Dugout Pond [India]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Mulchand Kag
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: Fabian Ottiger
Talawadi
technologies_1472 - India
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
30/09/2002
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches

Comprehensive watershed development [India]
Participatory approach that includes a package of measures leading to empowerment of communities to implement and sustain watershed development.
- Compiler: David Gandhi
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
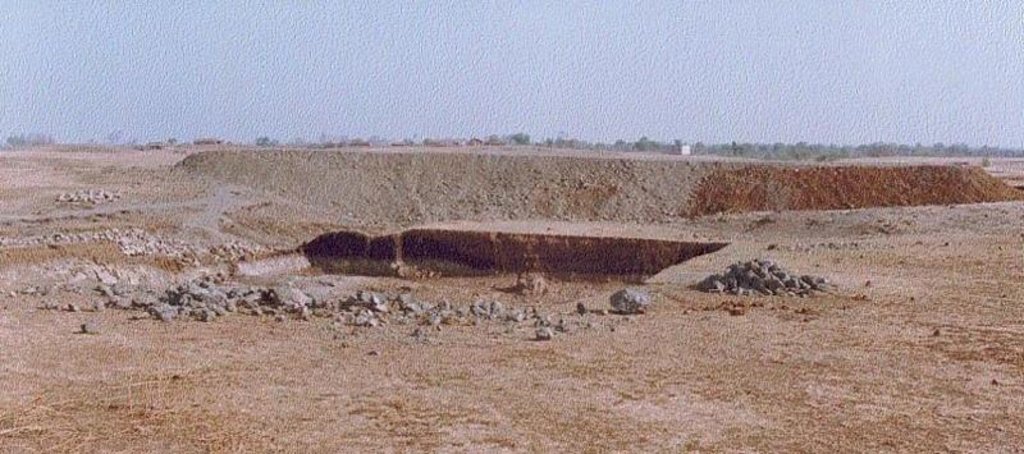
Dugout pond is a sunken water harvesting structure constructed along the rills in upper catchment for the purpose of storage of runoff and recharge of ground water.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
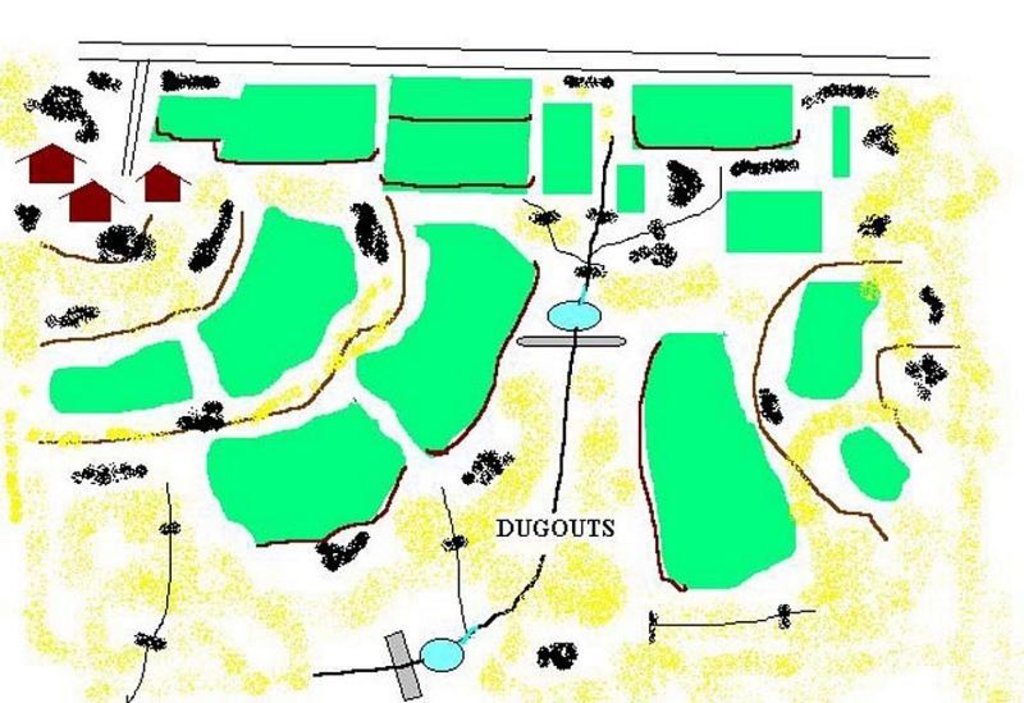
Dugout pond is a rectangular shape subsurface pond with the excavated material forming an embankment down stream. It is constructed in the upper catchment of the watershed, along the rill/shallow gully. The site for the pond should be where there is a depression. The size may vary from small to large depending on the size of catchment, needs of the farmers, availability of finance, bed rock strata.
Purpose of the Technology: 1- Storage of runoff. 2- Increase in water levels of shallow wells 'odees' through increased percolation. 3- Flood control through series of such structures. 4- Low cost, low risk alternative for poor community. 5- Benefits to community living in upper catchment.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: 1- Site selection with community. 2- Design and preparation of estimate by the project staff. 3- Descussion with VWDC and community, identification of users, descussion regarding contribution, agreement, work plan. 4- Layout and construction under VWDC supervision with technical support from the project. 5- Treatment of catchment.
Natural / human environment: Responsibility of user group.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
India
Region/ State/ Province:
Madhya Pradesh
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through projects/ external interventions
Comments (type of project, etc.):
The technology has been developed by the project as modification/improvement to Dugout pond constructed under NWDPRA (National Watershed Development Program for Rainfed Areas).
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- adapt to climate change/ extremes and its impacts
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Grazing land
Comments:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): 1. Utilisation of slopy and stony (class VI) land for agriculture. 2. Agriculture practices along the slope, use of erosion permitting crop eg. Cotton, Maize. 3. Excessive grazing of grass land.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): shallow soils, low soil moisture , low yields , non-availability of grazing land.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Monsoon - Cotton + Maize + Blackgram /Soyabean. Winter (with irrigation) - Wheat + Gram (excluding Cotton fields).
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
Comments:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 2
Specify:
Longest growing period in days: 150 Longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Mar Second longest growing period in days: 135 Second longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Sep
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- water harvesting
- irrigation management (incl. water supply, drainage)
- ground water management
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, indicate approximate area covered:
- 10-100 km2
Comments:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 48 m2.
The area comprises 36 villages with 1632 household mainly tribal. Villages comprise a larger settlement along with a number of hamlets. The topography is rolling and gently undulating. The area forms the catchment of the Larki stream, which forms the upper catchment of the river Mahi.
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wg: gully erosion/ gullying

water degradation
- Ha: aridification
Comments:
Main type of degradation addressed: Ha: aridification
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (Social causes - Lack of awareness and mobilisation amongst the communities.), Top down approach (Macro planning rather than micro (village level) planning.)
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
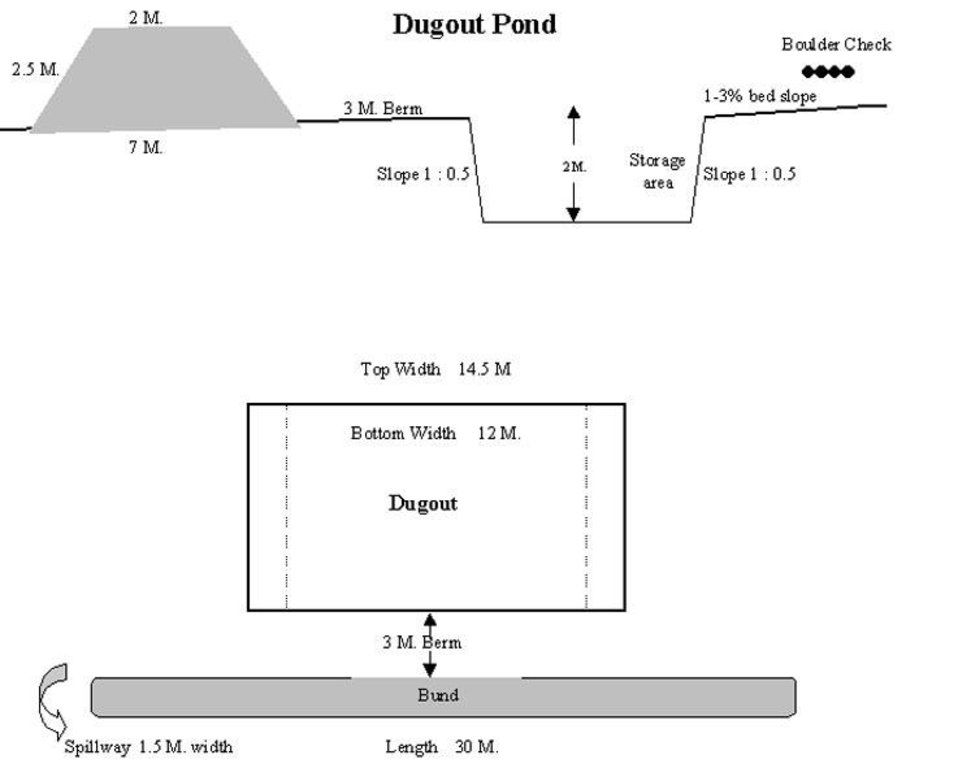
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
Technical Drawing of Dugout Pond
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase of infiltration
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, water harvesting / increase water supply
Construction material (earth): Excavated material used for embankment.
Construction material (stone): Excavated stones used for pitching.
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
other/ national currency (specify):
Rupees
Indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (if relevant): 1 USD =:
48.85
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
1.00
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Discussion in VWDC meeting | Structural | March-April |
| 2. | Site selection | Structural | March-April |
| 3. | Identification of beneficiaries, users group formation | Structural | March-April |
| 4. | Design & estimate | Structural | March-April |
| 5. | Agreement with VWDC | Structural | March-April |
| 6. | Treatment of catchment area | Structural | April-May |
| 7. | Construction of dugout pond | Structural | April-May |
| 8. | Seeding of embankment | Structural | June-July |
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
Comments:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Monitoring by users group | Structural | Year around/Regular |
| 2. | Report of damage, breakage in VWDC | Structural | Rainy season/After heavy shower |
| 3. | Decision regarding repair by VWDC/UG | Structural | Rainy season/After heavy shower |
| 4. | Necessary repaires carried out | Structural | Rainy season/After heavy shower |
| 5. | Desilting | Structural | Dry season/annual |
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
Comments:
The size of dugout described in 2.7.1 is :- Excavated area - 13m long X 12m wide X 2.5m Bund - 30m long X2.5m height X 2m top width X 7m bottom width
4.8 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
1- Cost of excavation increases with hardness of strata. 2- Non availability of stones locally for pitching.
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specify average annual rainfall (if known), in mm:
800.00
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
However for the past 4 years the area has received below average rainfall.
Agro-climatic zone
- semi-arid
90 - 120 days LGP - monsoon
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Comments and further specifications on topography:
Landforms: Ridges (ranked 1, gradually undulating topography) and hill slopes (ranked 2)
Slopes on average: Moderate (ranked 1, fields in upper catchment) and gentle (ranked 2, fields in valley portion)
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- low (<1%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
Soil depth on average: Shallow (ranked 1, fields on ridge/slopes), very shallow (ranked 2, ridge portion) and moderately deep (ranked 3, fields in valley)
Soil fertility: Medium (ranked 1) and low (ranked 2, fields on ridge/slopes, grass land)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good (ranked 1, sloping land, shallow soils) and medium (ranked 2, fields in valley)
Soil water storage capacity: Low (ranked 1, shallow soils) and medium (ranked 2, deep soils)
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Off-farm income:
- 10-50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- poor
- average
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: > 4%
33% of the land users are average wealthy and own 33% of the land (Few farmers with wells, fields in valley.).
50% of the land users are poor and own 57% of the land (Majority of farmers.).
17% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land (Very small holding.).
Off-farm income specification: While main income is from rainfed agriculture, significant income is obtained during migration, which increases during drought periods.
Level of mechanization: Animal traction (ranked 1, land preparation), manual labour (ranked 2, land preparation, weeding, harvesting) and mechanised (ranked 3, threshing)
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- communal/ village
Land use rights:
- open access (unorganized)
- individual
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
neutral/ balanced
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
If available, quantify (no. of households and/ or area covered):
1672
Comments:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
1632 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
40 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The community is very poor and hence requires some financial support to offset loss of wages.
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks

Comprehensive watershed development [India]
Participatory approach that includes a package of measures leading to empowerment of communities to implement and sustain watershed development.
- Compiler: David Gandhi
Modules
No modules