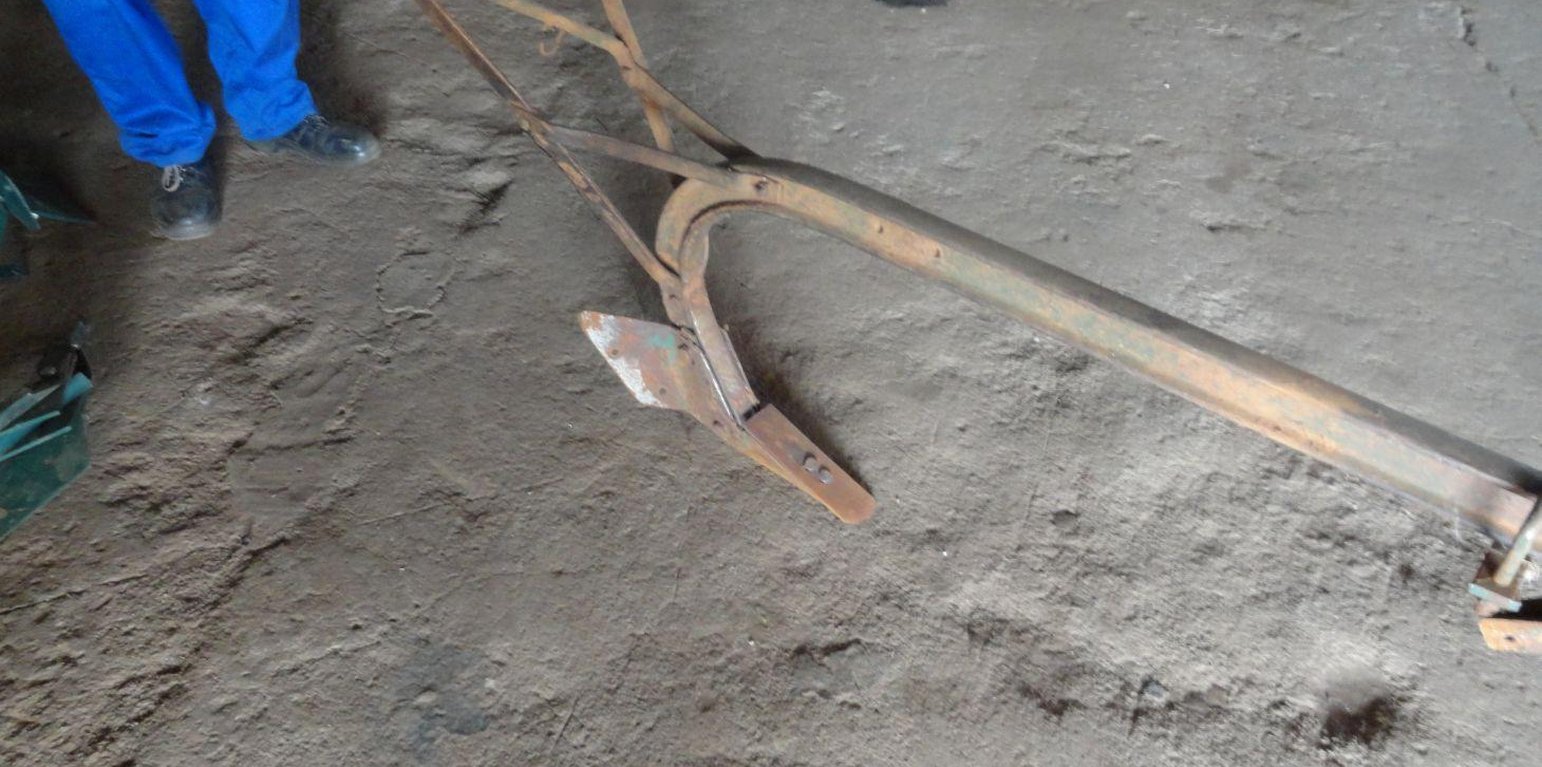




The Magoye Ripper is an animal drawn implement used for conservation tillage. The Ripper consists of a frame that is attached to a common plough beam and on this frame is fixed a tine at an angle that penetrates and breaks up the soil when pulled. Only the region where the crop furrow will be is loosened by the tine and by so doing reducing the amount of tillage and disruption of soil structure while preserving the crop residue cover. The frame has some ‘wings’ attached to it that throw the soil out of the ripped furrow to leave it open for planting and collecting of water. Ripping is done in one pass up to a depth of 15cm depending on the strength of the oxen, soil type, hitch assembly settings and the sharpness of the tine.
Purpose of the Technology: Reducing tillage first of all reduces tillage costs and tillage time allowing more time for the farmer to plant early and/or a bigger area. Reducing tillage also reduces the loss of soil organic matter and the destructive effects to the soil structure ultimately improving soil fertility and soil water conservation. Ripping does not invert the soil, hence it does not bury crop residues which further enhance organic matter levels and protect the soil from excessive evaporation and erosion. The open furrow left by the ripper collects water from the adjacent untilled soil much in the same way basins (zai system) are used for water harvesting. This together with the increased rooting depth resulting from the breaking of compacted soil, enhanced infiltration and early planting improves water conservation and hence the resilience of crop to extended dry spells.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The establishment of ripping based conservation tillage mainly involves the purchase of the ripper frame and the
replaceable tines. Liming acidic soils (low pH soils) followed by a final ploughing will be required to correct the soil pH which otherwise will be difficult to correct once conservation tillage has been established. The main establishment activity involves adopting a new mindset and increasing the knowledge base to apply the technology correctly. Knowledge about alternative weed control practices and herbicide use is particularly cardinal as the farmer will have to adopt new weeding practices and routines in the absence of ploughing. Maintenance activities are more or less the same as conventional tillage except for replacing the tillage tines which wear every now and then. The same applies for the inputs except for the increase in use of herbicides.
Natural / human environment: Ripping is best performed in dry season when the soil is dry although this may not be possible with some of the smaller and/or weak oxen when the soil is too dry. It is therefore recommended for farmers in regions that experience long dry seasons to rip at the end of harvest before the soils get too dry and hard and when the oxen are in good condition before they lose weight and strength due to less feed and water, excessive heat as the dry season progresses.
The ripper is mostly suited to small-scale farmers just adopting Conservation Agriculture (CA) since the tool can be easily adapted to the existing plough beam which most of the farmers already have. The small capital outlay for establishing the system makes it suited to resource poor and risk-averse farmers.
Location: Mazabuka/Magoye, Zambia/Southern Province, Zambia
No. of Technology sites analysed:
Spread of the Technology: evenly spread over an area (approx. 0.1-1 km2)
In a permanently protected area?:
Date of implementation: 10-50 years ago
Type of introduction






| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (Kwacha) | Total costs per input (Kwacha) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Equipment | |||||
| Magoye ripper | Tool | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| Knapsack sprayer | Tool | 1.0 | 80.0 | 80.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 130.0 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 26.0 | ||||
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (Kwacha) | Total costs per input (Kwacha) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| Slashing and spreading residues | ha | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| Ripping | ha | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| Liming | ha | 1.0 | 42.0 | 42.0 | 100.0 |
| Planting and fertilizing | ha | 1.0 | 40.0 | 40.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | |||||
| Seeds | kg | 20.0 | 2.5 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | |||||
| Fertilizer | kg | 400.0 | 0.8 | 320.0 | 100.0 |
| Other | |||||
| Herbicides | liters | 5.0 | 6.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour: Chemical weeding | ha | 1.0 | 24.0 | 24.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour: Harvesting | ha | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 596.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 119.2 | ||||
Quantity before SLM: 1.8ton/ha
Quantity after SLM: 2ton/ha
mostly due to early planting
crop residues needed for soil cover
Better tolerance to dry spells
Quantity before SLM: None
Quantity after SLM: 20%
purchase of herbicides
Quantity before SLM: None
Quantity after SLM: 15%
due to lower tillage cost, better yield
only if herbicicdes are used for weeding
due to improved yields and more time and labour to diversify
Less time spent preparing land
competition for crop residues with neighbours cattle
Technology not yet been applied on a large enough area to make significant impact at community level but increased farm incomes among farmers has led to better education and health among household members.
due to improved good drainage
open furows collect water
due to better soil cover
due to improved soil structure
not applied extensively
due to better soil cover
due to resulting improved soil srtucture
Due to non-inversion tillage
Due to less soil disturbance and better soil cover
Due to less soil disturbance
Due to less soil disturbance
Due to less soil disturbance
due to resulting good drainage
Due to less soil disturbance
Due to less soil disturbance
due to increased soil organic matter (SOM)
Open furrow collect water in times of excess rainfal
If furrow are made along the slope
only if applied on a large scale
only if applied on a large scale
only if applied on a large scale
only if applied on a large scale
only if applied on a large scale
only if applied on a large scale