

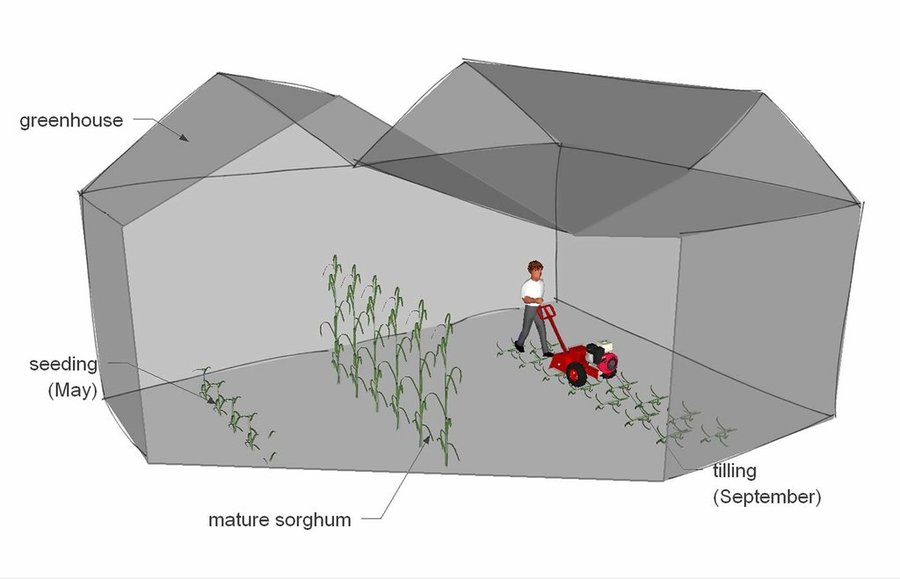
The angiosperm Sorghum vulgare is used in green house cultivations in coastal Timpaki, Crete, Greece, for green manuring through crop rotation with tomato plants. The crop rotation usually takes place every other summer when the green house is fallow. Sorghum plants are commonly used for grain, fibre and fodder, but this technology uses plants as soil conditioners.
Purpose of the Technology: The technology is applied as an effective agronomic measure for the increase of the productive capacity of soil, the reduction of pests (due to breaking or limiting pest cycles) and soil borne diseases and the mitigation of soil salinity. This technology mitigates and prevents soil degradation by improving the soil and subsoil structure through the deep root system of the plants (often >1 m) and increasing nutrient and organic matter availability through the incorporation of the plant biomass into the soil by tilling it under. Furthermore, the improved structure of the soil leads in higher infiltration rates, mitigates the salt accumulation in the root zone and combats soil salinity, one of the main soil degradation problems in the coastal zone. The increase of workload and the demand of irrigation water during the dry summer period constitute the main drawbacks of the SLM technology.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Initially, when the main crop (tomato- Solanum lycopersicum) is removed from the green house in June, about 7 kg of Sorghum seeds per 0.1 ha are sown and incorporated in the soil by ploughing at about 4-5 cm depth. Sorghum is drought- and heat-tolerant thus the irrigation needs are minimum and depend on the respective climatic conditions. As it is used for manuring and not fodder or fruit production, water stress conditions are favorable as the root system expands deeper in order to fulfill plant water needs thus improving the soil structure. In September, the farmer uses a branch grinder to fritter the Sorghum plants and then incorporates them in the soil by tillage.
Natural / human environment: The average annual precipitation in the area is 500 mm and the climate ranges between sub-humid Mediterranean and semi-arid. Average annual temperature is 18.5 degrees C with 6 months below 18 degrees C but above 5 degrees C, thus classifying the area as subtropical. In the location where the technology is applied, land is mostly privately owned and water rights can be public, cooperative or private. The financial means of the land user applying this technology are more or less on par with those of the rest of the community.
This Technology was documented within the scope of FP7 RECARE Project, funded grant agreement no 603498.
Location: Timpaki, Heraklion, Greece
No. of Technology sites analysed: single site
Spread of the Technology: applied at specific points/ concentrated on a small area
In a permanently protected area?: Nee
Date of implementation: 10-50 years ago
Type of introduction




| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (Euro) | Total costs per input (Euro) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| Labour | ha | 1.0 | 132.0 | 132.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | |||||
| Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 720.0 | 720.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | |||||
| Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 75.0 | 75.0 | 100.0 |
| Other | |||||
| Irrigation water | ha | 1.0 | 65.0 | 65.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 992.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 1'066.67 | ||||
Due to increased soil organic matter
Because of the diseases control
Due to reduced fertilizers