Фитопестициды. [Tajikistan]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Rustam Kalandarov
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Биопестициды
technologies_1064 - Tajikistan
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
SLM specialist:
Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Youth Ecological Center, Tajikistan (Youth Ecological Center, Tajikistan) - TajikistanName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Switzerland1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
05/05/2011
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
Использование фитопестицидов, не наносящих ущерба окружающей среде, и сделанных иp вытяжки растений для поддержки в борьбе с вредителями и болезнями.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
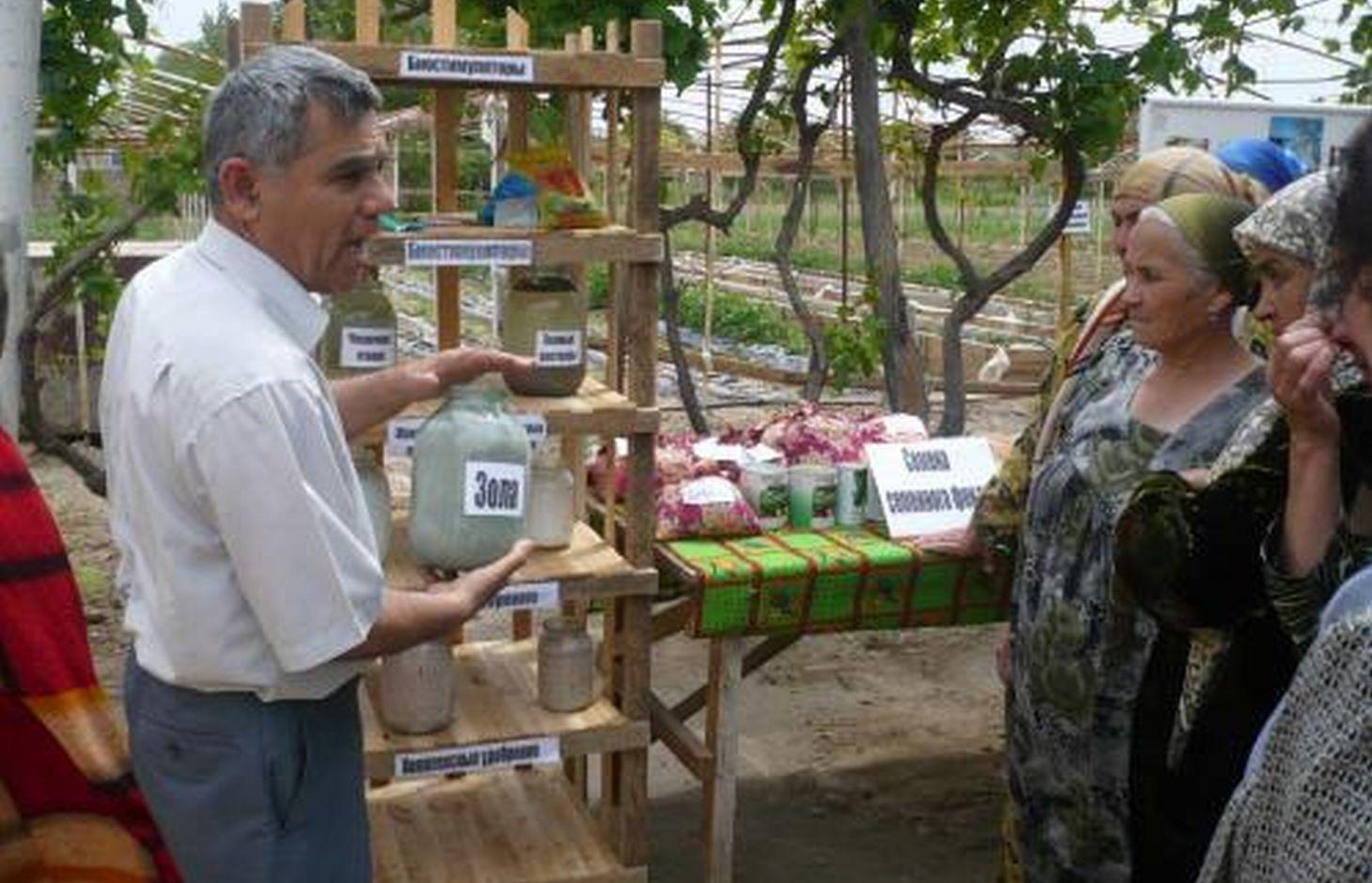
Фитопестициды в основном сделаны из растений, включая: плодоножки картофеля, лука или томата, а также вытяжки из чеснока, перца, одуванчика, полыни горькой и дурмана. Другие биологические пестициды могут быть произведены из золы или мыла. Фитопестициды можно хранить до года.
Назначение технологии: Основная цель фитопестицидов – это помощь в борьбе с вредителями и болезнями с использованием естественного метода, не наносящего ущерба окружающей среде, и без использования химических пестицидов. Они не влияют на окружающую флору и фауну и сохраняют биологические организмы в почве.
Основные действия и вложения: Это легко используемая и не дорогая технология, которая в основном требует сбор и просушку части растений для создания пестицидов.
Природная\социальная обстановка: Технология может использоваться при любой среде в период роста. Технология в настоящий момент используется в засушливой зоне южного Таджикистана, в дехканских хозяйствах и других участках.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Tajikistan
Region/ State/ Province:
Таджикистан
Further specification of location:
Хатлонская область. Н.Хусравский район.
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- more than 50 years ago (traditional)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
- Традиционный
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- conserve ecosystem
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping

Mixed (crops/ grazing/ trees), incl. agroforestry
Comments:
Основные проблемы землепользования (по мнению составителя): Данная технология позволяет избегать использование химических пестицидов. Фитопестициды не уничтожают органический материал почвы, фактически, они обогащают почву и не наносят вреда окружающей среде
Основные проблемы землепользования (по мнению землепользователя): также
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- mixed rainfed-irrigated
Comments:
Водопотребление: богарное, смешанное богарно-орошаемое, полностью орошаемое, полностью орошаемое
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Specify:
в течение вегетационного периода
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- integrated soil fertility management
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A1: Vegetation/ soil cover
Comments:
Основные мероприятия: агрономические
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

biological degradation
- Bp: increase of pests/ diseases, loss of predators
Comments:
Основные типы деградации: Бб (Bp): увеличение вредителей / заболеваний, потеря хищников
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- reduce land degradation
- restore/ rehabilitate severely degraded land
Comments:
Основная цель: реабилитация / восстановление голых земель, предотвращение / сокращение деградации
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
Необходимые технические навыки для работников: средний
Необходимые технические навыки для землепользователей: средний
Основные технические функции: сохранение биогумуса в почвенном составе, обогащение микроорганизм почвы, уменьшение вредителей
Агрономические мероприятия: Фитопестициды
Материал: картофель, лук, помидор, чеснок, перец, одуванчик, полынь, шип яблоки
Мероприятия, связанные с использованием растительности: сохранение микроорганики в почве
Растительный материал: Д: деревья / кустарники, Ф: фруктовые деревья / кустарники, К: многолетние культуры, Т: трава, Др: другие
Мероприятия, связанные с использованием растительности: Растительный материал: Д: деревья / кустарники, Ф: фруктовые деревья / кустарники, К: многолетние культуры, Т: трава, Др: другие
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify currency used for cost calculations:
- US Dollars
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Производство пестицидов | Vegetative | 3 часа |
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Оплата труда | - | 100.0 | 0.03 | 3.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 3.0 | |||||
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Подготовка материала | Agronomic | 1 чел / день |
| 2. | распыление | Vegetative | 1чел / день |
| 3. | покупка распылителя | Vegetative | 1 |
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | None | None | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | None | None | 100.0 | 0.03 | 3.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | None | None | 2.0 | 25.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 54.0 | |||||
4.8 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
Затраты только на покупку распылителя
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- arid
Термический класс климата: субтропики
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Topsoil organic matter:
- low (<1%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
< 5 m
Water quality (untreated):
good drinking water
Comments and further specifications on water quality and quantity:
Доступность поверхностной влаги: хорошая, средняя
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- medium
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Market orientation of production system:
- subsistence (self-supply)
Off-farm income:
- > 50% of all income
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
- mechanized/ motorized
Gender:
- women
- men
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Землепользователи, применяющие данную технологию, в основном среднестатистические
Плотность населения: 50-100 человек/км2
Годовой прирост населения: 2% - 3%
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- medium-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- group
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- open access (unorganized)
Water use rights:
- open access (unorganized)
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
product diversity
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
health situation
Ecological impacts
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
habitat diversity
pest/ disease control
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | Type of climatic change/ extreme | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | well |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| local rainstorm | well |
| local windstorm | well |
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| drought | well |
Hydrological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| general (river) flood | well |
Other climate-related consequences
Other climate-related consequences
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| reduced growing period | not known |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
very positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
very positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- more than 50%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 50-90%
Comments:
40 % семей землепользователей применяют эту технологию с дополнительной материальной поддержкой
60% семей землепользователей применяют эту технологию без дополнительной материальной поддержки
40 семей землепользователей применяют эту технологию без дополнительной материальной поддержки
Существует устойчивая тенденция к добровольному внедрению технологии
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| Технология приемлема |
|
Технология не наносит ущерба окружающей среды Как можно сохранять устойчивость или усилить? Технология заменяет химические пестициды на те, которые не наносят ущерба окружающей среде |
|
Не дорого Как можно сохранять устойчивость или усилить? Фитопестициды можно произвести в любое время |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Фитопестициды эффективны только лишь на две недели | Пестициды можно подготовить, и использовать в любое время |
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules