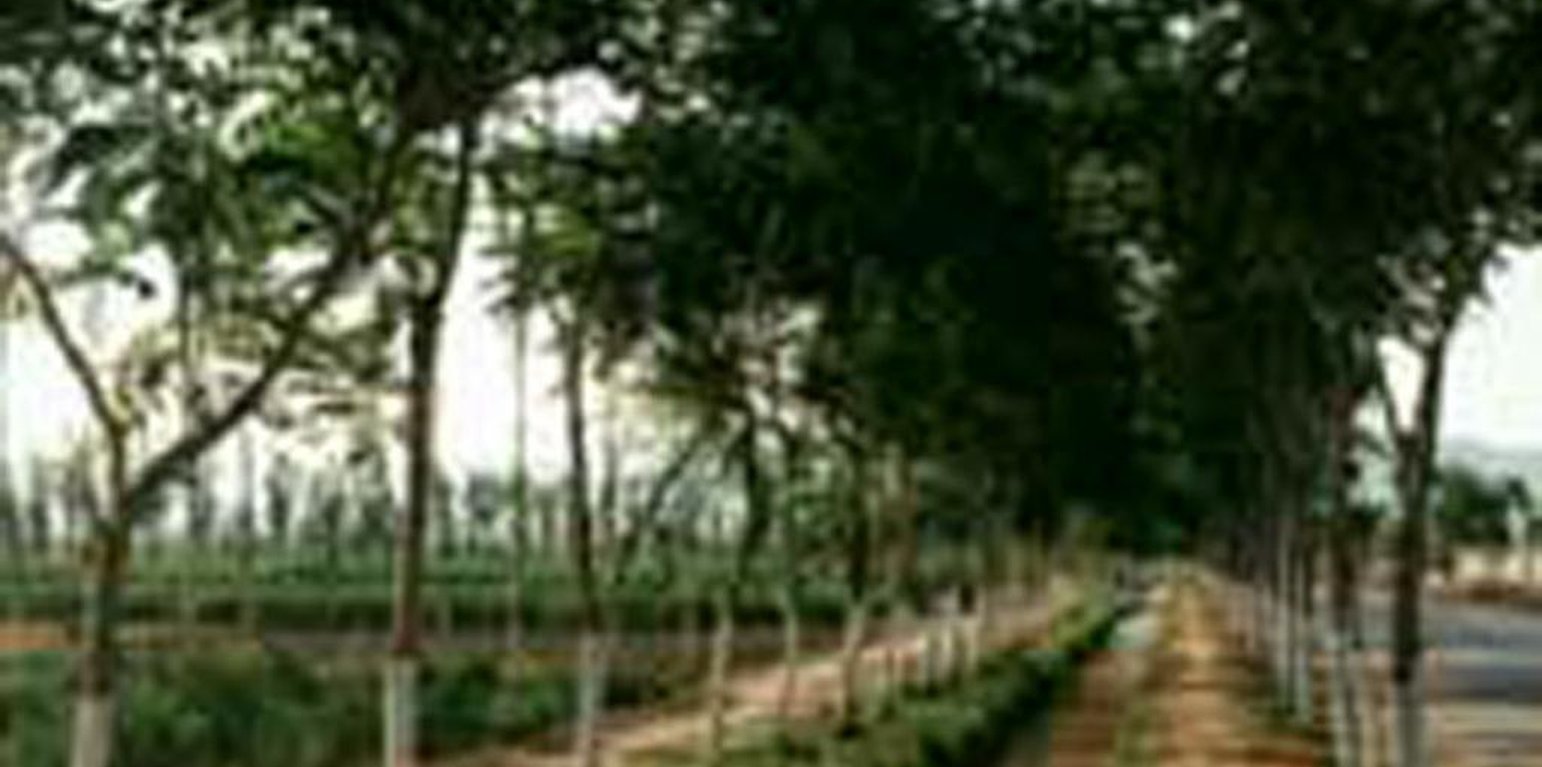




Aims / objectives: Overall purposes are improving environment, and then realization sustainable development of agriculture. Specific objectives are decreasing wind erosion of cropland, increasing foodstuff production. When this approach is decided to implement, the first things to be done are to investigate natural and social-economic environment. Then scope and stages of implementation are decided by government with provision of capital and policies. After that, the approach need to propagandize to people who live in the project area. To implement this approach step by step, local government and land users play an very important role in implementation of the approach.
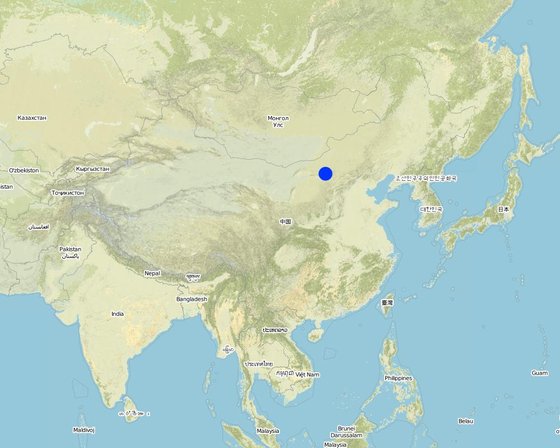
Location: Inner Mongolia, China
Initiation date: 1960
Year of termination: 1981
Type of Approach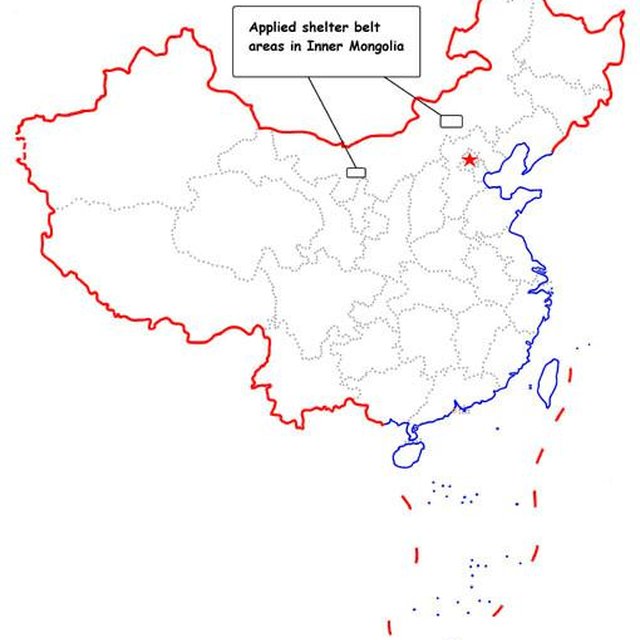
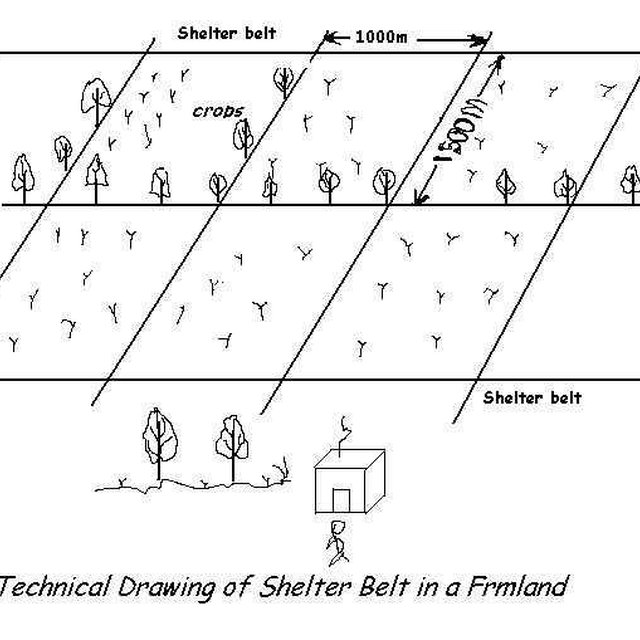
| What stakeholders / implementing bodies were involved in the Approach? | Specify stakeholders | Describe roles of stakeholders |
| local land users/ local communities | Mongolian, Moslem, Korean minority nationalities, etc Work equally divided between men and women | |
| SLM specialists/ agricultural advisers | A group of national and international specialists have been studying for a long time, and summarized this approach. | |
| national government (planners, decision-makers) | The implementing agencies are national government |
Decisions were taken by
Decisions were made based on
This approach is applied for improving environment so as to relief their poverty.
Research was carried out on station
Labour by land users was