



Wet-season rice is the predominantly grown crop in the area, but some land users also grow other crops (e.g. sweet potatoes, pumpkins, or peanuts). However, if droughts occur or if the rainfall patterns are erratic, the production can be harmed. Furthermore, due to the lack of water, the land users usually leave their fields bare during the dry season. This results in an increase of wind erosion and in negative impacts on the soil biota due to its exposure to the sun.
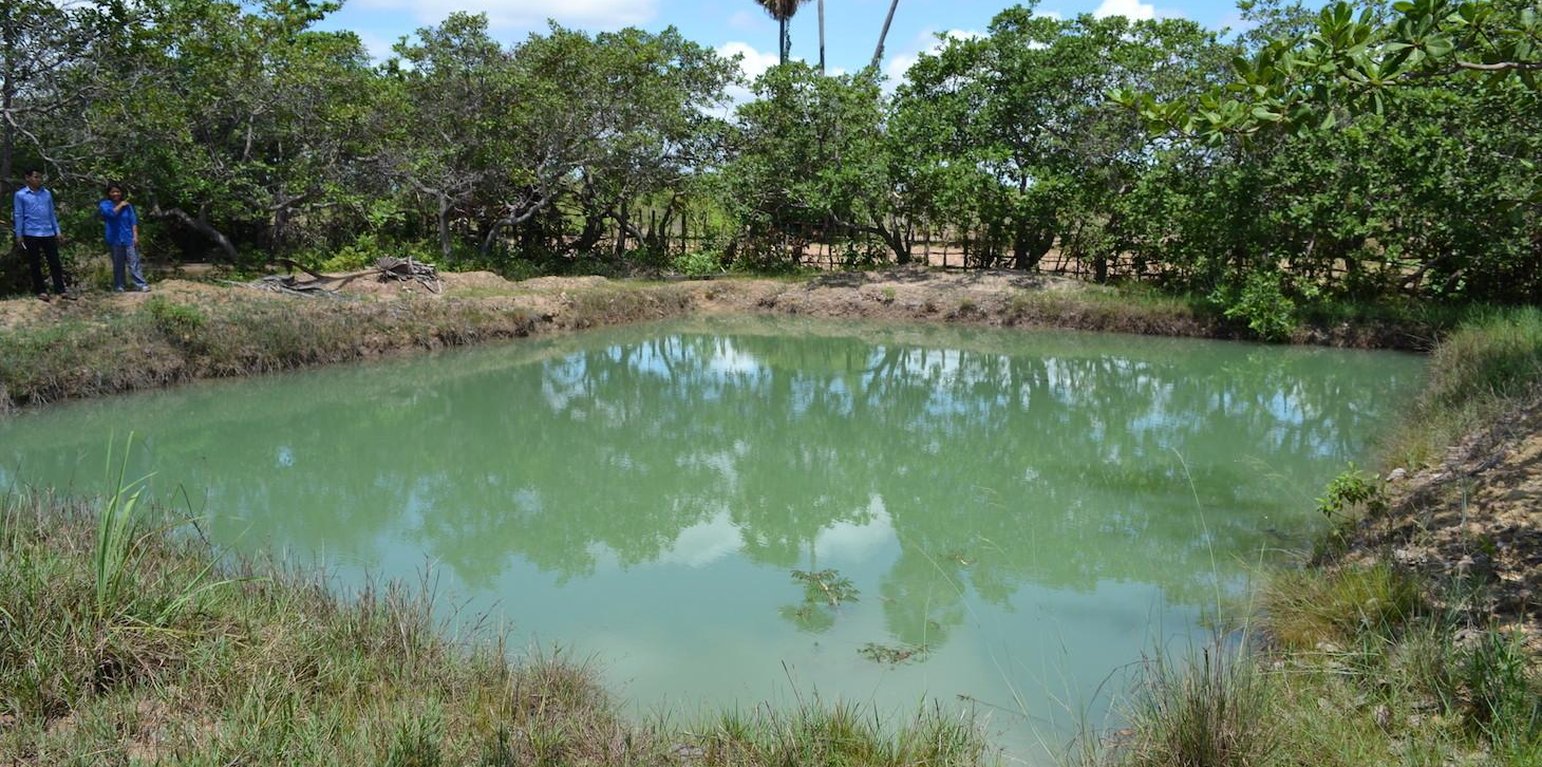
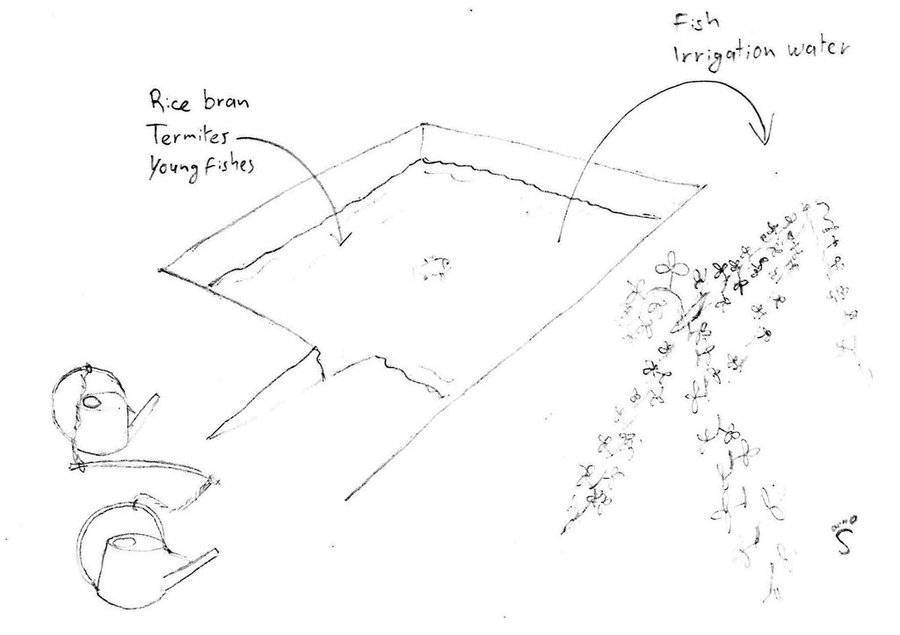
In order to tackle these challenges, ponds of 4 m depth (1 m deeper than the groundwater table during the dry season) are used at household level. By building ponds, some fields can be irrigated during the dry season, thus crops can be grown the whole year round. In this case study, sweet potatoes are the main cash crop grown on the irrigated fields during the dry season. The vines can be transplanted to the fields during the beginning of the rainy season, resulting in a better productivity of the crop. Peanuts and cucumbers are other cash crops grown on the irrigated fields.
Additionally, fish are introduced to the pond. These fish, which are caught during fishing for consumption in the flooded rice fields or nearby streams, increase the resilience of the land users: On one hand, they generate additional income and on the other hand, they allow the land users to eat fish the whole year round.
To build the ponds, the land users of this case study benefited from the road construction. The constructer needed soil, and offered to dig a pond for free if they could use the soil. They only dug 2 of the total 4 meters depth of the pond. The land users had to hire someone to dig deeper, as the groundwater level drops below 3 meters soil level during the dry season. The additional benefits from the pond, the fish are introduced as fingerlings when they are caught with the bigger fish. They are fed with termites (around 5 kg of termite nest each day) and with rice bran (1 kg every 3 days). As the pond is only 2 years old, the maintenance activities like digging out the mud did not have to be done yet.
The analysed area is flat (slope < 2%), tropic (dry and wet season), and the soils are mostly sandy or loamy. The soils contain little organic matter, the pH is sinking, the area has been deforested a long time ago and the groundwater table is rather high (1-2 m during the dry season, on the surface during wet season). and the groundwater table is rather high (3 m below soil level during the dry season, on the surface during the wet season).
Due to climate change, the rainfalls are more erratic, temperatures rise and droughts are more recurrent. Rice is the predominant crop grown in the area, since it serves as staple food (mix subsistence and commercial activities). Rice is often grown in monocultures and harvested once a year. Once the rice is harvested (dry season), some farmer release cattle to the paddy fields to eat the straw and weeds.
As an addition to rice, most land users grow vegetable and fruits in small home gardens (subsistence) and complement their income by producing handicrafts or through off farm income / remittances from family members working in other places. The increasing migration rate (the young generation leaves the villages to work in the cities, garment industry or abroad) results in a decrease of available labour force in the area which has detrimental effects on the agricultural activities. Furthermore, the civil war in the 1970s (Khmer Rouge) led to the loss of agricultural knowledge that different NGOs try to re-establish.
Location: Roloer pha-er/Bantheay Preal/Tob Srauv (Village), Kampong Chhnang, Cambodia
No. of Technology sites analysed:
Spread of the Technology: evenly spread over an area (approx. < 0.1 km2 (10 ha))
In a permanently protected area?:
Date of implementation: less than 10 years ago (recently)
Type of introduction





| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (n.a.) | Total costs per input (n.a.) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Equipment | |||||
| machine use | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 50.0 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 100.0 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 100.0 | ||||
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (n.a.) | Total costs per input (n.a.) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| labour | 1.0 | 134.5 | 134.5 | 100.0 | |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 134.5 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 134.5 | ||||
Fish
Ponds allow the land user to grow crops the whole year round. Furthermore, there are fish in the pond which provide a reliable source of food.