

Growing the same crop in the same place for many years in a row disproportionately depletes the soil of certain nutrients. With rotation, a crop that leaches the soil of one kind of nutrient is followed during the next growing season by a dissimilar crop that returns that nutrient to the soil or draws a different ratio of nutrients. Crop rotation mitigates the buildup of pathogens and pests that often occurs when one species is continuously cropped, and can also improve soil structure and fertility by increasing biomass from varied root structures.
Purpose of the Technology: Crop rotation improves crop's productivity, it reduces soil erosion and enhances maximum nutrient utilization. Crop rotation also improve soil properties and aeration. A nitrogen-fixing crop, like a legume, should always proceed a nitrogen depleting one; similarly, a low residue crop (i.e. a crop with low biomass) should be offset with a high biomass cover crop, like a mixture of grasses and legumes
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Crop rotation is practiced by subdividing the land into different portions. The portions are planted with crops e.g. cereals at first then in the next season, another plant is planted in the following manner; 1) Cereals crop with legumes, 2) Deep rooted with shallow rooted and a cover crop.
Natural / human environment: In Embu county, the main crops that are rotated includes, maize and legumes.
Location: Mbeere South District, Eastern Province, Kenya
No. of Technology sites analysed:
Spread of the Technology: evenly spread over an area (approx. 10-100 km2)
In a permanently protected area?:
Date of implementation: 10-50 years ago
Type of introduction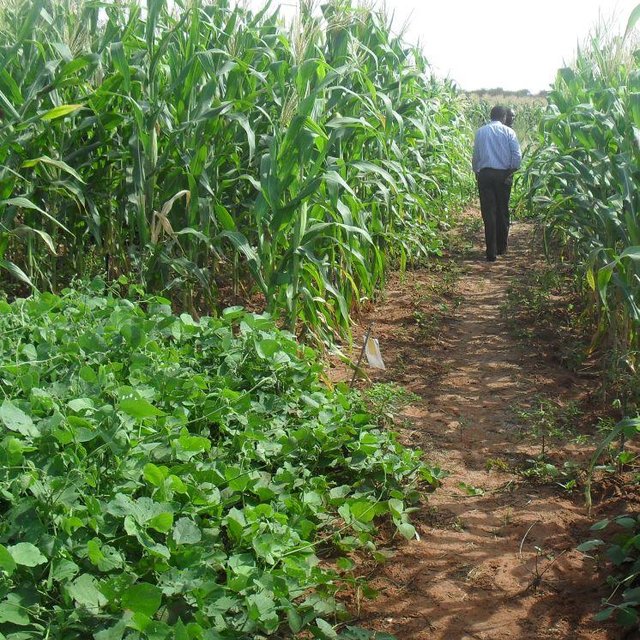




| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (Kshs) | Total costs per input (Kshs) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| Land preparation | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | |||||
| Tools | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | |||||
| Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 250.0 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 2.5 | ||||
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (Kshs) | Total costs per input (Kshs) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| Planting and weeding | ha | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | |||||
| Tools | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | |||||
| Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 250.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 2.5 | ||||