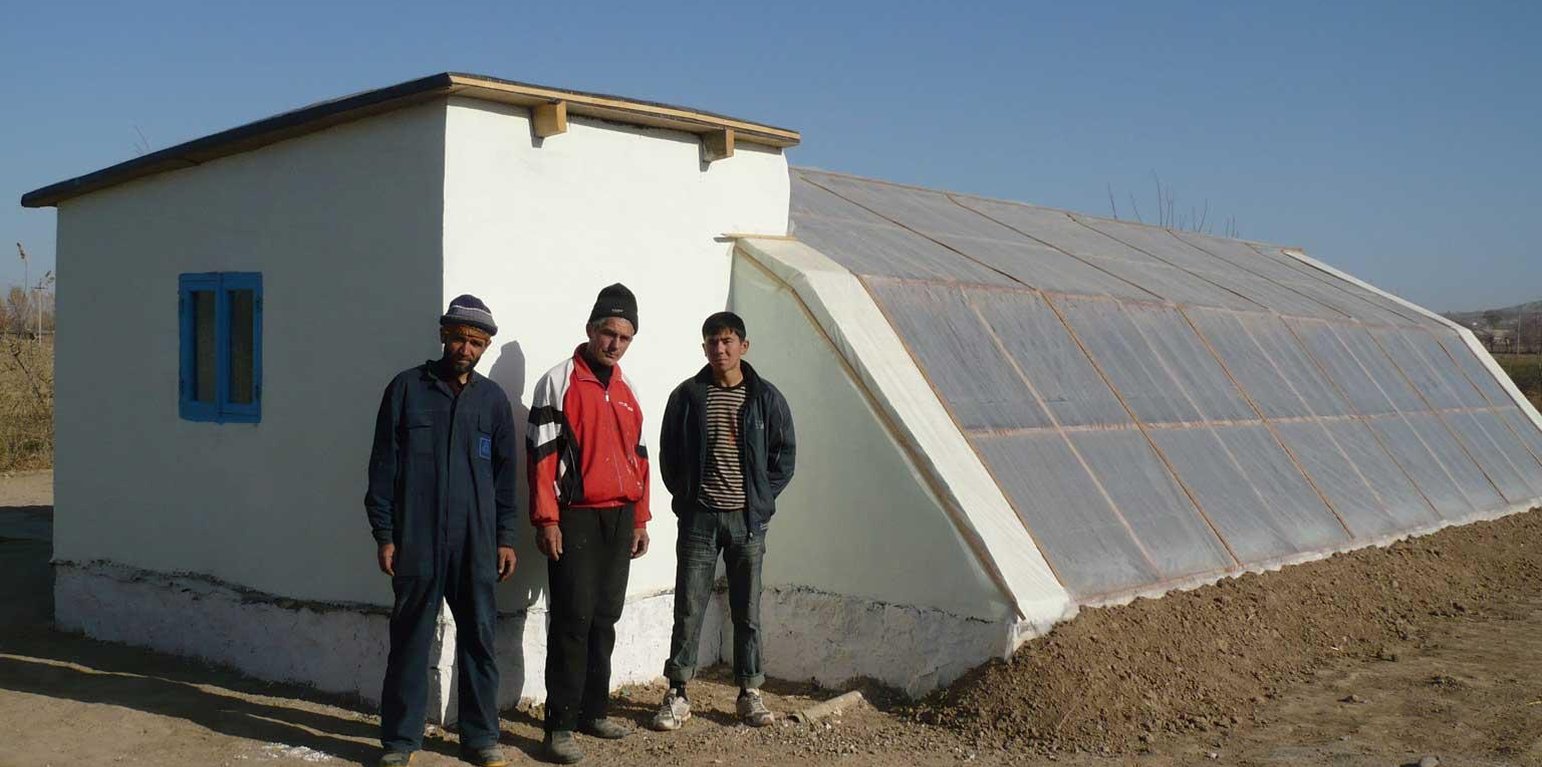




Производство овощей в закрытом грунте, при снижении тепло потерь за счёт применения теплоизоляции и максимального использования пассивной солнечной энергии. В этом теплицы можно использовать круглый год не зависимо от погодных условиях особенно зимой можно выращивать овощных культур за счёт тепло хранение самого теплицы без использование горючих материалов.За вегетационный пириди можно получит 3 - 4 урожая.
Назначение технологии: Предохранение высаженных растений от весенних и осенних похолоданий и даже заморозка, естественное продления вегетативного периода для созревания растений и получении продукции круглый год.
Основные действия и вложения: Выбор конструкции теплицы, выбор культур, эффективное проветривание и полив, ведение агротехники, борьба с заболеваниями против вредителей и болезней. Уход за почвой: обновление, дезинфекция почв, мульчирование, биогумус и капельное орошение в теплицах.
Природная\социальная обстановка: В условиях экстремального климата, засолённых почв, непредсказуемой погоды (заморозков), дефицита воды эксплуатируется много лет этот вид теплицы.
Location: Хатлонская область, Носири Хусравский рн, Таджикистан, Tajikistan
No. of Technology sites analysed:
Spread of the Technology: evenly spread over an area (approx. < 0.1 km2 (10 ha))
In a permanently protected area?:
Date of implementation: less than 10 years ago (recently)
Type of introduction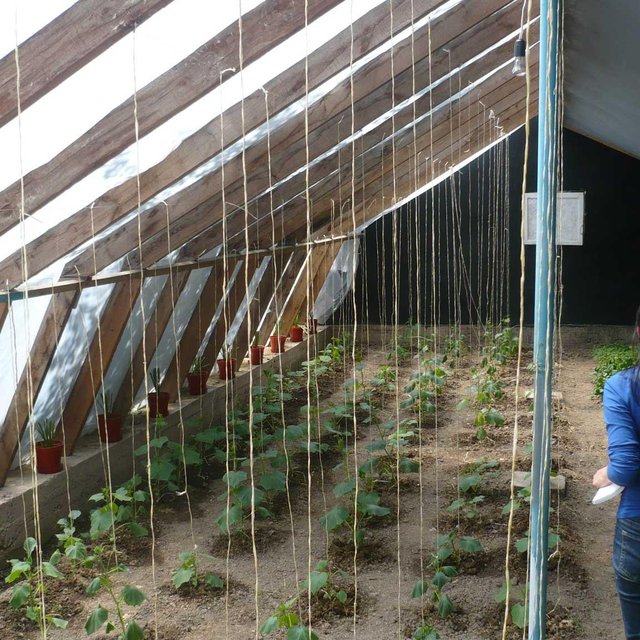









| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (USD) | Total costs per input (USD) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| высадка рассады | человек/день | 100.0 | 5.0 | 500.0 | 50.0 |
| борьба с заболеваниями | человек/день | 10.0 | 20.0 | 200.0 | 50.0 |
| обучение фермеров | человек/день | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 50.0 |
| Полив, ремонт теплицы | теплица | 10.0 | 130.0 | 1300.0 | |
| Plant material | |||||
| семена | теплица | 10.0 | 50.0 | 500.0 | 50.0 |
| компост, навоз | теплица | 10.0 | 20.0 | 200.0 | 50.0 |
| пестициды | теплица | 10.0 | 20.0 | 200.0 | 50.0 |
| Construction material | |||||
| Материал | теплица | 10.0 | 100.0 | 1000.0 | 50.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 4'000.0 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 4'000.0 | ||||
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (USD) | Total costs per input (USD) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| проветривание, полив, температурный режим,смена почвы, улучшение плодородия,борьба с заболеваниями растений | теплица | 10.0 | 200.0 | 2000.0 | 50.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 2'000.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 2'000.0 | ||||