Rockwall Terracing [Philippines]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: Fabian Ottiger
technologies_1700 - Philippines
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
SLM specialist:
Luistro Aida
273-2474
Department of Agriculture-STIARC, RFO IVA
RMIC Bldg., BPI Compound Visayas Ave Quezon City
Philippines
SLM specialist:
Gregorio Elizabeth
Department of Agriculture-STIARC, RFO IVA
RMIC Bldg., BPI Compound Visayas Ave Quezon City
Philippines
SLM specialist:
Dinamling Djolly Ma.
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Visayas Avenue, Vasra, Quezon City, Philippines
Philippines
SLM specialist:
Guttierez Albert
alfergu@yahoo.com
LGU of La Libertad
Negros Oriental
Philippines
Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Bureau of Soils and Water Management (Bureau of Soils and Water Management) - PhilippinesName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Southern Tagalog Integrated Agricultural Research Center (STIARC) - PhilippinesName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
LGU of La Libertad - Philippines1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
28/05/2015
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
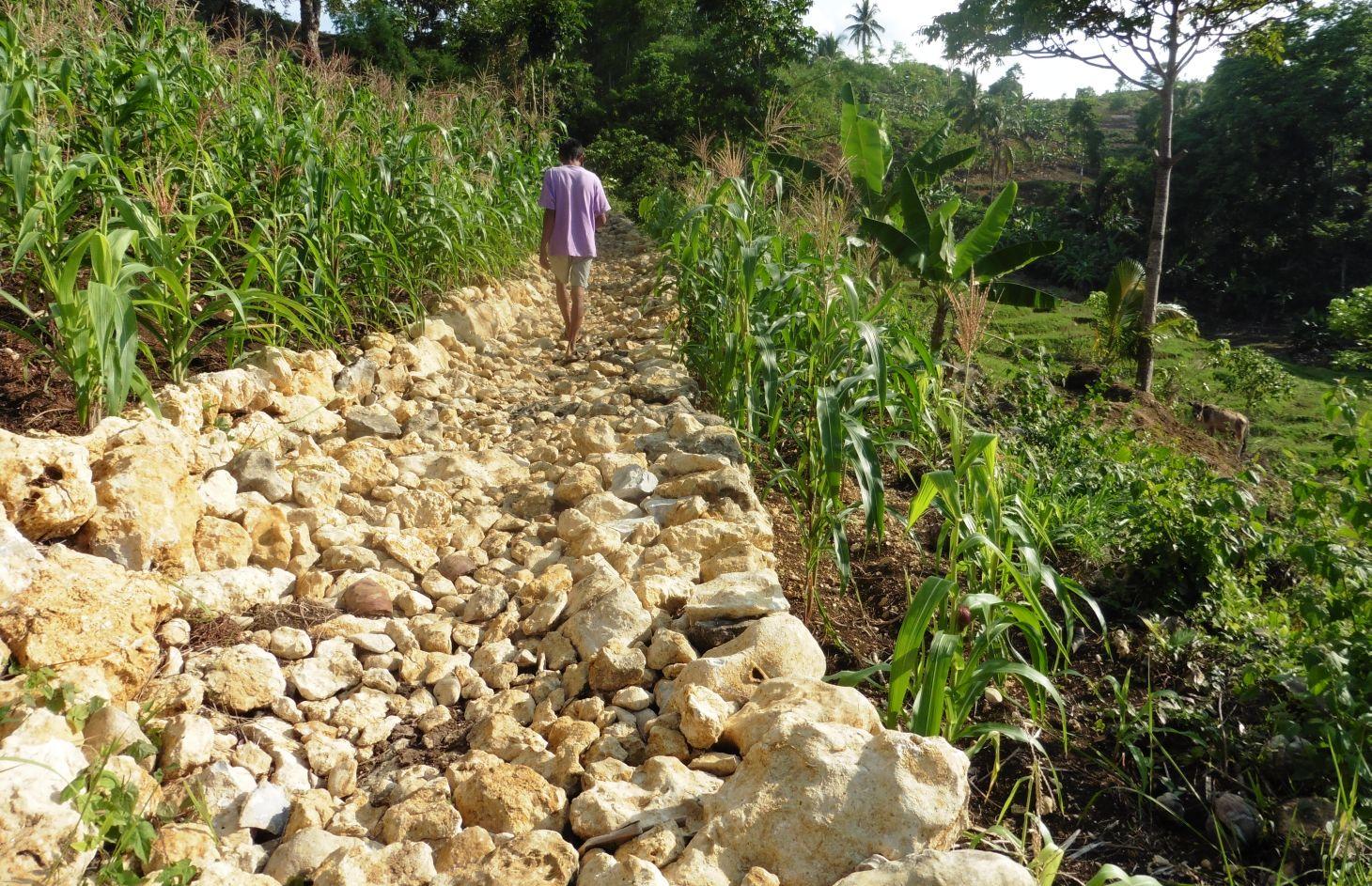
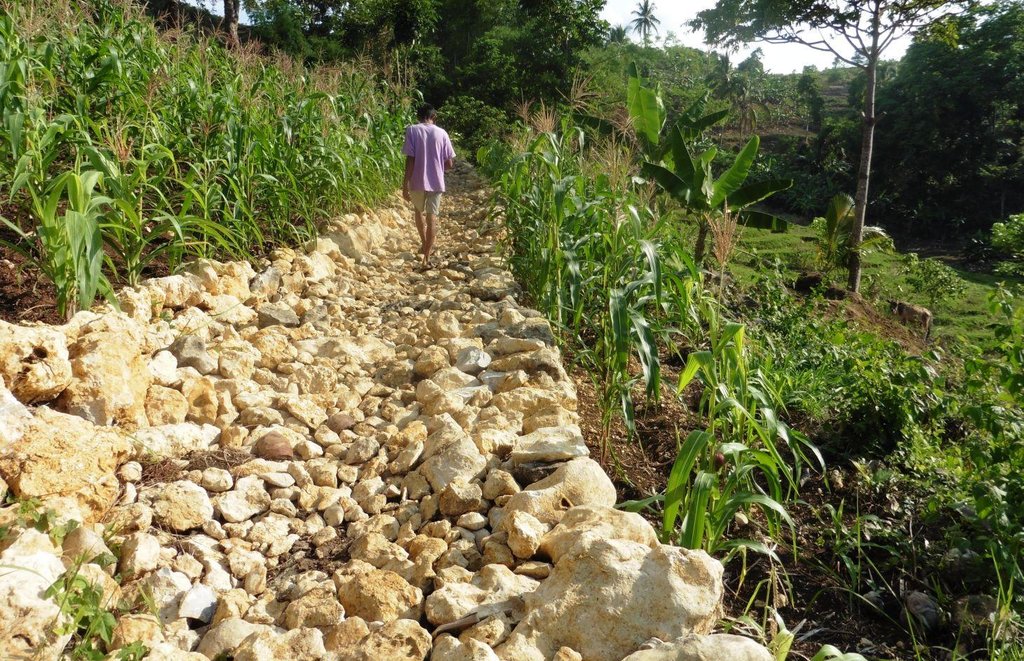
Rockwall terracing refers to the piling of stones or rocks along contour lines to reduce soil erosion in hilly areas.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
Rockwall terracing technology is widely practiced by farmers in hilly area of Barangay Nasunggan, La Libertad, Negros Oriental. Rocks piled along contours are indigenous to the area. The terrace bed is cultivated and planted with corn, watermelon, and vegetables. In some areas, livestock like cattle and native pigs are being raised. The technology is a traditional practice in the Philippines and one of the conservation techniques under the Conservation Farming Village (CFV) approach.
Purpose of the Technology: Rockwall terraces are built to reduce soil erosion and provide ease in land preparation through the removal of naturally present rocks in the cultivated area.It also contributes to the partial arrangement and diversification of land use. Before the implementation of the technology, the physical condition of the area is not recommended for farming practices due to the presence of rocks scattered all over the area.Dispersed and concentrated runoff are controlled in this technology. Raindrop splash is also restrained. Moreover, water storage is maintained in the soil.
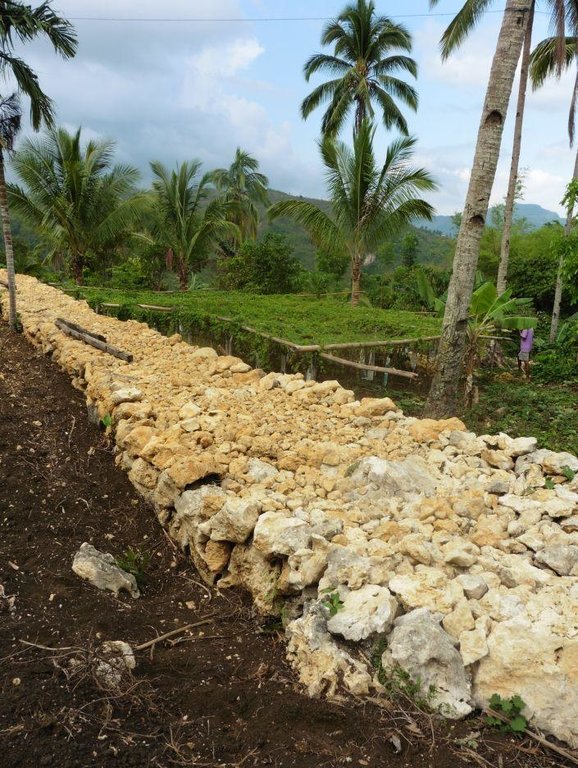
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: With the aid of an A-Frame, contours are determined. Rocks and/or stones are gathered from the area and piled along contours to form walls 1.10 m wide and 1.50 m high. It requires 14 person-day for a month to construct a 50-meter rockwall with a cost of 800 USD. Maintenance of the structure is done three times a year by repiling of dislodged rocks.
Natural / human environment: The area is classified under a humid agro-climate condition where an average annual rainfall of 1000-1500 mm per year are observed. The average cropland size of land user ranges from 0.5-1 hectare with a slope of 18-25%. Majority of their income are derived from on-farm activities. Crops planted in the terraced bed are sold in the town market and is also utilized for consumption.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Philippines
Region/ State/ Province:
La Libertad
Further specification of location:
Negros Oriental
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through land users' innovation
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
Main crops (cash and food crops):
Major cash crop: Vegetable, banana, cacao, coffee
Major food crop: Corn, forage legumes

Mixed (crops/ grazing/ trees), incl. agroforestry
- Agro-pastoralism
Main products/ services:
Main livestock species: swine, cattle, chicken
Comments:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The area is prone to soil erosion and land degradation due to absence of vegetation.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Not suitable for crop production because of the rocks or stones scattered in the area.
Mixed: (eg agro-pastoralism, silvo-pastoralism): swine, cattle, chicken
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mo: Other
If land use has changed due to the implementation of the Technology, indicate land use before implementation of the Technology:
Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
Comments:
Water supply: rainfed, mixed rainfed - irrigated
Water supply: rainfed, post-flooding
Livestock density (if relevant):
10-25 LU /km2
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- cross-slope measure
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Comments:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.278 m2.
At present, rockwalls are not constructed in contiguous manner. Construction were done prioritizing those highly eroded areas but the plan is to build and expand in the barangay, smallest administrative division in the Philippines.
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

structural measures
- S6: Walls, barriers, palisades, fences
Comments:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion

chemical soil deterioration
- Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content (not caused by erosion)

biological degradation
- Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Comments:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Main causes of degradation: soil management (intensive soil cultivation/tillage)
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (inappropriate cropping system), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (logging), education, access to knowledge and support services (limited access to learning facilities)
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- restore/ rehabilitate severely degraded land
Comments:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Author:
Patricio A. Yambot, Bureau of Soils and Water Management
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
Rockwall terrace built to utilize the rocks in the area.
Location: Brgy. Nasunngan. La Libertad, Negros Oriental
Date: May 25,2015
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control soil erosion
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, increase / maintain water stored in soil, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), spatial arrangement and diversification of land use, serve as access road
Wall/ barrier
Spacing between structures (m): 3-5m
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.5
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.1
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 50 m
Construction material (stone): limestones
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 18%
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
other/ national currency (specify):
Pesos
Indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (if relevant): 1 USD =:
45.0
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
2.22
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Contouring | Structural | 1 day |
| 2. | Digging along contour, Gathering and piling of stones along contours | Structural | 3 months |
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | labour | dam | 1.0 | 804.44 | 804.44 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Tools | dam | 1.0 | 22.22 | 22.22 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 826.66 | |||||
Comments:
Duration of establishment phase: 5 month(s)
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Repiling of stones and rocks that were dislodged | Structural | 3 times a year |
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Labour | 50m | 1.0 | 13.33 | 13.33 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 13.33 | |||||
Comments:
Machinery/ tools: A-Frame, Mattock, Shovel
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- humid
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Comments and further specifications on topography:
Altiudinal zones: 501-100 m a.s.l. (600m)
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
> 50 m
Availability of surface water:
poor/ none
Water quality (untreated):
good drinking water
Comments and further specifications on water quality and quantity:
Seasonality of water quality and source of pollution (good drinking water, year round, spring water )
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- low
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Market orientation of production system:
- subsistence (self-supply)
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- poor
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
- animal traction
Gender:
- women
- men
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly disadvantaged land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Level of mechanization: Manual work, animal traction
Market orientation: subsistence (self-supply)
Market orientation: Mixed (subsistence/commercial)
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%; 2%
30% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land.
70% of the land users are poor and own 70% of the land.
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- small-scale
Comments:
1-2ha of cropland and <0.5ha grazing land per household
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, not titled
Land use rights:
- individual
Water use rights:
- individual
Comments:
Sharing of water from spring during summer
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Quantity before SLM:
5000 ears for corn/ha
Quantity after SLM:
10000 ears for corn/ha
fodder production
fodder quality
product diversity
production area
Income and costs
expenses on agricultural inputs
farm income
diversity of income sources
Other socio-economic impacts
crop production area
Comments/ specify:
Reduced crop production area: medium (20-50%)
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
cultural opportunities
community institutions
national institutions
conflict mitigation
situation of socially and economically disadvantaged groups
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Comments/ specify:
yes, greatly
Ecological impacts
Soil
soil loss
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
downstream siltation
buffering/ filtering capacity
damage on neighbours' fields
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | Type of climatic change/ extreme | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | well |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| local rainstorm | not well |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
If available, quantify (no. of households and/ or area covered):
10 land user families/households
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 50-90%
Comments:
63% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
10 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
37% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
6 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Even without LGU assistance, rockwall technology will continue since most of the landusers in the area were trained on how to construct with the use of A-frame.
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| Rockwall terraces prevent downstream siltation thus preserving the topsoil in the upper part of the area. |
| Ease of land preparation since rocks are not scattered in the field.It improves the soil condition for crop establishment. |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
|
The technology involves indigenous material such as rocks and stones from the area. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Improvement of piling rocks/stones |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Production area is reduced due to the rock wall structure. |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Durability of the structure. | This could be improved by cementing the gaps between rocks (riprapping) to enhance durability, thus reducing maintenance cost. |
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules