បច្ចេកទេសដាំបន្លែឆ្លាស់គ្នាដែលទប់ទល់ការបំផ្លាញពីសត្វល្អិត នៅតាមច្រាំងទន្លេមេគង្គ [Cambodia]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Nary Lay
- Editors: Navin Chea, Sophea Tim
- Reviewers: SO Than, Nicole Harari
បន្លែធម្មជាតិ
technologies_2098 - Cambodia
- Full summary as PDF
- Full summary as PDF for print
- Full summary in the browser
- Full summary (unformatted)
- បច្ចេកទេសដាំបន្លែឆ្លាស់គ្នាដែលទប់ទល់ការបំផ្លាញពីសត្វល្អិត នៅតាមច្រាំងទន្លេមេគង្គ: Julie 12, 2018 (inactive)
- បច្ចេកទេសដាំបន្លែឆ្លាស់គ្នាដែលទប់ទល់ការបំផ្លាញពីសត្វល្អិត នៅតាមច្រាំងទន្លេមេគង្គ: Julie 12, 2018 (inactive)
- បច្ចេកទេសដាំបន្លែឆ្លាស់គ្នាដែលទប់ទល់ការបំផ្លាញពីសត្វល្អិត នៅតាមច្រាំងទន្លេមេគង្គ: Aug. 20, 2018 (inactive)
- បច្ចេកទេសដាំបន្លែឆ្លាស់គ្នាដែលទប់ទល់ការបំផ្លាញពីសត្វល្អិត នៅតាមច្រាំងទន្លេមេគង្គ: Sept. 4, 2019 (public)
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
ប្រធានទទួលបន្ទុករួមនៅការិយាល័យកសិកម្ម រុក្ខាប្រមាញ់ និងនេសាទ ស្រុកព្រែកប្រសព្វ:
land user:
សុខឡាង អ៊ី
(+855) 71 964752
មិនមានអ៊ីម៉ែល
កសិករ
ភូមិ តាម៉ៅលើ ឃុំ កំពង់គ ស្រុក ព្រែកប្រសព្វ ខេត្ត ក្រចេះ
Cambodia
ប្រធានការិយាល័យកសិកម្ម រុក្ខាប្រមាញ់ និងនេសាទ ស្រុកសំបូរ:
មន្ត្រីនៅការិយាល័យកសិកម្ម រុក្ខាប្រមាញ់ និងនេសាទ ស្រុកចិត្របុរី:
លី សារ៉ាវុធ
(+855) 89 796 786
saravuthly123@gmail.com
ការិយាល័យកសិកម្ម រុក្ខាប្រមាញ់ និងនេសាទ ស្រុកចិត្របុរី
ភូមិខ្សារ ឃុំដារ ស្រុកចិត្របុរី ខេត្តក្រចេះ
Cambodia
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Royal University of Agriculture (RUA) - Cambodia1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
13/04/2017
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
Nee
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
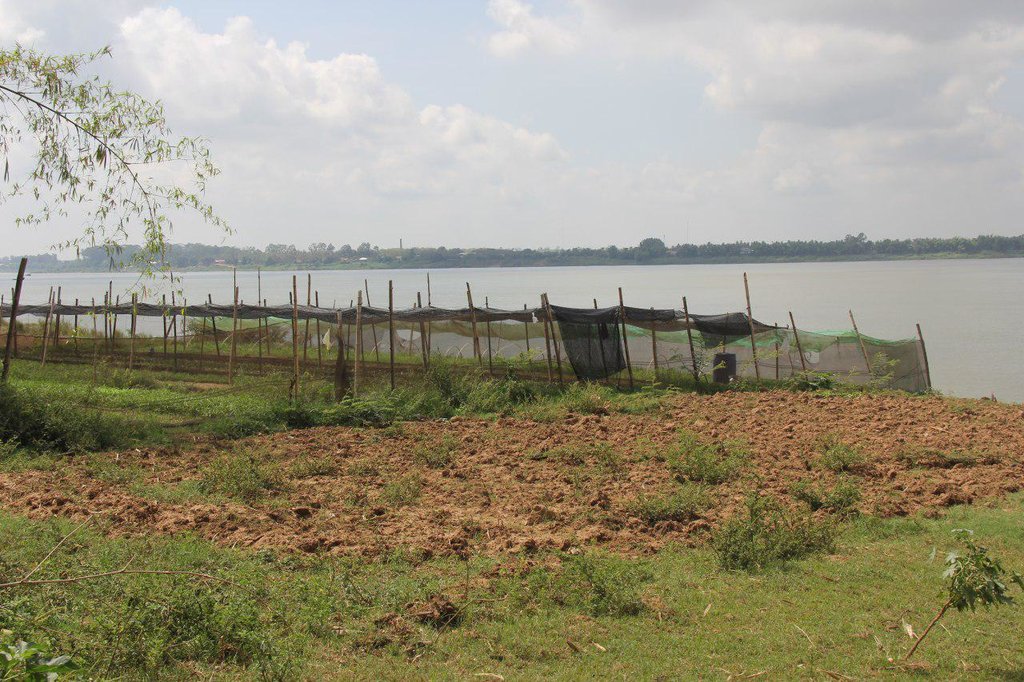
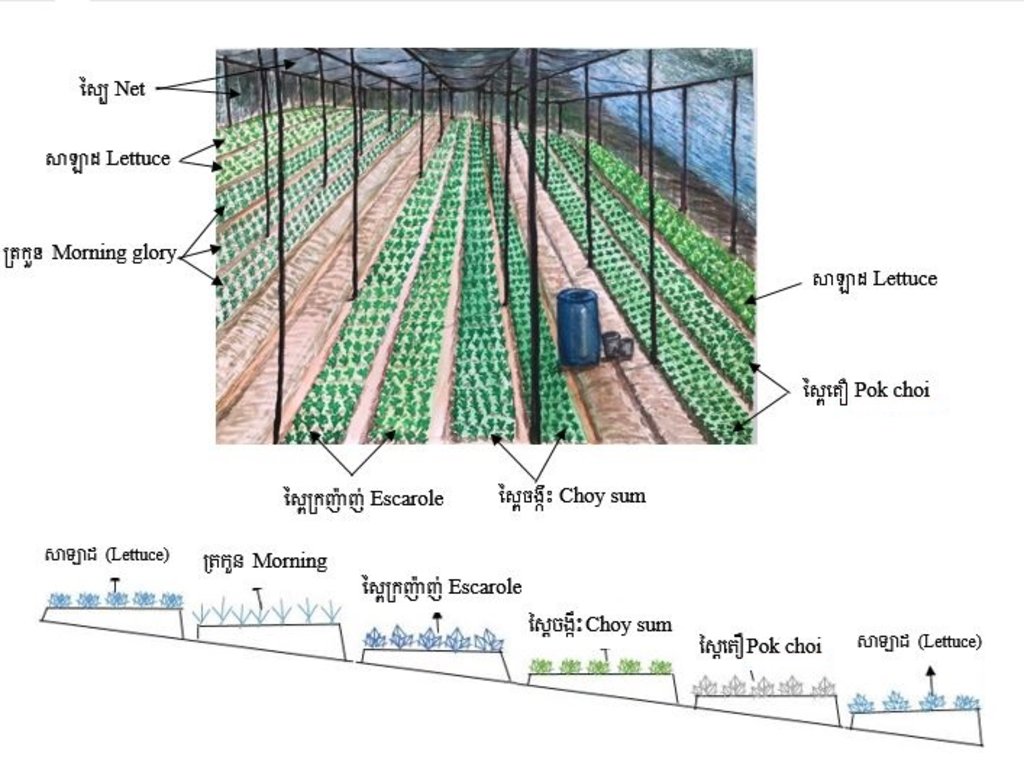
ការដាំបន្លែឆ្លាស់រង ដោយប្រើប្រភេទផ្សេងៗគ្នា (សាឡាដ ស្ពៃតឿ ស្ពៃចង្កឹះ ស្ពៃក្រញ៉ាញ់ និងត្រកួន) ដើម្បីកាត់បន្ថយការបំផ្លាញពីសត្វល្អិតដោយរួមផ្សំជាមួយការសម្លាប់មេរោគក្នុងដីមុនពេលដាំដោយប្រើកំបោរ ហើយក៏បានប្រើថ្នាំកំចាត់សត្វល្អិតផ្សំពីរុក្ខជាតិផងដែរក្នុងពេលដាំដុះ។ បច្ចេកទេសនេះបានអនុវត្តលើការដាំបន្លែតាមច្រាំងទន្លេមេគង្គក្នុងខេត្តក្រចេះ។
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
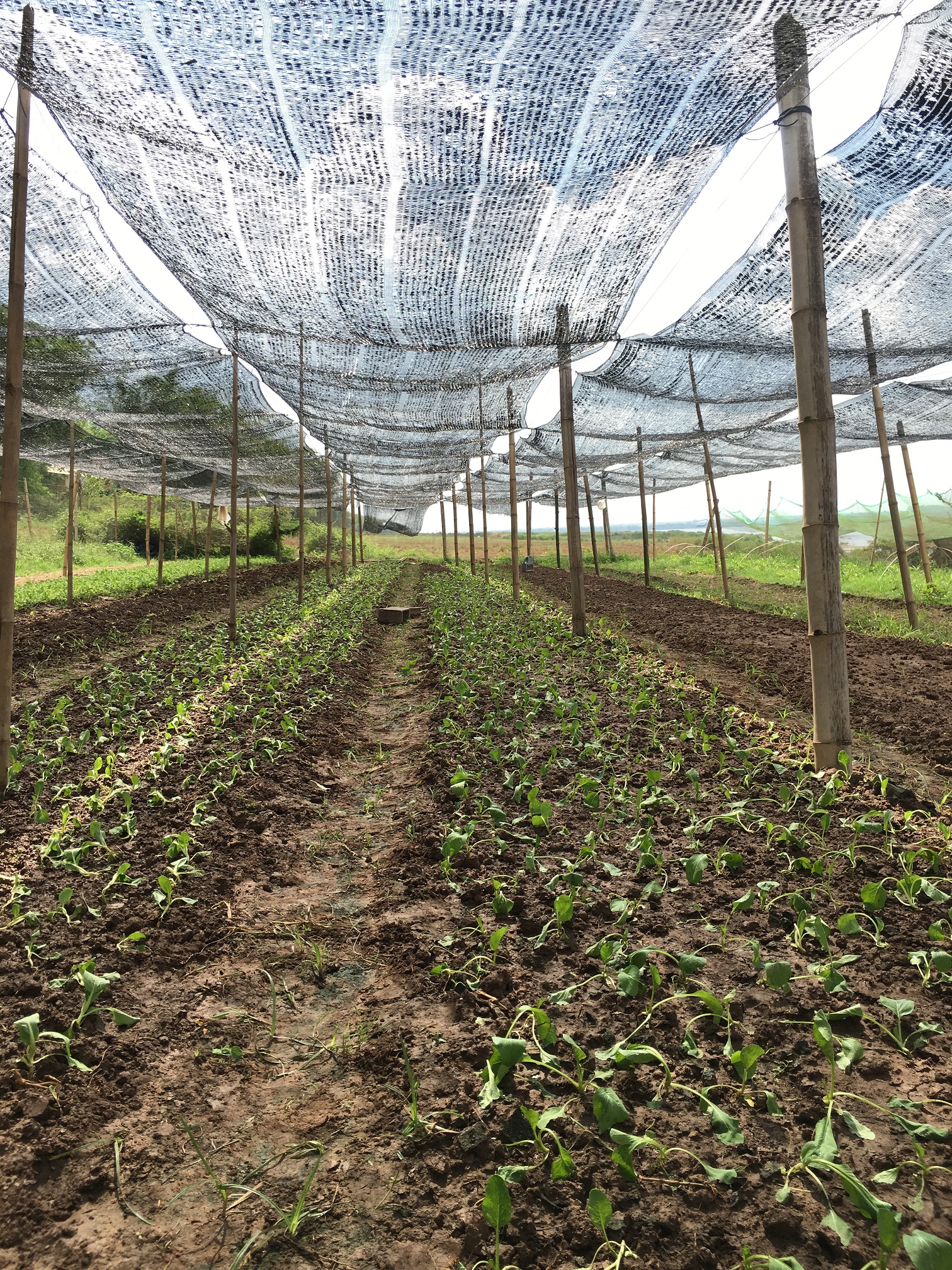
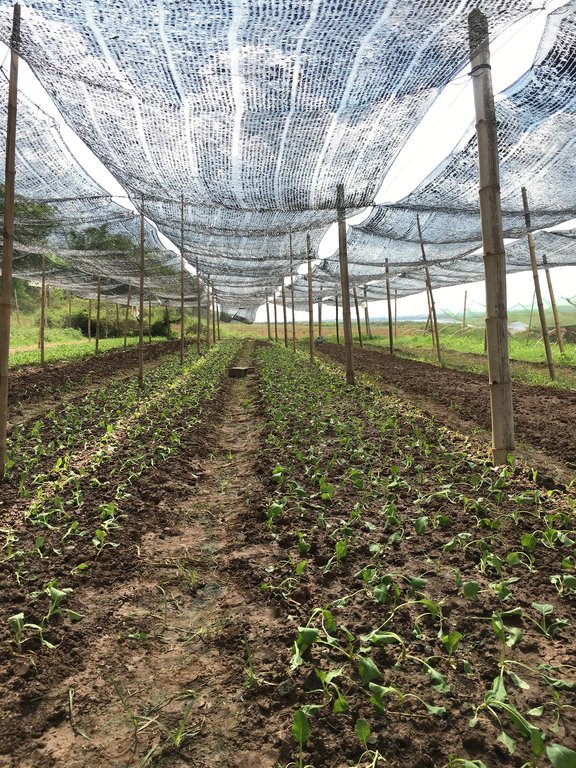
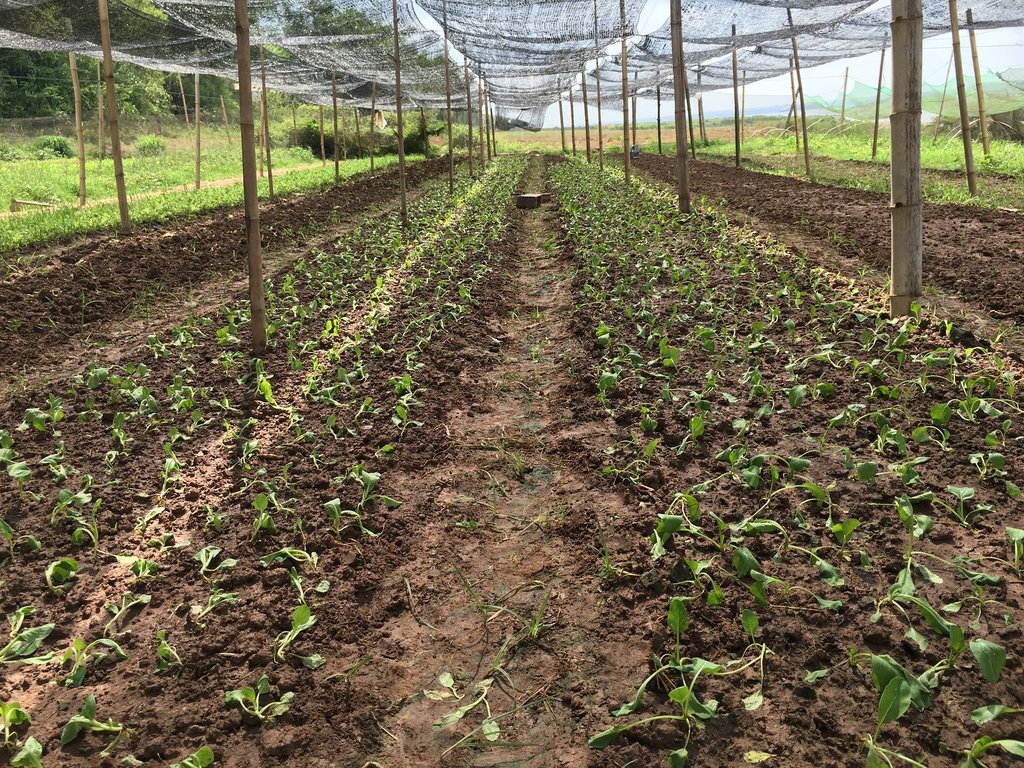
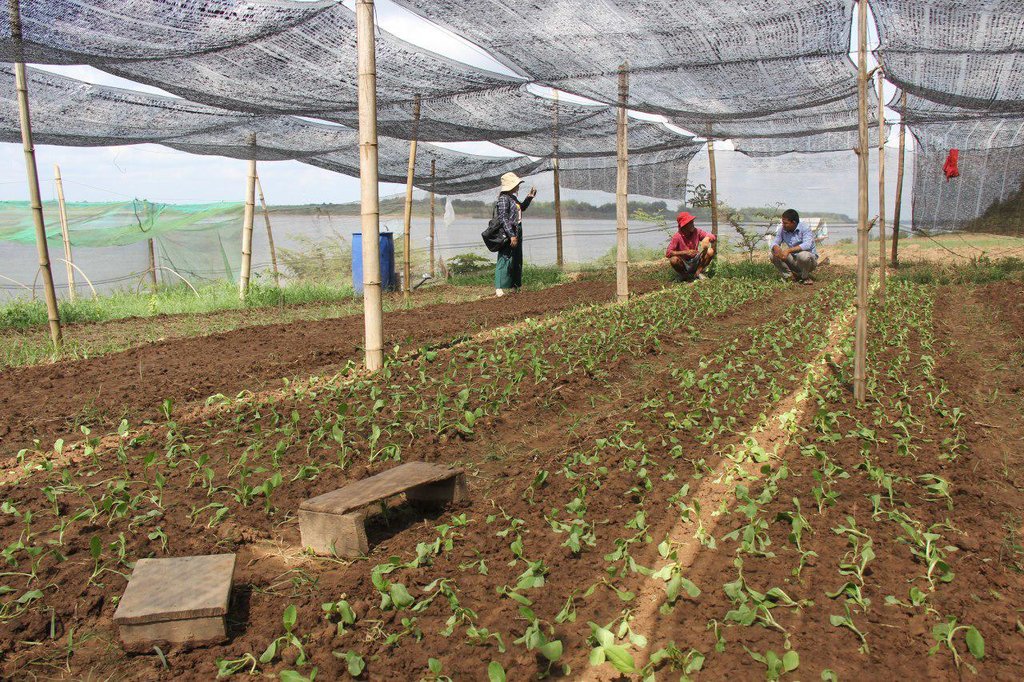
ការដាំដំណាំឆ្លាស់ជាវិធីសាស្ត្រនៃប្រព័ន្ធដាំដុះដែលមានការដាំដំណាំប្រភេទផ្សេងៗក្នុងរងដោយឡែកៗ ហើយឆ្លាស់រៀងគ្នាក្នុងពេលតែមួយ (Pawan et al., 2012)។ ដំណាំដែលកសិករបានជ្រើសរើសយកមកដាំរួមមាន សាឡាដ ស្ពៃតឿ ស្ពៃចង្កឹះ ស្ពៃក្រញ៉ាញ់ និងត្រកួន។ បច្ចេកទេសនេះបានអនុវត្តនៅលើផ្ទៃដីទំហំ ១០៨០ ម៉ែត្រការ៉េនៅតាមច្រាំងទន្លេមេគង្គ ក្នុងខេត្តក្រចេះ។ ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសនេះកសិករបានរៀបចំដី រួចហើយលើកជារងកាត់ទទឹងជម្រាលច្រាំងទន្លេ។ នៅរងដំបូងដាំសាឡាដរងបន្តបន្ទាប់ដាំស្ពៃតឿ ស្ពៃចង្កឹះ ស្ពៃក្រញ៉ាញ់ ត្រកួន រួចសារឡើងវិញដោយចាប់ផ្តើមពីសាឡាដដដែល។ ការដាំដំណាំចម្រុះ ហើយឆ្លាស់គ្នាបានជួយកាត់បន្ថយការបំផ្លាញពីសត្វល្អិតដោយដំណាំសាឡាដជាប្រភេទបន្លែដែលសត្វល្អិតមិនចូលចិត្តស៊ីដោយសារវាមានរសជាតិល្វីង។ នៅពេលដែលដាំដំណាំឆ្លាស់សត្វល្អិតដែលមិនត្រូវការប្រភេទដំណាំនេះវានឹងបកត្រឡប់ថយក្រោយវិញដែលជាហេតុជួយកាត់បន្ថយការបំផ្លាញពីសត្វល្អិតដល់ដំណាំនៅរងបន្ទាប់ដែលជាប្រភេទដែលសត្វល្អិតចូលចិត្ត និយាយរួម គឺការបំភ័ន្តសត្វល្អិតដោយ បន្លែដែលសត្វល្អិតមិនចូលចិត្ត។
ដំណាំងាយនឹងទទួលរងការបំផ្លាញទាំងស្រុងពីសត្វល្អិតនៅពេលដែលដាំដំណាំតែមួយប្រភេទកបនឹងសត្វល្អិតប្រភេទណាមួយនោះ តែបើដាំឆ្លាស់ទោះបីជារងការបំផ្លាញលើដំណាំប្រភេទណាមួយក៏នៅសល់ប្រភេទដំណាំផ្សេងទៀតដែលមិនរងការខូចខាតដែរ។ ដើម្បីអនុវត្តន៍បច្ចេកទេសនេះឱ្យកាន់តែមានប្រសិទ្ធភាពកសិករបានប្រើប្រាស់ថ្នាំពុលធម្មជាតិដែលអាចផលិតបានដោយខ្លួនឯងផ្ទាល់ដោយ ប្រើគ្រឿងផ្សំពីរុក្ខជាតិដូចជា សម្បកស្តៅ វល្លិបណ្តូលពេជ្រ សម្បកស្លែង មើមក្បៀស។ល។ យកមកបុកហើយត្រាំទឹកទុកក្នុងរយៈពេល ១៥ ថ្ងៃទើបអាចយកមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន (Yang et al, 2006)។ ទឹកថ្នាំ ១ លីត្រ លាយជាមួយទឹកធម្មតា ១៥ លីត្របាញ់ទៅលើដំណាំ ពេលសង្កេតឃើញមានវត្តមានសត្វល្អិតចង្រៃ ហើយធ្វើការត្រួតពិនិត្យជាទៀងទាត់រៀងរាល់ថ្ងៃ។
ចំពោះការរៀបចំដីវិញគឺ ភ្ជួរដីហាលពី ៧ ទៅ ៨ ថ្ងៃទើបលើកជារង និងរោយកំបោរសទុកផ្អាប់រយៈពេល ៦ ថ្ងៃដើម្បីសម្លាប់មេរោគនៅក្នុងដី។ ការសាបកូនស្ពៃក្រញ៉ាញ់ ស្តៃតឿ ស្ពៃចង្កឹះ គឺមានរយៈពេល ២០ ថ្ងៃ ទើបយកមកស្ទូង (ចំណែកត្រកួន គឺដាំដោយគ្រាប់ផ្ទាល់តែម្តង) ដោយឡែកសាឡាដសាបរយៈពេលតែ ១០ថ្ងៃ គឺអាចយកមកស្ទូងបាន។ សាឡាដក្រោយពេលស្ទូងបាន ៣០ ថ្ងៃ គឺអាចប្រមូលផលបាន ចំពោះស្ពៃ និងត្រកួនវិញ គឺប្រមូលផលក្រោយពេលស្ទូង រយៈពេល ៣៨ ថ្ងៃ។ កសិករប្រើជីសរីរាង្គ និងលាមកគោដើម្បីបង្កើនជីជាតិដី។ រីឯការធ្វើរង គឺធ្វើទទឹងជម្រាលដើម្បីការពារការហូរច្រោះដីនៅពេលមានភ្លៀង។ លើសពីនេះដើម្បីការពារកម្តៅថ្ងៃ និងការពារភ្លៀងដែលធ្វើឱ្យប៉ះពាល់ដល់ដំណាំកសិករបានសង់ជារោងបណ្តោះអាសន្នមានកម្ពស់ ២ ម៉ែត្រ ដោយប្រើបង្គោលឫស្សីធ្វើជារោងដោយប្រក់ដំបូលដោយស្បៃ និងហ៊ុមព័ទ្ធជុំវិញដោយស្បៃ ដើម្បីការពារសត្វល្អិត និងសត្វពាហនៈដូចជាឆ្កែ និងមាន់ជាដើម។ ចំពោះតម្លៃកសិផលក្នុង ១ គីឡូក្រាម គឺស្ពៃតឿលក់បានតម្លៃពី ៣០០០ រៀល ទៅ ៤០០០ រៀល ត្រកួនតម្លៃ ២០០០ រៀល ស្ពៃចង្កឹះតម្លៃ ២០០០ រៀល ទៅ ៣០០០ រៀល ស្ពៃក្រញ៉ាញ់តម្លៃពី ៣០០០ រៀល ទៅ ៣៥០០ រៀល និងសាឡាដតម្លៃ ៤០០០ រៀល។
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Cambodia
Region/ State/ Province:
ភូមិតាម៉ៅលើ ឃុំកំពង់គរ ស្រុកព្រែកប្រសព្វ ខេត្តក្រចេះ
Further specification of location:
ជាដីដែលនៅមាត់ច្រាំងទន្លេមេគង្គ
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through land users' innovation
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- create beneficial economic impact
- កាត់បន្ថយការហូរច្រោះដីដោយធ្វើរងទទឺងជម្រាល។ ការពារការចាំងចូលនូវពន្លឺខ្លាំងរបស់ព្រះអាទិត្យ និងទឹកភ្លៀង កាត់បន្ថយសត្វល្អិតចង្រៃ
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
Main crops (cash and food crops):
សាឡាដ ស្ពៃតឿ ស្ពៃចង្កឹះ ស្ពៃក្រញ៉ាញ់ និងត្រកួន
If land use has changed due to the implementation of the Technology, indicate land use before implementation of the Technology:
មុនពេលកសិករអនុវត្តន៍ការដាំដំណាំឆ្លាស់ និងដំណាំវិលជុំ គាត់ដាំតែខ្លឺមបារាំងតែមួយមុខគត់។
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- mixed rainfed-irrigated
Comments:
ប្រើទឹកទន្លេមេគង្គ
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 3
Specify:
កសិករដាំបន្លែចាប់ពីខែវិច្ឆិកា ដល់ខែកក្កដា ដោយដំណាំមានអាយុកាលជាមធ្យមគឺ ៤៥ ថ្ងៃ។
Livestock density (if relevant):
មិនមានចិញ្ចឹមសត្វទេ
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- rotational systems (crop rotation, fallows, shifting cultivation)
- integrated soil fertility management
- integrated pest and disease management (incl. organic agriculture)
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- applied at specific points/ concentrated on a small area
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A2: Organic matter/ soil fertility

structural measures
- S4: Level ditches, pits
- S9: Shelters for plants and animals

management measures
- M5: Control/ change of species composition
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wr: riverbank erosion

physical soil deterioration
- Pu: loss of bio-productive function due to other activities

biological degradation
- Bp: increase of pests/ diseases, loss of predators
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
- reduce land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
កសិករលើករងកម្ពស់ ១៥ សង់ទីម៉ែត្រ ទទឹង ១.២០ ម៉ែត្រ និងបណ្តោយ ៣០ ម៉ែត្រដោយលើករងទទឹងជម្រាលដើម្បីការពារការហូរច្រោះដីនៅពេលភ្លៀងខ្លាំង។ គាត់ដាំសាឡាដ ស្ពៃតឿ ស្ពៃចង្កឹះ ត្រកួន និងស្ពៃក្រញ៉ាញ់ឆ្លាស់រងគ្នាដើម្បីការពារសត្វល្អិតកុំឱ្យមកបំផ្លាញដំណាំ។ គាត់បានធ្វើរោងដំណាំកម្ពស់ ២ ម៉ែត្រដោយប្រើសំណាញ់ជាដំបូលដើម្បីការពារកម្តៅថ្ងៃ និងទឹកភ្លៀង។ សម្ភារសម្រាប់ប្រើប្រាស់ គឺសំណាញ់ ៣ ដុំ បង្គោលឫស្សី ២៦ ដើម និងស្បៃសម្រាប់ព័ទ្ធជុំវិញជារបងចំនួន ៥ ដុំ។ ចំណែកឯ សម្ភារសម្រាប់ស្រោចស្រពរួមមាន ធុងស្តុកទុកទឹកស្រោចបន្លែពេលដាំដំបូង ហើយទុយោទឹកប្រវែង ៧០០ ម៉ែត្រ សម្រាប់បូមទឹកស្រោចស្រព។
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology area
Indicate size and area unit:
១០៨០ ម៉ែត្រការ៉េ
other/ national currency (specify):
រៀល
Indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (if relevant): 1 USD =:
4000.0
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
17,000
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | ជួលដីសម្រាប់ដាំបន្លែ | Agronomic | ខែវិច្ឆិកា ដល់ខែមិថុនា |
| 2. | រៀបចំដី (ភ្ជួរដីហាល លើករង និងបាចកំបោរ) | Agronomic | ខែឧសភា |
| 3. | ទិញសម្ភារសម្រាប់សាងសង់ (ស្បៃនីឡុង បង្គោលឫស្សី ធុងទឹក ចានដែក) | Structural | ពេលដាំដុះ |
| 4. | គ្រាប់ពូជ | Agronomic | ពេលដាំដុះ |
| 5. | ជីសរីរាង្គ និងលាមកសត្វ | Agronomic | ពេលដាំដុះ និងថែទាំ |
Comments:
ជីសរីរាង្គទិញពីក្រុមហ៊ុនវ៉ាន់ ឡុង
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | រៀបចំដី | នាក់-ថ្ងៃ | 3.0 | 17000.0 | 51000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | ម៉ាស៊ីនបូមទឹក | គ្រឿង | 1.0 | 1000000.0 | 1000000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | ចបកាប់ | ផ្លែ | 1.0 | 13000.0 | 13000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | រនាស់ | រនាស់ | 1.0 | 15000.0 | 15000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | ទុយោ | ដុំ | 14.0 | 16000.0 | 224000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | កញ្ឆេរ | គូ | 1.0 | 50000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | គ្រាប់ពូជសាឡាដ | កញ្ចប់ | 15.0 | 10000.0 | 150000.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | ស្ពៃក្រញ៉ាញ់ | កញ្ចប់ | 15.0 | 6000.0 | 90000.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | ស្ពៃចង្កឹះ | កញ្ចប់ | 6.0 | 6000.0 | 36000.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | ត្រកួន | គីឡូក្រាម | 14.0 | 10000.0 | 140000.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | ស្ពៃតឿ | កំប៉ុង | 2.0 | 7000.0 | 14000.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | កំបោរ | គីឡូក្រាម | 2.0 | 2500.0 | 5000.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | ជីសរីរាង្គ | បាវ | 1.0 | 130000.0 | 130000.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | សំណាញ់សម្រាប់ប្រក់ | ដុំ | 3.0 | 260000.0 | 780000.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | ធុងដាក់ស្រោចទឹក | គូ | 1.0 | 50000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | ចានដែក | ចានដែក | 3.0 | 10000.0 | 30000.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | ធុងស្តុកទឹក | ធុងទឹក | 1.0 | 80000.0 | 80000.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | ស្បៃនីឡុងសម្រាប់ព័ន្ធជុំវិញ | ដុំ | 3.0 | 58000.0 | 174000.0 | 100.0 |
| Other | ជួលដី | ឆ្នាំ | 1.0 | 300000.0 | 300000.0 | 100.0 |
| Other | ឫស្សី | ដើម | 20.0 | 4000.0 | 80000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 3412000.0 | |||||
If land user bore less than 100% of costs, indicate who covered the remaining costs:
គាត់ចំណាយទាំងអស់ទៅលើការបង្កើតនេះដោយការទិញសម្ភារមួយចំនួនជំពាក់អ្នកលក់ខ្លះ
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | ដកស្មៅ ជ្រោយដី និងដាក់ជី | Agronomic | ពេលដំណាំអាយុបានមួយសប្តាហ៍ |
| 2. | ស្រោចទឹក (ព្រឹក និងល្ងាច) | Agronomic | រាល់ថ្ងៃ |
| 3. | បាញ់ថ្នាំពុលធម្មជាតិសម្រាប់កម្ចាត់សត្វល្អិត | Agronomic | ពេលមានវត្តមានសត្វល្អិត |
| 4. | ប្រេងបូមទឹកទុកសម្រាប់ស្រោចដំណាំ (មួយខែអស់ប្រេងម៉ាស៊ូត ៣០ លីត្រ) | Agronomic | ពេលព្រឹក និងល្ងាច |
Comments:
គាត់បាញ់ថ្នាំសត្វល្អិតនៅពេលមានវត្តមានសត្វល្អិត និងប្រេងម៉ាស៊ូតសម្រាប់បូមទឹកមួយខែអស់ ៣០ លីត្រ។
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | ការដកស្មៅ (ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង) | នាក់-ថ្ងៃ | 4.0 | 17000.0 | 68000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | ជ្រោយដី និងដាក់ដី (ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង) | នាក់-ថ្ងៃ | 4.0 | 17000.0 | 68000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | បាញ់ថ្នាំ | នាក់-ថ្ងៃ | 12.0 | 17000.0 | 204000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | ធុងបាញ់ថ្នាំប្រើដោយដៃ | គ្រឿង | 1.0 | 80000.0 | 80000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | ប្រេងម៉ាស៊ូត | លីត្រ | 90.0 | 2350.0 | 211500.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 631500.0 | |||||
Comments:
ពេលទិញជំពាក់អ្នកលក់ខ្លះ អោយលុយខ្លះ
4.8 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
តម្លៃជី និងពូជដំណាំប្រែប្រួលអាស្រ័យលើទីផ្សារ និងប្រភេទគ្រាប់ពូជ
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specify average annual rainfall (if known), in mm:
1138.20
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងនៅឆ្នាំ ២០១៥ គឺ ១១៣៨,២ មម ឆ្នាំ ២០១៤ គឺ ១៦៩៦,៥ មម និងឆ្នាំ ២០១៣ គឺ ១៦៦១,៨ មម។
Indicate the name of the reference meteorological station considered:
នាយកដ្ឋានឧត្តុនិយមនៃក្រសួងធនធានទឹក និងឧត្តុនិយម ២០១៥
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- not relevant
Comments and further specifications on topography:
ជាដីជម្រាលនៅច្រាំងទន្លេមេគង្គ
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- high (>3%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
ដីមានកម្រិត pH = 5
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
5-50 m
Availability of surface water:
good
Water quality (untreated):
good drinking water
Is water salinity a problem?
Nee
Is flooding of the area occurring?
Ja
Regularity:
frequently
Comments and further specifications on water quality and quantity:
មានទឹកជំនន់រាល់ឆ្នាំព្រោះនៅជាប់ទន្លេ។
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- low
Habitat diversity:
- low
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- commercial/ market
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
- mechanized/ motorized
Gender:
- men
Age of land users:
- middle-aged
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
កសិករភេទប្រុសមានអាយុ 37 ឆ្នាំ
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- small-scale
Comments:
ដីផ្ទាល់ខ្លួន 1 ហិចតា ជួលដីគេនៅខែវស្សា 1000 ម៉ែត្រការ៉េ តម្លៃ 200000៛/ឆ្នាំ និងជួលដីមួយកន្លែងទៀតទំហំ 1080 ម៉ែត្រការ៉េ តម្លៃ 300000៛/ឆ្នាំ
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, titled
- ជួលគេ
Land use rights:
- leased
- individual
Water use rights:
- open access (unorganized)
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Comments/ specify:
កាលពីមុនដាំខ្ទឹមបារាំងតែមួយមុខ តែឥឡូវដាំបន្លែចម្រុះឆ្លាស់គ្នា។
crop quality
Comments/ specify:
កាលពីមុនកសិករប្រើថ្នាំពុលកសិកម្ម និងជីគីមី តែឥឡូវកសិករប្រើថ្នាំពុលធម្មជាតិ និងជីធម្មជាតិ។
risk of production failure
Comments/ specify:
កសិករបានដាំដំណាំច្រើនមុខហើយឆ្លាស់រងគ្នាដែលជាហេតុកាត់បន្ថយការបំផ្លាញពីសត្វល្អិត និងប្រើប្រាស់ថ្នាំពុលធម្មជាតិ។
product diversity
Comments/ specify:
កាលពីមុនកសិករដាំតែដំណាំមួយមុខគឺខ្ទឹមបារាំង ប៉ុន្តែឥឡូវកសិករដំណាំច្រើនមុខដូចជាស្ពៃក្រញាញ់ ស្ពៃចង្កឹះ ស្ពៃតឿ សាឡាដ ត្រកួន។
land management
Comments/ specify:
ដោយសារការដាំដំណាំច្រើនប្រភេទឆ្លាស់គ្នា និងវិលជុំធ្វើឱ្យការស្រូបជីជាតិពីដីក៏ខុសគ្នាដែរ និងប្រើប្រាស់ជីធម្មជាតិធ្វើឱ្យដីសម្បូរជីជាតិ។
Water availability and quality
irrigation water quality
Comments/ specify:
កាលពីមុនប្រើថ្នាំពុលកសិកម្មដើម្បីកំចាត់សត្វល្អិត តែក្រោយមកប្រើថ្នាំពុលធម្មជាតិដើម្បីការពារសត្វល្អិត។
Income and costs
expenses on agricultural inputs
Comments/ specify:
កាលពីមុនទិញថ្នាំពុលកសិកម្ម តែឥឡូវមិនទិញថ្នាំពុលកសិកម្មទេព្រោះកសិករចេះធ្វើថ្នាំពុលធម្មជាតិដោយខ្លួនឯង។
farm income
Comments/ specify:
ដោយកាត់បន្ថយការទិញ និងប្រើថ្នាំពុលកសិកម្ម និងជីគីមី ដោយត្រឡប់មកប្រើជីធម្មជាតិ និងថ្នាំពុលធម្មជាតិវិញ។
economic disparities
Comments/ specify:
ជីវភាពរបស់កសិករប្រសើរជាងមុនបន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តន៍បច្ចេកទេសនេះដោយសារគាត់ទទួលបានប្រាក់ចំណូលច្រើនដោយសារមានដំណាំច្រើនប្រភេទ និងពុំចាំបាច់ទិញថ្នាំពុលកសិកម្ម ព្រមទាំងទទួលបានសុខភាពល្អ។
workload
Comments/ specify:
បន្ទុកការងារកើនឡើងតិចតួចដោយសារឥលូវមានដាំដំណាំច្រើនជាងមុន។
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
Comments/ specify:
ចំពោះសន្តិសុខស្បៀងមានភាពល្អប្រសើរជាងមុនដោយសារកសិករអាចទទួលបានចំណូលប្រសើរឡើងព្រោះពីមុនគាត់ដាំដំណាំតែមួយមុខ តែឥឡូវប្តូរមកដាំដំណាំច្រើនមុខ។
health situation
Comments/ specify:
ដោយសារមិនប្រើប្រាស់ថ្នាំពុលកសិកម្មដែលមិនធ្វើឱ្យប៉ះពាល់ដល់សុខភាព។
SLM/ land degradation knowledge
Comments/ specify:
កសិករចេះផលិតថ្នាំពុលធម្មជាតិដោយខ្លួនឯង និងត្រឡប់មកប្រើប្រាស់ជីធម្មជាតិវិញ។
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
surface runoff
Comments/ specify:
ទឹកជំនន់ធ្វើឱ្យបាត់បង់ដីល្បាប់ និងកើនកករនៅខ្សែទឹកផ្នែកខាងក្រោមដោយសារការកាប់ជ្រោយដីច្រាំងទន្លេ។
excess water drainage
Comments/ specify:
រោងដាំដំណាំប្រក់សំណាញ់ និងធ្វើរងកាត់ទទឹងជម្រាលច្រាំងទន្លេ។
evaporation
Comments/ specify:
ដំណាំបានជួយរក្សាសំណើមដី និងការធ្វើរោងបណ្តោះអាសន្នកាត់បន្ថយ រំហួត ៦០%។
Soil
soil moisture
Comments/ specify:
ដំណាំអាចជួយរក្សាសំណើមដីបានល្អ។
soil compaction
Comments/ specify:
កសិករប្រើប្រាស់លាមកគោដែលទិញពីកសិករផ្សេងទៀត ឬដើររើសនៅតាមវាលស្រែ ចំណែកជីសរីរាង្គទិញពីក្រុមហ៊ុនលក់ជី។
nutrient cycling/ recharge
Comments/ specify:
ការដាំដំណាំច្រើនមុខ និងវិលជុំ ដែលដំណាំនីមួយៗស្រូបយកជីជាតិខុសៗគ្នាធ្វើឱ្យដីមានតុល្យភាព។
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
pest/ disease control
Comments/ specify:
កាត់បន្ថយបញ្ហាដង្កូវយោលទោង សត្វទៀគូរ និងមេអំបៅ។
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
downstream siltation
Comments/ specify:
នៅពេលកសិករភ្ជួរ និងរាស់ ឬជ្រោយដី ដីនៅស្រទាប់លើនឹងហូរច្រោះនៅពេលដែលមានភ្លៀងធ្លាក់។ ដើម្បីកាត់បន្ថយការហូរច្រោះដីស្រទាប់លើ កសិករបានសង់រោងប្រើដោយដើមឫស្សីប្រក់ស្បៃ និងធ្វើរងកាត់ទទឹងជម្រាល ដូចនេះកករដីដែលហូរទៅខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោយកើនឡើងតិចតួច។
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | Type of climatic change/ extreme | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | well | |
| seasonal temperature | wet/ rainy season | increase | well |
| annual rainfall | decrease | well | |
| seasonal rainfall | wet/ rainy season | decrease | well |
| other gradual climate change | ឆ្នាំនេះភ្លៀងញឹកញ៉ាប់តែឆ្នាំមុនមិនសូវភ្លៀងទេ | moderately |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| tropical storm | not well |
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| heatwave | moderately |
| extreme winter conditions | not well |
| drought | well |
Hydrological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| general (river) flood | moderately |
| flash flood | moderately |
Biological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| epidemic diseases | not well |
| insect/ worm infestation | well |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly positive
Long-term returns:
positive
Comments:
សម្រាប់រយៈពេលខ្លី កសិករចំណាយលុយច្រើនទិញជីធម្មជាតិ ឬជីសរីរាង្គពីព្រោះនៅពេលចាប់ផ្តើមដំបូងដីមិនសូវសម្បូរជីជាតិ ប៉ុន្តែបន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសយូរទៅកសិករមិនចំបាច់ចំណាយលុយច្រើនសម្រាប់ទិញជីធម្មជាតិ ឬជីសរីរាង្គ។
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- single cases/ experimental
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 90-100%
Comments:
នៅក្នុងភូមិអនុវត្តការដាំដំណាំបែបនេះមានតែគាត់ម្នាក់ទេ។
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
Ja
If yes, indicate to which changing conditions it was adapted:
- changing markets
Specify adaptation of the Technology (design, material/ species, etc.):
កសិករដាំដំណាំទៅតាមតម្រូវការរបស់ទីផ្សារ ឧទាហរណ៍៖ទីផ្សាររបស់ឡាដនៅរដូវប្រាំង ជាពិសេសនៅខែមីនា និងខែមេសា សាឡាដមានតម្លៃខ្ពស់ គឺមួយគីឡូអាចមានតម្លៃចន្លោះពី ៤០០០រៀល ទៅ ៥០០០រៀល។
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| មានចំណូលខ្ពស់ |
| ការពារដីកុំឱ្យហាប់ដោយប្រើប្រាស់ជីលាមកគោ និងជីសរីរាង្គ ព្រមទាំងកាត់បន្ថយកម្តៅដោយប្រើរោងបណ្តោះអាសន្ន។ |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| ជួយបង្កើនប្រាក់ចំណូលប្រចាំថ្ងៃ។ |
| កាត់បន្ថយការប្រើប្រាស់ជី និងថ្នាំពុលគីមី។ |
| ជួយបង្កើនគុណភាពដី។ |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| ជួបដង្កូវយោលទោង និងទៀគូរ។ | បាញ់ថ្នាំគីមីនៅតែមិនបាត់ ដូចនេះពួកគាត់ប្តូរប្រភេទដំណាំ និងប្រើថ្នាំសម្លាប់សត្វល្អិតធម្មជាតិដែលជួយកំចាត់ដង្កូវយោលទោង និងទៀគូរ។ |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| ជួបបញ្ហាសត្វល្អិតបំផ្លាញ (ដង្កូវយោលទោង និងទៀគូរ)។ | ប្រើប្រាស់ថ្នាំពុលធម្មជាតិធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង និងដាំដំណាំឆ្លាស់មុខគ្នា។ |
| ការកាប់ដីជ្រោយដីច្រាំងទន្លេធ្វើឱ្យបាត់បង់ដីល្បាប់ និងបង្កើនកករល្អក់នៅខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោមនៅពេលទឹកជន់។ | កាត់បន្ថយការកាប់ដី ការជ្រោយដីមុនពេលទឹកជំនន់។ |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
ចំនួន ១ កន្លែង
- interviews with land users
ចំនួន ១ នាក់
- interviews with SLM specialists/ experts
ចំនួន ៣ នាក់
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
DanChurchAid/Christian Aid. (2015). Farmer book: Kit of best Agriculture Technologies to Adapt with climate change. Phnom Penh: Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Finsheries. (in Khmer)
Available from where? Costs?
Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Finsheries
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Pawan K. et al., (2012).Manual on cropping system and sustainable agriculture:Department of Agronomy CCS Haryana Agricultural University Hisar-125004
Available from where? Costs?
Department of Agronomy CCS Haryana Agricultural University Hisar-125004
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Yang S. et al.,(2008). Kit of botanical pesticide.CEDAC. (in Khmer)
Available from where? Costs?
The Cambodian Center for Study and Development in Agriculture
7.3 Links to relevant information which is available online
Title/ description:
Chan M. (2015). VOA program: Cambodian Farmers Prosper by Going Organic. Retrieved on 15/01/2018 from
URL:
www.voacambodia.com/a/cambodian-farmes-prosper-by-going-organic/2993415.html
Title/ description:
AGRISUD CAMBODGE (2017).Crop production. Retrieve on 20/12/2017 from
URL:
https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B3kkBprEzhDoX3NuYjI0X1FoSVU/edit
Title/ description:
Deen B. (2016). Intercropping: Principle and Types. Retrieve on 20/12/2017 from
URL:
http://www.agrihortieducation.com/2016/09/intercropping-principles-and-types.html#more
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules