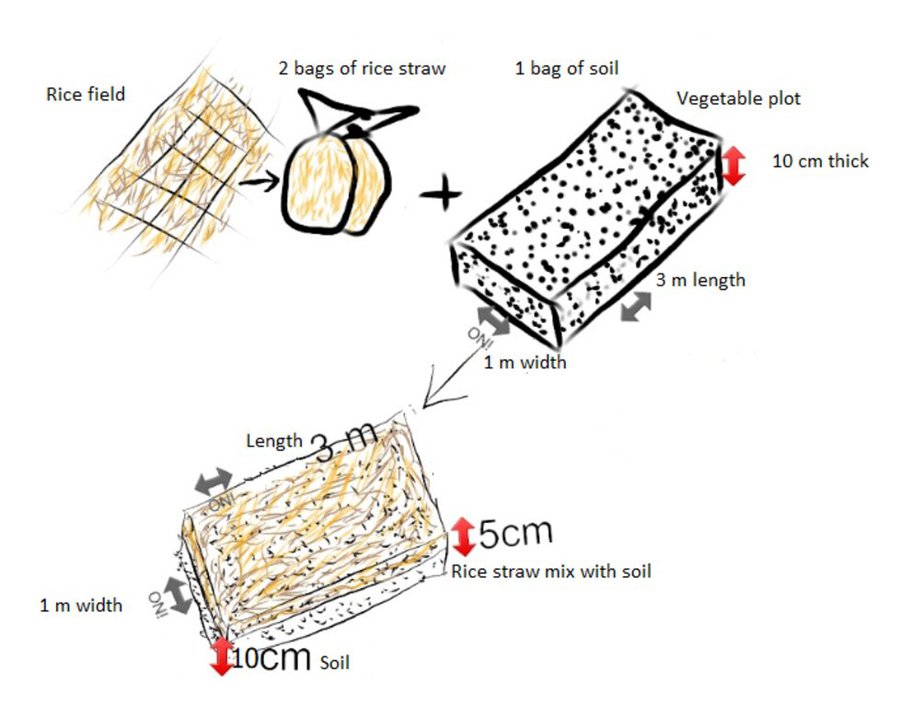
ເຕັກນິກການເຮັດຝຸ່ນເຟືອງ ແມ່ນເປັນເຕັກນິກ ທີ່ໄດ້ລິເລີ່ມ ໂດຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ຢຸ່ບ້ານດາກຕະອອກນ້ອຍ ເມືອງດາກຈືງ ແຂວງເຊກອງ ສປປລາວ ຊື່ງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ແມ່ນໄດ້ລິເລີ່ມ ທົດລອງ ຄົ້ນຄິດເຮັດຝຸ່ນເຟືອງ ໃນປີ 2014 ເນື່ອງຈາກວ່າ ໃນເມື່ອກ່ອນ ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ເຄີຍໃຊ້ພຽງແຕ່ ຝຸ່ນຄອກ (ຂີ້ງົວ ແລະ ຂີ້ຄວາຍ) ເພື່ອປັບປຸງດິນ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ປູກຜັກສວນຄົວ ແຕ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ດິນ ກໍ່ຍັງໄດ້ພົບບັນຫາ ບົ້ງຫຼາຍ ແລະ ເກີດມີເພ້ຍ ຢູ່ໃນສວນຜັກ ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ເຮັດໃຫ້ຜົນຜະລິດຜັກບໍ່ງາມ ແລະ ບໍ່ສາມາດ ຂາຍເປັນສິນຄ້າໄດ້. ດັ່ງນັນ, ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ຈື່ງມີແນວຄວາມຄິດ ລິເລີ່ມ ທົດລອງ ເກັບເອົາເຟືອງ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈາກນາຕົນເອງ ພາຍຫຼັງ ການເກັບກ່ຽວເຂົ້າ ໃນເດືອນຕຸລາ ທີ່ປະໄວ້ປະມານ 4 ຫຼື 5 ເດືອນ ຈື່ງໄປເກັບເອົາເຟືອງທີ່ເປື່ອຍຈາກນາ ມາໃສ່ພື້ນທີ່ປູກຜັກ ແລະ ໄດ້ສັງເກດເຫັນວ່າ ພື້ນທີ່ດັ່ງກ່າວນັ້ນ ດິນມີຄວາມອຸດົມສົມບູນຂຶ້ນ ທີ່ສົ່ງດີເຮັດໃຫ້ ດິນມີຄວາມຊຸ່ມຊຶ່ນ ແລະ ເພີ່ມສານອາຫານໃນດິນ. ດັ່ງນັ້ນ, ຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ຈຶ່ງໄດ້ທ້ອນເຟືອງໄວ້ເປັນກອງ ຢູ່ທົ່ງນາ ພາຍຫຼັງ ສຳເລັດການເກັບກ່ຽວເຂົ້ານາ ເພື່ອເປັນການບົ່ມເຟືອງໃຫ້ເສດເຟືອງເນົ່າເປື່ອຍ ກ່ອນນຳມາໃຊ້. ໂດຍປົກກະຕິແລ້ວ, ຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ນຳເອົາເສດເຟືອງ ມາເຮັດຝຸ່ນເຟືອງ ຈຳນວນ 2 ຄັ້ງ ຕໍ່ ປີ. ໃນຄັ້ງທີ່ 1 ແມ່ນເຮັດໃນເດືອນຕຸລາ ພາຍຫຼັງເກັບກ່ຽວເຂົ້ານາ ໃນຊ່ວງທີ່ຝົນບໍ່ໍຕົກຫຼາຍ ແລະ ໃນຄັ້ງທີ່ 2 ແມ່ນເຮັດໃນເດືອນມັງກອນ ເຖິງ ເດືອນກຸມພາ. ວັດຖຸດິບ ທີ່ສຳຄັນ ໃນການເຮັດຝຸ່ນເຟືອງ ແມ່ນເສດເຟືອງ ແລະ ດິນ ເພື່ອປະສົມເຂົ້າກັນ. ສຳລັບອຸປະກອນ ກໍ່ມີພຽງແຕ່ກ່ຽວເຂົ້າ ໄວ້ຕັດເຟືອງ, ກະສອບ ໃສ່ເສດເຟືອງ ແລະ ສຽມ ເພື່ອໃຊ້ເຂົ້າໃນການກະກຽມ ພື້ນທີ່ປູກຜັກ. ວິທີການເຮັດຝຸ່ນເຟືອງ ແມ່ນນຳເອົາເສດເຟືອງ ຈຳນວນ 2 ກະສອບ (ປະມານ 20 ກິໂລກຣາມ) ແລະ ປະສົມເຂົ້າກັບດິນ 1 ກະສອບ (10 ກິໂລກຣາມ) ແລ້ວກໍ່ສາມາດນຳໄປໃຊ້ຄຸມໜານປູກຜັກ ທີ່ໄດ້ກະກຽມດິນໄວ້ເລີຍ (ກ່ອນເອົາເບ້ຍຜັກມາບົງ). ຫຼັງຈາກ, ການນໍາໃຊ້ຝຸ່ນເຟືອງ ຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ເຫັນວ່າ ຜັກສາມາດ ຂະຫຍາຍຕົວໄດ້ດີ ໂດຍບໍ່ມີສັດຕູພືດ ຫຼື ແມງໄມ້ລົບກວນ. ດິນໄດ້ຄ່ອຍໆປ່ຽນເປັນສີດຳເຂັ້ມ ຂື້ນກວ່າເກົ່າ ເຊິ່ງເປັນຕົວຊີ້ບອກ ຂອງຄວາມອຸດົມສົມບູນ ຂອງດິນ. ສົ່ງຜົນເຮັດໃຫ້ ຜະລິດຜັກເພີ່ມຂື້ນ ແລະ ຊາວກະສິກອນ ຍັງສາມາດ ປູກພືດຜັກ ໄດ້ຫຼາຍຊະນິດ ລວມທັງ ຜັກບົ່ວ ແລະ ຜັກຫອມປ້ອມ ຊື່ງກ່ອນຫນ້ານີ້ ບໍ່ສາມາດປູກໄດ້. ໃນປະຈຸບັນ, ຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ສາມາດສ້າງແຫຼ່ງລາຍຮັບ ໃນຄອບຄົວ ໂດຍການຂາຍຜັກ. ນອກຈາກນັ້ນ, ການນໍາໃຊ້ຝຸ່ນເຟືອງ ຍັງສາມາດປັບຕົວ ເຂົ້າກັບການປ່ຽນແປງ ດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ໂດຍສະເພາະ ແມ່ນໃນຊ່ວງເວລາ ທີ່ມີຝົນຕົກຫນັກ, ເນື່ອງຈາກວ່າ ດິນໄດ້ຖືກປົກຫຸ່ມ ໂດຍເຟືອງ, ມັນສາມາດ ປ້ອງກັນການເຊາະລ້າງ ຂອງໜ້າດິນ ຈາກນ້ຳຝົນ. ໂດຍທົ່ວໄປແລ້ວ, ປະຊາຊົນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ ມີຄວາມພໍໃຈ ກັບເຕັກນິກນີ້ ເພາະວ່າມັນໄດ້ ໃຊ້ພຽງແຕ່ແຮງງານ ໃນການເກັບເຟືອງ ຊື່ງຊາວກະສິກອນ ສາມາດເຮັດໄດ້ ໂດຍທີ່ບໍ່ມີຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເພີ່ມເຕີມ. ວິທີການນຳໃຊ້ຝຸ່ນເຟືອງ ກ່ອນອື່ນແມ່ນ ຂຸດໜານຜັກ ເລິກປະມານ 15 ຊັງຕີແມັດ, ຫຼັງຈາກນັ້ນ ໃຊ້ຝຸ່ນເຟືອງທີ່ກຳລັງເປື່ອຍ ມາປະສົມກັບດິນ ທີ່ກຽມໄວ້ ຢູ່ໜານຜັກ ແລ້ວເອົາມາຄຸມດິນ ໜາປະມານ 10 ຊັງຕີແມັດ, ໃນໜານຜັກ ທີ່ມີຂະໜາດຄວາມກວ້າງ 1 ແມັດ, ຍາວ 3 ແມັດ, ແລ້ວຈື່ງເອົາເບ້ຍຜັກລົງປູກ ໄລຍະຫ່າງ ລະຫວ່າງເບ້ຍ ປະມານ 15 ຊັງຕີແມັດ ຫຼື ຫວ່ານແກ່ນພັນຜັກໃສ່ເລີຍ. ຈາກນັ້ນ, ກໍ່ນຳເອົາເຟືອງສົດ ທີ່ກຳລັງເປື່ອຍ ມາປົກປະມານ 5 ຊັງຕີແມັດ ອີກເທື່ອໜື່ງ ເພື່ອປ້ອງກັນນ້ຳຝົນ ຫຼື ເພື່ອຮັກສາຄວາມຊຸ່ມຂອງດິນ. ຊ່ອງຫວ່າງ ລະຫວ່າງ ໜານຜັກຄວນຫ່າງ ປະມານ 20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ ເພື່ອສະດວກໃນການຍ່າງໄປມາ ພາຍໃນເນື້ອທີ່ສວນປູກຜັກ ທັງໝົດ 25 ຕາແມ້ດ.
Location: ບ້ານດາກຕະອອກນ້ອຍ ເມືອງດາກຈືງ, ແຂວງເຊກອງ, Lao People's Democratic Republic
No. of Technology sites analysed: single site
Spread of the Technology: evenly spread over an area (approx. < 0.1 km2 (10 ha))
Date of implementation: 2014; less than 10 years ago (recently)
Type of introduction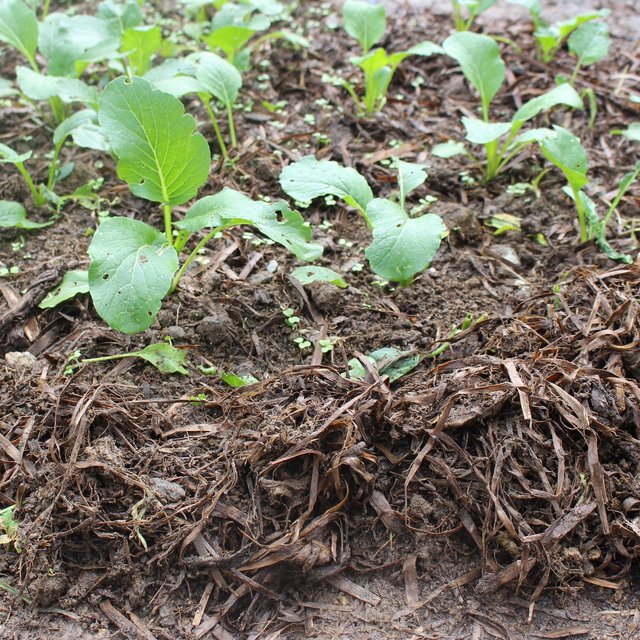







| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (ກີບ) | Total costs per input (ກີບ) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| ແຮງງານ ເກັບເສດເຟືອງ | ວັນງານ | 4.0 | 50000.0 | 200000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | |||||
| ຈົກ | ດວງ | 1.0 | 50000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| ກະສອບ | ກະສອບ | 30.0 | 2000.0 | 60000.0 | 100.0 |
| ສຽມ | ດວງ | 1.0 | 35000.0 | 35000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 345'000.0 | ||||
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (ກີບ) | Total costs per input (ກີບ) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| ແຮງງານ ເກັບເສດເຟືອງ | ວັນງານ | 2.0 | 50000.0 | 100000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | |||||
| ຈົກ | ດວງ | 1.0 | 50000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| ກະສອບ | ກະສອບ | 30.0 | 2000.0 | 60000.0 | 100.0 |
| ສຽມ | ດວງ | 1.0 | 35000.0 | 35000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 245'000.0 | ||||
Quantity before SLM: 25 ມັດ
Quantity after SLM: 30 ມັດ
ສານອິນຊີ ໃນດິນ ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ ເຮັດໃຫ້ດິນ ມີຄວາມອຸດົມສົມບູນ ສົ່ງຜົນໃຫ້ ຜົນຜະລິດຜັກ ກໍ່ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ.
ກ່ອນຫນ້ານ້ີ ດິນບໍ່ງາມ ສົ່ງຜົນເຮັດໃຫ້ ຄຸນນະພາບ ຂອງຜັກກ່ໍບໍ່ງາມ. ພາຍຫັຼງ ນໍາໃຊ້ຝຸ່ນເຟືອງແລ້ວ ເຫັນວ່າ ດິນມີຄວາມອຸດົມສົມບູນຂື້ນ.
ຜົນຜະລິດຜັກກຸ້ມກິນ ພາຍໃນຄອບຄົວ ພ້ອມມທັງສາມາດ ຂາຍເປັນສິນຄາ້ ສາມາດສ້າງລາຍຮັບໄດ້
ເປັນການເພີ່ມວຽກ ເນ່ືອງຈາກຕ້ອງ ໄປເກັບເສດເຟືອງ ພາຍຫັຼງ ສໍາເລັດການເກັບກ່ຽວເຂົ້ານາ ແລ້ວມາກອງໄວ້ ເພື່ອເຮັດໃຫ້ເຟືອງເປ່ືອຍດີ ກ່ອນນໍາມາປະສົມກັບດິນ.
ມີຜກັ ໄວ້ກິນ ພາຍໃນຄອບຄົວ ແລະ ຍັງສາມາດຂາຍ ເພື່ອສ້າງລາຍຮັບ ໃຫ້ຄອບຄົວ
ເສດເຟືອງ ສາມາດເກັບກັກນໍາ້ໄດ້ ເປັນຢ່າງດີ ພາຍຫັຼງ ຈາກປະສົມເສດເຟືອງເຂົ້າກັບດິນແລວ້ ກ່ໍເຮັດໃຫ້ດິນມີຄວາມຊຸ່ມຊ່ືນ
ໃນເວລາທີ່ຜູ້ໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ປະສົມດິນ ດ້ວຍເຟືອງທີ່ເປື່ອຍ ດິນຈະປ່ຽນເປັນສີເຂັ້ມ ແລະ ມີຄວາມຜຸ່ຍຫຼາຍຂື້ນ.
ເຟືອງ ຈະຖືກຍ່ອຍ ໂດຍໂຕຍ່ອຍສະຫຼາຍເຊັ່ນ: ຂື້ກະເດືອນ ແລະ ຈຸລິນຊີອື່ນໆ ໃນດິນ ໂດຍຜ່ານລໍາໄສ້ ຂອງພວກມັນ ແລະ ຂະບວນການຍ່ອຍສະຫຼາຍນີ້ ສາມາດ ສະໜອງທາດອາຫານສໍາລັບຜັກ.