



កំណើននៃការបាត់បង់គម្របព្រៃឈើកាន់តែកើនឡើង ជាពិសេសនៅតំបន់ខ្ពង់រាប ដែលបណ្តាលមកពីកំណើនប្រជាជន កំណើនផ្ទៃដីកសិកម្ម ជាមូលហេតុនៃការធ្វើឱ្យដីមានការហូរច្រោះ ជីជាតិដីកាន់តែថយចុះ ដែលជាសញ្ញាណនៃឱនភាពដី (MPWT et al., 2016)។ កសិរុក្ខកម្មជាជម្រើសដ៏ល្អដែលអាចជួយដោះស្រាយបញ្ហានេះ ដោយផ្អែកលើអត្ថប្រយោជន៍របស់វាដូចជា កាត់បន្ថយការហូរច្រោះ បង្កើនសេដ្ឋកិច្ច ទិន្នផលដំណាំ ជីជាតិដី ថែមទាំងជួយរក្សាសំណើមដីផងដែរ។ កសិរុក្ខកម្មជាការដាំប្រភេទដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំជាមួយដំណាំអាយុកាលវែងដូចជាដំណាំស្វាយ ក្រូច ជាមួយប្រភេទដំណាំបន្លែ ឬដំណាំផ្សេងៗនៅផ្នែកខាងក្រោម (MoE et al., 2016)។
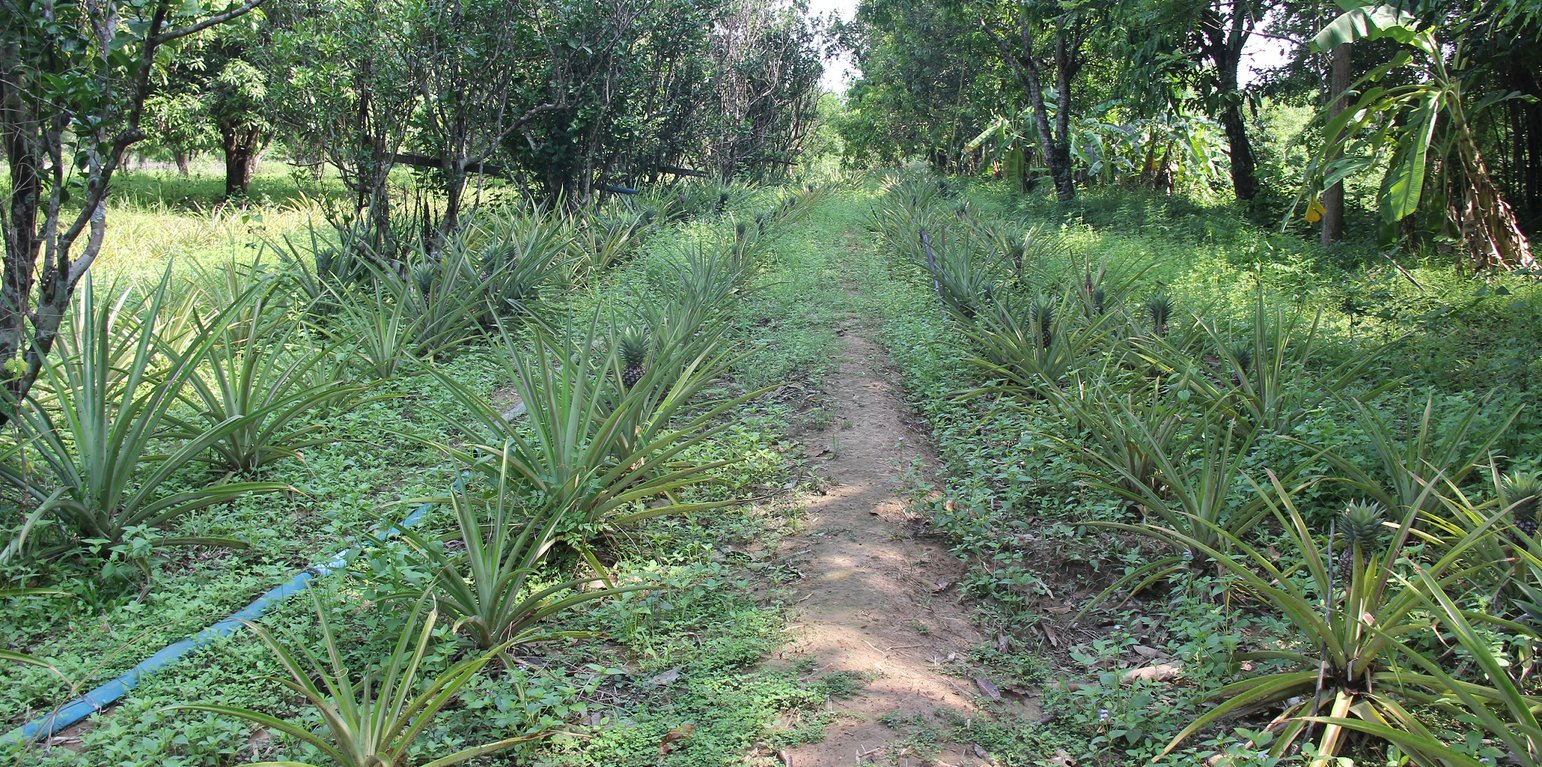
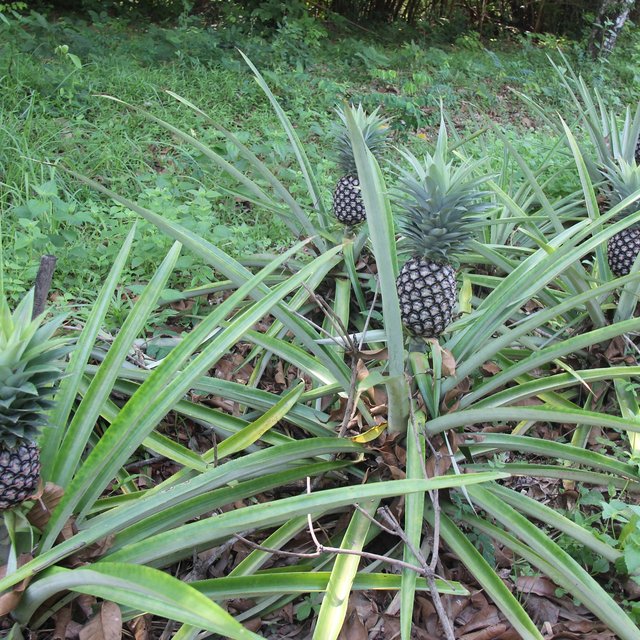
កសិករអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសកសិរុក្ខកម្មនេះក្នុងគោលបំណងកាត់បន្ថយការប្រើប្រាស់ជីគីមី សន្សំសំចៃទឹក បង្កើនសំណើមដី បង្កើនចំណូល និងផលិតកម្មដំណាំ។ ក្នុងបច្ចេកទេសនេះកសិករបានដាំស្វាយ និងក្រូចពោធិ៍សាត់ ហើយដាំម្នាស់នៅតាមចន្លោះ ដោយសារម្នាស់ជាដំណាំ មិនត្រូវការពន្លឺថ្ងៃខ្លាំងអាចដាំក្រោមម្លប់បាន ហើយក៏ជាដំណាំធន់នឹងទឹកជំនន់ (រហូតដល់ ៧ថ្ងៃ) ដែរ។ តំបន់នេះម្តងម្កាល់តែងជន់លិចនៅពេលមានភ្លៀងខ្លាំង ដោយសារតែស្ថិតនៅជិតស្ទឹងដែលអាចជន់លិចត្រឹមតែរយៈពេល ២៤ម៉ោង ប៉ុណ្ណោះរួចទឹកនឹងស្រកទៅវិញ ។ ម្យ៉ាងវិញទៀត កសិករមិនបានប្រើប្រាស់ជី ឬថ្នាំគីមីឡើយ គឺប្រើតែកាកសំណល់ដំណាំ ស្លឹកឈើ រុក្ខជាតិតូចៗ ស្មៅដែលកាត់ចោលជាដើម។ ជាធម្មតាដំណាំស្វាយ និងក្រូចពោធិ៍សាត់ជាដំណាំអាយុកាលវែង ពេលដើមនៅតូច គឺចន្លោះគុម្ពមានគម្លាតឆ្ងាយ។ បើទុកដីមិនប្រើប្រាស់ (ចំហរ) នឹងមានស្មៅចង្រៃដុះទ្រុបទ្រុល ពិបាកក្នុងការសម្អាត និងថែទាំដំណាំ។ ដូចនេះការដាំម្នាស់តាមចន្លោះនឹងទទួលបានចំណូលជាបណ្តើរៗមុនពេលស្វាយ និងក្រូចផ្តល់ផល ចំណេញពេលវេលាថែទាំ ស្រោចទឹក ដាក់ជី ដកស្មៅ។ លើសពីនេះទៅទៀតនៅពេលស្វាយ និងក្រូចធំ ម្នាស់ក៏នៅតែអាចបន្តផ្តល់ផល បើទោះជាដុះក្រោមម្លប់ហើយមានពន្លឺតិចតួចក្តី តែទិន្នផលមិនបានច្រើនទេ។ ម៉្យាងទៀតការដាំម្នាស់ គឺជាការបង្កើនមុខដំណាំសម្រាប់ទីផ្សារ ដោយនៅតំបន់នេះមិនទាន់មានអ្នកដាំម្នាស់នៅឡើយទេ។
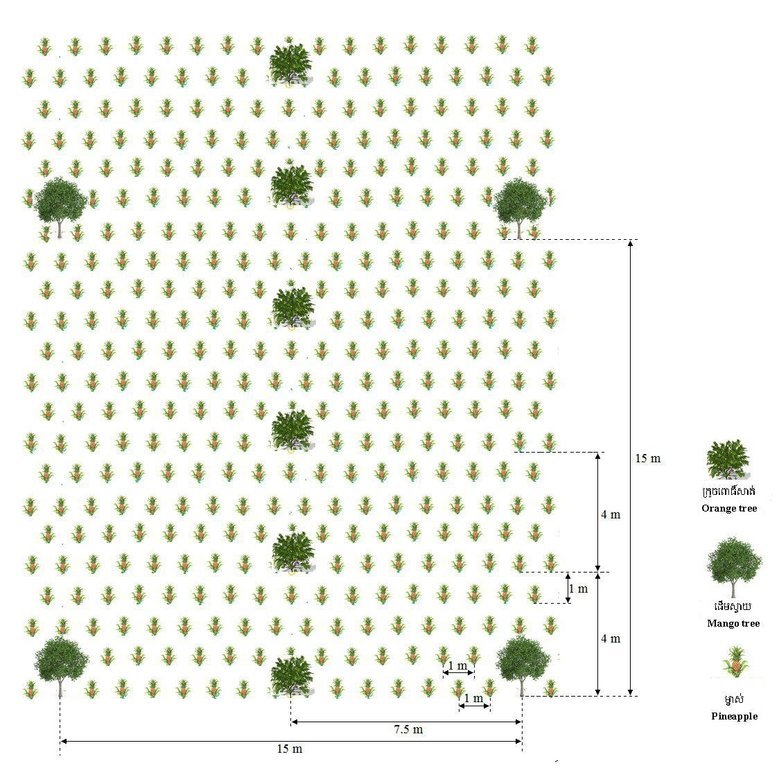
នៅក្នុងទំហំផ្ទៃ ២០០០ ម៉ែត្រការ៉េ (ទទឹង ២០ម៉ែត្រ X ១០០ ម៉ែត្រ) ដែលមានដាំក្រូចពោធិ៍សាត់ចំនួន ១០ដើម ស្វាយចំនួន ១៤ដើម និងម្នាស់ប្រមាណជា ១០០០ដើម។ ក្នុងនោះស្វាយដាំជា ២ជួរនៅព្រំដីសងខាងដែលមួយជួរមានដើមស្វាយ ៦ ទៅ ៧ដើម ហើយដាំក្រូចពោធិ៍សាត់នៅចន្លោះកណ្តាល និងមានម្នាស់នៅចន្លោះស្វាយ និងក្រូចពោធិ៍សាត់ផងដែរ។ ការដាំស្វាយត្រូវជីករណ្តៅកន្លះម៉ែត្របួនជ្រុង និងជម្រៅ ០,៥ម៉ែត្រ ហើយប្រមូលស្លឹកឈើជាមួយកាកសំណល់ផ្សេងៗទុកមួយឆ្នាំមុននឹងដាក់ដាំ និងដាំនៅចន្លោះ ១៥ម៉ែត្រ បួនជ្រុង។ ក្រូចពោធិ៍សាត់ដាំក្នុងចន្លោះ ៤ម៉ែត្របួនជ្រុង ដោយមានលើកភ្លឺកម្ពស់ ២០សង់ទីម៉ែត្រ ប្រវែង ២ម៉ែត្រជុំវិញ ហើយជីករណ្តៅដូចការដាំស្វាយដែរ ។ ការដាំប្រព្រឹត្តទៅនៅអំឡុងខែឧសភា ឬមិថុនា និងបន្ទាប់ពីមានភ្លៀងធ្លាក់ម្តង ឬពីរដងបានចាប់ផ្តើមដាំ ហើយក្រោយពេលដាំ ៣ ទៅ ៤ខែធ្វើស្មៅម្តង និងបន្ថែមលាមកគោក្រោយដាំបានមួយឆ្នាំ។ ដោយឡែកម្នាស់ត្រូវបានដាំក្នុងចន្លោះមួយម៉ែត្រពីគ្នាហើយដាំជារាងមុំចង្ក្រាន ដោយជីករណ្តៅ ២០សង់ទីម៉ែត្របួនជ្រុង ជម្រៅ ១០សង់ទីម៉ែត្រ បើជ្រៅពេកវាអាចរលួយ។ ក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំគាត់ដាំតែម្តងទេ ព្រោះថាម្នាស់បន្ទាប់ពីដាំរហូតដល់ប្រមូលផលមានរយៈពេល ៩ ទៅ ១០ ខែ ហើយបន្ទាប់ពីប្រមូលផលរួចត្រូវចំណាយពេល ១ ទៅ ២ខែបន្ថែមដើម្បីឱ្យវាចេញខ្នែង និងត្រូវរងចាំដល់ខ្នែងនោះលាស់ស្លឹកប្រមាណជា ១០សន្លឹកទៀតទើបកាត់ខ្នែងនោះសម្រាប់ដាំបន្ត។ កាកសំណល់ដើមម្នាស់ដែលសេសសល់ត្រូវប្រមូលសម្អាតហើយកប់ក្នុងដីនៅផ្នែកណាមួយនៃផ្ទៃដីដាំដុះសម្រាប់ផ្តល់ជាជីជាតិវិញ។
Location: ភូមិគោកស្រឡៅ ឃុំជាំក្សាន្ត ស្រុកជាំក្សាន្ត ខេត្តព្រះវិហារ, Cambodia
No. of Technology sites analysed: single site
Spread of the Technology: evenly spread over an area (approx. < 0.1 km2 (10 ha))
In a permanently protected area?:
Date of implementation: 2007; 10-50 years ago
Type of introduction






| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (រៀល) | Total costs per input (រៀល) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| ភ្ជួរដី | នាក់/ថ្ងៃ | 7.5 | 20000.0 | 150000.0 | 100.0 |
| ជីករណ្តៅ | នាក់/ថ្ងៃ | 3.0 | 20000.0 | 60000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | |||||
| ប៉ែល | ប៉ែល | 1.0 | 8000.0 | 8000.0 | 100.0 |
| ចបកាប់ | ចប | 1.0 | 15000.0 | 15000.0 | 100.0 |
| ចបជីក | ចប | 2.0 | 13000.0 | 26000.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | |||||
| កូនស្វាយ | ដើម | 15.0 | 4000.0 | 60000.0 | 100.0 |
| កូនក្រូច | ដើម | 10.0 | 15000.0 | 150000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 469'000.0 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 117.25 | ||||
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (រៀល) | Total costs per input (រៀល) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| ស្រោចទឹក | នាក់/ថ្ងៃ | 52.0 | 20000.0 | 1040000.0 | 100.0 |
| ធ្វើស្មៅ និងជ្រោយដី | នាក់/ថ្ងៃ | 20.0 | 20000.0 | 400000.0 | 100.0 |
| ការដាក់លាមកសត្វ | នាក់/ថ្ងៃ | 1.0 | 20000.0 | 20000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | |||||
| ម៉ាស៊ីនបូមទឹក | គ្រឿង | 1.0 | 2000000.0 | 2000000.0 | 100.0 |
| ម៉ាស៊ីនកាត់ស្មៅ | គ្រឿង | 1.0 | 300000.0 | 300000.0 | 100.0 |
| គោយន្ត | គ្រឿង | 1.0 | 4700000.0 | 4700000.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | |||||
| លាមកសត្វ | គីឡូក្រាម | 100.0 | 200.0 | 20000.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | |||||
| ប្រេងសម្រាប់បូមទឹក | លីត្រ | 30.0 | 3500.0 | 105000.0 | 100.0 |
| ប្រេងសម្រាប់កាត់ស្មៅ | លីត្រ | 260.0 | 3500.0 | 910000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 9'495'000.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 2'373.75 | ||||
ពីមុនដាំច្រើនមុខជាងដែលបណ្តាលឱ្យថយផលិតកម្មដំណាំតិចតួច ប៉ុន្តែមានតម្រូវការទីផ្សារខ្ពស់ជាងមុន។
មានរុយចោះ ៧-៨ឆ្នាំចុងក្រោយ
មានដាំដំណាំរយៈពេលវែង និងដំណាំរយៈពេលខ្លី ដែលជួយកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យបានតិចតួច ហើយកសិករក៏មិនមានប្រើប្រាស់ជីថ្នាំគីមីដែរ។
មានដំណាំ ៣ប្រភេទនៅលើដី
វាមានដំណាំ ២ប្រភេទ គឺដំណាំរយៈពេលវែង និងដំណាំរយៈពេលខ្លី ហើយវាជួយកាត់បន្ថយស្មៅចង្រៃ និងទឹកសម្រាប់ស្រោចស្រពដែរ។
ដាំម្នាស់ចំណាយច្រើនជាងដោយសារត្រូវចំណាយលើការប្រេងសម្រាប់ស្រោចស្រពព្រោះមានរយៈពេលយូរជាង។
ផលិតកម្មថយចុះបន្តិច ប៉ុន្តែកសិករទទួលបានតម្លៃប្រសើរជាងមុនដោយសារតម្រូវការទីផ្សារស្វាយ ក្រូចពោធិ៍សាត់ និងម្នាស់កើនឡើង។
បន្ទុកការងារត្រូវបានកាត់បន្ថយដោយសារមិនសូវមានស្មៅដុះ និងការស្រោចស្រពតិចជាងមុន។
កសិករមិនបានប្រើថ្នាំគីមីក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសនេះទេ។
គាត់បានផ្លាស់ប្តូរពីការប្រើប្រាស់ជីគីមីមកប្រើជីធម្មជាតិវិញ។
សំណើមដីត្រូវបានកើនឡើងដោយសារដីត្រូវបានគ្របដណ្តប់ដោយដំណាំ។
ដំណាំរយៈពេលវែង និងប្រចាំឆ្នាំត្រូវបានដាំសម្រាប់ជាប្រចាំ។
ដីប្រេះបែកក្រហែងត្រូវបានកាត់បន្ថយតាមរយៈការដាំឈើហូបផ្លែដែលអាចបង្កើនសំណើមដី។
ឈើហូបផ្លែ ឬដំណាំរយៈពេលវែងត្រូវបានដាំដូចនេះឫសរបស់វាអាចជួយកាត់បន្ថយការហាប់ណែននៃដីជាងការដាំបន្លែទូទៅ។
វដ្តនៃសារធាតុចិញ្ចឹមបានកើនឡើងដោយសារតែការប្រើប្រាស់កាកសំណល់ដំណាំ និងស្លឹកឈើ ឬស្លឹករុក្ខជាតិផ្សេងៗ។
សព្វថ្ងៃគាត់ប្រើជីធម្មជាតិជំនួសជីគីមីដែលធ្វើឱ្យសារធាតុសរីរាង្គក្នុងដីកើនឡើង។
ដំណាំរយៈពេលវែង និងដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំត្រូវបានដាំជាប្រចាំ។
ប្រភេទសត្វដែលមានប្រយោជន៍ត្រូវបានកើនឡើងដោយសារតែការប្រើប្រាស់ជីធម្មជាតិ។
ឫសរបស់ឈើហូបផ្លែ និងម្នាស់បានចាក់ចូលក្នុងដី ហើយម្នាស់គឺជាដំណាំគម្របដី និងផ្តល់ជាម្លប់ ដែលជួយការពារដីកុំឱ្យស្ងួត (ដីមានសំណើម)។
កាកសំណល់ដំណាំ និងដំណាំវាជួយរក្សាលំនឹងនៃរំហួតរំភាយចំហាយទឹក និងសីតុណ្ហភាព។