



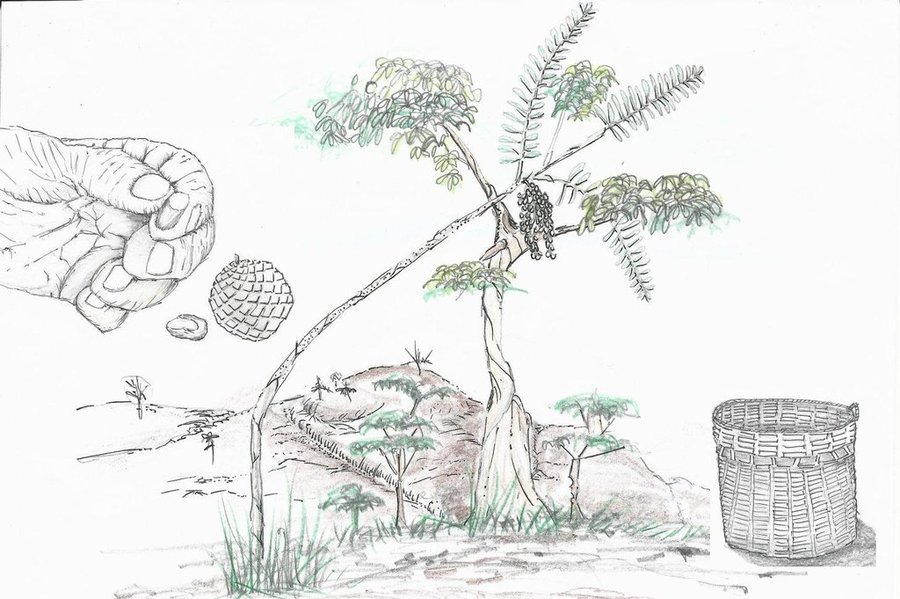
Littuko (Calamus manilensis) is a large rattan variety belonging to the climbing-palm family Arecaceae which is commonly found in the Cordillera, Caraballo, and Sierra Madre mountain ranges. It matures in seven years and bears 50 to 70 kilos of fruits each year. Its fruits are sweetish sour when ripe and are gathered around April to September.
Purpose of the Technology: The littuko provides green cover to the trees even in the dry months and in case of wildfire,they reinforce the forest's capacity to serve as firebreaks or greenbreaks. It also attract a lot of wildlife ranging from insects (bees, fire flies, and beetles) to birds, bats, and cloud rats. Forests with littuko become equipped with natural guards since the littuko's spines with sturdy thorns discourage people and stray animals to freely enter the forest area and disturb the ecosystem.Conservation of trees is also promoted on this technology.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: For the cultivation of littuko, the following procedures are done: (1) Before planting into a seedbed or polyethylene bags (plastic planting bag), the hilar cover of the littuko seed is gently scraped with the use of a sharp knife. Removing the hilar cover enables the tiny plant to easily break out of the seed. (2) The sprout is transplanted to the designated area under the host tree when it reaches six inches in height and with at least three leaves. The chosen host tree is where the littuko can cling on for support to prevent lodging or breakage of stems. (3) Within one to three years, ring weeding is done around the littuko plant. (4) Maintenance and inputs are needed after three years to ensure its growth.
Natural / human environment: Littuko grows underneath of growing trees in the natural forest. They grow best in rainforests and no cultivation is needed.The area is under a humid agro climate with an average annual rainfall of 2000-3000 mm per year. Land users have an average holding of 0.5-1 hectare for the forestlands or woodlands.Most of them are stewards of the forest through the Community Based Forest Management Agreement (CBFMA) for 25 years and renewable for another 25 years.
Location: Nueva Vizcaya, Bayombong, Philippines
No. of Technology sites analysed:
Spread of the Technology: evenly spread over an area (approx. 0.1-1 km2)
In a permanently protected area?:
Date of implementation: 10-50 years ago
Type of introduction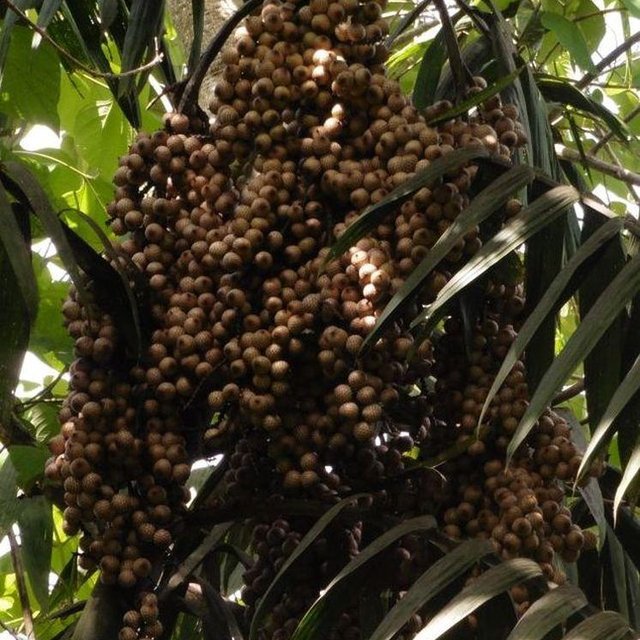






| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (Pesos) | Total costs per input (Pesos) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| Labour for nursery | Person/day | 1.0 | 3.3333 | 3.33 | 100.0 |
| Transplanting | Person/day | 1.0 | 3.3333 | 3.33 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | |||||
| Seedling | Seeds | 1000.0 | 0.22222 | 222.22 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 228.88 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 5.09 | ||||
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (Pesos) | Total costs per input (Pesos) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| Weeding | Person/day | 2.0 | 3.333 | 6.67 | 100.0 |
| Harvesting | Person/day | 4.0 | 3.333 | 13.33 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 20.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 0.44 | ||||
Difficult to harvest since host tree is tall
The littuko fruits provide additional income to community based forest management implementer/participants.
Conservation of trees is promoted because trees serve as hosts for the growing of rattan