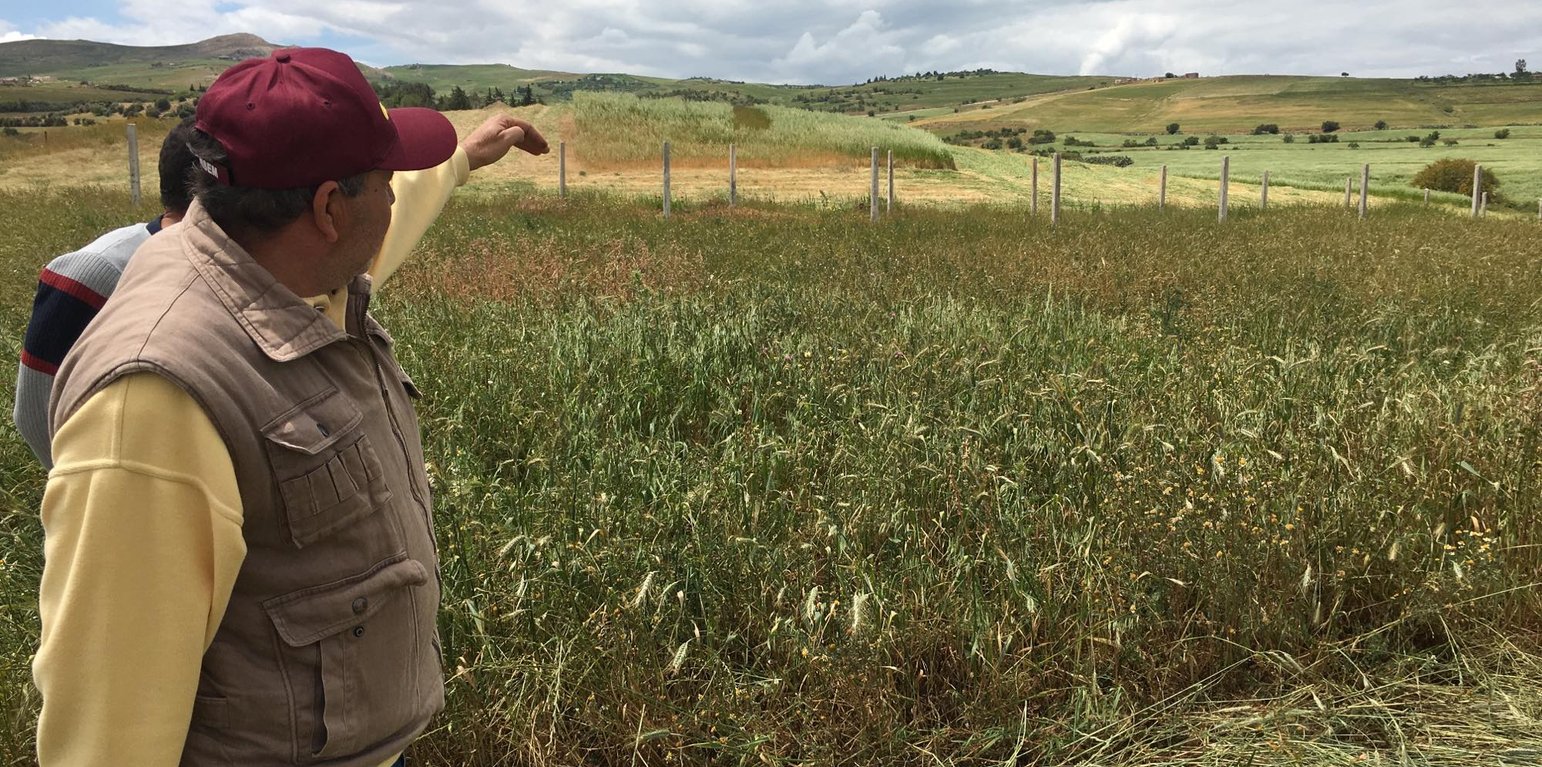




Vu les problèmes de dégradation des terres par l’érosion hydrique et le baisse de la fertilité chimique et biologique des sols qui ont conduit à une diminution des rendements des grandes cultures, l’agriculture et lors d’une réunion avec les représentants du ministère de l’agriculture ou un groupe étranger a présenté l’agriculture de conservation comme alternative à la dégradation des terres et l’amélioration de sa fertilité, il s’est convaincu de l’utilité de cette technologie et il a testé l’application de l’agriculture de conservation avec ses trois principes dans ses terres avec l’appui d’un groupe d’experts français du CIRAD à travers l’agence française de développement AFD et le centre technique des céréales en Tunisie.
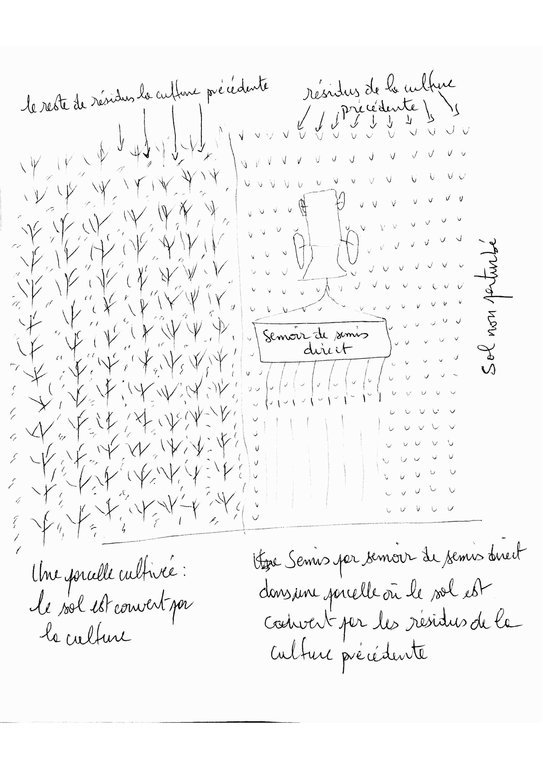
En faite l’agriculture de conservation consiste à éliminer le labour de la terre et le remplacer par un désherbage chimique pour éliminer les mauvaises herbes et de semer directement par un semoir spécial appelé semoir de semis direct. Ensuite l’agriculture conduit ses cultures comme il le faisait auparavant après récolte, l’agriculture doit laisser une partie des résidus des cultures sur le sol pour le couvrir durant l’été, la période ou il n’y a pas des cultures. L’agriculture de conservation exige aussi l’élimination de la monoculture et le diversification des cultures qu’on appelle rotation ou séquence des cultures des différentes familles.
Location: Krib, Siliana, Tunisia
No. of Technology sites analysed: single site
Spread of the Technology: evenly spread over an area (approx. 1-10 km2)
In a permanently protected area?:
Date of implementation: 1999; 10-50 years ago
Type of introduction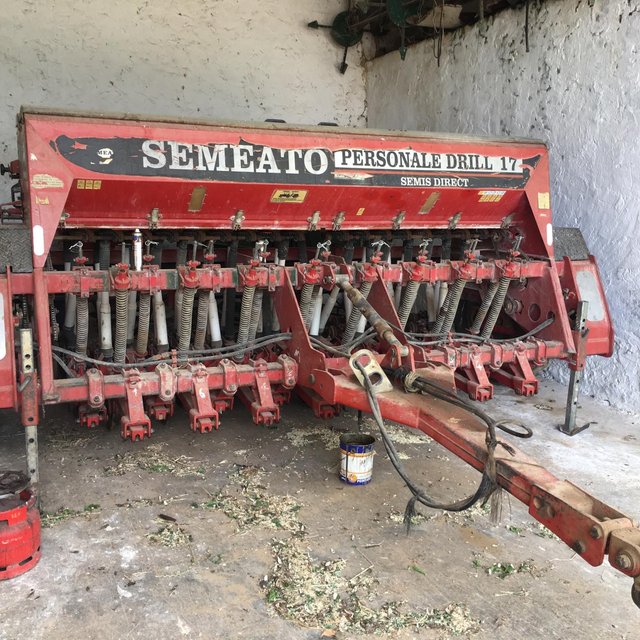



| Species | Count |
| cattle - dairy | 200 |
| poultry | 10 |









| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (Dinar Tunisien) | Total costs per input (Dinar Tunisien) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| ouvriers | personne/jour | 2.0 | 8.0 | 16.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | |||||
| location tracteur | heure | 6.0 | 18.0 | 108.0 | 100.0 |
| location semoir | heure | 1.0 | 45.0 | 45.0 | 100.0 |
| location moisonneuse | heure | 1.25 | 30.0 | 37.5 | 100.0 |
| location presse paille | balle | 120.0 | 0.4 | 48.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | |||||
| semences | quintal | 1.7 | 60.0 | 102.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | |||||
| herbicides | litre | 3.0 | 20.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| fertilisation azotée | quintal | 2.5 | 22.0 | 55.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 471.5 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 188.6 | ||||