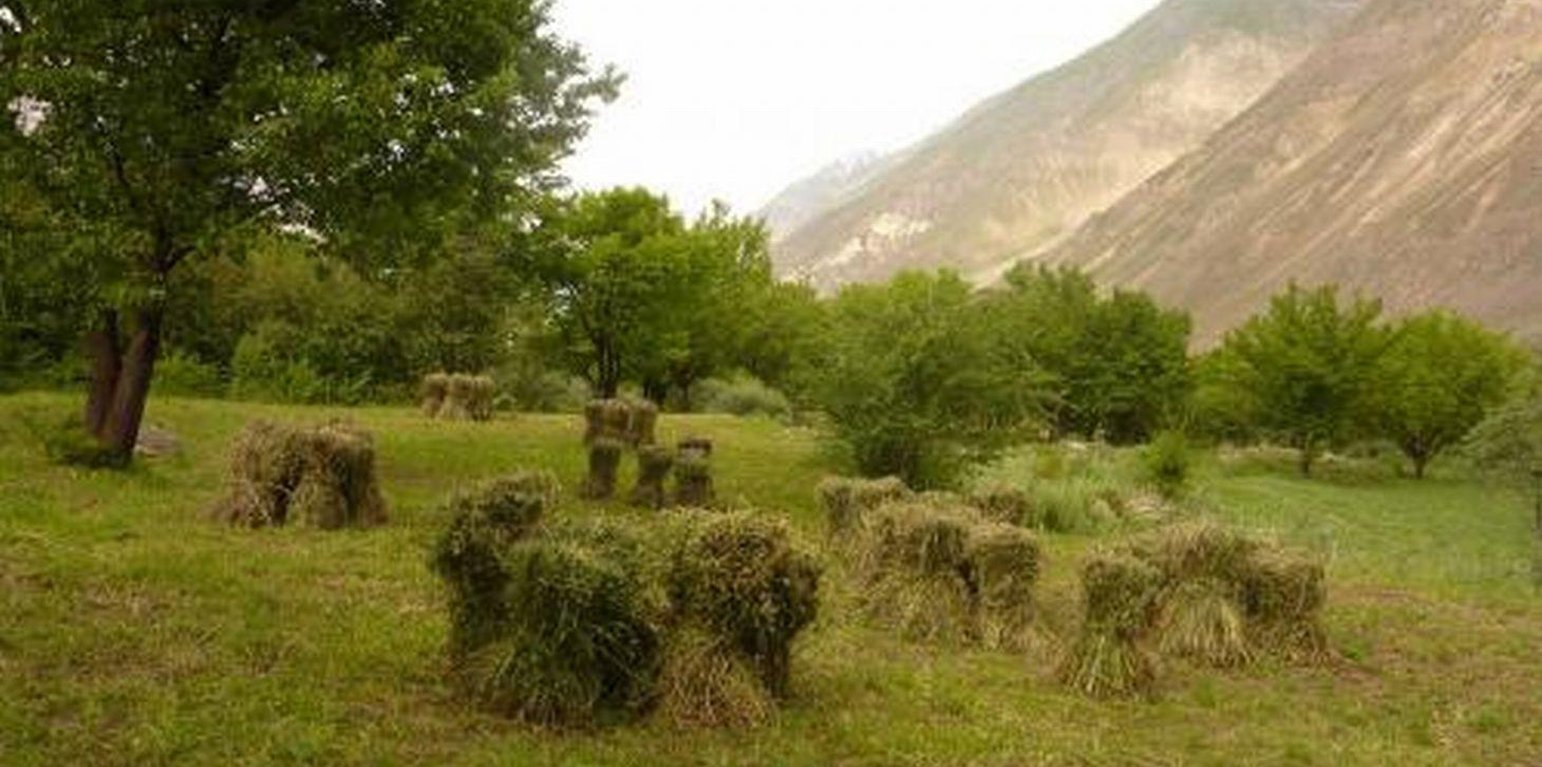




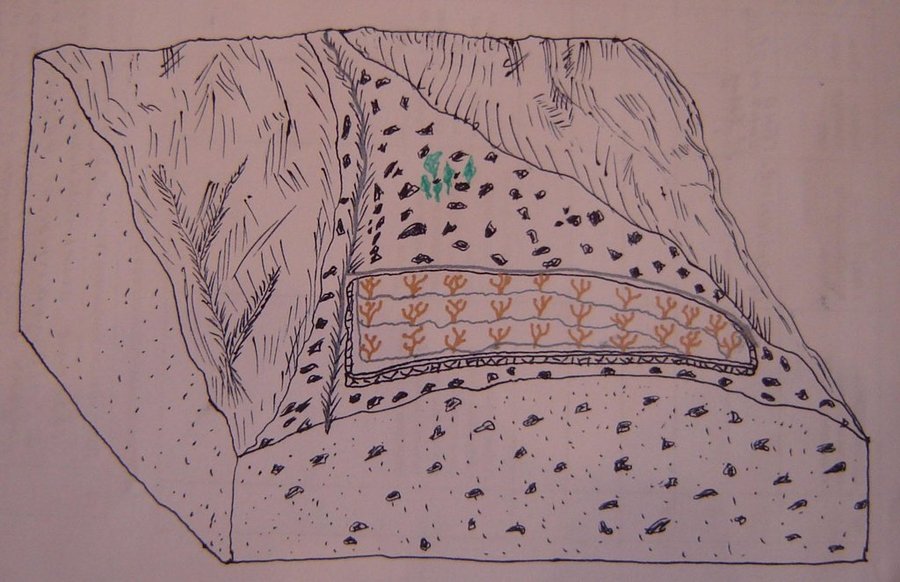
Сильно каменистый конус выноса до внедрения технологии использовался как низкопродуктивное пастбище. На участке внедрения технологии проведена камнеуборка. Камни и глыбы использовались для строительства ограждения (забора) вокруг участка. Часть камней складировалась в кучи на территории участка. Вдоль верхней границы участка построен оросительный канал. Из него на территорию участка, по горизонтали мезорельефа, проведены оросительные арыки. Планировка поверхности участка не проводилась из за сильной каменистости. Деревъя абрикоса посажены вдоль оросительных арыков. Междурядьях сада возделываются многолетние травы -эспарцет, люцерна. Камни убранные с площади участка использовались для строительство забора вокруг участка. Забор необходим для того, чтобы предотвратить проникновения на территорию сада мелко и крупно рогатого скота.
Назначение технологии: Цель технологии, повышение продуктивности сильно каменистых, склоновых земель конуса выноса с применением орошения и возделыванием комбинированных культур-абрикосового сада и многолетних трав.
Основные действия и вложения: уборка камней на участке, строительство ограждения, строительство оросительного канала, проведение оросительных арыков по площади участка, посадка деревьев, вспашка междурядье и посев многолетних трав.
Природная\социальная обстановка: Участок расположен в аридной зоне на сильно каменистой почве конуса выноса, на левом берегу реки Ванч. До освоения этих земель поверхность почвы на 60% было покрыта камнями. Растительность была представлена эфемерами, имеющие короткий период вегетации. Эти земли использовались под летние низкопродуктивные выпаса.
Location: ГБАО, Ванж, Жовид, Таджикистан, Tajikistan
No. of Technology sites analysed:
Spread of the Technology: evenly spread over an area (approx. 0.1-1 km2)
In a permanently protected area?:
Date of implementation: 10-50 years ago
Type of introduction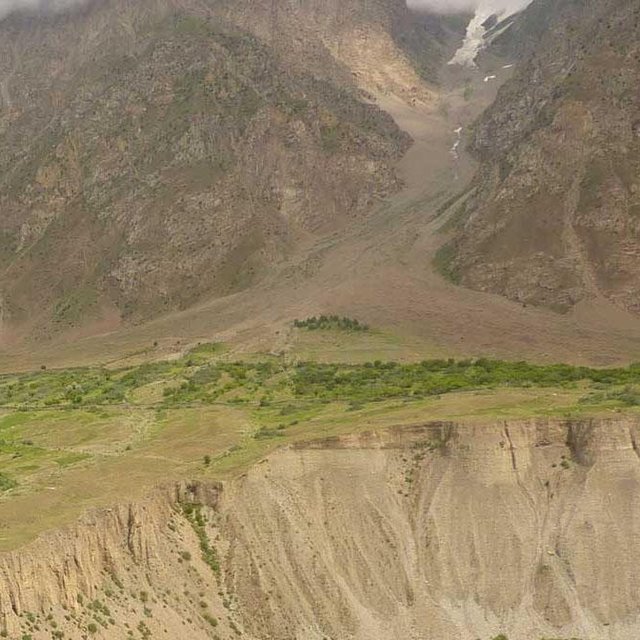









| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (Сомони) | Total costs per input (Сомони) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| Строительство забора | м | 3000.0 | 15.0 | 45000.0 | 30.0 |
| Строительство оросительного канала | м | 1300.0 | 23.07692 | 30000.0 | 10.0 |
| Посадка саженцев | шт | 6400.0 | 1.0 | 6400.0 | 100.0 |
| Камнеуборка | га | 20.0 | 2625.0 | 52500.0 | 30.0 |
| Plant material | |||||
| саженцы | шт | 6400.0 | 5.0 | 32000.0 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 165'900.0 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 36'866.67 | ||||
Внедрение технологии позволило фермерам зарабатывать 12500 сомони с продажи сено и абрикосов. Этот доход дает шанс на получение образования, медицинской помощи и увеличивает количество благ и необходимых вещей для хозяства