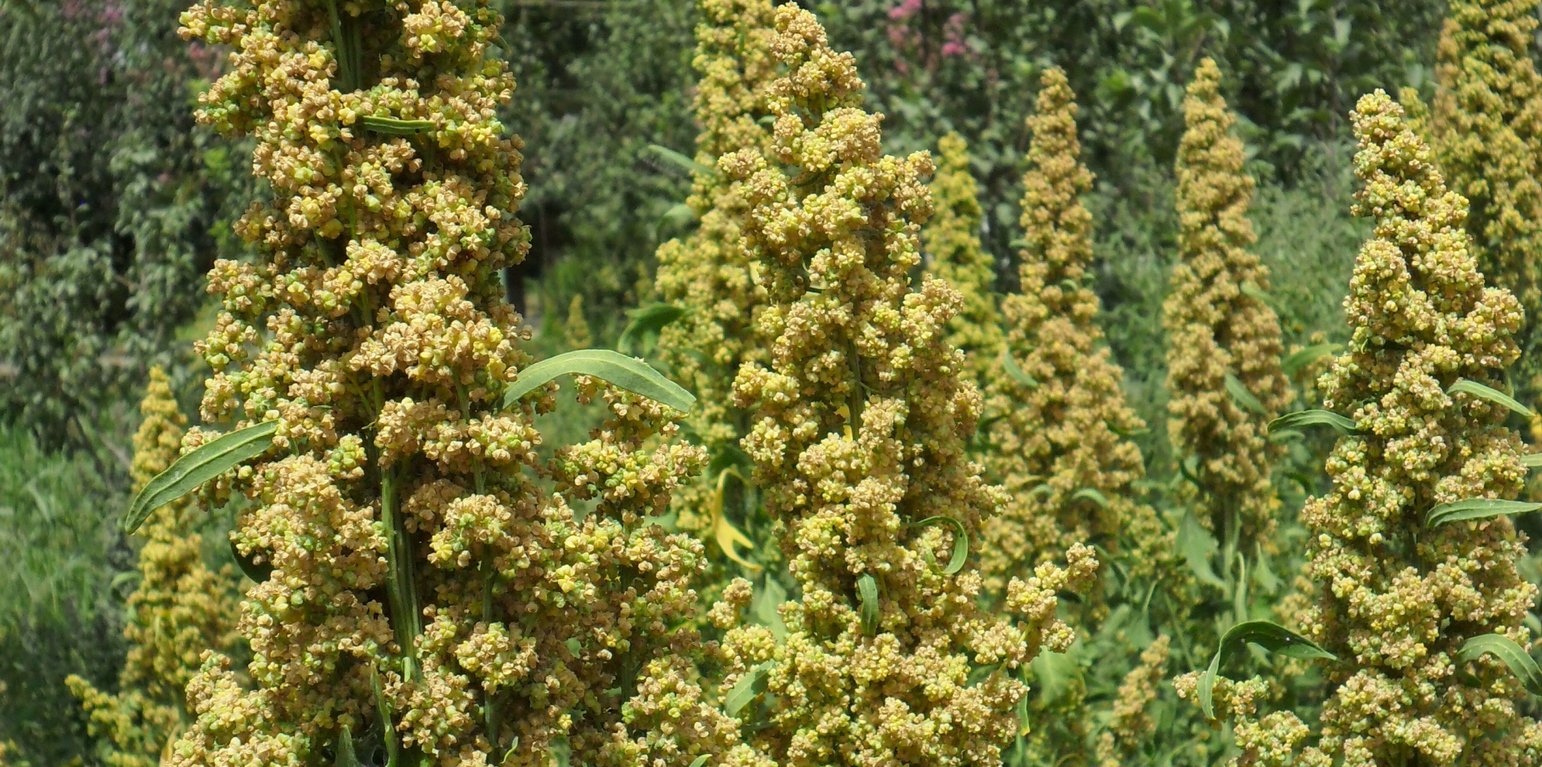




Location: Tajikistan
No. of Technology sites analysed: 2-10 sites
Spread of the Technology: applied at specific points/ concentrated on a small area
In a permanently protected area?:
Date of implementation: 2013; less than 10 years ago (recently)
Type of introduction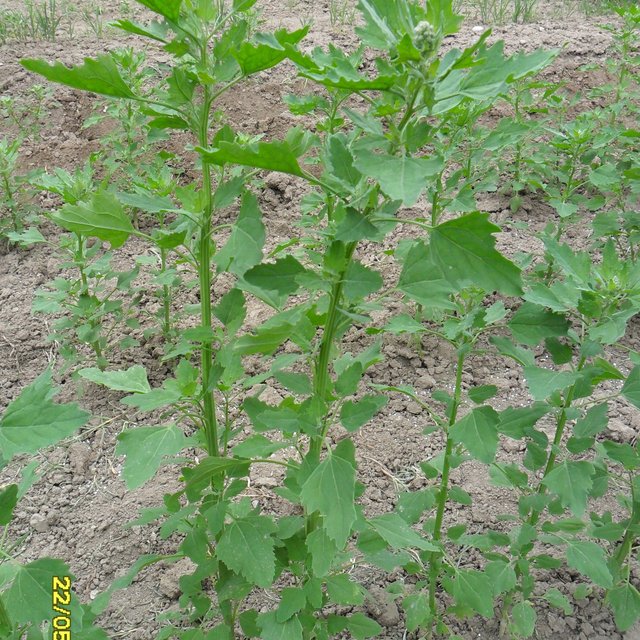
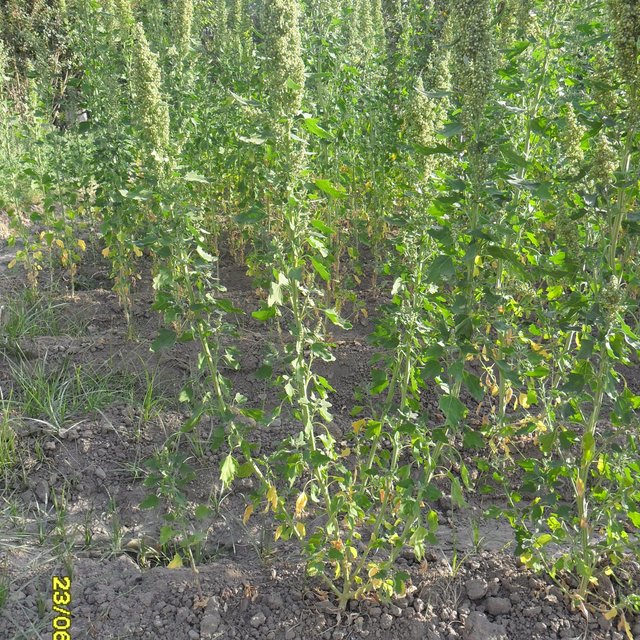









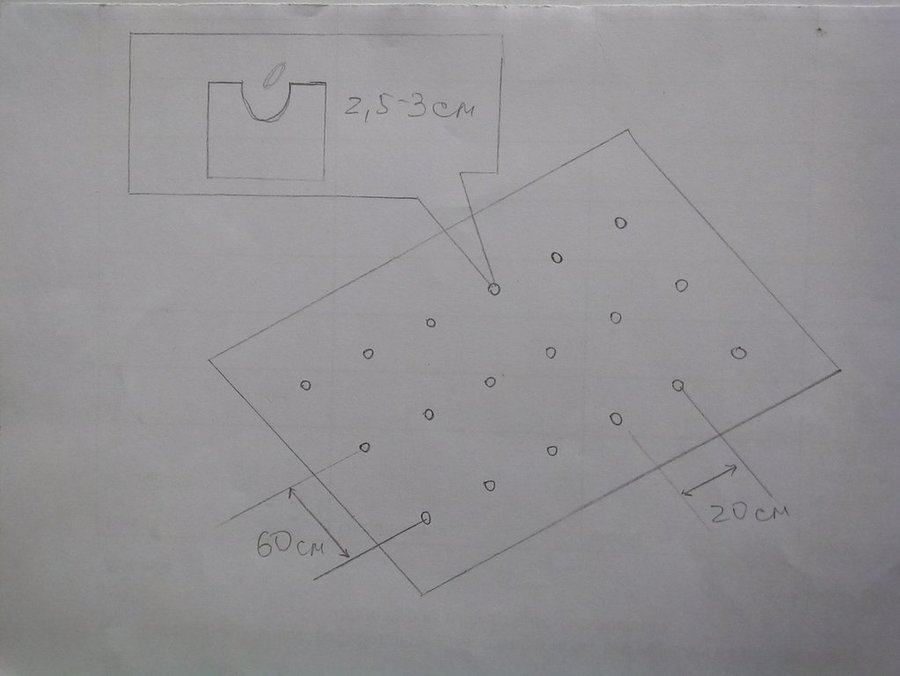
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (n.a.) | Total costs per input (n.a.) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| 1.0 | 150.0 | 150.0 | |||
| 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |||
| 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |||
| 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |||
| Equipment | |||||
| 80.0 | 6.7 | 536.0 | |||
| Plant material | |||||
| 4.0 | 40.0 | 160.0 | |||
| Fertilizers and biocides | |||||
| 10000.0 | 2.0 | 20000.0 | |||
| 150.0 | 4.5 | 675.0 | |||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 21'821.0 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 21'821.0 | ||||
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (n.a.) | Total costs per input (n.a.) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| 20.0 | 30.0 | 600.0 | 100.0 | ||
| 2.0 | 100.0 | 200.0 | 100.0 | ||
| 1.0 | 250.0 | 250.0 | |||
| 2.0 | 100.0 | 200.0 | 100.0 | ||
| Equipment | |||||
| 10.0 | 25.0 | 250.0 | 100.0 | ||
| 40.0 | 6.7 | 268.0 | |||
| Fertilizers and biocides | |||||
| 150.0 | 3.5 | 525.0 | |||
| 150.0 | 4.0 | 600.0 | |||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 2'893.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 2'893.0 | ||||