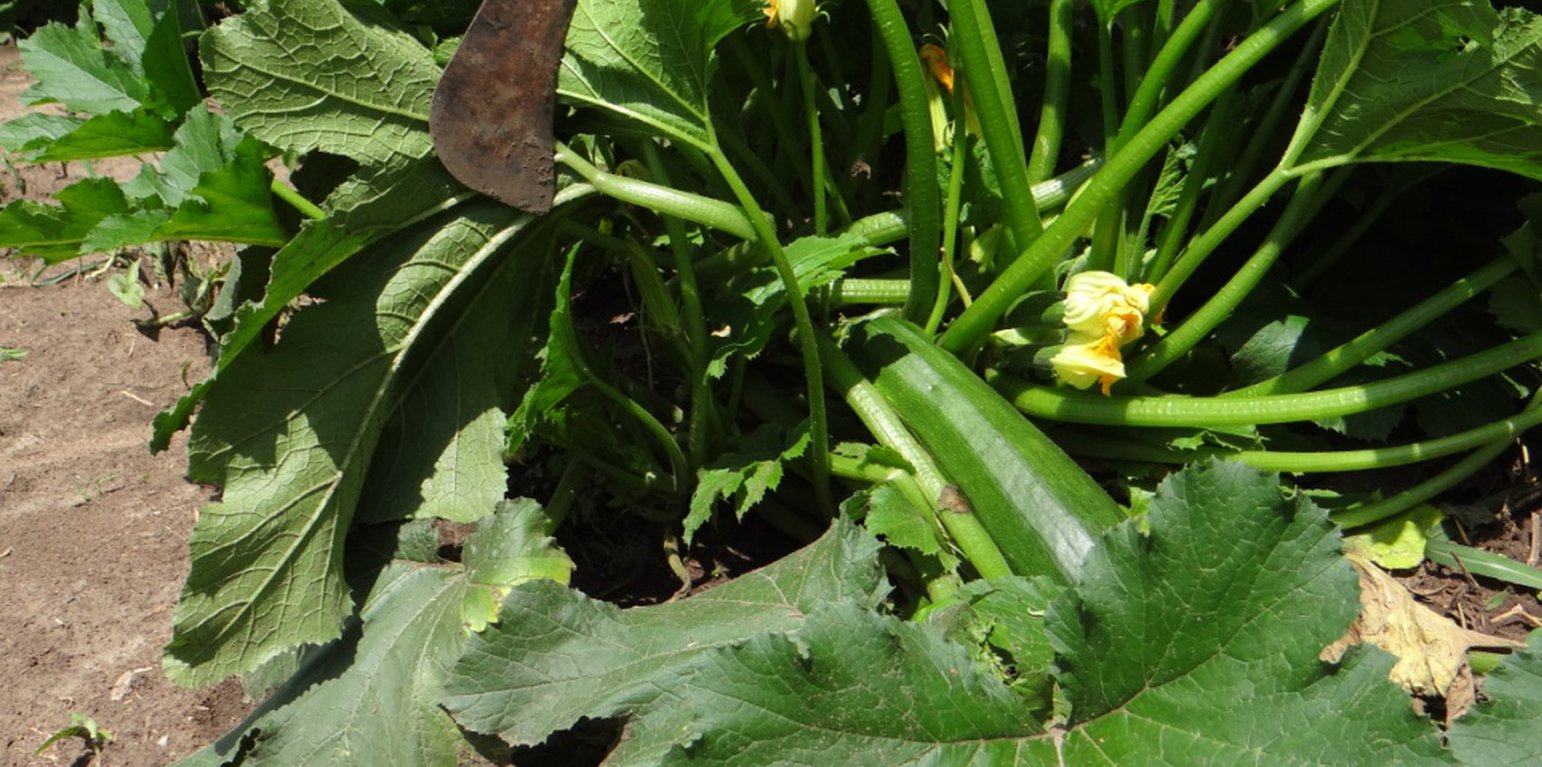




Baby melon, as a cover crop, protects soil from erosion and compaction due to rain drops. The cover crop also conserves soil moisture during drought periods. Besides soil conservation, baby melon is used as source of food and income to the land user. It is a vegetable crop which looks like pumpkin with wide leave and scroll on the surface of the land and has the ability to prevent soil erosion from run-off. The crop is also commonly grown along streams where it protects the banks from erosion, provides manure through leaf-fall, and reduces the risk of flooding by increasing the evopo-transpiration from its wide leaves.
To establish this cover crop, farmers use seeds, which is locally conserved from previous fruiting or bought from agro-input shop. Seeds are sown directly into a pre-cultivated garden. Usually planting is at a spacing of two meters. Planting is usually done at the start of the rainy season. Weeding, as well as pest and disease management is done the way pumpkins are usually managed. Fruits are harvested at a relatively early stage (~2 months after planting). A more juvenile fruit is preferred to the more grown one for its nutritional value.
The benefit of the technology is first for food, income and also for protection of the soil from the effect of running water and rain drops. The farmer obtains nutritious food from the fruits of this plant. The plants also prevent soil erosion and take a very short time to mature. When the plant covers an area, it reduces weed growth, thus reducing the cost of weeding. One disadvantage of this technology is that the pumpkins do not have a popular market and have a very short shelf life. Fruits therefore, have to be sold immediately after harvesting. The market value of the crop is generally low.
Location: Koro Subcounty, Omoro District, Northern Region,Uganda, Uganda
No. of Technology sites analysed: single site
Spread of the Technology: evenly spread over an area (approx. < 0.1 km2 (10 ha))
Date of implementation: less than 10 years ago (recently)
Type of introduction



Technical specifications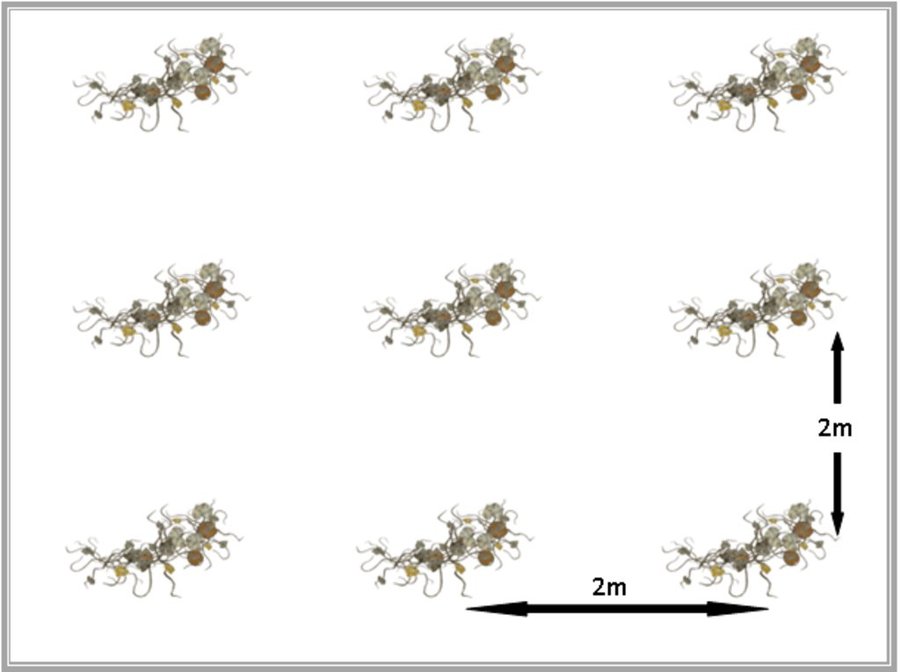
Author: Amale Balla Sunday
Spacing between baby melon plants is 2m by 2m. This spacing enables vigorous growth and quick soil surface cover.
|
|||||||||||
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (Uganda Shillings) | Total costs per input (Uganda Shillings) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| labor | 1 | 5.0 | 5000.0 | 25000.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | |||||
| Seed | kg | 1.0 | 200000.0 | 200000.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | |||||
| Manure | Bags | 5.0 | 20000.0 | 100000.0 | 100.0 |
| Fungicides | Litters | 2.0 | 30000.0 | 60000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 385'000.0 | ||||
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (Uganda Shillings) | Total costs per input (Uganda Shillings) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| labor | 1 | 3.0 | 5000.0 | 15000.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | |||||
| Fungicides | Litters | 2.0 | 30000.0 | 60000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 75'000.0 | ||||