



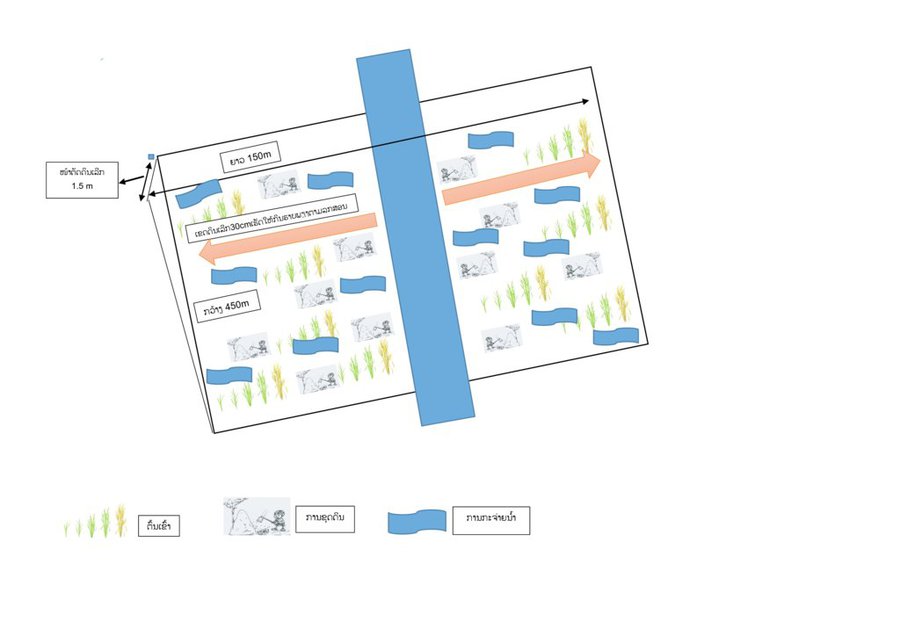
ເຕັກນິກ ການເຮັດນາ ລະດູແລ້ງ ຢູ່ແຄມຫ້ວຍ ເປັນແນວຄວາມຄິດ ລິເລ່ີມ ຈາກໂຄງການ Oxfarm Australia. ຊ່ຶງໃນເມ່ືອກ່ອນ ປະຊາຊົນ ພາຍໃນທອ້ງຖ່ີນ ເຄີຍຖາງປ່າເຮັດໄຮ່ເຂົ້າ ເປັນກິດຈະກໍາຫັຼກ ໃນການດໍາລົງຊີວິດ ຂອງປະຊາຊົນ ໃນເຂດພູດອຍ ແລະ ປະຊາຊົນ ກໍ່ບໍ່ເຄີຍເຮັດນາມາກ່ອນ.ຈາກສະພາບ ການດັ່ງກ່າວນັ້ນ, ປະຊາຊົນກ່ໍໄດ້ພົບບັນຫາ ການຂາດເຂົ້າກິນ ແລະ ເນື່ອງຈາກ ຈໍາກັດ ເນ້ືອທ່ີການຜະລິດ ແລະ ຈໍານວນ ຂອງປະຊາກອນເພີ່ມຂ້ຶນ ແລະ ເກີດມີການຍາດແຍ່ງ ພື້ນທ່ີ ທໍາການຜະລິດ. ດັ່ງນັ້ນ, ທາງໂຄງການ Oxfarm Australia ໄດ້ລິເລ່ີມເຂົ້າມາເມືອງຕະໂອ້ຍ ໃນຊຸມປີ 1996 ພາຍໃຕ້ ຈຸດປະສົງ ໂຄງການ ເພື່ອຫຸຼດຜອ່ນ ການບຸກລຸກ ທໍາມະຊາດ ໃນເຂດທຸລະການດານ ໂດຍໄດ້ມີການສ້າງຕັ້ງ ຄະນະ ກໍາມາທິການ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ໄພພິບັດ ທາງທໍາມະຊາດ ໃນຂັນບາ້ນ. ໂດຍທາງໂຄງການ ໄດ້ເລັງເຫັນຄວາມສໍາຄັນ ແລະ ການຈັດສັນ ອາຊີບຄົງທີ່ ເພື່ອສະເຫນີ ໃຫ້ປະຊາຊົນ ໂດຍເລັງເຫັນ ເຕັກນິກ ການເຮັດນາ ລະດູແລ້ງ ຢູ່ແຄມຫ້ວຍ ເປັນອີກທາງເລືອກຫນ່ືງ ໃຫ້ແກ່ປະຊາຊົນ ເພື່ືຶ່ອປັບປຸງ ຊີວິດການເປັນຢູ່ ຂອງເຂົາເຈົ້າ ທັງສາມາດ ຄໍາ້ປະກັນ ສະບຽງອາຫານ ແລະ ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນບັນຫາ ການເຮັດວຽກໜັກຂອງສະມາຊີກ ພາຍ ໃນຄອບຄົວ. ໃນເບ້ືອງຕົ້ນ ທາງໂຄງການ ແມ່ນໄດ້ມີການຝຶກອົບຮົມ ໃຫ້ປະຊາຊົນ ຮູ້ຈັກນຳໃຊ້ຄວາຍ ໃນການໄຖນາ ເພາະປະຊາຊົນ ບໍ່ເຄີຍເຮັດນາມາກ່ອນ. ພ້ອມທັງ ການສະໜອງແນວພັນເຂົ້າ, ຈົກ ແລະ ຊວ້ນ ໃນການບຸກເບີກ ແລະ ກະກຽມດິນນາ. ຊ່ືງໃນໄລຍະເບ້ືອງຕົ້ນ ທ່ີທາງໂຄງ ການ ເຂົ້າມາສົ່ງເສີມ ການເຮັດນາ ຢູ່ໃນບາ້ນ ບ່ໍມີຫຼາຍຄອບຄົວ ສົນໃຈເຮັດທົດລອງ ກັບທາງໂຄງການ ເນ່ືອງຈາກເຂົາເຈົ້າ ຢ້ານຜິດຮີດຄອງປະ ເພນີ ເພາະປະຊາຊົນ ເຊ່ືອວ່າ ການປູກເຂົ້າ ແມ່ນຕອ້ງປູກໃສ່ດິນຢູ່ສູງ ແລະ ບ່ໍປູກແຊ່ກັບນໍາ້ ຄືກບັການເຮັດນາ. ແຕ່ເຖິງຢ່າງໃດກ່ໍຕາມ, ໃນເວລານັ້ນ ກໍ່ມີຄອບຄົວ ຈໍານວນຫນ່ືງ ທ່ີຕັດສິນໃຈ ເຂົ້າຮ່ວມທົດລອງ ກັບທາງໂຄງການ ຊຶ່ງທາງໂຄງການ. ຂັ້ນຕອນ ແລະ ວິທີການ ໃນການເຮັດເຕັກ ນິກດັ່ງກ່າວ ແມ່ນປະຊາຊົນ ປະກອບສ່ວນ ໂດຍການໃຊ້ແຮງງານຄົນ ໃນການຂຸດດິນ, ກະກຽມດິນປັບຫນ້າດິນ ຢູ່ແຄມຫ້ວຍ ເພື່ອເຮັດໃຫ້ເປັນດິນຫຸຼບ ຫືຼ ພຽງເທົ່າກັບ ລະດັບ ນໍາ້ຫ້ວຍ ເພື່ອເຮັດໃຫ້ນໍ້າໃນຫ້ວຍ ສາມາດໄຫຼຍູ້ອອກໄປ ສູ່ພື້ນທີ່ ທ່ີດິນພຽງ ທ່ີປະຊາຊົນ ໄດ້ຂຸດ ແລະ ບຸກເບິກກຽມດິນໄວ້. ໂດຍສ່ວນໃຫ່ຍ ປະຊາຊົນ ຈະເລ່ີມຂຸດດິນ ໃນເດືອນທັນວາ ເຖິງ ເດືອນມັງກອນ ພາຍຫັຼງ ທ່ີນໍາ້ຢູ່ຫ້ວຍລົດລົງ ເນ່ືອງຈາກວ່າ ດິນບໍ ລິເວນດັ່ງກ່າວນັ້ນ ນໍາ້ໄດ້ຖ້ວມທຸກໆປີ ໃນເວລາລະດູຝົນ ຊ່ຶງເຮັດໃຫ້ ດິນເຂດດັ່ງກ່າວນັ້ນ ອຸດົມສົມບູນ ແລະ ຮັບນໍາ້ໄດ້ເປັນຢ່າງດີ. ມາເຖິງປະຈຸ ບັນ, ເຫັນໄດ້ວ່າ ປະຊາຊົນ ພາຍໃນບ້ານມີຄວາມສົນໃຈຫຼາຍ ໃນການເຮັດນາ ລະດູແລ້ງ ຢູ່ສອງຟາກຫ້ວຍ ແລະ ໄດ້ຂະຫຍາຍເນື້ອທີ່ນາອອກ ໃນບ່ອນທ່ີມີເງ່ືອນໄຂ ເປັນຕົ້ນ ແມ່ນບ່ອນທ່ີມີຫ້ວຍ ພາຍໃນບາ້ນ ແລະ ປະຊາຊົນ ກ່ໍມີຄວາມສຸກຫຼາຍ ທ່ີໄດ້ເຮັດນາ ຊ່ຶງສາມາດ ລົບລ້າງແນວຄວາມຄິດ ເຊ່ືອຖືແບບດັ້ງເດີມ ແລະ ຄວາມເຊ່ືອ ຈາກເມ່ືອກ່ອນ ທ່ີບ່ໍເຄີຍເຮັດນາ ແລະ ຢ້ານຜິດຮີດຄອງ ມາເຖິງປະຈຸບັນ ເຂົາເຈົ້າ ມີເຂົ້ານາ ໄວ້ກິນພາຍ ໃນຄອບຄົວ ເຫັນໄດ້ວ່າເຂົາເຈົ້າ ສາມາດ ຫຸຼດຜອ່ນ ເນ້ືອທ່ີ ການຖາງປ່າເຮັດໄຮ່ໄດ້ ທັງເປັນການຊ່ວຍປະຢັດ ແຮງງານ ໃນການເຮັດໄຮ່ເຂົ້າ ແລະ ນໍາໃຊ້ພື້ນທ່ີ ໃຫ້ເກີດປະໂຫຍດສູງສຸດ. ນອກຈາກນ້ີ, ປະຊາຊົນພາຍໃນບາ້ນ ທ່ີຢູ່ໃກ້ຄຽງ ກໍ່ໄດ້ນາໍເອົາບົດຮຽນດັ່ງກ່າວ ໄປຫມູນໃຊ້ ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິ ບັດ ໃນບາ້ນຂອງເຂົາເຈົ້າ.
Location: ເມືອງຕະໂອ້ຍ, ແຂວງສາລະວັນ, Lao People's Democratic Republic
No. of Technology sites analysed: 2-10 sites
Spread of the Technology: evenly spread over an area (approx. < 0.1 km2 (10 ha))
In a permanently protected area?:
Date of implementation: 10-50 years ago
Type of introduction





| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (ກີບ) | Total costs per input (ກີບ) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| ແຮງງານ ປັບໜ້າດີນ | ວັນງານ | 60.0 | 50000.0 | 3000000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | |||||
| ຈົກ | ອັນ | 2.0 | 30000.0 | 60000.0 | 100.0 |
| ພ້າ | ອັນ | 2.0 | 20000.0 | 40000.0 | 100.0 |
| ຄວາຍ | ໂຕ | 1.0 | 7000000.0 | 7000000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 10'100'000.0 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 1'262.5 | ||||
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (ກີບ) | Total costs per input (ກີບ) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| ແຮງງານ ຕົກກ້າ | ວັນງານ | 2.0 | 50000.0 | 100000.0 | 100.0 |
| ແຮງງານ ດຳນາ | ວັນງານ | 14.0 | 50000.0 | 700000.0 | 100.0 |
| ແຮງງານ ໃນການເກັບກ່ຽວ | ວັນງານ | 14.0 | 50000.0 | 700000.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | |||||
| ແນວພັນເຂົ້າ | ກິໂລ | 10.0 | 4000.0 | 40000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 1'540'000.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 192.5 | ||||
Quantity before SLM: 500 ກິໂລ/ເຮັກຕາ
Quantity after SLM: 1200 ກິໂລ/ 0.7 ເຮັກຕາ
ສາມາດ ເກັບເອົາເຟືອງ ມາເກືອ ເປັນອາຫານໃຫ້ງົວກິນໄດ້ ໂດຍສະເພາະ ໃນຊ່ວງລະດູແລ້ງ ທ່ີງົວອຶດຫຍາ້ກິນ
ງົວ ໄດ້ກິນເຟືອງ ເຮັດໃຫ້ແຂງແຮງດີ
ກິດຈະກໍາ ການເຮັດນາ ສາມາດຫຸຼດຜອ່ນ ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຂອງຜົນຜະລິດ ສົມທຽບກັບ ກິດຈະກໍາ ການເຮັດໄຮ່ເຂົ້າ ຊ່ຶງມີຄວາມສ່ຽງຫຼາຍ.
ຊາວກະສິກອນ ມີນາທົ່ງພຽງ ເຮັດໃຫ້ມີຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງດ້ານພືດພັນ ເນື່ອງຈາກສາມາດ ນໍາໃຊ້ເຟືອງ ໄປຄຸມໜານປູກຜັກ ເພື່ອປັບປຸງດິນ ເຮັດໃຫ້ມີຜັກໄວ້ກິນ ແລະ ມີນາ ທີ່ສາມາດ ຫາປາໄວ້ກິນ ພາຍໃນຄອບຄົວ.
ເນື້ອທີ ເຮັດໄຮ່ເຂົ້າຫຸຼດລົງ ແຕ່ມີເນື້ອທີ່ນາແຄມຫ້ວຍເພີ່ມຂຶ້ນ
ທາງໂຄງການ Oxfarm Australia ໄດ້ສະຫນອງຄວາຍ ໃຫ້ຊາວກະສິກອນ ແລະ ຊາວກະສິກອນ ໃຊ້ແນວພັນເຂົ້າ ພື້ນເມືອງ ທ່ີບໍ່ໄດ້ສີ້ນເປືອງລາຍຈ່າຍ.
ຊາວກະສິກອນ ສາມາດ ຫຸຼດຜອ່ນວຽກຫນັກ ສົມທຽບໃສ່ ກິດຈະກໍາ ການເຮັດໄຮ່ເຂົ້ົາທ່ີໃຊ້ແຮງງານຫຼາຍ.
ເພີ່ມຜົນຜະລີດເຂົ້າ ໄວ້ກິນພຽງພໍ ພາຍໃນຄອບຄົວ
ສາມາດ ປ່ຽນແນວຄວາມຄິດ ຂອງຊາວກະສິກອນ ທ່ີມີຄວາມເຊ່ືອຖື ບ່ໍໃຫ້ປູກເຂົ້າ ໃສ່ນໍາ້ ເພາະຜິດຮີດຄອງປະເພນີ.
ຊາວກະສິກອນ ສາມາດ ໃຊທົ່ງນາ ເປັນບ່ອນພັກຜອ່ນ ຊ່ຶງມີອາກາດ ທ່ີບໍລິສັດ
ຊາວກະສິກອນ ສາມາດ ເພີ່ມຜົນຜະລິດເຂົ້ານາໄດ້ ທັງເປັນການຫຸຼດຜອ່ນ ຄວາມບໍ່ຍຶນຍົງໃນການຖາງປ່າເຮັດໄຮ່ແບບເລ່ືອນລອຍ.
ສາມາດ ຫຸຼດຜອ່ນບັນຫາ ຂໍ້ຂັດແຍ່ງ ທ່ີດິນ ຈາກກິດຈະກໍາ ການຖາງປ່າເຮັດໄຮ່ ແບບເລືອນລອຍ
ເພີ່ມຈໍານວນ ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ຂອງພືດ ທ່ີເກີດຢູ່ຕາມແຄມຫ້ວຍ
ເພີ່ມຈໍານວນ ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ບ່ອນທ່ີຢູ່ອາໃສ ຂອງສ່ີງທ່ີມີຊີວິດ
ຫຸຼດຜອ່ນ ການປ່ອຍທາດອາຍພິດ ກະຈົກເຮືອນແກ້ວ ໂດຍການຢູດຕິ ການຖາງປ່າ ເຮັດໄຮ່ ໃນເຂດບໍລິເວນ ທ່ີເຮັດເຕັກນິກນ້ີ.