Participatory SLM Action Planning [Bhutan]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Karma Dorji
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: Fabian Ottiger
approaches_2489 - Bhutan
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Approach
SLM specialist:
Wangdi Tashi
NSSC, DoA, MoAF, RGoB
Bhutan
SLM specialist:
Dorji Tshering
NSSC, DoA, MoAF, RGoB
Bhutan
Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Approach (if relevant)
National Soil Services Centre (National Soil Services Centre) - BhutanName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Approach (if relevant)
MoA (MoA) - Bhutan1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
14/03/2011
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
2. Description of the SLM Approach
2.1 Short description of the Approach
A methodology to identify in a participatory manner at village level land-based problems, its causal factors and mitigation measures to reduce land degradation and enhance rural livelihoods
2.2 Detailed description of the Approach
Detailed description of the Approach:
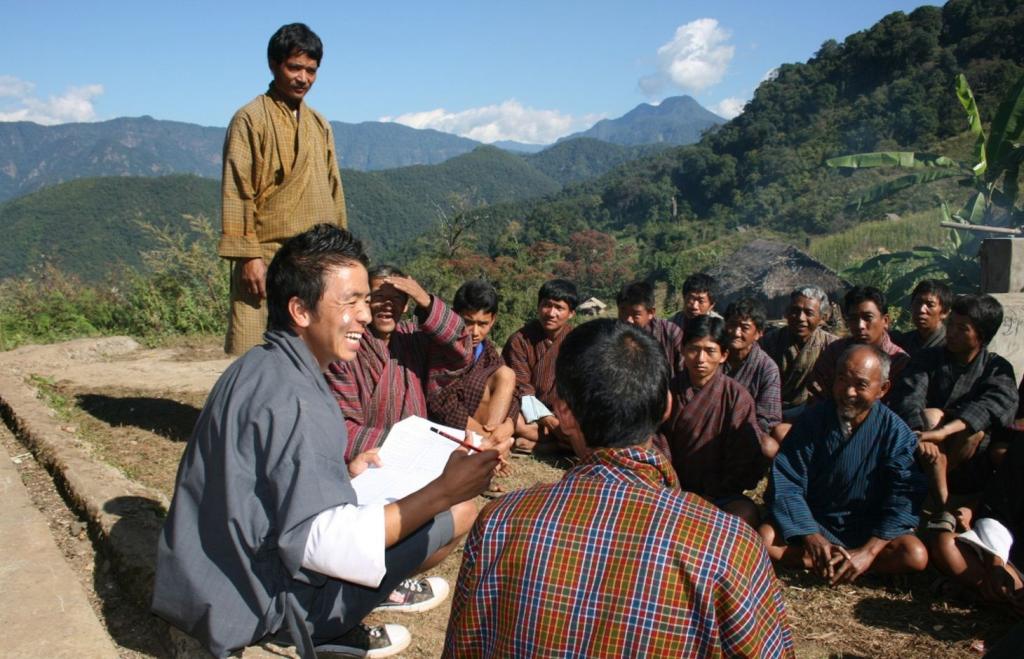
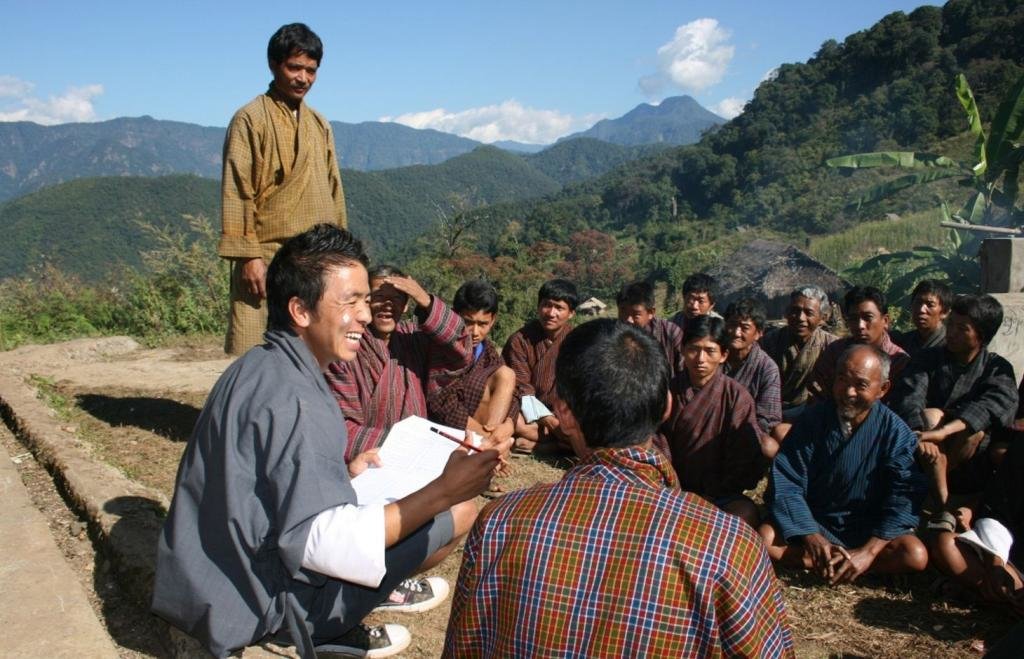
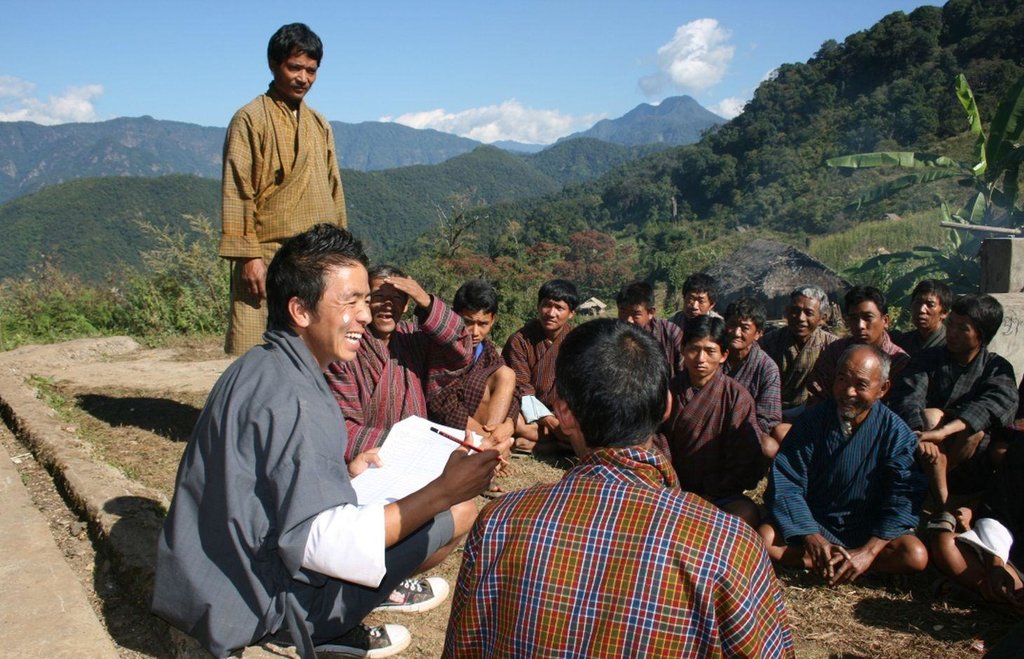
Aims / objectives: Participatory SLM Action Planning (SLM AP) is a methodology that aims at prioritiz-ing possible SLM interventions to mitigate the most critical land degradation issues. Priorities are based on the identification of land-based livelihoods and livelihood resources, the key area-based problems and their causes. SLM AP is carried out in the SLMP geogs (block) at chiog (village) level, including all community households. It involves elements of PRA/PLA such as problem census, cropping calendars, history lines, natural resource mapping and builds on the in-depth knowledge and understanding of farming households of their land, their problems and opportunities. The process is highly visual to include the illiterate and very interactive by giving the communities the lead in prioritizing their problems and deciding on SLM interventions.
Methods: The SLM AP is an iterative process, starting with building and training SLM planning teams (GSPTs) at geog level, comprising of extension staff and locally recruited geog SLM planners (GSPs) and geog administration staff. The GSPTs start awareness and mobilization activities in the first year at geog council level. This is followed by a 3 day SLM AP in each and every chiog of the geog to compile a chiog SLM action plan. The village SLM APs are combined into a geog SLM AP and discussed, amended and endorsed in a public meeting by the geog council. The necessary budget is allocated by SLMP project and implementation of the planned activities takes place at chiog level.
Stages of implementation: Implementation is preceded by intensive training and capacity building of the communities in SLM activities. In the second year a new SLM AP round is made, lasting only one day, with review of the previous SLM AP at chiog level. Potential new activities are identified, based on field experiences, to complete the new SLM AP for year 2. In the final year 3, a last SLM AP round is made in all chiogs to compile chiog and ultimately a geog SLM AP.
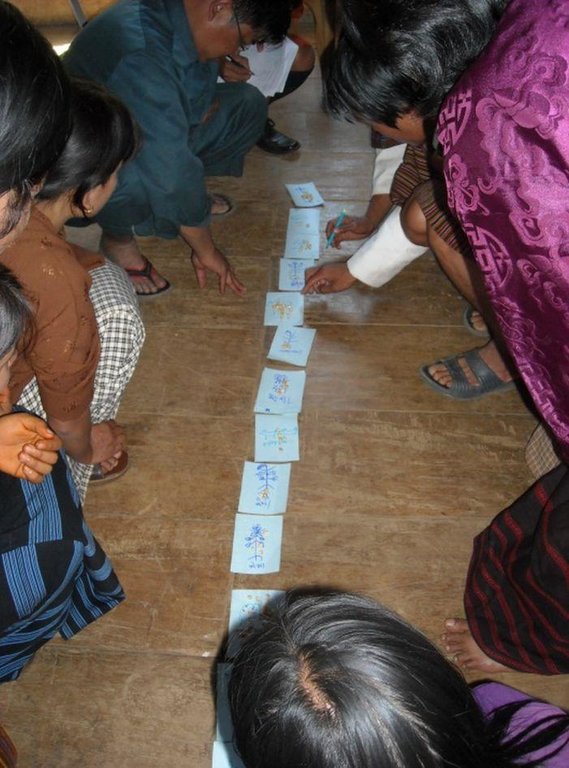
Role of stakeholders: SLM AP is an inclusive process and gender sensitive, with focus on vulnerable households. The approach includes participatory Natural Resource mapping at chiog level and participatory Monitoring & Evaluation to track implementation progress and impact and to get feedback of the communities.
Other important information: Environmental and social screening procedures are applied to exclude any negative impact on the land or on social groups. SLM AP was piloted in 3 geogs in 3 Dzongkhags since 2006 and has been rolled out to more than 130 chiogs in 9 geogs.
2.3 Photos of the Approach
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Approach has been applied
Country:
Bhutan
Region/ State/ Province:
Chhukha, Trashigang and Zhemgang Dzongkhags
Further specification of location:
9 separate geogs
2.6 Dates of initiation and termination of the Approach
Indicate year of initiation:
2006
Year of termination (if Approach is no longer applied):
2012
2.7 Type of Approach
- project/ programme based
2.8 Main aims/ objectives of the Approach
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (livelihoods, cash income, food security, capacity building, awareness raising)
- To build community capacity to assess land degradation and identify and prioritize mitigation measures
- Enhancement of rural livelihoods
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: - Lack of awareness of land degradation processes, combined with limited technical knowledge to tackle its causes.
- Planning procedures are top-down and do not incorporate land-based issues adequately and fail to build local ownership and sustainability.
2.9 Conditions enabling or hindering implementation of the Technology/ Technologies applied under the Approach
availability/ access to financial resources and services
- hindering
Large amount of cash to handle at municipality level
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Training, monitoring and limitation of cash amounts
institutional setting
- hindering
Delays in financial releases to decentralised level because of lengthy/complicated administrative chain
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Training of key financial staff to shorten procedure and minimize frequency of budget releases
legal framework (land tenure, land and water use rights)
- enabling
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights helped a little the approach implementation: Individual land titles of households favour greatly the planning and implementation of SLM activities
- hindering
Lack of efforts in implementing SLM technologies on land without ownership and living as tenants
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Awareness on the importance of proper management to prevent decline in productivity and their own livelihoods through loss of soil fertility and or loss of land physically due to landslides and mass movements.
knowledge about SLM, access to technical support
- hindering
Awaraness of communities and technical confidence of teams
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Training and capacity buidling
workload, availability of manpower
- hindering
Large volume of work, especially in growing season
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Make of use of lean winter season for labour-intensive SLM interventions
other
- hindering
Small land holding sizes to spare a portion for SLM technologies
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Awareness on the advantages of SLM
3. Participation and roles of stakeholders involved
3.1 Stakeholders involved in the Approach and their roles
- local land users/ local communities
communities of all chiogs
In all villages the most vulnerable community members were identified (wealth / well-being ranking), ranked and specific effort made to include them in most interventions, where possible.
- SLM specialists/ agricultural advisers
- teachers/ school children/ students
- local government
GSPT and Dzongkhag staff (Local government)
- national government (planners, decision-makers)
RGoB, MoAF, DoA
- international organization
GEF, World Bank
- monk body
3.2 Involvement of local land users/ local communities in the different phases of the Approach
| Involvement of local land users/ local communities | Specify who was involved and describe activities | |
|---|---|---|
| initiation/ motivation | interactive | National level stakeholders in consultation with district and municipality staff developed the methodology through an iterative consultation process |
| planning | interactive | Decentralised training and planning of SLM interventions at chiog level (130+ chiogs) in 9 geogs in 3 Dzongkhags |
| implementation | interactive | Range of SLM and livelihood activities at chiog level (130+ villages) during 6 year project period |
| monitoring/ evaluation | interactive | Regular participatory M&E at chiog and geog level |
| Research | passive | Few focused SLM related research topics commissioned to governmental research institutions |
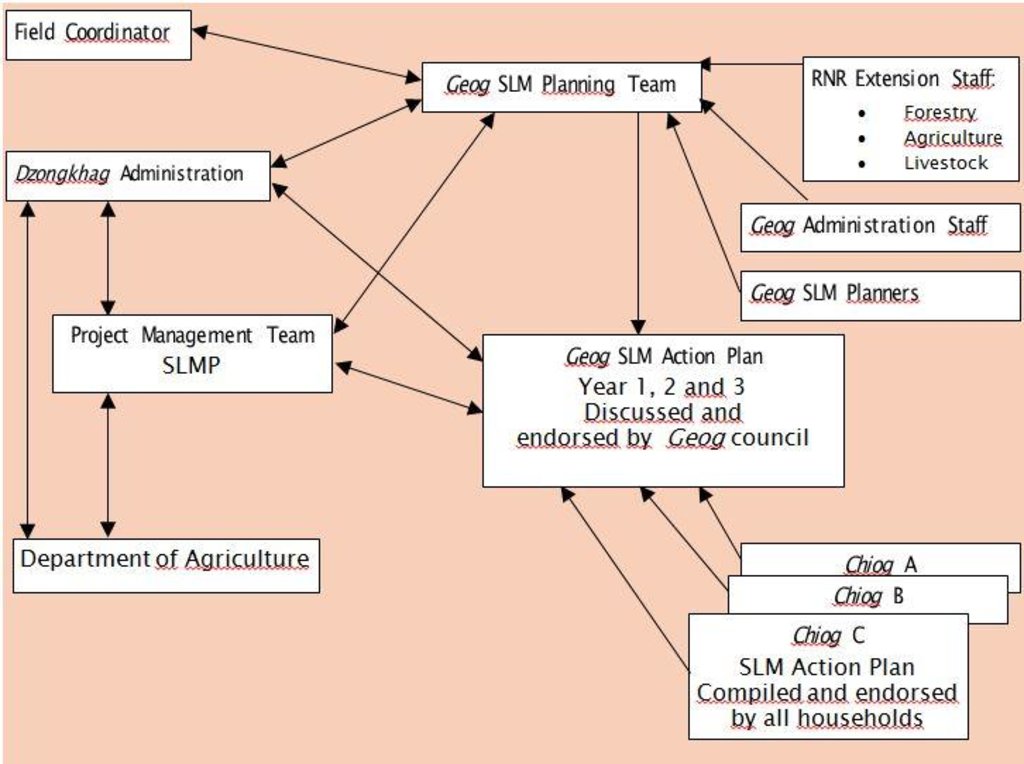
3.3 Flow chart (if available)
Description:
Overview of network of Stakeholders at chiog (village), geog and district level
Author:
Hans van Noord (Schoutenkamp 43 Heteren The Netherlands)
3.4 Decision-making on the selection of SLM Technology/ Technologies
Specify who decided on the selection of the Technology/ Technologies to be implemented:
- mainly land users, supported by SLM specialists
Explain:
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by SLM specialists with consultation of land users. The SLM planning was done in a very participatory manner with the land users as they best know the problems in their land i.e. where, how, when, etc. Planning done using participatory planning tools and field visits. Based on the problems at the site (site specific problems) then SLM Specialists make problem specific recommendations of SLM technologies. The main Monitoring and Evaluation was done after every six months when comprehensive information was collected with structured questionnaires along with site visits and meeting with the communities. M&E was also done as frequently as possible even while visiting the site for other purposes during the year without compulsory group meetings.
4. Technical support, capacity building, and knowledge management
4.1 Capacity building/ training
Was training provided to land users/ other stakeholders?
Ja
Specify who was trained:
- land users
- field staff/ advisers
- Project management staff
Form of training:
- on-the-job
- farmer-to-farmer
- demonstration areas
- public meetings
- courses
Subjects covered:
Extensive training programmes for project management staff and field coordinators and the decentralised extension staff (forestry, livestock and agriculture) at geog level together with the geog administration staff and finally to all chiog communities (130+). Initial training was on SLM action planning and Natural Resource mapping; later on a range of technical intervention such as hedgerow establishment, check dam construction, bioengineering, afforestation, community forestry, fodder development, bamboo plantation, bench terracing etc.
4.2 Advisory service
Do land users have access to an advisory service?
Ja
Specify whether advisory service is provided:
- on land users' fields
Describe/ comments:
Name of method used for advisory service: SLM planning knowledge transfer; Key elements: participatory planning, capacity and skills building of RNR extension staff; Whole range of extension advisory services by all extension teams related to SLM, cash generation and group formation
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; Capacity built, awareness raised, institutions supported. Adequate human and institutional capacities and awareness have been created during the GEF/World Bank SLM Project period and the effort is still being continued. The actual implementation of the SLM technologies in the field is constrained by inadequate fund support and small land holdings.
4.3 Institution strengthening (organizational development)
Have institutions been established or strengthened through the Approach?
- yes, a little
Specify the level(s) at which institutions have been strengthened or established:
- local
Specify type of support:
- capacity building/ training
- equipment
- curriculum development support, seeds, seedlings
Give further details:
Moderate support to monk body, schools, Non-Formal Education and geog administrations
4.4 Monitoring and evaluation
Is monitoring and evaluation part of the Approach?
Ja
Comments:
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by project staff through observations; indicators: Regular measurements and observations of acreage of improved vulnerable land through SLM interventions; annual soil erosion plot measurements
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by project staff through measurements; indicators: Regular measurements and observations of acreage of improved vulnerable land through SLM interventions; annual soil erosion plot measurements
technical aspects were regular monitored by project staff through observations; indicators: Regular measurements and observations of acreage and properties of specific areas of improved vulnerable land
technical aspects were regular monitored by project staff through measurements; indicators: Regular measurements and observations of acreage and properties of specific areas of improved vulnerable land
socio-cultural aspects were regular monitored by project staff, land users through observations; indicators: Regular observations through participatory M&E meetings
economic / production aspects were regular monitored by project staff through observations; indicators: Regular observations and measurements by field extension staff (crop cut, animal production, volume of bamboo marketed; CBA study to establish economic viability
economic / production aspects were regular monitored by project staff through measurements; indicators: Regular observations and measurements by field extension staff (crop cut, animal production, volume of bamboo marketed; CBA study to establish economic viability
area treated aspects were regular monitored by project staff, land users through measurements; indicators: Regular measurements of area treated: range of project indicators for vulnerable land improved
no. of land users involved aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff, government through measurements; indicators: Regular measurements of households and farmers (male/female) participating
management of Approach aspects were regular monitored by None through observations; indicators: WB, MTAC, Regular reviews with key stakeholders (Annual Review Workshops)
There were several changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: Two-tier approach: combination of inclusion of all household combined with limited areal focus; vulnerable households focus; financial disbursement system; ch more cash-generating activities; more group/community focus; labour-saving machinery
There were few changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation: change of type and variety of seeds and seedlings
4.5 Research
Was research part of the Approach?
Ja
Specify topics:
- sociology
- economics / marketing
- ecology
Give further details and indicate who did the research:
Little involvement, apart from some focused research on group formation at chiog level and studies on CBA, SLM-poverty linkage, rangeland management, rural-urban transition etc.
Research was carried out both on station and on-farm
5. Financing and external material support
5.1 Annual budget for the SLM component of the Approach
If precise annual budget is not known, indicate range:
- > 1,000,000
Comments (e.g. main sources of funding/ major donors):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international (GEF-World Bank): 70.0%; government (RGoB): 20.0%; local community / land user(s): 10.0%
5.2 Financial/ material support provided to land users
Did land users receive financial/ material support for implementing the Technology/ Technologies?
Ja
If yes, specify type(s) of support, conditions, and provider(s):
Incentives for specific SLM interventions per area and through short-term input support (seeds and seedlings)
5.3 Subsidies for specific inputs (including labour)
- equipment
| Specify which inputs were subsidised | To which extent | Specify subsidies |
|---|---|---|
| tools | partly financed | |
- agricultural
| Specify which inputs were subsidised | To which extent | Specify subsidies |
|---|---|---|
| seeds | partly financed | |
| Seedlings | partly financed | |
- construction
| Specify which inputs were subsidised | To which extent | Specify subsidies |
|---|---|---|
| for fencing and dams | partly financed | |
- infrastructure
| Specify which inputs were subsidised | To which extent | Specify subsidies |
|---|---|---|
| FYM sheds, irrigation channel renovation | partly financed | |
Comments:
Mostly voluntary and some paid in cash (for labour-intensive SLM interventions) and limited other material support such as tools and seeds and seedlings
Not financed: roads, fertilizers, schools
5.4 Credit
Was credit provided under the Approach for SLM activities?
Nee
6. Impact analysis and concluding statements
6.1 Impacts of the Approach
Did the Approach help land users to implement and maintain SLM Technologies?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Considerable area of vulnerable land brought under SLM, reduction of loss of land, improved yields, improved income, improved animal production, improved fodder base
Did the Approach empower socially and economically disadvantaged groups?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Moderate improvement of vulnerable households (poorest and single-headed households) through targeted interventions and pro-active inclusion. The labour sharing approach in implementing SLM activities greatly benefited the resource (human and capital) constrained household.
Did the Approach improve issues of land tenure/ user rights that hindered implementation of SLM Technologies?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
The problem is unlikely to be overcome in the near future. Individual land titles of households favour greatly the planning and implementation of SLM activities
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Other government and donor-funded projects have adopted elements of the participatory SLM action planning methodology (DANIDA, REAP)
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
cash income, food self-sufficiency, community sense/bonding, reduced exposure to natural hazards related to land degradation/flooding
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Improvement of food self-sufficiency and cash generation opportunities
6.2 Main motivation of land users to implement SLM
- increased production
- reduced workload
- payments/ subsidies
- prestige, social pressure/ social cohesion
- affiliation to movement/ project/ group/ networks
- environmental consciousness
- well-being and livelihoods improvement
6.3 Sustainability of Approach activities
Can the land users sustain what has been implemented through the Approach (without external support)?
- uncertain
If no or uncertain, specify and comment:
Rural communities will need continued support by government staff through advice, finance and other support.
6.4 Strengths/ advantages of the Approach
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
|
Decentralised, village level bottom-up planning and implementation ensures capacity building, ownership and empowerment of rural land users Participatory character gives a voice to farmers with in-depth knowledge of land-based issues and its causes and history Inclusiveness of approach, reaching to all households Helps to build community sense (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continued annual AP Continued annual AP; add with NR mapping and ITK studies and participatory M&E Continued annual AP; targeted focus on most vulnerable households Additional group formation and community group support ) |
6.5 Weaknesses/ disadvantages of the Approach and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
|
Time-consuming and resource demanding Requires large workload of both extension staff and farmers Costly as the approach also covers actual implementation of all of planned SLM activities and reaches more than 130 villages for 3 year period |
Combine and align with Five Year Plan planning procedures; mainstreaming into governmental decentralised planning procedures Mainstreaming into regular planning and budgeting Spread over calendar year; labour-intensive SLM activities in lean winter season. |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
- interviews with land users
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Working the Land - Documenting the Key Lessons of Sustainable Land Management on Steep to Very Steep Slopes in Bhutan 2011
Available from where? Costs?
NSSC, DoA, MoAF, RGoB
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Indigenous Technical Knowledge (ITK) on Soil & Soil Fertility Management 2011
Available from where? Costs?
NSSC, DoA, MoAF, RGoB
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Participatory Approaches in Sustainable Land Management – Planning, Implementation & Monitoring as Continuous Learning Processes 2011
Available from where? Costs?
NSSC, DoA, MoAF, RGoB
Title, author, year, ISBN:
National Action Plan to Combat Land Degradation 2010, 2014
Available from where? Costs?
NSSC, DoA, MoAF, RGoB
Title, author, year, ISBN:
BHUCAT, Best Practices and Guidelines from Bhutan for SLM on Steep to very Steep Slope
Available from where? Costs?
NSSC, DoA, MoAF, RGoB
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Documentary of the achievements made in SLM through SLM Project
Available from where? Costs?
NSSC, DoA, MoAF, RGoB
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Bhutan Land Cover Assessment 2010-Technical Report, NSSC, 2011
Available from where? Costs?
NSSC, DoA, MoAF, RGoB
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Soil Erosion – Measurement and analysis of soil erosion plot data, NSSC, 2010, 2011
Available from where? Costs?
NSSC, DoA, MoAF, RGoB
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Integrated Biodiversity Survey of the Lower Wangchhu Watershed, Bhutan 2010
Available from where? Costs?
NSSC, DoA, MoAF, RGoB
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Rangeland Management in Bhutan 2009
Available from where? Costs?
NSSC, DoA, MoAF, RGoB, A consultancy report
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Study on Poverty Sustainable Land Management Linkages in Bhutan-A consultancy Report-2009 2009
Available from where? Costs?
NSSC, DoA, MoAF, RGoB, A consultancy report
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Sustainable Land Management Participatory Action Planning Manual & Tool Kit 2009
Available from where? Costs?
NSSC, DoA, MoAF, RGoB, A consultancy report
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Sustainable Land Management Interventions: Cost Benefit Analysis Report 2009
Available from where? Costs?
NSSC, DoA, MoAF, RGoB, A consultancy report
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Rural Livelihoods and Peri-Urban Analysis 2008
Available from where? Costs?
NSSC, DoA, MoAF, RGoB, A consultancy report
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Review of Mainstreaming of sustainable Land Management in Government Policies and Plans in Bhutan 2008
Available from where? Costs?
NSSC, DoA, MoAF, RGoB, A consultancy report
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules