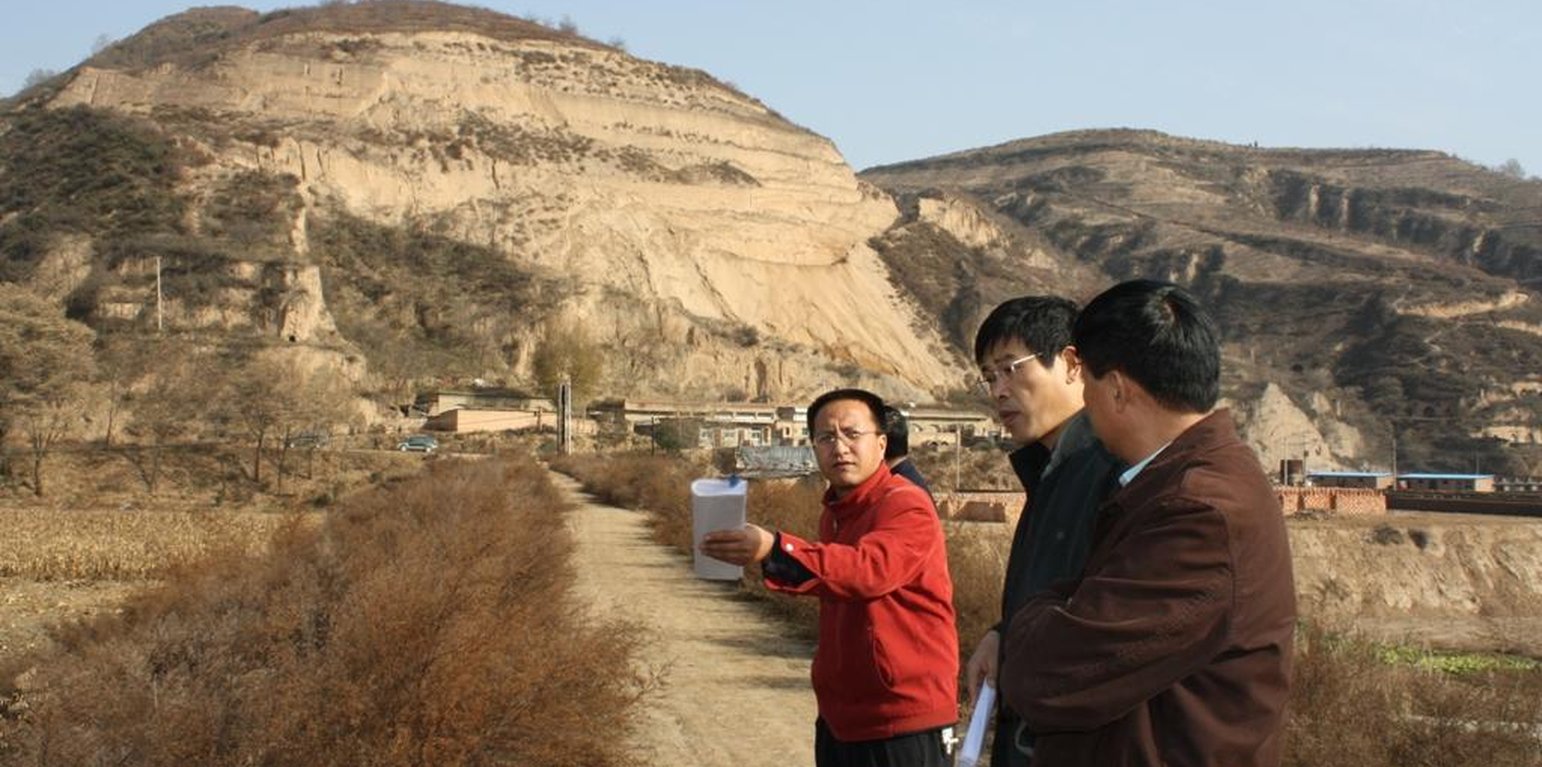
Project of check-dam for land
(China)
淤地坝工程
Description
Approach of check dam for land is a kind of soil and water conservation activity to reduce the sediment discharge and improve the agricultural condition through building a dam across the valley in order to silt the sediment from upstream untill it convert to land with few soil erosion and flash floods.
Aims / objectives: The aims of this approach are to reduce sediment discharge of the rivers and to create cropland in the valley. A wall across the valley is built to hold up the muddy flash flood and to slow down the runoff and to silt the sediment. The water in the check dam could be used as waterbody or discharge as clear water. The local farmers and governments want to improve the agricultural condition in the valley near to village and select the check dam for land.
Methods: Normally the farmers and the local experts judge the feasibility of the technology firstly and then apply the support of local government. The construction should be finished by group (village) with labour input combining with finicial support outside.
Stages of implementation: The first stage to implenment this technology is to call on the local farmers with benefits show of such technologies. Then, an application should be submitted to local gevernment. After getting the support, the construction begin.
Role of stakeholders: The local farmers, experts and local government are main participants in this approach.
Location
Location: Baota County, Yan'an City, Shaanxi Province, China
Geo-reference of selected sites
Initiation date: 18
Year of termination: 16
Type of Approach
-
traditional/ indigenous
-
recent local initiative/ innovative
-
project/ programme based
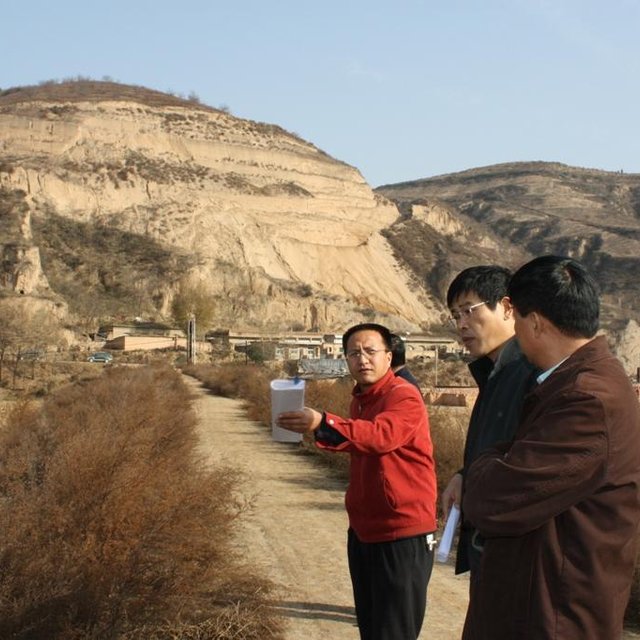

The check dam for land (where the experts standing) is across the gully. Normally with grass and shrubs on the both sides. (Wang Fei (Yangling, China))
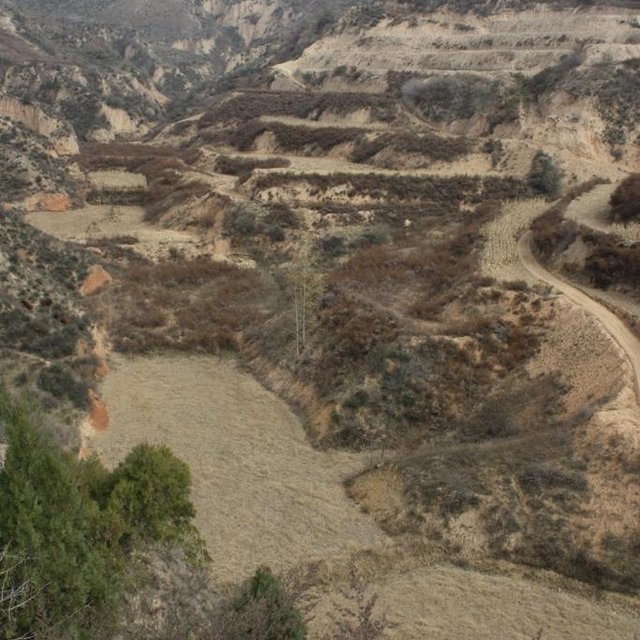

Check dam system with several wall to make land at different levels. (Wang Fei (Yangling, China))
Approach aims and enabling environment
Main aims / objectives of the approach
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (Structural practices; crop land; reduction of sediment load downstream)
1. it reduces the sediment load of the downstream or main river. 2. it improves the agricultural condition through the gain of new cropland in the valleys; 3. it reduces the soil erosion of gullies by down-cutting erosion; 4. it to reduces the gravity erosion or collapse of slopes because the land would increase the stability of slopes. 5. it designs the check dam well and search funds in order to construct the check dam.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: The problems include: lack of flat areas for crop production, high soil erosion on the slopes, poverty induced by low production, requirement of sediment control , lack of cash, and so on.
Conditions enabling the implementation of the Technology/ ies applied under the Approach
-
Legal framework (land tenure, land and water use rights): The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights greatly helped the approach implementation: The approach has many advantages for the different stakeholders. The existing land ownship, land user rights and water rights could help the approach implementation.
Conditions hindering the implementation of the Technology/ ies applied under the Approach
-
Availability/ access to financial resources and services: the input for a check dam is high for small households and villages
Treatment through the SLM Approach: financial support from outside such as local or central governemnt, or the management organization of water basin.
-
Knowledge about SLM, access to technical support: A huge flood would destroy the dam
Treatment through the SLM Approach: To improve the quality which is depending on calculation of the possibility of flood and during extrem storms the control area of the dam.
Participation and roles of stakeholders involved
Stakeholders involved in the Approach and their roles
| What stakeholders / implementing bodies were involved in the Approach? |
Specify stakeholders |
Describe roles of stakeholders |
| local land users/ local communities |
|
Some check dams were implemented by villagers, before
The land area of local farmers is very small, and the decision at the village level should be decided by the group. |
| SLM specialists/ agricultural advisers |
The geologist designs the site of engineering, the hydyologist designs the ability of dam according the strom records and landform of the basin; the civil engineers design the number of engineers. |
They can evaluate the properity of check dam for land and design it |
| local government |
The departments with certification to implement |
They decide the planning of soil and water conservation. |
| national government (planners, decision-makers) |
By politicians / leaders |
|
Involvement of local land users/ local communities in the different phases of the Approach
none
passive
external support
interactive
self-mobilization
initiation/ motivation
the local farmers and village head involved normally. They could build the check dam before but they submit the proposal for the building now.
planning
the experts in hydrology, soil erosion, landform involved. They survey, calculate and design the check dam.
Flow chart
Organization Chart of check dam land.
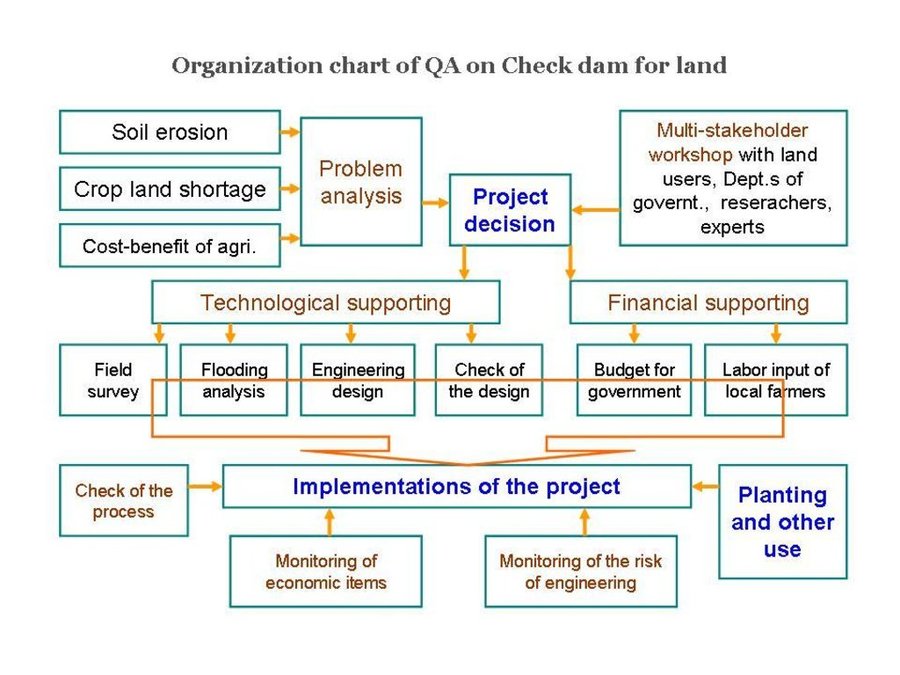
Author: Wang Fei (Yangling, China)
Decision-making on the selection of SLM Technology
Decisions were taken by
-
land users alone (self-initiative)
-
mainly land users, supported by SLM specialists
-
all relevant actors, as part of a participatory approach
-
mainly SLM specialists, following consultation with land users
-
SLM specialists alone
-
politicians/ leaders
Decisions were made based on
-
evaluation of well-documented SLM knowledge (evidence-based decision-making)
-
research findings
-
personal experience and opinions (undocumented)
Technical support, capacity building, and knowledge management
The following activities or services have been part of the approach
-
Capacity building/ training
-
Advisory service
-
Institution strengthening (organizational development)
-
Monitoring and evaluation
-
Research
Capacity building/ training
Training was provided to the following stakeholders
-
land users
-
field staff/ advisers
Form of training
-
on-the-job
-
farmer-to-farmer
-
demonstration areas
-
public meetings
-
courses
Advisory service
Advisory service was provided
-
on land users' fields
-
at permanent centres
Consultation and Discussion; Key elements: Determine and classify the questions and problems of the project, Analysis the problems and discussion it wth the relative experts, Explain the whole condition of the project to the participants; it is not so difficult in the Loess Plateau because the local farmers are familiar with the check dam for land more or less.
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; the technology is not new in the Yan River Basin
Institution strengthening
Institutions have been strengthened / established
-
no
-
yes, a little
-
yes, moderately
-
yes, greatly
Describe institution, roles and responsibilities, members, etc.
Type of support
-
financial
-
capacity building/ training
-
equipment
Further details
To show the benefits and process of construction for local farmers.
Monitoring and evaluation
technical aspects were regular monitored by project staff through measurements; indicators: Professional is necessary in measure and design.
economic / production aspects were regular monitored by project staff, land users through observations; indicators: To know the benefit of project
economic / production aspects were regular monitored by project staff through measurements; indicators: To monitor sometime.
no. of land users involved aspects were regular monitored by government through measurements; indicators: To know how many people participating
management of Approach aspects were regular monitored by government through measurements; indicators: To manage the whole project
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: the safety of the dam should be checked after flood season in order that the check dam management can be adapted to changing risks.
There were several changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation: the sediment from slopes decreased recently, the drainage channel changed to lower level since the stage of designing.
Research
Research treated the following topics
-
sociology
-
economics / marketing
-
ecology
-
technology
The experts should know the important parameters of the technology for improved designing. The researchers also need to judge and evaluate the permission and support of the project based on the econonic and ecological impacts.
Research was carried out both on station and on-farm
Financing and external material support
Annual budget in USD for the SLM component
-
< 2,000
-
2,000-10,000
-
10,000-100,000
-
100,000-1,000,000
-
> 1,000,000
Precise annual budget: n.a.
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (the input is mainly from government): 90.0%; local community / land user(s) (labour work input): 10.0%
The following services or incentives have been provided to land users
-
Financial/ material support provided to land users
-
Subsidies for specific inputs
-
Credit
-
Other incentives or instruments
Financial/ material support provided to land users
by state
partly financed
fully financed
equipment: machinery
by government
construction: stone
loess around the site of the dam
Labour by land users was
-
voluntary
-
food-for-work
-
paid in cash
-
rewarded with other material support
Impact analysis and concluding statements
Impacts of the Approach
No
Yes, little
Yes, moderately
Yes, greatly
Did the Approach help land users to implement and maintain SLM Technologies?
1. the land in the valley is prone to incision by flash flood, the check dam could prevent the erosion; 2. crop land is very useful for the local farmers because of its good condition of soil properities, the local farmers paid more attention to protect this land;3. the ability of production is hig
Did the Approach empower socially and economically disadvantaged groups?
agricultural condition improved so that the yield, income and spare time increases. There are no special changes on gender, age and ethnicity induced by this approach.
Did the Approach improve issues of land tenure/ user rights that hindered implementation of SLM Technologies?
The problem is unlikely to be overcome in the near future. The approach has been approved that the ability of anti-flooding is high. The possible extream storm is out of the consideration till now.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
the Ministry of Water Resources of China developed a project for check dam engineering land based on its the integrated functions. The local government and land users (local farmers) also try to find financial support for this project.
Main motivation of land users to implement SLM
-
increased production
-
increased profit(ability), improved cost-benefit-ratio
-
reduced land degradation
-
reduced risk of disasters
-
reduced workload
-
payments/ subsidies
-
rules and regulations (fines)/ enforcement
-
prestige, social pressure/ social cohesion
-
affiliation to movement/ project/ group/ networks
-
environmental consciousness
-
customs and beliefs, morals
-
enhanced SLM knowledge and skills
-
aesthetic improvement
-
conflict mitigation
-
well-being and livelihoods improvement
Sustainability of Approach activities
Can the land users sustain what hat been implemented through the Approach (without external support)?
Conclusions and lessons learnt
Strengths: land user's view
-
Could get the finicial from government (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue to support the construction at the suitable place)
-
To create 'good' land for themselves (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Share the land fairly)
Strengths: compiler’s or other key resource person’s view
-
Make more people know its benefits (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Show the integrated impacts of project )
-
Professional design (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: To improve the quanlity of project through field survey and calculation. )
-
to organize the local farmers working together (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Plan and make the local farmers to know they can share fairly within the local farmers. )
Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks: land user's viewhow to overcome
-
very few, sometimes the are is temporary flooded
drainage of the flash water on time
Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks: compiler’s or other key resource person’s viewhow to overcome
-
change of landform
can not be overcome
-
The farmer does not plan to build check dam for land with their own invest
New approach is necessary for some farmers or small farmer group to implenment project themselves
References
Date of documentation: Junie 6, 2011
Last update: Julie 9, 2017
Resource persons
-
Fei WANG (wafe@ms.iswc.ac.cn) - SLM specialist
Full description in the WOCAT database
Documentation was faciliated by
Institution
- Northwest A&F University (NWAFU) - China
Project
Key references
-
Experiment and Practice of Check Dam Land, Zheng Baoming, Wang Xiao, Tianyonghong, Shangguomei, Mu Zhenlian. 2004: Yellow River Conservancy Press【YRCP】
-
Effect of soil-retaining dams on flood and sediment reduction in middle reaches of Yellow River. Ran Dachuan, Luo Quanhua, Liu Bin, Wang Hong. 2004: JOURNAL OF HYDRAULIC ENGINEERING ,2004, (5)
Links to relevant information which is available online







