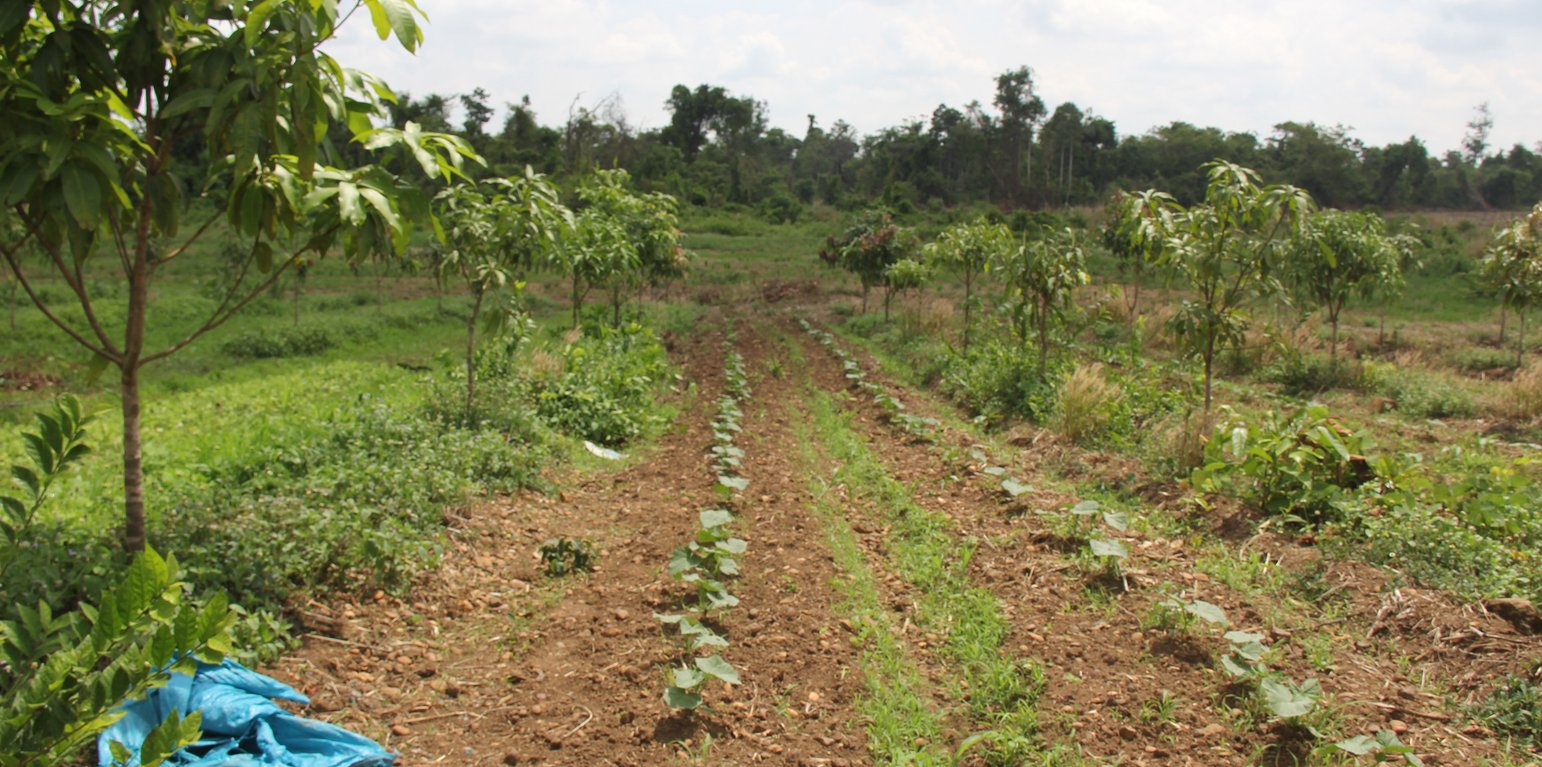




កសិរុក្ខកម្ម គឺជាការអនុវត្តដាំដំណាំ និង/ឬចិញ្ចឹមសត្វនៅលើផ្ទៃដីតែមួយដោយដាំដុះលាយជាមួយនឹងដើមឈើ ដូចជាឈើហូបផ្លែ ដូង ឫស្សី និងដើមឈើផ្សេងទៀត ដើម្បីបង្កើនផលិតភាពកសិកម្ម និងទទួលបានអត្ថប្រយោជន៍ផ្សេងៗទៀត (MoE et al., 2016)។ កសិរុក្ខកម្មដើរតួនាទីយ៉ាងសំខាន់ក្នុងការផ្តល់ផលប្រយោជន៍ដល់ប្រព័ន្ធអេកូឡូស៊ី និងសេដ្ឋកិច្ច ដូចជា ការប្រមូលផលឈើ និងដំណាំរួមផ្សំ ធ្វើឲ្យដីកាន់តែមានជីជាតិ កាត់បន្ថយការប្រើប្រាស់ជី និងថ្នាំគីមីដែលនាំឲ្យថ្លៃដើមផលិតថយចុះ បន្ស៊ាំបានកាន់តែប្រសើរទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ (MoE et al., 2016) ក៏ដូចជាការជួយកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃការខូចខាតផលដំណាំផងដែរ (FA and DANIDA, 2005)។
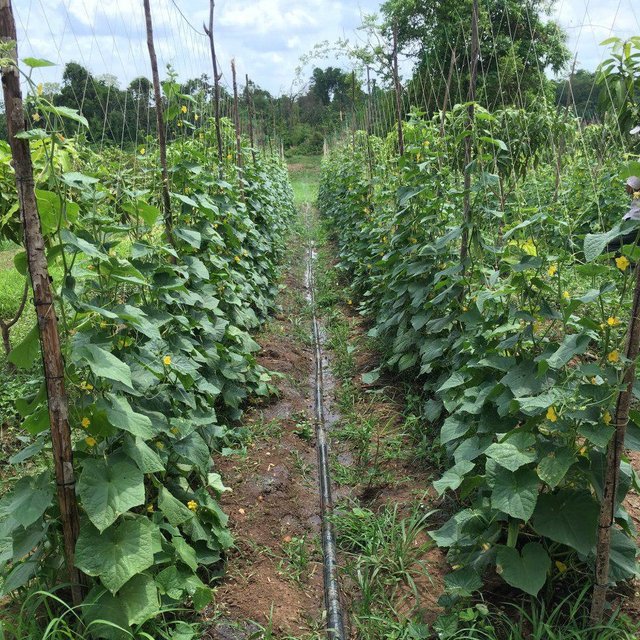
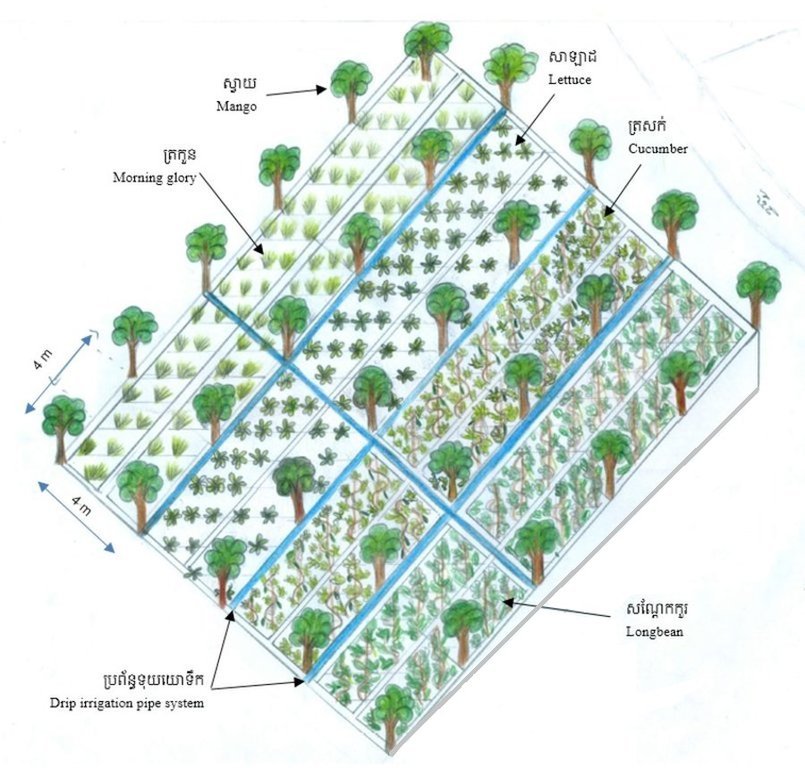
លោក ហួរ គឺជាកសិករមួយរូបក្នុងចំណោមកសិករច្រើននាក់ដែលបានផ្លាស់ប្តូរពីកសិកម្មឯកវប្បកម្មមកអនុវត្តប្រព័ន្ធកសិរុក្ខកម្ម។ រូបគាត់ និងក្រុមគ្រួសារ រស់នៅភូមិសោបក្រោម ឃុំ សោប ស្រុក ព្រែកប្រសព្វ ខេត្តក្រចេះ ដែលជាខេត្តមួយស្ថិតនៅប៉ែកឦសាននៃប្រទេសកម្ពុជា។ លើផ្ទៃដីដាំដុះទំហំ ២១០០ម៉ែត្រការ៉េ នៅតំបន់ជម្រាលភ្នំ គាត់មានស្វាយសរុបចំនួន ១៣៥ដើម ដោយដាំជា ៩ជួរ ហើយចន្លោះជួរ និងចន្លោះដើមមានប្រវែង ៤ម៉ែត្រដូចគ្នា។ តាមចន្លោះជួរស្វាយមានដាំបន្លែឆ្លាស់គ្នាជាច្រើនប្រភេទ ដូចជាសណ្តែកកួរ ត្រសក់ ត្រកួន ស្ពៃ និងសាលាដ ។ ស្វាយត្រូវបានដាំបន្ទាប់ពីភ្ជួរដីហាលរយៈ ១៥ថ្ងៃ ដោយជីករណ្តៅទំហំ ០,៥ម៉ែត្របួនជ្រុង ជាមួយជម្រៅ ០,៥ម៉ែត្រ និងបំពេញដោយលាមកគោ អង្កាម និងកន្ទក់ដែលបានផ្អាប់ទុក ១៥ថ្ងៃ ក្នុងមួយរណ្តៅប្រមាណជា ២ ទៅ ៣ គ.ក្រ។ កសិករបានប្រើប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រពជាតំណក់ទឹក ដោយរាយទុយោដល់គល់ស្វាយ និងតាមបណ្តោយរងបន្លែទាំងអស់។ ការរៀបចំរងបន្លែ គឺប្រែប្រួលតាមរដូវកាល នៅរដូវប្រាំងគេលើករងកម្ពស់ ១០សង់ទីម៉ែត្រ ហើយនៅរដូវវស្សាគេលើករងកម្ពស់ ២០សង់ទីម៉ែត្រ ដើម្បីកុំឱ្យជាំទឹក។ ជាងនេះទៅទៀតការធ្វើកសិកម្មបែបនេះមិនមានការចំណាយច្រើន ហើយថែមទាំងជួយបង្កើនប្រាក់ចំណូលនៅពេលដំណាំអាយុកាលវែងមិនទាន់បានទទួលផល។ លើសពីនេះកសិករបានប្រើជីកំប៉ុស្តិ៍ទឹក និងថ្នាំសំលាប់សត្វល្អិតផ្សំពីធម្មជាតិ ដែលគាត់បានផលិតដោយខ្លួនឯង ធ្វើឲ្យគ្មានផលប៉ះពាល់អវិជ្ជមានដល់បរិស្ថានផងទៀតផង។ ការធ្វើជីកំប៉ុស្តិ៍ទឹក គឺគាត់ប្រើកម្ទេចកម្ទីត្រី កន្ទក់ និងស្ករក្រហម លាយជាមួយទឹក រួចរក្សាទុករយៈពេល ១៥ថ្ងៃ ទើបយកមកលាយទឹកបាញ់លើបន្លែ។ ចំណែកឯថ្នាំកំចាត់សត្វល្អិតត្រូវបានផ្សំពីសមាសធាតុរុក្ខជាតិផ្សេងៗដែលមានក្លិនក្រពុលខ្លាំង និងរសល្វីង ដូចជា សំបកស្លែង ក្តុល ស្តៅ វល្លិ៍បណ្តូលពេជ្រ និងរំដេង ដោយចិញ្ច្រាំវាឱ្យម៉ត់ ហើយលាយជាមួយស្ករក្រហម និងទឹក រួចបន្ទាប់មកត្រាំវាទុករយៈពេល ១៥ថ្ងៃ។ សម្រាប់ការប្រើប្រាស់ គឺត្រូវលាយទឹកថ្នាំចំណុះ ១លីត្រ ជាមួយទឹក ២៥លីត្រ។
សរុបមកបច្ចេកទេសកសិរុក្ខកម្មនេះបានផ្តល់នូវអត្ថប្រយោជន៍ច្រើនយ៉ាង។ ការដាំដំណាំបែបនេះអាចបង្កើនសេដ្ឋកិច្ចដោយការប្រមូលផលដំណាំផ្សេងៗគ្នា ទាំងក្នុងរដូវប្រាំង និងរដូវវស្សា ជាពិសេសក្នុងរយៈពេល ៣ឆ្នាំ ដំបូងដែលស្វាយមិនទាន់បានផ្តល់ផល ដូច្នេះ គឺទប់ទល់បាននឹងការចំណាយផ្សេងៗក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន។ ការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសនេះក៏ផ្តល់នូវភាពត្រជាក់ដល់ដីតាមរយៈម្លប់នៃដើមស្វាយ កាត់បន្ថយការបាត់បង់សំណើមដី ទប់ស្កាត់ការហូរច្រោះ ព្រមទាំងជួយបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងភាពហួតហែងដែលបណ្តាលមកពីការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុទៀតផង។ លើសពីនេះ ការអនុវត្តបែបនេះ គឺមិនទុកឱ្យដីនៅទំនេរចោលនាំឱ្យដុះស្មៅចង្រៃដែលជាជម្រកនៃការកកើតសត្វល្អិត និងជំងឺផ្សេងៗ ជាមូលហេតុនាំឱ្យបាត់បង់អត្ថប្រយោជន៍ផ្នែកសេដ្ឋកិច្ច។
បើមើលមួយភ្លែត វាអាចជាគុណវិបត្តិមួយដែរ ដែលកសិករត្រូវចំណាយច្រើនក្នុងគ្រាដំបូង ឧទាហរណ៍ដូចជាការតម្លើងប្រព័ន្ធតំណក់ទឹកជាដើម ប៉ុន្តែគេអាចប្រើបានក្នុងរយៈពេលច្រើនឆ្នាំ និងបន្ថយការចំណាយលើកម្លាំងពលកម្មស្រោចស្រព។ ចំពោះដំណាំបន្លែ កសិករមានភាពប្រឈមជាមួយនឹងតម្លៃបន្លែលើទីផ្សារមិនទៀងទាត់ ប្រសិនបើតម្លៃទីផ្សារមានស្ថេរភាព នោះកសិករនឹងទទួលបានចំណូលកាន់តែច្រើនសម្រាប់ការលើកកម្ពស់ជីវភាពគ្រួសារ។ ដូចនេះស្ថាប័នពាក់ព័ន្ធគួរយកចិត្តទុកដាក់លើបញ្ហាទីផ្សារនេះផងដែរ។
Location: ភូមិសោបក្រោម ឃុំសោប ស្រុកព្រែកប្រសព្វ ខេត្តក្រចេះ, Cambodia
No. of Technology sites analysed: single site
Spread of the Technology: evenly spread over an area (approx. < 0.1 km2 (10 ha))
In a permanently protected area?:
Date of implementation: 2015
Type of introduction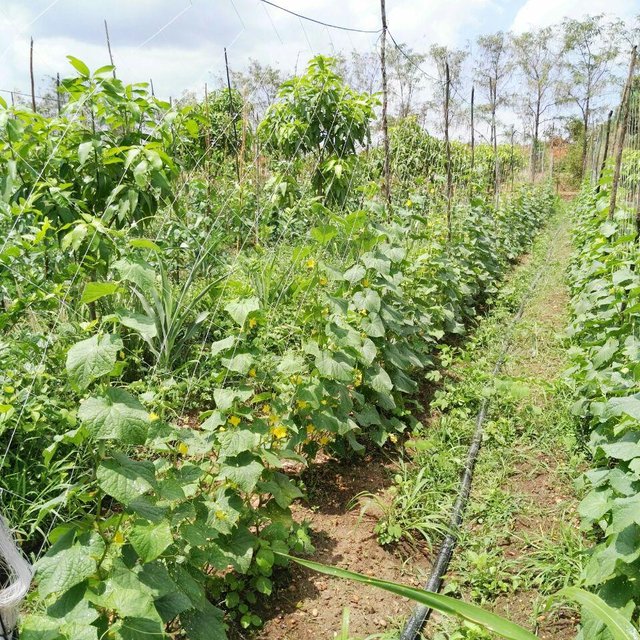







| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (រៀល) | Total costs per input (រៀល) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| ភ្ជួរ និងរាស់ដី | នាក់/ថ្ងៃ | 3.0 | 20000.0 | 60000.0 | 100.0 |
| ជីករណ្តៅ | នាក់/ថ្ងៃ | 5.4 | 20000.0 | 108000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | |||||
| ប្រព័ន្ធដំណក់ទឹក | ឈុត | 1.0 | 800000.0 | 800000.0 | 100.0 |
| ក្បាលចម្រោះ | គ្រឿង | 1.0 | 120000.0 | 120000.0 | 100.0 |
| ចបជីក | ចប | 2.0 | 15000.0 | 30000.0 | 100.0 |
| គោយន្ត | គ្រឿង | 1.0 | 4800000.0 | 4800000.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | |||||
| ដើមស្វាយ | ដើម | 135.0 | 5000.0 | 675000.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | |||||
| ជីត្រី | លីត្រ | 200.0 | 300.0 | 60000.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | |||||
| សំណាញ់សម្រាប់ធ្វើទ្រើង | ដុំ | 18.0 | 15000.0 | 270000.0 | 100.0 |
| ឫស្សីទ្រើង | សរុប | 1.0 | 100000.0 | 100000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 7'023'000.0 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 1'755.75 | ||||
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (រៀល) | Total costs per input (រៀល) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| លើករង | នាក់/ថ្ងៃ | 3.0 | 20000.0 | 60000.0 | 100.0 |
| ស្ទូងបន្លែ ឬដាំ | នាក់/ថ្ងៃ | 2.0 | 20000.0 | 40000.0 | 100.0 |
| ធ្វើស្មៅ | នាក់/ថ្ងៃ | 9.0 | 20000.0 | 180000.0 | 100.0 |
| បាញ់ថ្នាំការពារ | នាក់/ថ្ងៃ | 1.0 | 20000.0 | 20000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | |||||
| ទុយោ | ដុំ | 3.0 | 100000.0 | 300000.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | |||||
| ពូជត្រសក់ | កញ្ចប់ | 4.0 | 10000.0 | 40000.0 | 100.0 |
| ពូជសណ្តែកកួរ | កញ្ចប់ | 1.0 | 3500.0 | 3500.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | |||||
| ថ្នាំកំចាត់សត្វល្អិត | លីត្រ | 20.0 | 2000.0 | 40000.0 | 100.0 |
| Other | |||||
| ដូរទុយោ | នាក់/ថ្ងៃ | 1.0 | 20000.0 | 20000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 703'500.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 175.88 | ||||
ជាក់ស្តែងកសិករដាំដំណាំច្រើនប្រភេទជាងពីមុននៅលើផ្ទៃដីដដែល ដូចនេះគាត់អាចប្រមូលផលបន្តបន្ទាប់ពីដំណាំទាំងនោះ ដូចជាដំណាំអាយុកាលវែង និងដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ។
តាមរយៈការដាំដំណាំរយៈពេលវែង និងដំណាំរយៈពេលខ្លីជាមួយគ្នា បានជួយកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃភាពបរាជ័យបាន។
ដោយសារមានដាំដំណាំជាប្រព័ន្ធចម្រុះដែលមានដំណាំច្រើនប្រភេទចម្រុះគ្នា។
ដីកាលដើមឡើយជាប្រភេទដីព្រៃសឹករេចរិល ប៉ុន្តែឥលូវគាត់អាចដាំដំណាំបានតាមបច្ចេកទេស SLM នេះ។
គាត់ដាំដំណាំច្រើនប្រភេទ ហើយប្រើប្រាស់តែជីធម្មជាតិ និងថ្នាំពុលការពារដំណាំផ្សំពីរុក្ខជាតិដែលបានផលិតដោយគាត់ផ្ទាល់។
បច្ចុប្បន្ននេះគាត់មិនចាំបាច់ទិញជីថ្នាំគីមីទៀតទេ ហើយគាត់ព្យាយាមប្រើប្រាស់ថ្នាំសំលាប់សត្វល្អិតដែលផលិតដោយខ្លួនឯង។
គាត់អាចទទួលបានចំណូលពេញមួយឆ្នាំពីព្រោះគាត់បានដាំទាំងដំណាំអាយុកាលវែង និងខ្លី។
តាមរយៈការដាំដំណាំច្រើនជាងមួយប្រភេទលើផ្ទៃដីដដែលបណ្តាលឱ្យគាត់ទទួលបានប្រភពចំណូលកើនឡើងប៉ុន្តែតិចតួចប៉ុណ្ណោះ។
គម្របដីល្អដែលបានពីការដាំដំណាំឆ្លាស់បានជួយបញ្ជៀសការដុះលូតលាស់នៃស្មៅចង្រៃ និងជួយកាត់បន្ថយកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងធ្វើស្មៅផងដែរ។
គាត់ដាំដំណាំច្រើនជាងមុនធ្វើឱ្យសន្តិសុខស្បៀងកាន់តែប្រសើរ។
ការបំពុលបរិស្ថានត្រូវបានកាត់បន្ថយដោយសារគាត់ប្រើប្រាស់តែជីធម្មជាតិ និងថ្នាំពុលការពារដំណាំផ្សំពីរុក្ខជាតិប៉ុណ្ណោះ។ ដូចនេះស្ថានភាពសុខភាពកាន់តែប្រើសើរឡើង។
ចំណេះដឹងដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងដី គឺគាត់ទទួលបានពីបទពិសោធន៍របស់គាត់ និងតាមរយៈឯកសារ ឬវីដេអូលើប្រព័ន្ធអ៊ីនធឺណេត។
មានដំណាំគម្របដីកាន់តែច្រើន គឺបានជួយកាត់បន្ថយរំហួតតាមនោះដែរ។
តាមរយៈការដាំបន្លែឆ្លាស់គ្នាបានធ្វើឱ្យគម្របដីល្អប្រសើរ
ឫសរបស់ដំណាំស្វាយបានចាក់ចូលទៅក្នុងដីធ្វើឱ្យដីផុសល្អ
ដោយសារតែមានដំណាំគម្របដីជាអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍ពេញមួយឆ្នាំ
ប្រភេទរាតត្បាត គឺត្រូវបានកាត់បន្ថយតាមរយៈការដាំដំណាំវិលជុំ និងការប្រើប្រាស់ថ្នាំពុលការពារដំណាំផ្សំពីរុក្ខជាតិ។
ប្រភេទសត្វមានប្រយោជន៍កើនឡើងពីព្រោះតែការប្រើប្រាស់ជីកំប៉ុស្តិ៍ទឹក។
ថ្នាំសម្លាប់សត្វល្អិតផ្សំពីធម្មជាតិដែលគាត់ផលិតដោយខ្លួនគាត់ គឺមានប្រសិទ្ធភាពខ្ពស់។