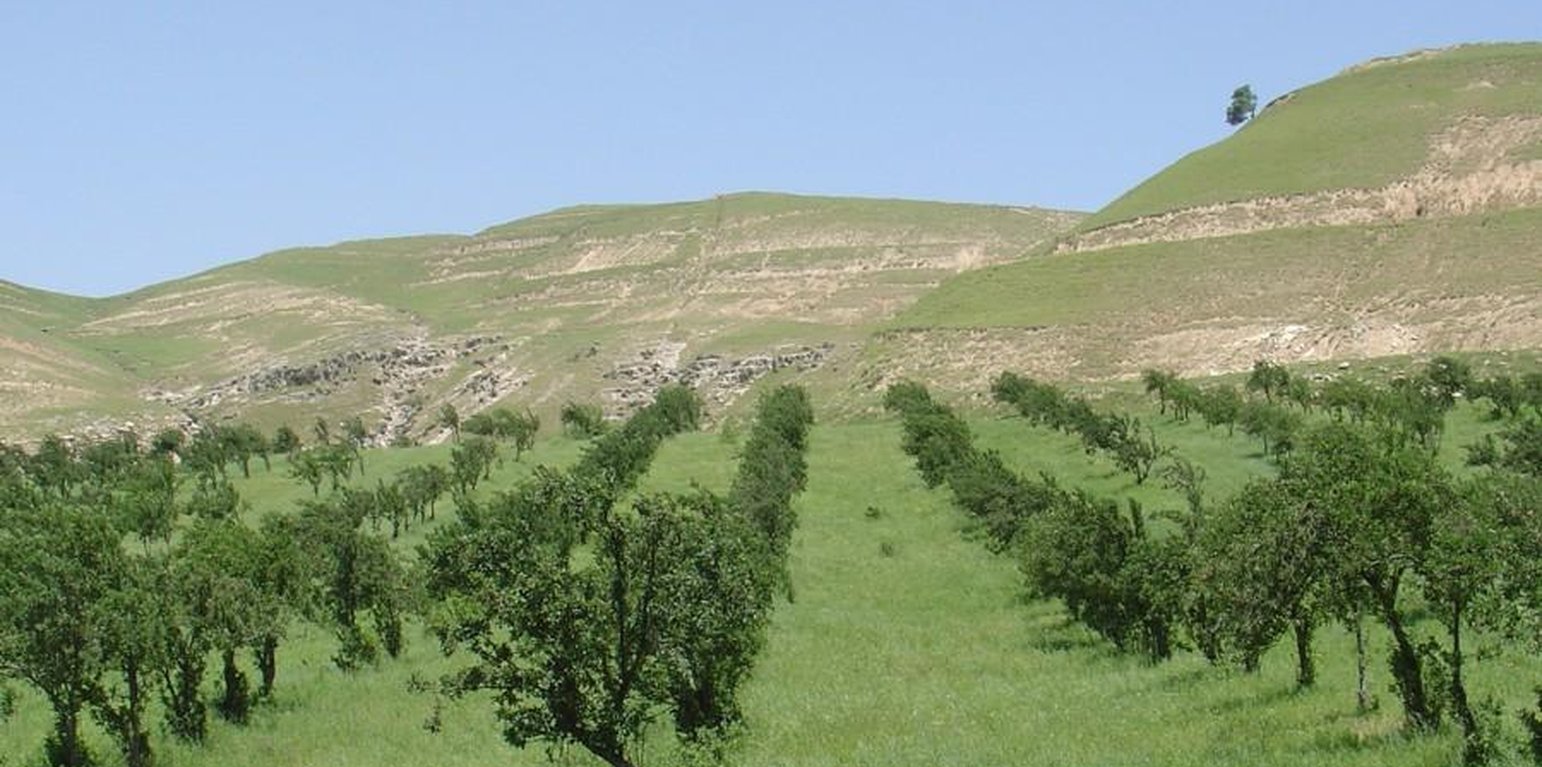




In the Faizabad region, Tajikistan, an area which is characterised by hilly topography, and deep but highly erodible loess soils, farmers traditionally cultivate beans and wheat in combination with fruit trees. This was a rather unsystematic agroforestry system, and during Soviet times (in the 1980s) fruit production was intensified. Pure-stand orchards were established: the land was levelled and on slopes exceeding 20%, terraces were constructed mechanically. The density of trees was increased, and the little space remaining between was used for hay production. Annual cropping was stopped.
Purpose of the Technology: After the Soviet era, farmers reduced the number of trees, allowing room for inter-cropping. They also established new orchards according to this same pattern. Those who farm rented land merely inter crop wheat, whereas the few farmers who own their land, rotate crops with two years of wheat, followed by one of legumes (beans or lucern). Crops are grown both for home consumption and sale.
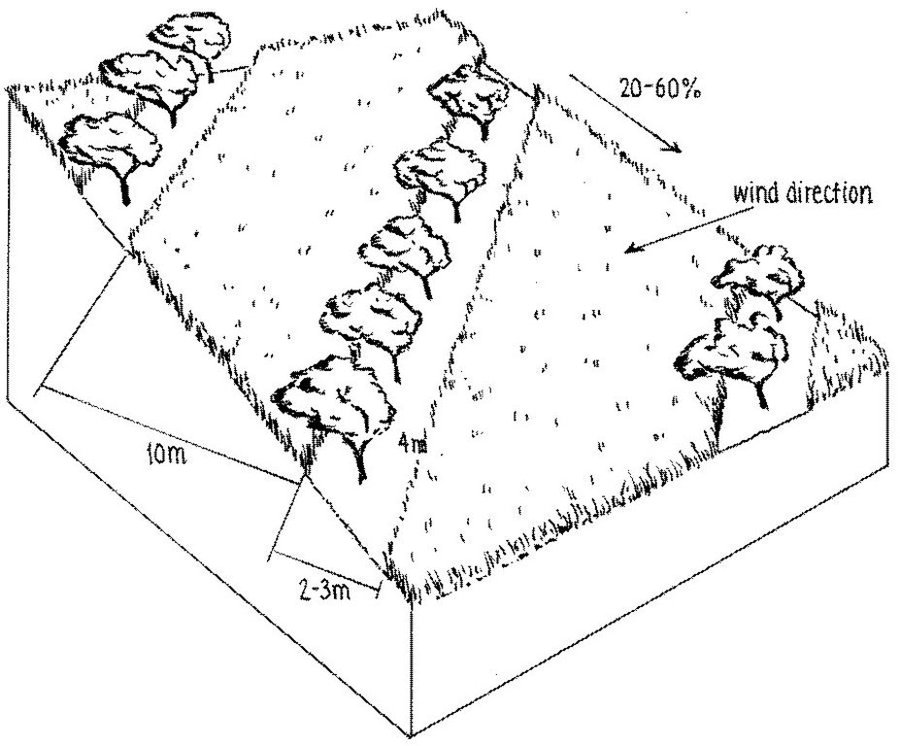
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The density of apples was reduced by expanding the spacing from approx 5 m to 10 m between rows, and from 2 m to 4 m within rows. Along each row of trees a 2-3 m strip of grass was left to grow. The layout of fruit trees in lines is a compromise between being along the contour, and against the prevailing wind. After harvesting of the fruit, between August and October, farmers sow their annual crops.
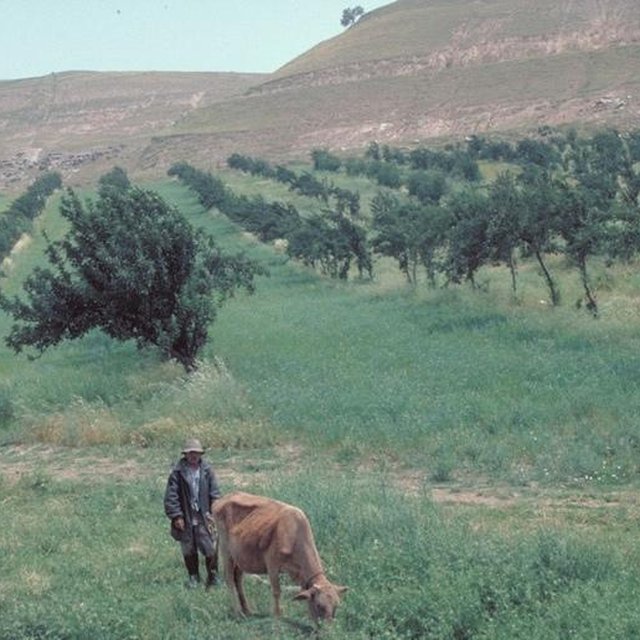
Natural / human environment: This agroforestry system provides protection against strong winds, heavy rains and flooding. Soil erosion (by water) has been reduced due to improved soil cover by the inter cropping, and through leaf litter, which is left to decompose on the ground. Furthermore, after harvesting, about three quarters of the crop residues are left on the field as mulch. The remainder is used as fodder. Soil organic matter within the current agroforestry system is considerably higher than in the surrounding grazing areas. Soil fertility has improved also: beans can fix 60-80 kg/ha/year of nitrogen. Compared with other crops, wheat provides the best erosion protection. Since the lateral rooting system of the apple trees reaches only 1-1.5 m from the trunk, competition for nutrients is not a major problem. Neither is there a problem with shade, since during the crop establishment period the trees have lose their leaves. In order to increase production, farmers plan to apply supplementary irrigation where possible.
Location: Faizabad, Tajikistan, Faizabad, Tajikistan
No. of Technology sites analysed:
Spread of the Technology:
In a permanently protected area?:
Date of implementation: 10-50 years ago
Type of introduction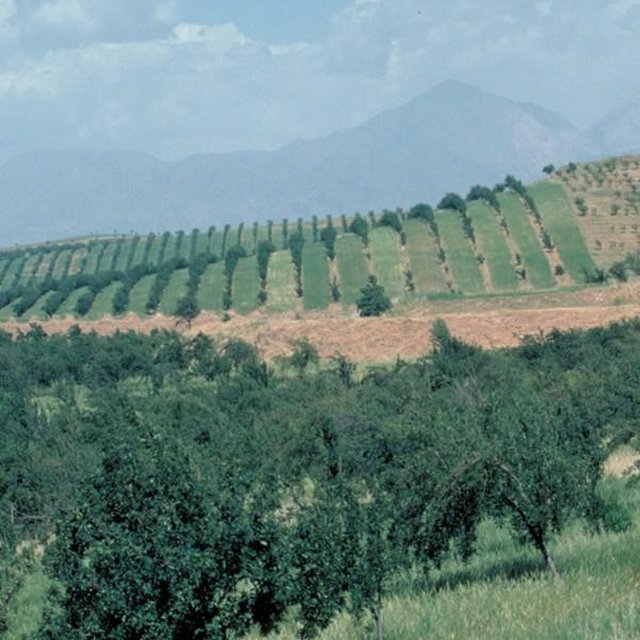








| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (USD) | Total costs per input (USD) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| Planting of fruit orchard | ha | 1.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| Thinning and hand lanting | ha | 2.0 | 10.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | |||||
| machine use | ha | 1.0 | 120.0 | 120.0 | 100.0 |
| tools | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 | |
| Plant material | |||||
| seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 250.0 | 250.0 | |
| Fertilizers and biocides | |||||
| fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| biocides | ha | 1.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| pesticides | ha | 1.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 570.0 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 570.0 | ||||
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (USD) | Total costs per input (USD) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| applying organic manure for crops and trees | ha | 1.0 | 45.0 | 45.0 | 100.0 |
| ploughing | ha | 2.0 | 10.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | |||||
| labour animal traction | ha | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| labour harvesting | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | ||
| labour mulching and cutting | ha | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | |||||
| seeds | ha | 1.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | |||||
| fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| biocides | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| compost manure | ha | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 220.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 220.0 | ||||
difficult to apply pesticides using machinery and pesticides are very expensive.
Pruning is important, but farmers are new to the system and don’t always have the skills required
Also biodiversity enhancement is medium (20-50%)