With increasing water demand and with the changing climate, water availability or water security is critical for the agriculture sector as this resource is a fundamental prerequisite in crop production. Various solutions are tapped and one of it is harnessing the potential of wastewater to be used for irrigation.
In the Philippines, one of the companies that utilize their treated wastewater is the BUSCO SUGAR MILLING CO., INC. located in Brgy. Butong, Quezon, Bukidnon. This treated wastewater is currently being re-used as irrigation water for the BUSCO Cane Farms areas, adjacent to the Mill Site covering 493 hectares and also to their leased adjacent 323-ha agricultural land.
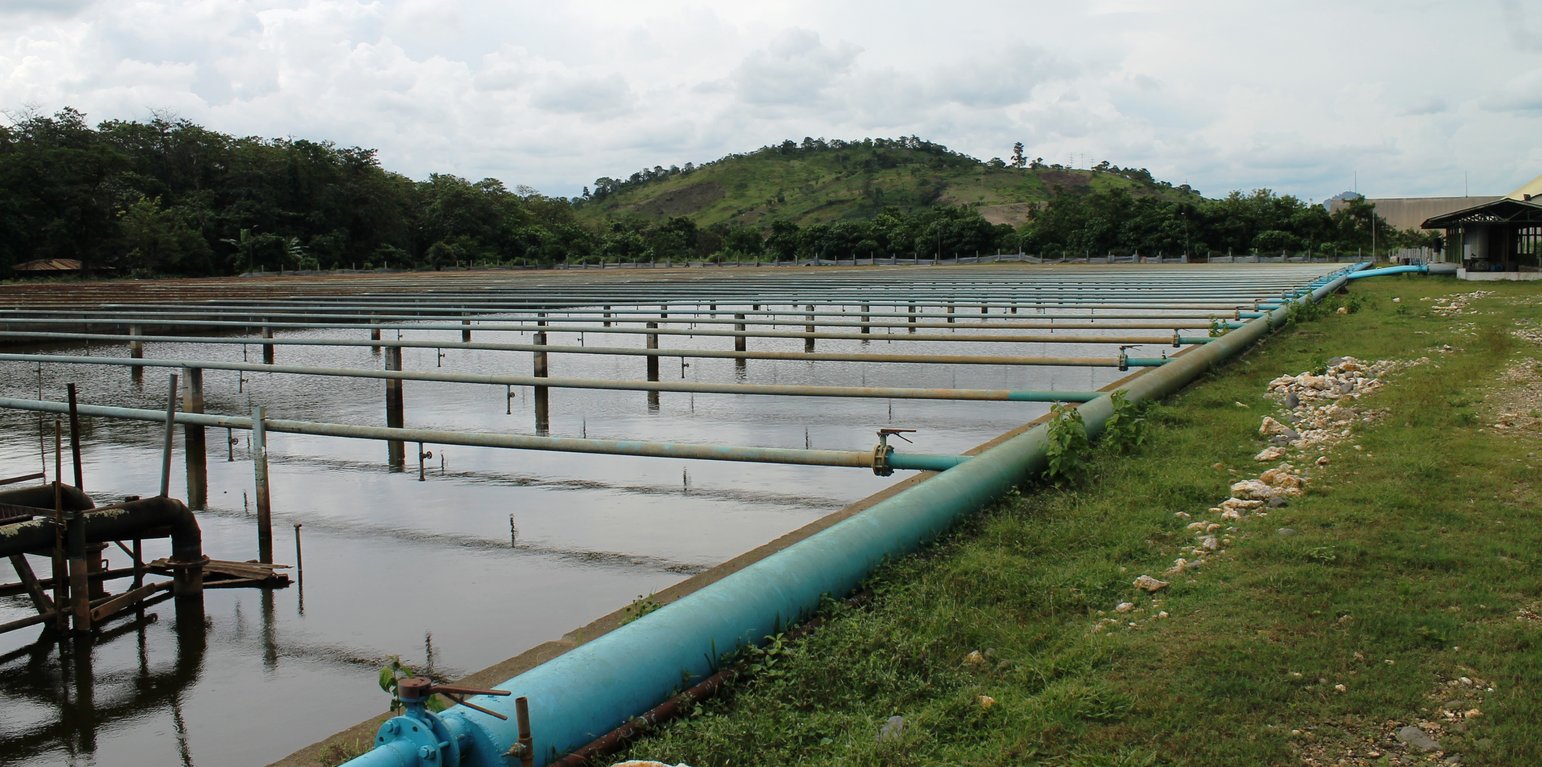
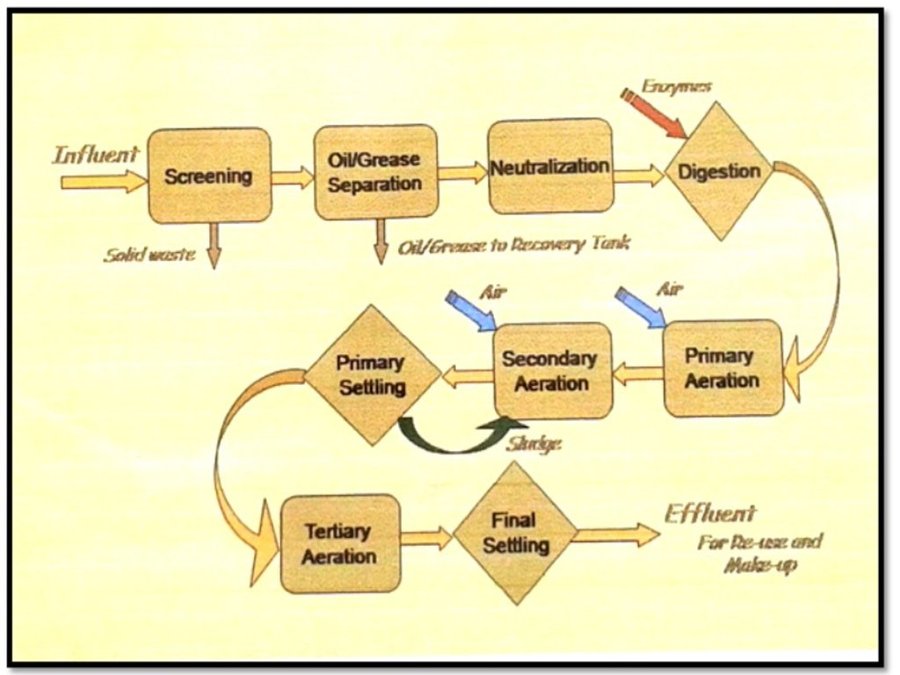
Primarily, water as an industrial by-product is evident in both raw and refined sugar milling process. Volume of wastewater can be generated in the following sources or stations of sugar production: mill and cane handling station, process and/or boiling house, refinery house, and boiler house. In BUSCO, this wastewater all goes to their common wastewater treatment plant with a capacity of 100,000 volumetric meter and uses primary and secondary treatment.
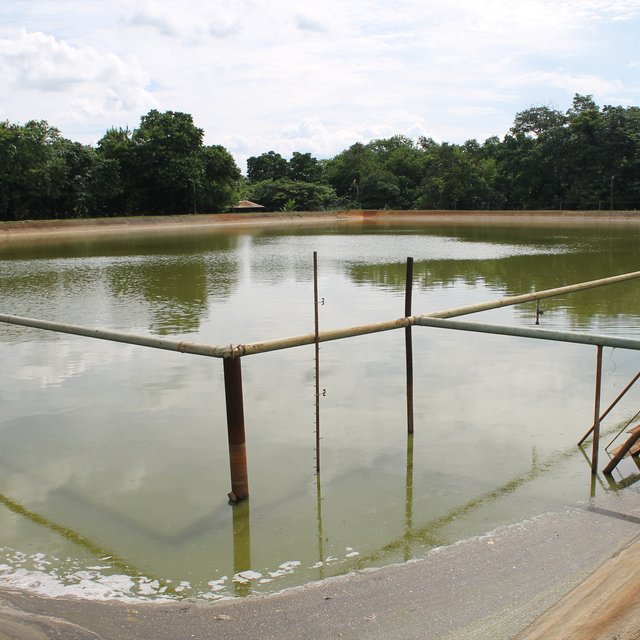
The treatment started with the screening of influent (waste water) which passes through a motor driven conveyor type system to separate the solid waste such as bagasse, bagacillo, silt/mud, sand, and trash canes. After the screening, it now proceeds to the oil/grease separation at the separator tank. Oil and grease that usually floats were removed via manual skimming. The next treatment process is called neutralization wherein the acidic influent (phof 4.0–5.0) will be added with chemicals (i.e. Lime and/or caustic soda) to neutralize and maintain the pH at 6.0–8.0. The neutralized wastewater is then impounded in a digester tank to undergo the process of digestion. Enzymes or bacteria are being introduced to enhanced biodegradation. Aeration is also applied to minimize suspended solids and scum formation. After this, wastewater is transferred to the lagoon for primary aeration process. Lagoons are belted with air diffuser membrane to produced fine bubbles and efficiently dissolved oxygen. Waste water was aerated and polluting substance decomposed. Further, the wastewater and the activated sludge are again mixed and aerated in the secondary and tertiary aeration where the polluting substances are further decomposed by oxidation and are absorbed. Finally, it will store in the final settling pond which will then be utilized for irrigation. The treated wastewater in BUSCO has a Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) value of 50mg/L which is within the prescribed standard BOD parameters of wastewater quality to be used for crop irrigation (< 150mg/L).
Irrigation is done through the hand move spray irrigation system. It uses aluminum pipes backed by centrifugal pumps and spray nozzles. Aside from supporting the sugarcane water requirement particularly during dry months, the treated wastewater/effluent contains nutrients (Nitrogen- 2.5mg/L; Phosphorus- 3.8 mg/L; Potassium- 3.8 mg/L) which reduce fertilizer requirements of the sugarcane farm.
Location: Butong, Quezon, Bukidnon, Philippines
No. of Technology sites analysed: single site
Spread of the Technology: evenly spread over an area (approx. 1-10 km2)
In a permanently protected area?:
Date of implementation: 10-50 years ago
Type of introduction