



The natural ecosystems in north-west China, especially in Xinjiang Province, are dominated by steppes, semi-deserts and desert. Riparian forests along the Tarim River Basin have been reduced and degraded by the expansion of irrigated agriculture since the 1950s. The main crop planted is cotton. In the arid temperate cold desert climate, precipitation is very low and evaporation high. The only water source for the region is the Tarim River. Xinjiang is being promoted to become the main cotton production area of China, especially in the upper reaches of the Tarim River, and reservoirs with a large irrigation infrastructure have been established. Farmers water their fields with flood and drip irrigation. But most of the fields have no drainage system. With the high evaporation and the capillary rise of the shallow groundwater, salts dissolved in the water accumulate on the soil surface and in the soil. This salinization makes the fields unusable for cotton production and are abandoned as farmers move on. These barren saline soils are prone to wind erosion, as almost no plants can grow on them. Large-scale desertification is the result.
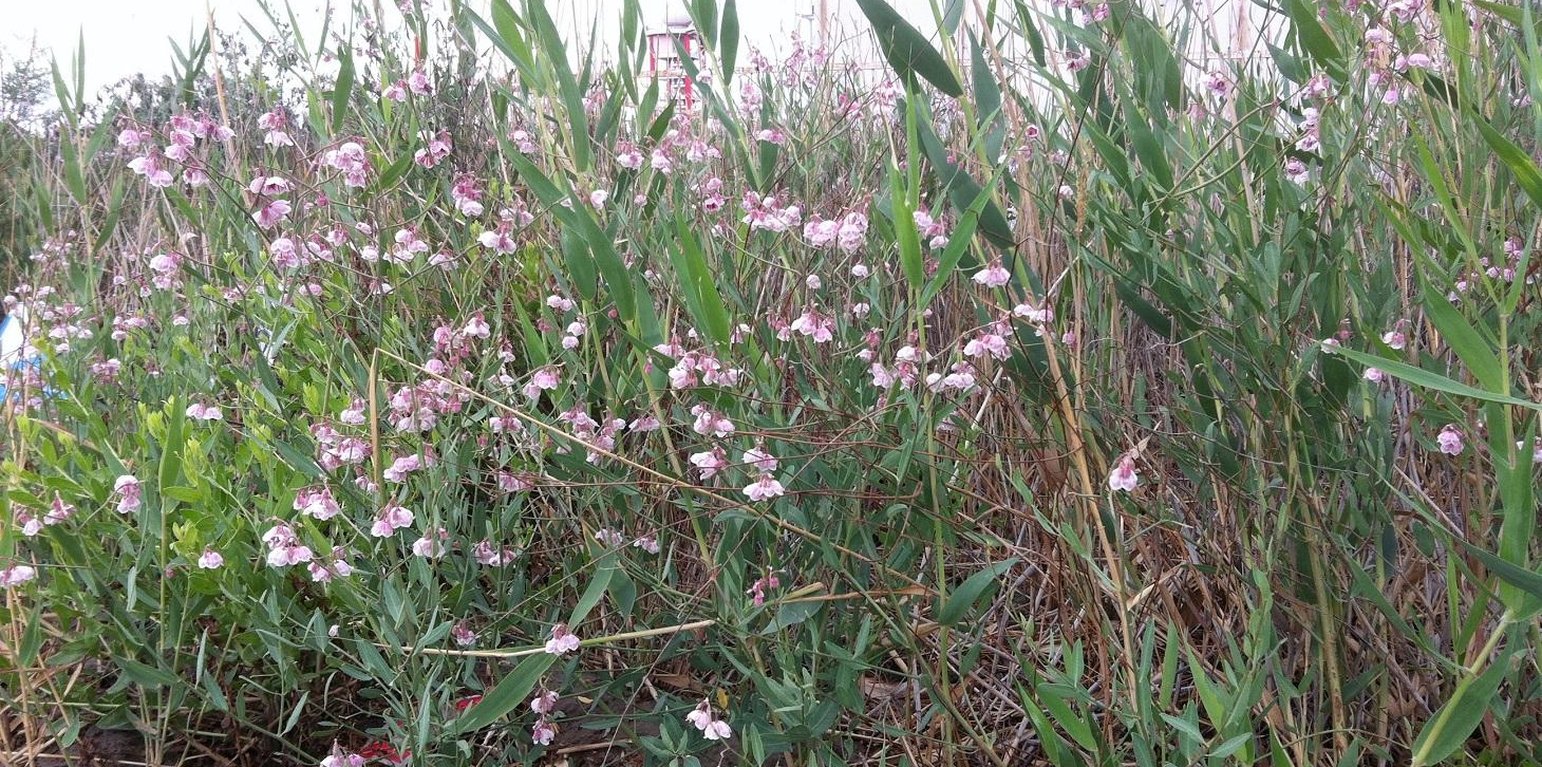
Purpose of the Technology: To halt desertification the barren saline soils need to be protected by vegetation to avoid soil loss by wind. But if this can be done through vegetation that yields an income then the advantage is double: a win-win situation. Apocynum venetum and Apocynum pictum are indigenous and both are drought and salt tolerant. They are phreatophytes: deep-rooted plants that tap groundwater or the soil layer just above the water table. A.venetum and A. pictum are rhizomatous perennials – and importantly they are cash crops too. Fibre from the stems are used to produce textiles, though the extraction process is time and labor consuming. The advantage of apocynum yarn is that it has antibacterial properties. The leaves and flowers are also sold and used to produce tea which is a Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) that reduces blood pressure. On a per hectare basis, the stem generates a potential income of US$ 3,650, the leaves US$ 1,995, and the flowers US$ 1,815: nevertheless the market for apocynum products is small. In Xinjiang most of the apocynum plantations are under commercial large-scale farmers. They have the capital to deal with the costly establishment of apocynum.
Natural / human environment: Fields on which apocynum is sown should have a groundwater level not deeper than 2m. Nevertheless the soil should be well-drained: best is a sandy loam. Waterlogged, calcareous, clayey soils are not suitable. Apocynum can withstand periods of water inundation; however, prolonged submergence or waterlogging inhibits its growth. The topsoil under apocynum is often saline, reaching salt contents of up to 20%. Apocynum can grow on sites with a pronounced surface salinization, as long as the subsoil and the groundwater are not strongly salinized. There are two methods of planting apocynum: by seed or by vegetative means. While irrigation helps establishment and good yields, this is at a much lower level than for cotton. In conclusion, A.venetum and A. pictum provide profitable options on saline soils, grow with minimal irrigation, and protect the land against wind erosion.
Location: Tarim River Basin, China / Xinjiang Province, China
No. of Technology sites analysed:
Spread of the Technology: evenly spread over an area (6000.0 km²)
In a permanently protected area?:
Date of implementation: more than 50 years ago (traditional)
Type of introduction






| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (USD) | Total costs per input (USD) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| Site establishment/ preparation | ha | 2.0 | 18.7 | 37.4 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | |||||
| Seeds | ha | 100.0 | 2.5 | 250.0 | |
| Seedlings | ha | 100.0 | 6.18 | 618.0 | |
| Other | |||||
| Manure | ha | 171.1 | 18.7 | 3199.57 | 100.0 |
| Waterfee | - | 1.0 | 460.0 | 460.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 4'564.97 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | -10'868.98 | ||||
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (USD) | Total costs per input (USD) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| irrigation and weeding labor | ha | 10.0 | 114.0 | 1140.0 | 100.0 |
| Harvest labor | ha | 1.0 | 359.0 | 359.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | |||||
| Transport | ton | 1.0 | 11.0 | 11.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | |||||
| Fertilizer (Phosporus) | kg | 150.0 | 4.12 | 618.0 | |
| Other | |||||
| Waterfee | 1.0 | 2280.0 | 2280.0 | ||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 4'408.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | -10'495.24 | ||||