Check Dam [China]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Haiyan WEI
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: David Streiff
approaches_2397 - China
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Approach
SLM specialist:
Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Approach (if relevant)
Department of Resources and Environmental Science, Beijing Normal University (Department of Resources and Environmental Science, Beijing Normal University) - China1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
1.4 Reference(s) to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Technologies

Check Dam [China]
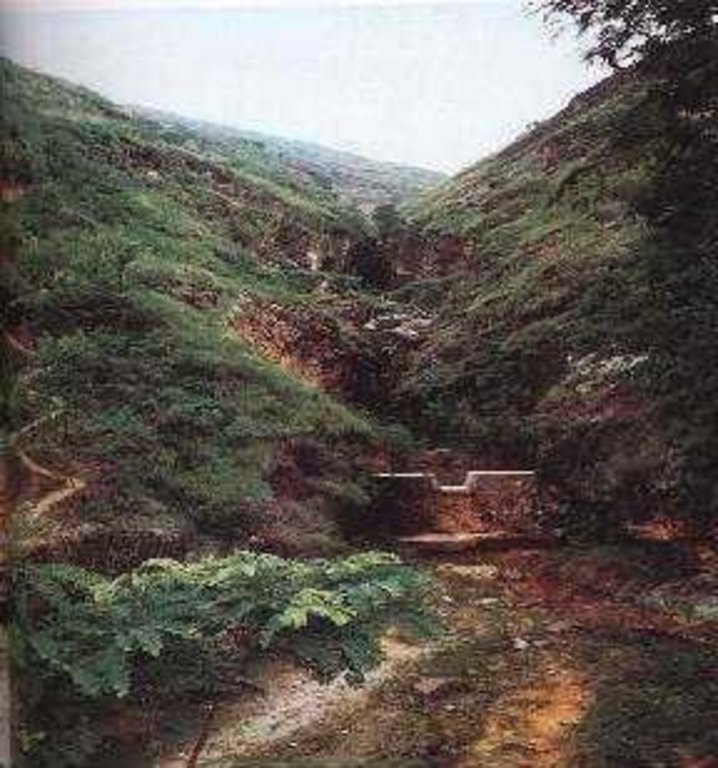
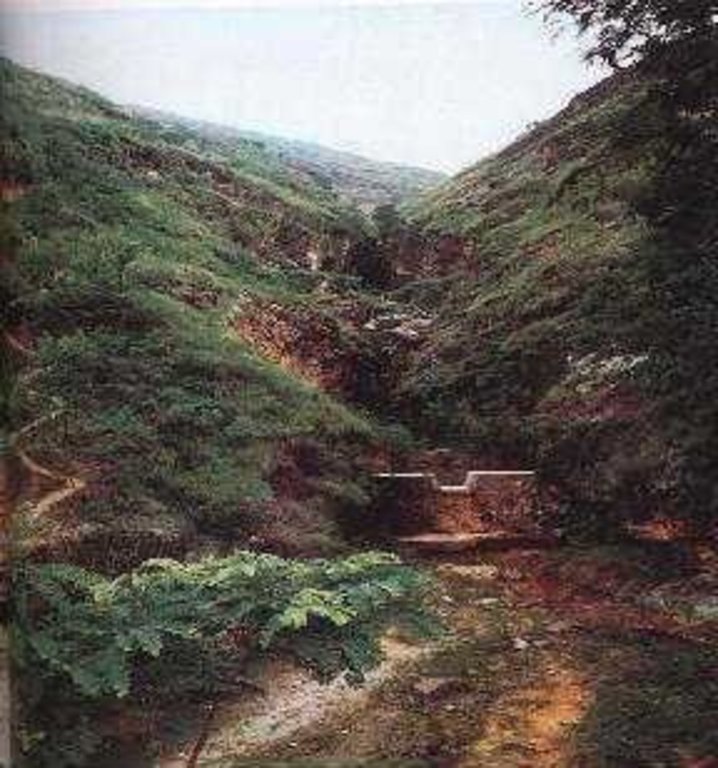
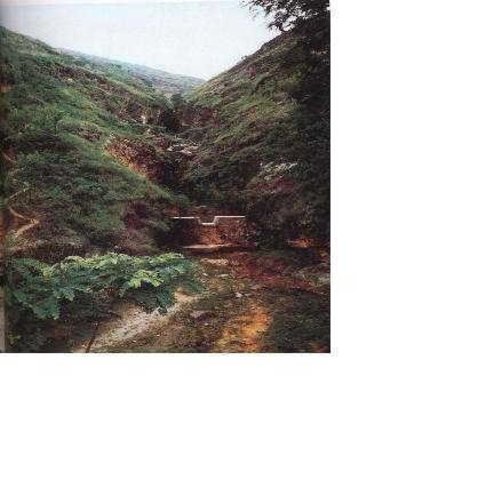
Check dam refers to dam that constructed in the gullies or river ways and the height of the dam is often lower than 5m.
- Compiler: Haiyan WEI
2. Description of the SLM Approach
2.1 Short description of the Approach
Check dam is a kind of sediment storage dam of 5m below and is built in channels to control the down cutting of channel bed.
2.2 Detailed description of the Approach
Detailed description of the Approach:
Aims / objectives: Xifeng county is one of the key areas of soil erosion control in China. In order to reduce the local soil erosion, and also to bring certain economic benefits to local residents, the Ministry of Water Resources is in charge of check dam construction activities.
Check dam is widely used in controlling soil erosion. The training is a main approach to promotion of the check dam technology. It is necessary to mobilize local people to participate in construction, while providing to them some cash subsidies. In such a way local people can get economic benefits, and strengthen their awareness and
knowledge of soil and water conservation.
Methods: Main objectives: (1) Elevating erosion basis of channel bed to prevent the channel down cutting and channel bank expansion, and decrease channel gradient. (2) Storing silt and reducing the amount of sediment, transported into the rivers. (3) Decreasing channel flow rates and reducing the flood risk of the lower reaches. (4) Debris flow control by use of strong permanent check dams. (5) Making channel silted to form sediment-covered terraces for future use.
Stages of implementation: Implemetation procedure: (1) site selection and design; (2) material preparation, labor recruitment and temporary road buliding; (3) main project construction.
Other important information: The construction cost of check dam is determined by project quality requirements, difficulty of construction, work size, construction technology, and some other factors. Regional factors have also an important impact. Therefore, the investment is mainly made by government with local supporting funds. Check dam construction is often
associated with plant cultivation, aquaculture design and other measures to make comprehensive use of sediment retention and water storage. It can increase agricultural productivity and farmers’ income in addition to improve local environment.
2.3 Photos of the Approach
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Approach has been applied
Country:
China
Region/ State/ Province:
Shanxi, Beijing
Further specification of location:
Xifeng
Map
×2.6 Dates of initiation and termination of the Approach
Indicate year of initiation:
1960
2.7 Type of Approach
- traditional/ indigenous
2.8 Main aims/ objectives of the Approach
The Approach focused on SLM only
1) Fixation and raise of erosion basis, preventing down cutting of channel and channel bank expansion. 2) Making channel silted to form sediment-covered terraces for farming. 3) Decreasing channel gradient and flow rates and reducing the flood risk of the lower reaches.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: 1) Serious debris flow which causes tremendous economic loss and threats to the residents safety. 2) Serious soil erosion, especially down cutting and expansion of gully. 3) Poor local economy, lack of funds and technology for soil erosion control.
2.9 Conditions enabling or hindering implementation of the Technology/ Technologies applied under the Approach
social/ cultural/ religious norms and values
- hindering
Unawareness of soil and conservation knowledge.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Strengthening education and training.
availability/ access to financial resources and services
- hindering
More investment needed for mortar stone check dam.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Government and company investment to develop eco-industry.
legal framework (land tenure, land and water use rights)
- hindering
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights hindered a little the approach implementation The state has ownership of the land resources, land users can only lease the land for a period of time, they worry about their land would be transferred to others.
knowledge about SLM, access to technical support
- hindering
Check dam design and construction need qualified technicians.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Professionals and training.
3. Participation and roles of stakeholders involved
3.1 Stakeholders involved in the Approach and their roles
- local land users/ local communities
Working land users were mainly men (In 1960s and 1970s, the SWC activities mainly distributed and administrated to farmers to do in leisure time(winter), and grouped to build check dams, terraces, etc
Existing groups of land users;
Those who live in gully areas and have less flat crop land provide their advices and requirement to the government and decision makers.
- national government (planners, decision-makers)
3.2 Involvement of local land users/ local communities in the different phases of the Approach
| Involvement of local land users/ local communities | Specify who was involved and describe activities | |
|---|---|---|
| initiation/ motivation | external support | Mainly:public meetings; partly: workshops/seminars; Series of site meetings to explain the SWC to the land users. |
| planning | external support | Mainly: public meetings; partly: workshops/seminars |
| implementation | interactive | casual labour |
| monitoring/ evaluation | interactive | Mainly: interviews/questionnaires; partly: reporting; |
| Research | self-mobilization | on-station |
3.4 Decision-making on the selection of SLM Technology/ Technologies
Specify who decided on the selection of the Technology/ Technologies to be implemented:
- politicians/ leaders
Explain:
consultative.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by by politicians / leaders. directive (top-down).
4. Technical support, capacity building, and knowledge management
4.1 Capacity building/ training
Was training provided to land users/ other stakeholders?
Ja
Specify who was trained:
- land users
- extensionists/trainers, politicians/decision makers
Form of training:
- farmer-to-farmer
- public meetings
- courses
Subjects covered:
The approach provide the training about the technology, such as check dam dimension and materials etc.
4.2 Advisory service
Do land users have access to an advisory service?
Ja
Specify whether advisory service is provided:
- on land users' fields
Describe/ comments:
The Basic Farmland Construction; Key elements: Government plan, design, distribute, Farmers implement; 1) Advisory service was carried out through: government's existing extension system 2) Advisory service was carried out through: government's existing extension system; Extension staff: mainly government employees 3) Target groups for extension: land users; Activities: Field visit and demonstration
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; At each government level, there is a SWC division which is in charge of SWC activities including extension.
4.3 Institution strengthening (organizational development)
Have institutions been established or strengthened through the Approach?
- yes, moderately
Specify the level(s) at which institutions have been strengthened or established:
- local
Specify type of support:
- financial
- capacity building/ training
4.4 Monitoring and evaluation
Is monitoring and evaluation part of the Approach?
Ja
Comments:
bio-physical aspects were ad hoc monitored by 0 through observations; indicators: debris flow frequency,speed,volume, time and damage
technical aspects were ad hoc monitored by 0 through observations; indicators: damage degree
socio-cultural aspects were ad hoc monitored by 0 through measurements; indicators: accredited attitude for debris flow control and part icipation in check dam building.
economic / production aspects were ad hoc monitored by 0 through observations; indicators: control area
area treated aspects were ad hoc monitored by 0 through measurements; indicators: science and rationality of Management
no. of land users involved aspects were ad hoc monitored by 0 through observations; indicators: None
management of Approach aspects were regular monitored by 0 through measurements; indicators: None
There were several changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: Improving the construction method so as to make the check dams much durable.
4.5 Research
Was research part of the Approach?
Ja
Specify topics:
- economics / marketing
- ecology
- technology
Give further details and indicate who did the research:
Manual and criteria for standardization design and construction.
Research was carried out both on station and on-farm
5. Financing and external material support
5.1 Annual budget for the SLM component of the Approach
If precise annual budget is not known, indicate range:
- 100,000-1,000,000
Comments (e.g. main sources of funding/ major donors):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (national): 90.0%; local community / land user(s) (-): 10.0%
5.2 Financial/ material support provided to land users
Did land users receive financial/ material support for implementing the Technology/ Technologies?
Ja
5.3 Subsidies for specific inputs (including labour)
- equipment
| Specify which inputs were subsidised | To which extent | Specify subsidies |
|---|---|---|
| machinery | fully financed | |
If labour by land users was a substantial input, was it:
- paid in cash
Comments:
Before 1970s, the SWC activities were obligation, but after that some subsidies were provided by government.
Labour can also be voluntarely or rewarded with other material support
5.4 Credit
Was credit provided under the Approach for SLM activities?
Ja
Specify conditions (interest rate, payback, etc.):
Interest rate charged: 2.0%
Interest was lower than market rate.
6. Impact analysis and concluding statements
6.1 Impacts of the Approach
Did the Approach help land users to implement and maintain SLM Technologies?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Harvesting runoff in the rainy season and making 'deposited flat land'.
Did the Approach improve issues of land tenure/ user rights that hindered implementation of SLM Technologies?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
The SWC activities were organized to implement by local communities which can properly deal with the relationship. The problem is likely to be overcome in the near future. The SWC applied area can be contracted for a long time between land ownership and users.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
The method will help to control debris flow; the check dam is widely used
6.3 Sustainability of Approach activities
Can the land users sustain what has been implemented through the Approach (without external support)?
- yes
6.4 Strengths/ advantages of the Approach
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| Mitigating damage caused by debris flow and floods (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Making planning and design on watershed management) |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| Erosion control to decrease sediment (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Check dams building.) |
| More effective use of rainfall resources (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Develop compound management with cultivation and aquaculture.) |
| Increasing farmer’s income (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Completing irrigation facility and establishing economic forest) |
6.5 Weaknesses/ disadvantages of the Approach and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| After abolition of the compulsory labor and accumulative labor service, the enthusiasm and willingness of farmers to participation is lowered | Some measures shoule be taken by government at all levels to stimulte and encourage farmers to participate in the construction work |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Large investment. | Multi-level investment system, which includes national investment with local support, labor input by farmers, and use of foreign and social funds. |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- compilation from reports and other existing documentation
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Special Planning of Soil and Water Conservation in Xinzhou Region , Shanxi Province (1986-2000)
Available from where? Costs?
Library of the Resource and Environmental Department of the Beijing Normal Univ.
Title, author, year, ISBN:
The application of the Check dam with willow in controlling gully erosion.Tu xingwen. Soil and water conservation in China, 1986.
Available from where? Costs?
Library of the Resource and Environmental Department of the Beijing Normal Univ.
Title, author, year, ISBN:
How to design the dry masonry dam in the Hanjiachuan watershed. Tianyuzhu, Wangzuliang. Beijing. Water conservation in Beijing, 2000.3
Available from where? Costs?
Library of the Resource and Environmental Department of the Beijing Normal Univ.
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Consideration about the check dam design and application. Liu shunzong. Soil and water conservation in China, 1990.6
Available from where? Costs?
Library of the Resource and Environmental Department of the Beijing Normal Univ.
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks

Check Dam [China]
Check dam refers to dam that constructed in the gullies or river ways and the height of the dam is often lower than 5m.
- Compiler: Haiyan WEI
Modules
No modules