Полив молодого сада бутылочним способом [Tajikistan]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Pjotr M Sosin
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: David Streiff
Обёрии катраги ба воситаи зарфхои пласмаси
technologies_1029 - Tajikistan
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Tajik Soil Insitute (Tajik Soil Institute) - Tajikistan1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
12/04/2011
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
Для приживаемости саженцев молодого сада в аридных условиях и дефицит воды, использоваться экономный полив при помощи пластиковых бутылок.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
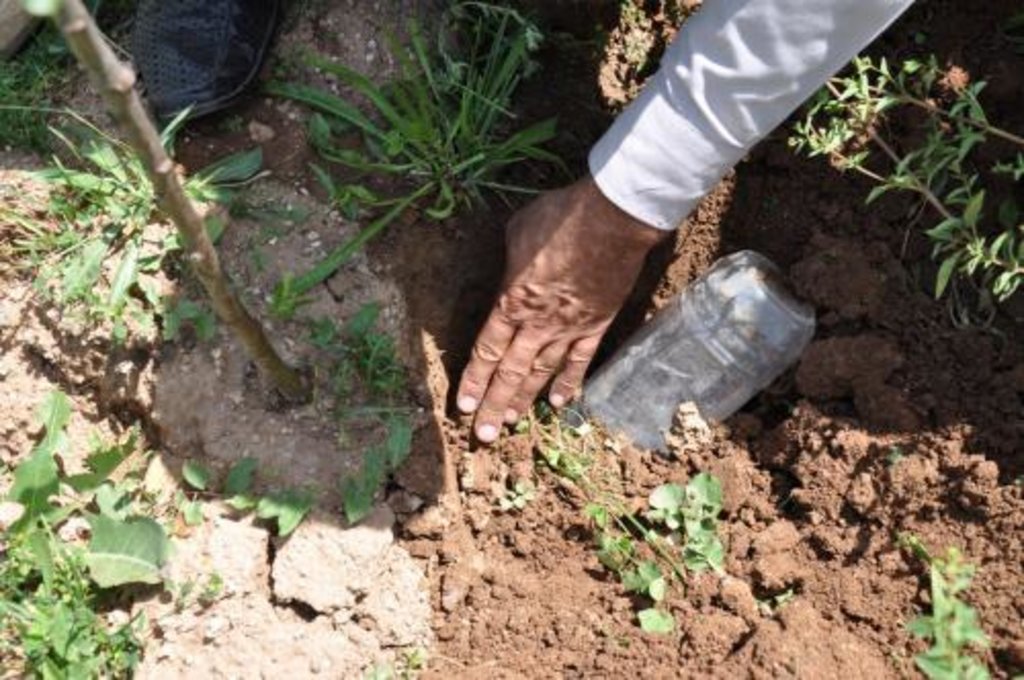
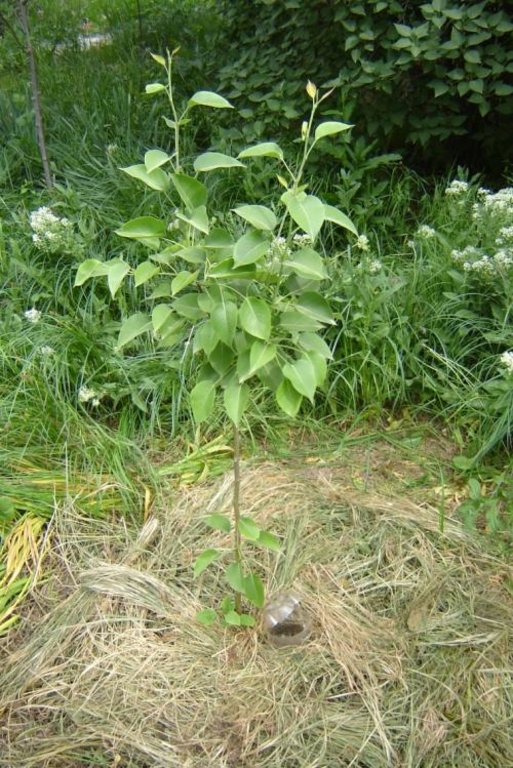
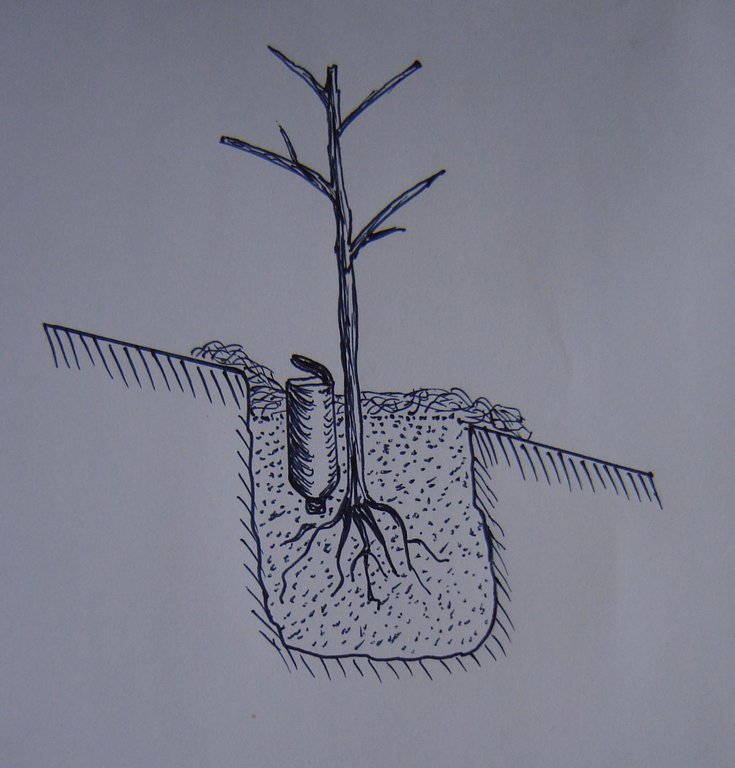
В этой технологии используются пластиковые бутылки 1,5, 2 литра. У бутылки предварительно подрезается дно, так чтобы оно играло роль крышки. Бутылка переворачивается дном вверх и заполняется водой. Медленным откручиванием крышки на бутылке добиваются вытекания воды из бутылки 5 капель в секунду. При достижение такой скорости вытекания воды, крышку фиксируют скотчем к бутылке. При такой скорости вытекания воды, из 1,5 л. бутылке вода вытекает за 90-100 минут. Бутылку закапывают в почву одновременно с посадкой саженца пробкой вниз, пробка должна быть на уровне корневой шейки. Дно бутылки выступает на поверхности почвы до 10 см. Поверхность почвы вокруг саженца мульчируют травой, соломой, или плёнкой черного цвета. Вода из бутылки подаётся непосредственно в корневую зону для того, чтобы исключить потерю воды на замачивание верхнего над корневого слоя почвы, и уменьшить испарение с поверхности почвы. В вегетативный период полив производится один раз в 5 дней, заполнением бутылок водой. Бутылки должны заполнятся чистой водой во избежание засорения крышки.
Использование данной технологии целесообразно применять в течении 2-3 года.
Склоны сложенные лёссами обладают просадочными свойствами. При орошении таких склонов по бороздам или дождеванием подаётса большое количество воды. Это приводит к образованию просадок грунта, насыщению грунта водой впоследствии чего уменьшается сцепление грунта. Всё это приводит к возникновению оползней. При бутылочном поливе подаётся минимальное количество воды не способствующее образованию просадок грунта и оползней.
Purpose of the Technology: Цель технологии, увеличение приживаемости саженцев при минимальном использовании воды, а так же исключение развития эрозионных и оползневых процессов которые могли происходить при поливе сада по бороздам на крутых склонах, сложенных лёссовыми породами.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Выбор участка, подготовка посадочных ям, приобретение саженцев, сетки для ограждения участка, приобретение пластиковых бутылок, подготовка бутылок, посадка саженцев, мульчирование, уход за саженцами, полив.
Ограждение участка выполнялось для того, что бы защитить сад от скота.
Natural / human environment: Среднегорная зона, почва горная коричневая типичная, склоны крутизной до 30°, летний период без дождей. Растительность представлена крупно злаковой полу саванной. Местное население занимается скотоводством и садоводством.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Tajikistan
Region/ State/ Province:
Таджикистан
Further specification of location:
Нурабадский район
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- during experiments/ research
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
- Tree and shrub cropping

Grazing land
Extensive grazing land:
- Semi-nomadism/ pastoralism
Comments:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Использование земель под сельская хозяйство сопровождаются развитием эрозии почв. Крутые склоны подвержены оползневым процессам. Существует дефицит оросительной воды. Травянистая растительность сильно изрежена в следствии пере выпаса скота.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Yes
Forest products and services: топливо, плоды и орехи
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ct: Tree and shrub cropping
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
If land use has changed due to the implementation of the Technology, indicate land use before implementation of the Technology:
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
Comments:
Water supply: богарное, богарное
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Livestock density (if relevant):
1-10 УГ/км2
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- improved ground/ vegetation cover
- irrigation management (incl. water supply, drainage)
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Comments:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0,05 m2.
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A6: Others

vegetative measures
- V1: Tree and shrub cover

structural measures
- S11: Others

management measures
- M1: Change of land use type
Comments:
Main measures: vegetative measures, structural measures, management measures
Type of agronomic measures: мульчирование
Type of vegetative measures: урегулированный: -градуированная полоса *3
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion
- Wg: gully erosion/ gullying
Comments:
Main type of degradation addressed: Во (Wg): овражная эрозия / образование оврага
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Вв (Wt): потеря верхнего слоя почвы / поверхностная эрозия
Main causes of degradation: чрезмерный выпас, сильные / чрезмерные дожди (интенсивность/количество), землепользование
Secondary causes of degradation: чрезмерное использование растительного покрова для бытовых целей, другие природные причины (лавина, извержение вулкана, сели, высоко уязвимые природные ресурсы, экстремальная топография и т.д.) укажите какие, интенсивная эксплуатация населением
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
Comments:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
Схема установки бутылки при посадки саженца.
Location: Джамоат Муджихарв. Нурабад.
Date: 2011,04,05
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: высокий
Technical knowledge required for land users: средний
Secondary technical functions: стабилизация почвы (например, с помощью корней деревьев против оползней), повышение / поддержание сохранения воды в почве
Aligned: -graded strips
Number of plants per (ha): 400
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify currency used for cost calculations:
- US Dollars
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Покупка сетки для ограждения участка | Management | 7 дней |
| 2. | Приобретение саженцев | Management | 1 месяц |
| 3. | Посадка саженцев | Management | 10 дней |
| 4. | Ограждение участка | Management | 10 дней |
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | None | None | 2000.0 | 0.227 | 454.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | None | None | 0.7 | 194.285 | 136.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | None | None | 100.0 | 28.2 | 2820.0 | |
| Equipment | None | None | 2000.0 | 0.0045 | 9.0 | |
| Plant material | None | None | 2000.0 | 1.8865 | 3773.0 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 7192.0 | |||||
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Мульчирование | Agronomic | |
| 2. | Полив | Agronomic | |
| 3. | Пластиковые бутылки | Agronomic |
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | None | None | 1.0 | 454.0 | 454.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | None | None | 1.0 | 273.0 | 273.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | None | None | 2000.0 | 0.023 | 46.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 773.0 | |||||
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- semi-arid
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
> 50 m
Availability of surface water:
medium
Water quality (untreated):
good drinking water
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- medium
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Market orientation of production system:
- subsistence (self-supply)
- commercial/ market
Off-farm income:
- 10-50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- animal traction
Gender:
- men
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Жена занимается домохозяйством (еда, дети)
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: > 4%
Off-farm income specification: По сравнению с фермерами не использовавших УУЗР технологии доход вне хозяйство ниже на 30%
Market orientation of production system: subsistence (self-supply), subsistence (self-supply), commercial/ market
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- small-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- communal/ village
Land use rights:
- leased
Water use rights:
- leased
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
product diversity
Water availability and quality
demand for irrigation water
Income and costs
farm income
diversity of income sources
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
recreational opportunities
SLM/ land degradation knowledge
conflict mitigation
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
surface runoff
evaporation
Soil
soil moisture
soil cover
soil loss
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
biomass/ above ground C
plant diversity
habitat diversity
pest/ disease control
Other ecological impacts
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
water availability
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | Type of climatic change/ extreme | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | well |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| local rainstorm | not well |
| local windstorm | well |
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| drought | well |
Hydrological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| general (river) flood | not known |
Other climate-related consequences
Other climate-related consequences
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| reduced growing period | well |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
neutral/ balanced
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
neutral/ balanced
Long-term returns:
positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- 1-10%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
Comments:
2% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
7 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Расширение технологии ограничивается денежными ресурсами.
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
|
Предотвращает развития водной эрозии на крутых склонах How can they be sustained / enhanced? Данная технология будет востребована фермерами по мере их заинтересованности развития садоводства и предотвращения стихийных бедствий связанных с оползневыми процессами, селями и эрозией почв. |
|
Предотвращает развитие оползней. How can they be sustained / enhanced? На период существования сада |
|
Позволяет увеличить процент приживаемости саженцев плодовых культур How can they be sustained / enhanced? Применяется на срок два три года, до углубления корневой системы до глубины двух метров |
|
Бутылочный полив позволяет экономно расходовать воду. How can they be sustained / enhanced? На срок два три года |
|
Бороздковая техника полива для крутых склонов неприемлема так как избыток воды подаваемый на полив приводит к насыщению лессовых грунтов и образованию оползней. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Не рекомендуется в целом к применению |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Бутылочный полив требует частого полива, это увеличивает трудозатраты. | Внедрить капельное орошение |
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules