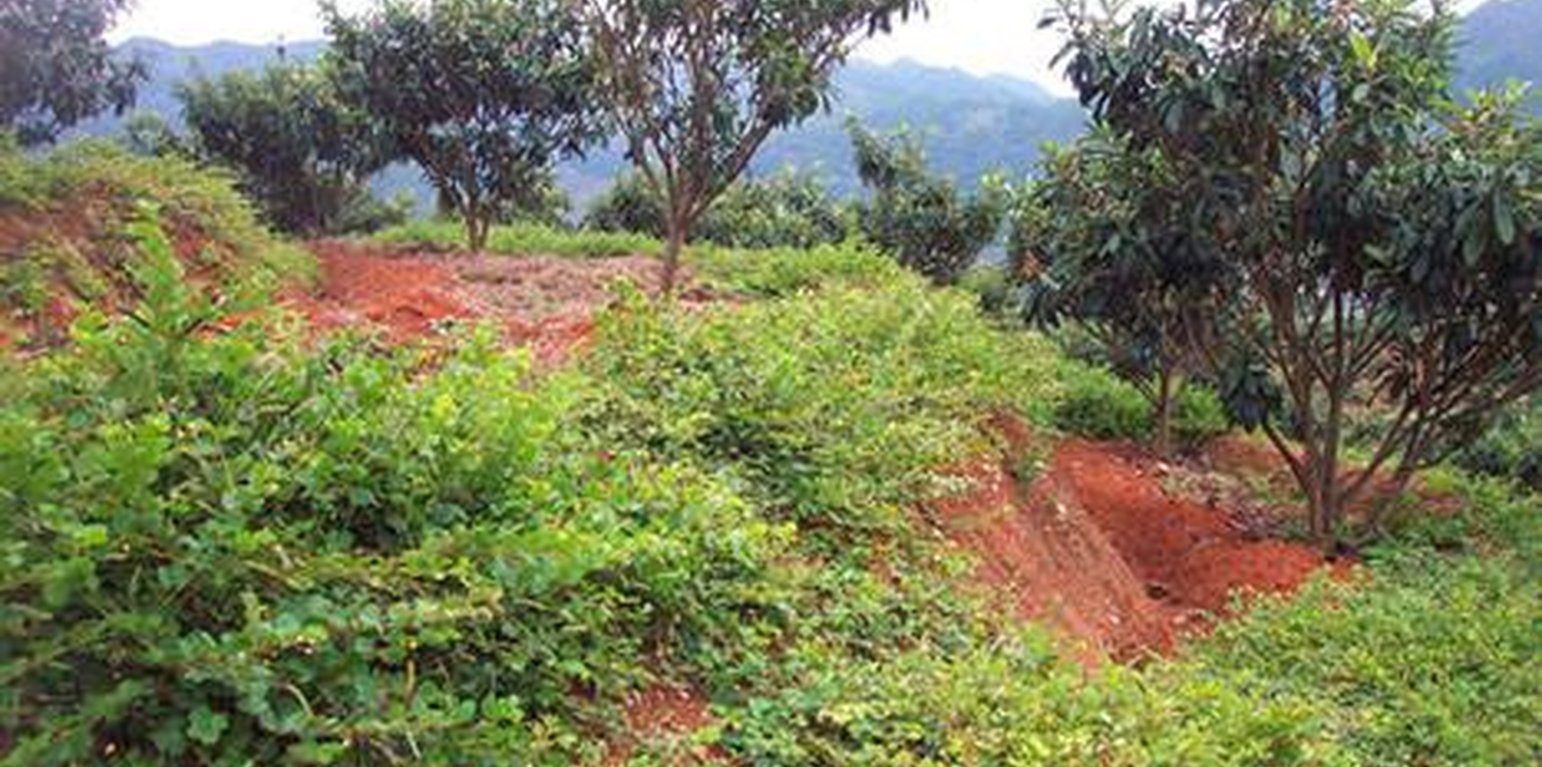
Front Bank, Back Ditch on Contour Terraces
(China)
Description
Using contour principle, constructing terraces with the front bank and back ditch in order to control soil & water erosion.
In the area with sufficient rainfall, overflow and runoff often destroy the existing terraces causing much cost for maintaining. Sluice system of terraces is important when building a terrace. The technology of the Front Bank and Back Ditch on Terrace is to solve this problem. The approach is that building front bank on a terrace edge and digging a ditch on the back terrace as well as digging a ditch upright the terrace along a relatively low rill to induct overflow out.
Location
Location: Fujian, China
Geo-reference of selected sites
Initiation date: 1991
Year of termination: 1996
Type of Approach
-
traditional/ indigenous
-
recent local initiative/ innovative
-
project/ programme based
Location of the Front Bank and Back Ditch on Terraces in Fengting Town.

Front Bank, Back ditch on the terraces in Fengting town.
Approach aims and enabling environment
Main aims / objectives of the approach
Controlling the soil erosion and raising farmers' consciousness of soil conservation.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: The poor quality of fruit trees and seedlings and Disafforestation of the natural vegetation by the man-made factors resulted in the soil erosion and low agricultural production and hindered the local socio-economic development. In addition, the local farmers lack fund.
Conditions enabling the implementation of the Technology/ ies applied under the Approach
-
Legal framework (land tenure, land and water use rights): The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights moderately helped the approach implementation: Separation between ownership and usufruct of land, to some extent, enhances the land users' enthusiasm of SWC investment.
Conditions hindering the implementation of the Technology/ ies applied under the Approach
-
Availability/ access to financial resources and services: Lack of fund
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Raising fund and obtain subsidy from government.
-
Knowledge about SLM, access to technical support: Enhancing training propaganda of SWC technology to farmers.
Participation and roles of stakeholders involved
Stakeholders involved in the Approach and their roles
| What stakeholders / implementing bodies were involved in the Approach? |
Specify stakeholders |
Describe roles of stakeholders |
| local land users/ local communities |
working land users were work equally divided between men and women (Among the farmers and the soil conservation agencies.) |
taking in charge of the program |
| SLM specialists/ agricultural advisers |
|
|
| local government |
assisting the programe design, soil conservation institute |
|
Involvement of local land users/ local communities in the different phases of the Approach
none
passive
external support
interactive
self-mobilization
implementation
responsibility for major steps
monitoring/ evaluation
interviews/questionnaires;
Decision-making on the selection of SLM Technology
Decisions were taken by
-
land users alone (self-initiative)
-
mainly land users, supported by SLM specialists
-
all relevant actors, as part of a participatory approach
-
mainly SLM specialists, following consultation with land users
-
SLM specialists alone
-
politicians/ leaders
Decisions were made based on
-
evaluation of well-documented SLM knowledge (evidence-based decision-making)
-
research findings
-
personal experience and opinions (undocumented)
Technical support, capacity building, and knowledge management
The following activities or services have been part of the approach
-
Capacity building/ training
-
Advisory service
-
Institution strengthening (organizational development)
-
Monitoring and evaluation
-
Research
Capacity building/ training
Training was provided to the following stakeholders
-
land users
-
field staff/ advisers
-
SWC specialists, Planners(3)
Form of training
-
on-the-job
-
farmer-to-farmer
-
demonstration areas
-
public meetings
-
courses
-
farm visits
Subjects covered
Teaching them how to control pests and diseases and new techniques on management of orchards.
Advisory service
Advisory service was provided
-
on land users' fields
-
at permanent centres
Name of method used for advisory service: Soil Conservation in Orchard; Key elements: Setup a demonstration area, field visit, organizing; 1) Mainly: projects own extension structure and agents, Partly: government's existing extension system 2) Mainly: projects own extension structure and agents, Partly: government's existing extension system; Extension staff: Mainly government employees 3) Target groups for extension: Land users, SWC specialists; Activities: demonstration of the field; extend the techniques.
Institution strengthening
Institutions have been strengthened / established
-
no
-
yes, a little
-
yes, moderately
-
yes, greatly
Describe institution, roles and responsibilities, members, etc.
Type of support
-
financial
-
capacity building/ training
-
equipment
Further details
Monitoring and evaluation
technical aspects were regular monitored through measurements
socio-cultural aspects were ad hoc monitored by through observations
economic / production aspects were ad hoc monitored through measurements
area treated aspects were regular monitored through measurements
land users involved aspects were ad hoc monitored through measurements
management of Approach aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: Through in situ observation and demonstration
Research
Research treated the following topics
-
sociology
-
economics / marketing
-
ecology
-
technology
Studying on engineering and vegetative measures. Research was carried out both on station and on-farm
Financing and external material support
Annual budget in USD for the SLM component
-
< 2,000
-
2,000-10,000
-
10,000-100,000
-
100,000-1,000,000
-
> 1,000,000
Precise annual budget: n.a.
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international: 30.0%; national non-government: 15.0%; local community / land user(s): 55.0%
The following services or incentives have been provided to land users
-
Financial/ material support provided to land users
-
Subsidies for specific inputs
-
Credit
-
Other incentives or instruments
Financial/ material support provided to land users
Labour by land users was
-
voluntary
-
food-for-work
-
paid in cash
-
rewarded with other material support
Impact analysis and concluding statements
Impacts of the Approach
No
Yes, little
Yes, moderately
Yes, greatly
Did the Approach help land users to implement and maintain SLM Technologies?
They apply much more organic fertilizers to improve the soil fertility.
Did the Approach improve issues of land tenure/ user rights that hindered implementation of SLM Technologies?
The land use right can help the land users to better develop and manage their lands after signing land use right contract.
The problem is likely to be overcome in the near future. Well organizing work can overcome it.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
Main motivation of land users to implement SLM
Sustainability of Approach activities
Can the land users sustain what hat been implemented through the Approach (without external support)?
Conclusions and lessons learnt
Strengths: land user's view
-
Increasing yield (fruit trees and crops), and income. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: introducing new species in.)
Strengths: compiler’s or other key resource person’s view
-
Harvesting or inducing excrescent rainfall and runoff. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Maintaining timely)
-
Making fully use of the mountain and hilly areas with SWC and developing local economy. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Introducing new species in.)
Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks: land user's viewhow to overcome
-
Cost much and liitle fund available.
Raising money and trying to use mechanic tools in stead of manual labor.
Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks: compiler’s or other key resource person’s viewhow to overcome
-
Cost much for the construction.
subsidy from government, and planting cash crops and fruit trees etc. to increase the return.
References
Date of documentation: Des. 31, 2008
Last update: Julie 12, 2017
Resource persons
-
Wengian Lin - SLM specialist
Full description in the WOCAT database
Documentation was faciliated by
Institution
- Soil & Water Conservation Office of Putian - China
Project






