Выращивание картофеля в лунке [Tajikistan]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Rustam Kalandarov
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: David Streiff
technologies_1038 - Tajikistan
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
SLM specialist:
Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Youth Ecological Center, Tajikistan (Youth Ecological Center, Tajikistan) - TajikistanName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - Kyrgyzstan1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
03/05/2011
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
Технология выращивание картошки в лунке
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
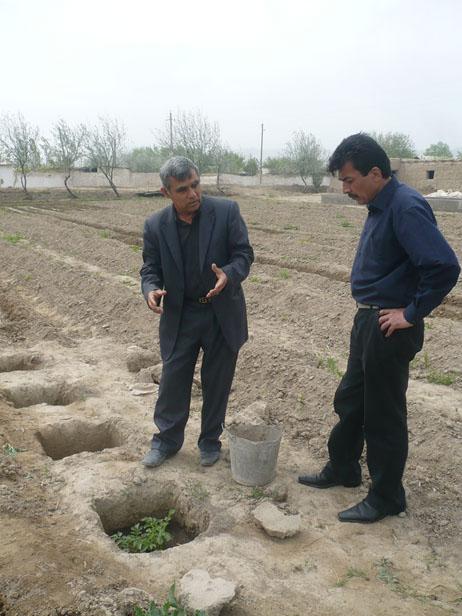
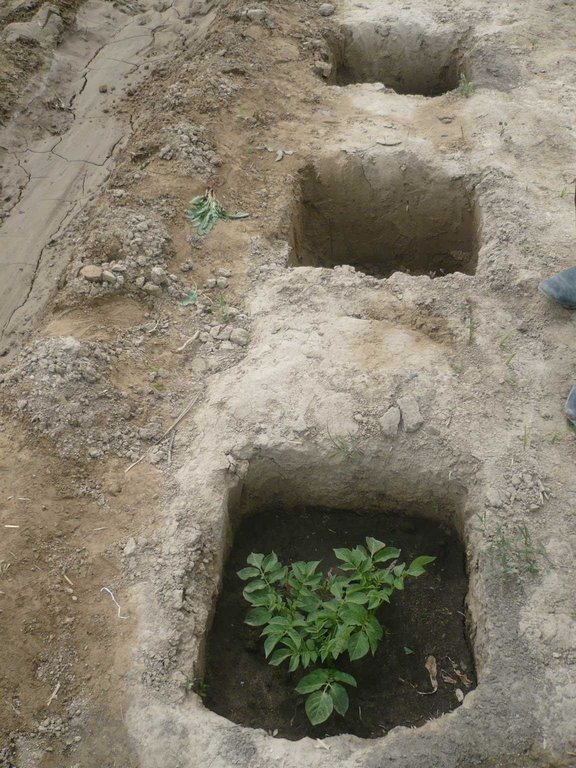
Это технология используется для получения продукции в зонах дефицита воды и экстремальных условиях. Технология очень проста: капают яму размером 50 х 50 х50 см. на дно ямы засыпают компост или обогащенную почву, и сажают одну или две семенные картошки. По мере роста ботва закапывается, полив осуществляется регулярно.
Purpose of the Technology: Цель технологии: улучшение производства картофеля, и тем самым, повышение дохода фермера в таких климатических условиях. Технология показывает хорошие адаптационные возможности в засушливых районах. Метод улучшает доступ к воде.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Технология очень простая и не требует больших затрат. Основным вкладом для фермеров является приготовление компоста и покупка высококачественных семян. Физическая работа требуется для приготовления ямы и для дальнейшего ухода за картофелем.
Natural / human environment: Данная технология может быть внедрена, как и в дехканских фермах, так и в приусадебных участках
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Tajikistan
Region/ State/ Province:
Таджикистан
Further specification of location:
Хатлонский район, Н.Хусравский район
Map
×3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
Comments:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Основная проблема связана с оптимальным использованием земли
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- full irrigation
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 2
Specify:
Longest growing period in days: 150
Longest growing period from month to month: январь- май
Second longest growing period in days: 180
Second longest growing period from month to month: июнь- ноябрь
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- irrigation management (incl. water supply, drainage)
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
Comments:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 1га m2.
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A2: Organic matter/ soil fertility
Comments:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: ранняя посадка, сменное возделывание культур, мульчирование, навоз / компост / остатки, борозды (дренаж, ирригация)
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

chemical soil deterioration
- Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content (not caused by erosion)

physical soil deterioration
- Pk: slaking and crusting
- Pi: soil sealing
Comments:
Main type of degradation addressed: Ха (Cn): снижение плодородия почвы и органических веществ в почве (не вызванные эрозией), Фк (Pk): уплотнение и образование коры
Main causes of degradation: управление с/х культурами (однолетние, многолетние, деревья/кустарники), землепользование
Secondary causes of degradation: управление землеи, изменение температуры, изменение сезонных дождей, засуха, бедность / богатство
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
- reduce land degradation
Comments:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
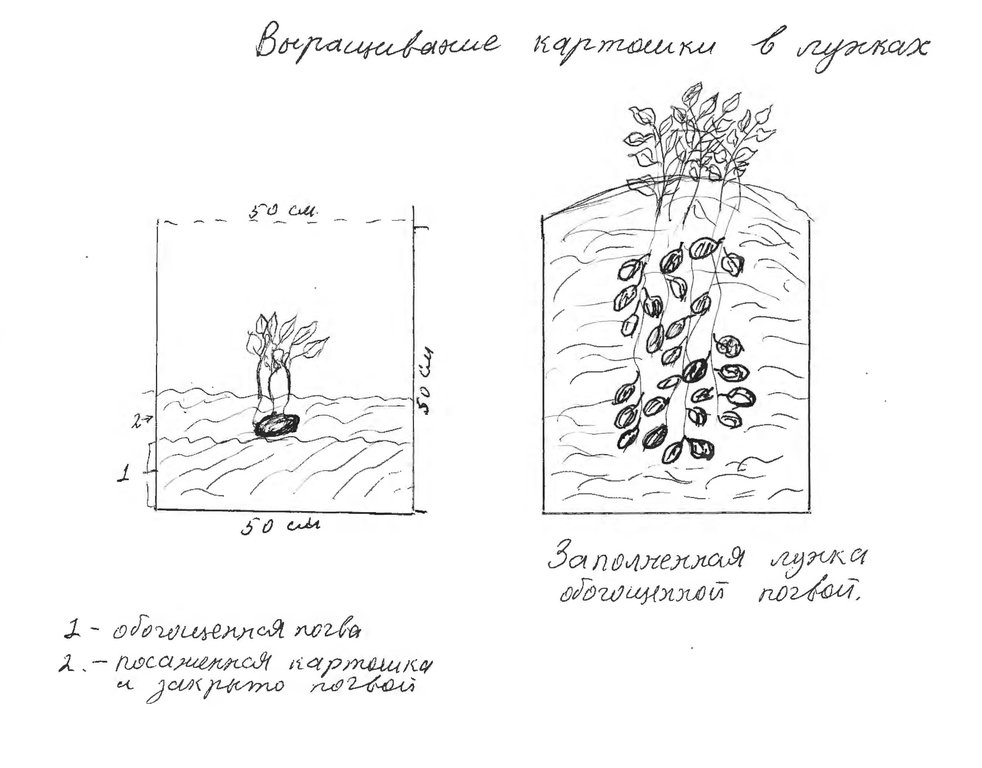
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
Схема показывает нижнею часть ямы заполняемую компостом и почвой по мера роста побегов Постепенно до поверхности лунка засыпается обогащенной почвой.
Location: Юг Таджикистана. Н.Хусравский Район, Хатлонская область
Date: 11.05.2011
Technical knowledge required for land users: средний
Main technical functions: улучшение поверхностной структуры (покрытие коркой, уплотнение)
Relay cropping
Material/ species: семена картошки
Remarks: лункавания
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: компост
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify currency used for cost calculations:
- US Dollars
other/ national currency (specify):
450
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | None | Structural |
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | None | None | 1.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | None | None | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | None | None | 200.0 | 0.45 | 90.0 | 1.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 103.0 | |||||
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | копка ям | Agronomic | человек ден |
| 2. | заполнения лунки почвой | человек/день |
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | None | None | 0.1 | 5.0 | 0.5 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 0.5 | |||||
4.8 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
основной фактор - копка лунки
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- arid
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- low (<1%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
< 5 m
Availability of surface water:
medium
Water quality (untreated):
good drinking water
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- medium
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Market orientation of production system:
- subsistence (self-supply)
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial
Off-farm income:
- 10-50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
- animal traction
Gender:
- women
- men
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
Market orientation of production system: subsistence (self-supply), subsistence (self-supply), mixed (subsistence/ commercial
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- medium-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- state
Water use rights:
- open access (unorganized)
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Water availability and quality
demand for irrigation water
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
surface runoff
Climate and disaster risk reduction
drought impacts
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | Type of climatic change/ extreme | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | well |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| local rainstorm | not known |
| local windstorm | well |
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| drought | well |
Hydrological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| general (river) flood | not well |
Other climate-related consequences
Other climate-related consequences
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| reduced growing period | not known |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
very positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
very positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
Comments:
15% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
50 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Технология постепенно улучшается и развивается
Comments on adoption trend: Постепенное внедрение
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
|
Технология новая How can they be sustained / enhanced? по мере возможности |
|
при выращивании в лунках урожайность повышается How can they be sustained / enhanced? при соблюдении агротехники можно получить хороший урожай |
|
водосберегательная технология How can they be sustained / enhanced? полив воды производиться индивидуально |
|
технологию можно использовать даже на небольших земельных участках (на приусадебных участках) How can they be sustained / enhanced? при использовании этой технологии, можно обеспечить картофелем одну семью |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| все что указано выше |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| технология применима только на малых участках | |
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules