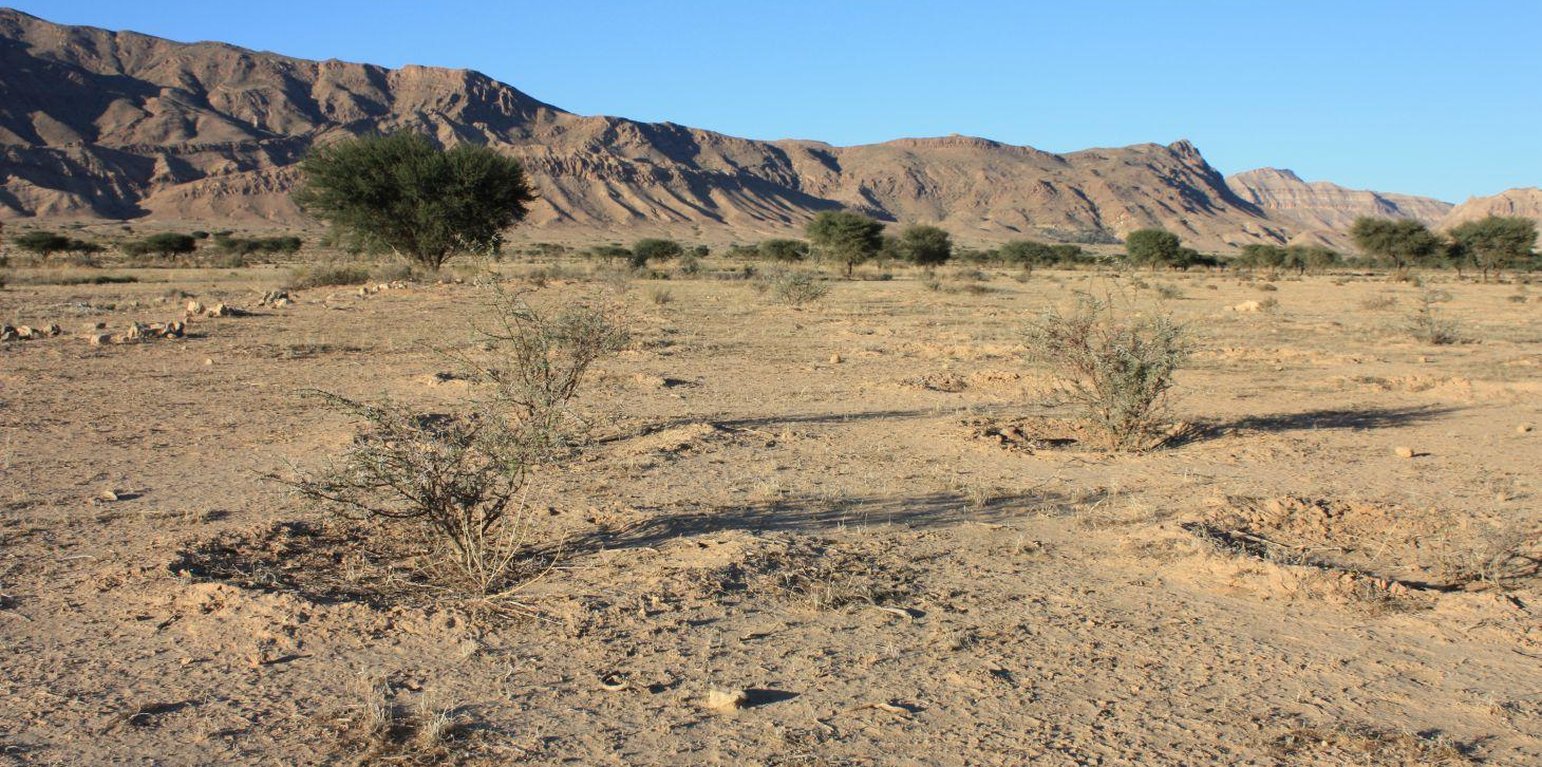




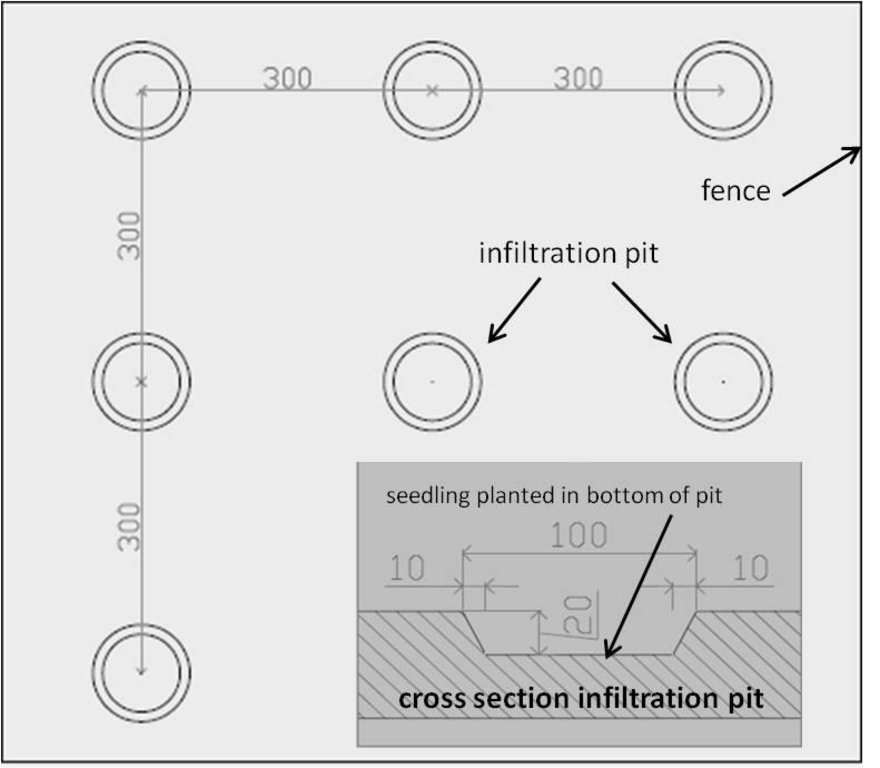
Protection and reforestation of degraded arid lands in central and southern Tunisia (Bled Talah region) with tree species Acacia tortilis subsp. raddiana. A. raddiana is a native trees species which is able to tolerate extreme droughts and to persist on the edge of the Sahara desert. Acacia plantations are set up following a 3m x 3m grid using seedlings of A. raddiana. Seedlings are planted in the bottom of infiltration pits which are constructed for rainwater harvesting. Protection of the plantation area is established by means of a fence.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of afforestation is the rehabilitation of degraded drylands and restoration of the original forest-steppe ecosystem in the Bled Talah region, which suffered for over a century from overexploitation of natural resources and intensification of agricultural activities. Focus is put on the synergy between the protection of the natural resources with the involvement of local people and the improvement of their livelihoods.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The protection of the Bled Talah region was initiated in 1936 and from then on several actions were undertaken such as the construction of a tree nursery and the creation of Integral Protection Zones through complete fencing. The Bled Talah area was designated as a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve in 1977. Bou Hedma National Park was officially created by the Ministry of Forests in 1980 covering an area of approximately 16.000 ha. The park consists of three Integral Protection Zones or core areas which are completely fenced, two agricultural zones and two buffer zones. Since the 1970s, several reforestation campaigns with A. raddiana are conducted in the Integral Protection Zones.
Natural / human environment: Arid Tunisia, i.e. the central and southern part of Tunisia, is characterized by an extremely irregular spatiotemporal rainfall pattern, a limited amount of rain (350 mm maximum per year), a limited number of days of rain (15 to 40 days a year) and a high average annual temperature (18 to 21 °C).
Location: Sidi Bouzid/Gafsa, Tunisia
No. of Technology sites analysed:
Spread of the Technology:
In a permanently protected area?:
Date of implementation: 10-50 years ago
Type of introduction










| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (Tunisian Dinar) | Total costs per input (Tunisian Dinar) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| Labour | ha | 1.0 | 330.0 | 330.0 | |
| Construction material | |||||
| Iron wire fence | ha | 1.0 | 1600.0 | 1600.0 | |
| iron poles | ha | 1.0 | 800.0 | 800.0 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 2'730.0 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 1'654.55 | ||||
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (Tunisian Dinar) | Total costs per input (Tunisian Dinar) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| Labour | ha | 1.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 30.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 18.18 | ||||
The technology improves the livelihoods of local people directly through income generation from employment in the park and indirectly by the improvement of climatological conditions in the neighbourhood of the park.