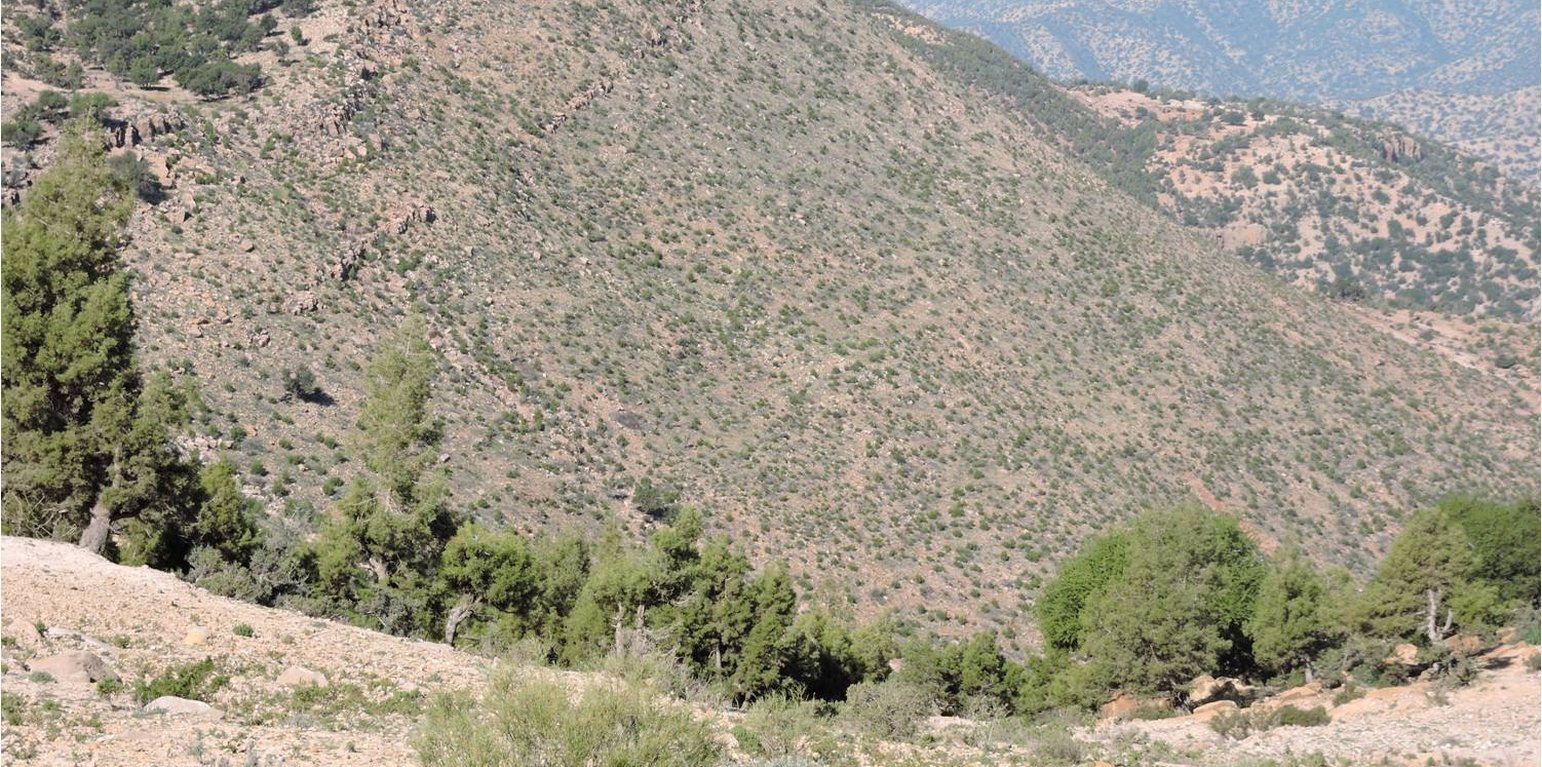




La mise en défens est instaurée après l'incendie de forêt de 2013.. La superficie incendiée était de l’ordre de : 1200 ha.
En plus de la l'interdiction des usages habituels de la population locale (paturage, ramassage du bois mort, etc) et tous les sujets incendiés sont recépés.
Avec uniquement l'exclusion des usages habituels et le respect de la mise en défens on attend une reprise de la végétation spontannée naturellement.
La restriction au parcours et autres activités humaines de prélèvement de produit est une mesure qui ne peut être efficace que grace à l'adhésion des usagers pour le respect de la mise en défens. Dans ce cas, les usagers se sont organisés en association et bénéficient de la compensation à raison de 350 dh/an/ha en application de la réglementation relative à la suspension des droits d'usages mise au point depuis 2002.
Après 5 à 6 ans de mise en défens, on remarque bien que la mise en défens a donné des résultats très satisfaisants en matière de réhabilitation du couvert arboré et du développement des espèces locales.
Location: Commune d'Amskroud, Agadir et tout le pays., Morocco
No. of Technology sites analysed: 2-10 sites
Spread of the Technology: evenly spread over an area (approx. 10-100 km2)
In a permanently protected area?:
Date of implementation: 2012
Type of introduction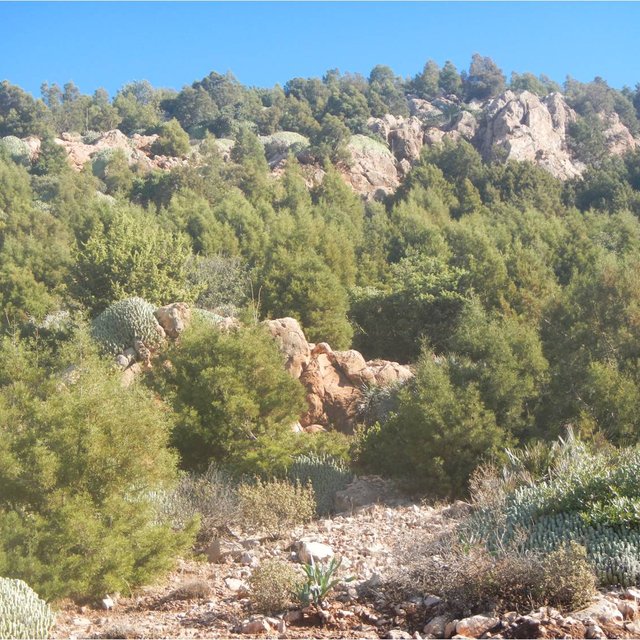






| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (USD) | Total costs per input (USD) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| Recepage | ha | 750.0 | 1000.0 | 750000.0 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 750'000.0 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 75'000.0 | ||||
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (USD) | Total costs per input (USD) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Other | |||||
| Compensation mise en défens | ha | 750.0 | 35.0 | 26250.0 | |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 26'250.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 2'625.0 | ||||
Non utilisable.
Quantity before SLM: brulé
Quantity after SLM: En réhabilitation
Suspendu.
Réhabilitation du couvert.
Quantity before SLM: brulé
Quantity after SLM: En réhabilitation
En réhabilitation
Quantity before SLM: dénudé
Quantity after SLM: réhabilitation
Couvert du sol.