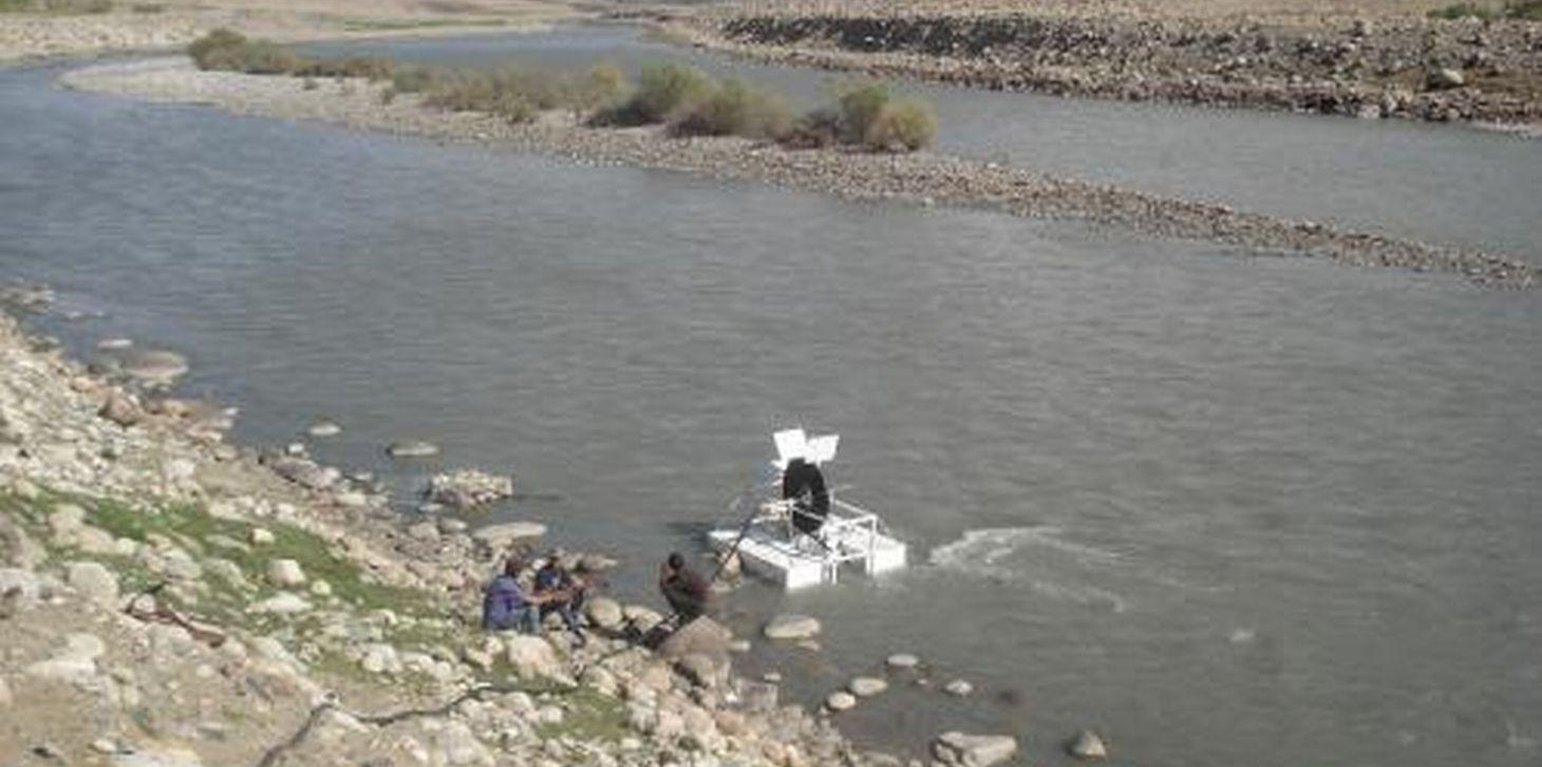




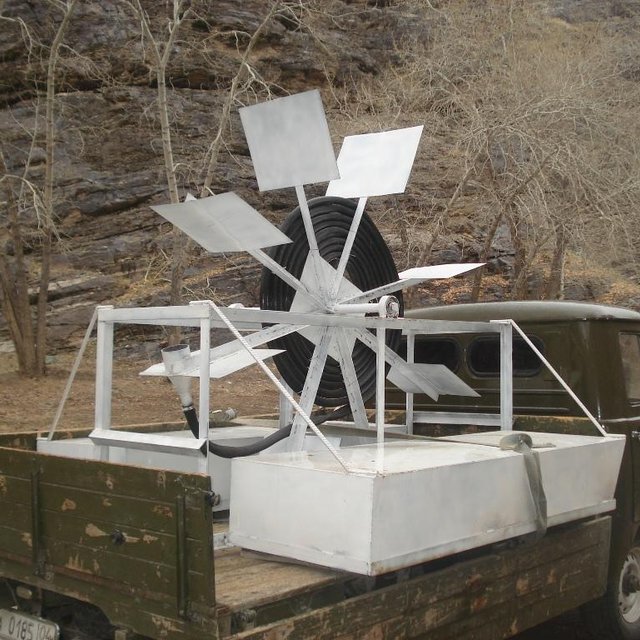
A Spiral tube water pump is a method of pumping water by using an undershot water wheel which has a scoop connected to a spiral tube. As the wheel turns, the scoop will alternatively introduce either water or air into the spiral tube. The pressure from the hydrostatic head generated from the column of water introduced by the scoop, is added to the pressure from previous scoops, and so as the wheel turns it will increase the water pressure with every turn of the spiral. The main characteristic of the spiral water pump is that it can pump water without the input of electricity or fuel. It works with the power of the water flow. Once built, the spiral water pump is able to push water up to 30 metres high (horizontal push) and up to 70 metres away (vertical push). The water push (how far water will be pushed horizontally and vertically) depends on how big the wheel of the Spiral Water Pump is built, and how much tube is put around the wheel.
Purpose of the Technology: The spiral tube water pumps were installed with the aim to provide irrigation water from rivers to higher level crop fields. Land users in GBAO are dependent on irrigation water to grow their crops and without the use of water pumps they can not access the water from rivers that are at a lower level than the fields.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The type, size and thus material costs of a spiral water pump will depend on 2 parameters: first, the irrigation needs (how far the water needs to go and how much is used per day) and second, the available water flow (the velocity and depth of the water source). There is only an initial investment in material for the water wheel, after that the pump should work without any further costs incurred.
Natural / human environment: The spiral water pumps were installed in 4 different districts of the semi-arid to arid GBAO region where the availability of irrigation water is crucial to crop production. So far, 4 spiral water pumps have been installed for test runs but it is very likely that they will be adopted by other farmers as they observe the benefits created by the ones that are already in place.
Location: Roshtkalah, Ishkashim, Vanj, Rushnan, GBAO, Tajikistan
No. of Technology sites analysed:
Spread of the Technology: evenly spread over an area (approx. 100-1,000 km2)
In a permanently protected area?:
Date of implementation: less than 10 years ago (recently)
Type of introduction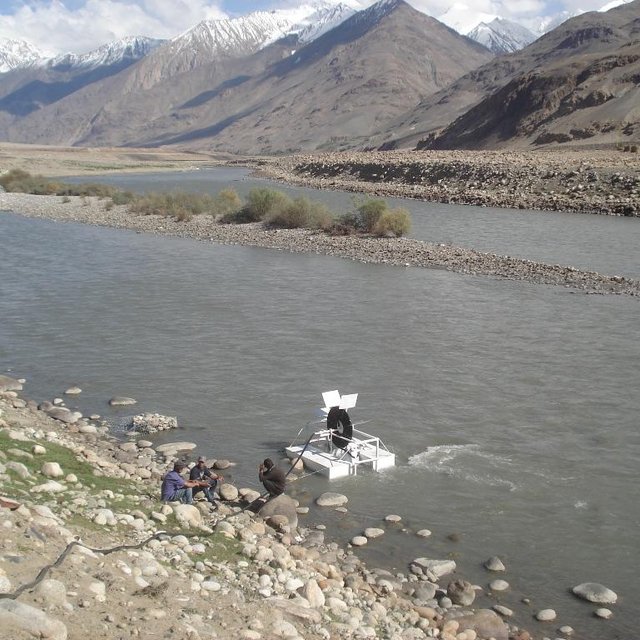








| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (Somoni) | Total costs per input (Somoni) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| Putting in polyethylene tube | Persons/day | 5.0 | 40.0 | 200.0 | |
| Equipment | |||||
| Electrode for welding | Pieces | 80.0 | 0.375 | 30.0 | |
| Construction material | |||||
| Tin plates | Pieces | 7.0 | 200.0 | 1400.0 | |
| Chain hooks | Pieces | 8.0 | 3.0 | 24.0 | |
| Scoop | Pieces | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | |
| Clamps | Pieces | 60.0 | 0.7 | 42.0 | |
| Gabion grid | Pieces | 1.0 | 135.0 | 135.0 | |
| Steel | meter | 32.0 | 8.375 | 268.0 | |
| Axle (pipe), 32 cm | meter | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | |
| Bushing | Pieces | 2.0 | 35.0 | 70.0 | |
| Other | |||||
| Rotary fitting | Pieces | 1.0 | 200.0 | 200.0 | |
| Polyethylene tube | meter | 50.0 | 13.0 | 650.0 | |
| White paint | liter | 3.0 | 15.0 | 45.0 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 3'139.0 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 697.56 | ||||
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (Somoni) | Total costs per input (Somoni) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| Maintenance of pump | Pump | 1.0 | 45.0 | 45.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 45.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 10.0 | ||||
This has improved the amount of area that can be utilised for cultivation of several varieties of crops.