ການປູກຜັກສວນຄົວ ຢູ່ດິນຄ້ອຍຊັນ [Lao People's Democratic Republic]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Khampheng Bounpanya
- Editors: Bounthanom Bouahom, kang phanvongsa, anousit namsena
- Reviewers: Nivong Sipaseuth, Stephanie Jaquet, Nicole Harari
technologies_3139 - Lao People's Democratic Republic
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
land user:
Lao People's Democratic Republic
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
National Agriculture and Forestry Research Institute (NAFRI) - Lao People's Democratic Republic1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
28/08/2017
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
Nee
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
ເຕັກນີກ ການເຮັດຫນານຜັກ ຢູ່ດິນຄ້ອຍຊັນ ເປັນເຕັກນິກນຶ່ງ ທ່ີຊາວກະສິກອນ ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ມາເປັນເວລາ ດົນນານ. ອີງຕາມປັດໃຈ ທາງດ້ານລັກສະນະ ພູມສັນຖານ ຂອງທ້ອງຖີ່ນ ທ່ີເປັນເຂດຄ້ອຍຊັນ ຊື່ງເປັນຂ້ໍຈໍາກັດ ໃຫ້ການຜະລິດ ກະສິກໍາ ເປັນຕົ້ນ ແມ່ນກິດຈະກໍາ ປູກຜັກສວນຄົວ ຂອງປະຊາຊົນ ທ້ອງຖ່ີນ.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
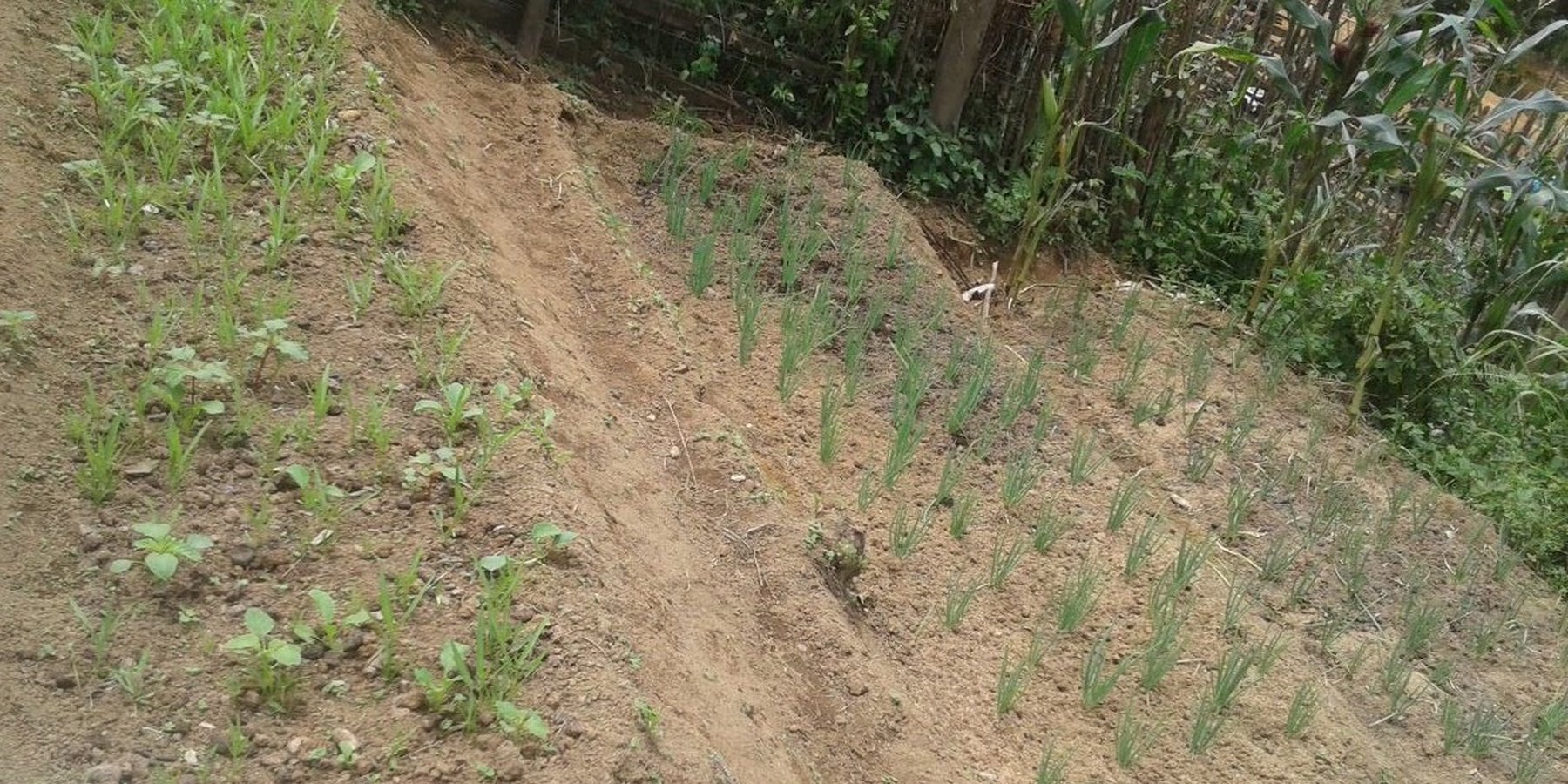
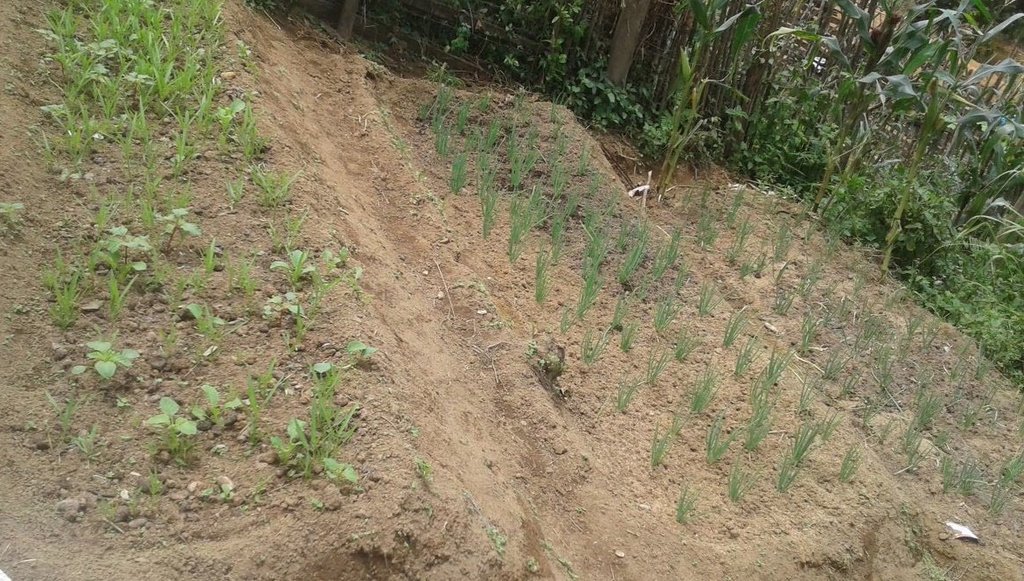
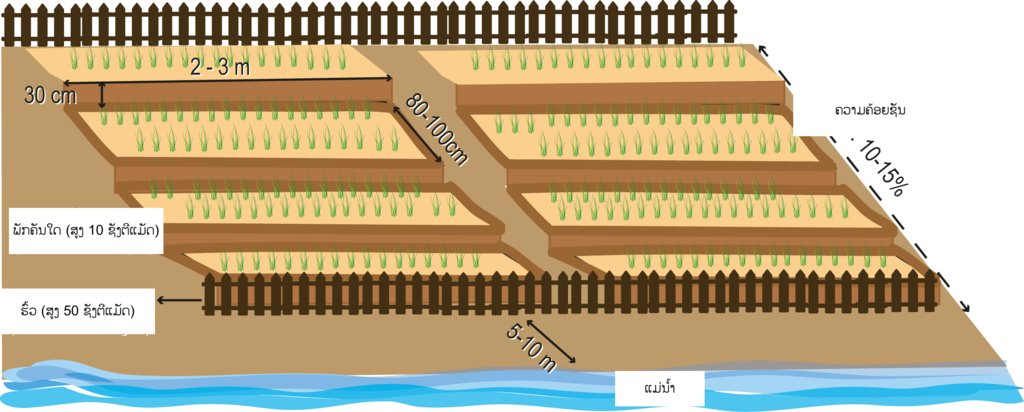
ໂດຍສ່ວນໃຫຍ່ ປະຊາຊົນ ທອ້ງຖ່ີນ ປູກຜັກ ໃສ່ໄຮ່ເຂົ້າ ແລະ ປູກໃສ່ສວນຄົວ. ນອກຈາກນ້ີ, ພວກເຂົາກໍ່ປູກ ລຽບຕາມແມ່ນໍາ້ ໃນລະດູແລ້ງ. ສຳລັບ ຊາວກະສິກອນ ທີອາໃສ ຢູ່ເຂດພູດອຍ ຈະປູກຜັກ ໃນຊ່ວງລະດູຝົນ ເປັນສວນໄຫຍ່ ແລະ ປູກໃນລະດູແລ້ງ ສໍາລັບ ຜູ້ທີ່ມີເງ່ືອນໄຂ ຢູ່ໃກ້ແຄມຫ້ວຍ. ການປູກຜັກ ໃນພື້ນທ່ີດິນຄອ້ຍຊັນ ຈະມີຂໍ້ຈຳກັດ ກ່ຽວກັບ ຄວາມຊັນຂອງດິນ (ດິນບໍ່ຮາບພຽງ) ແລະ ການສະຫນອງນໍາ້. ການປູກຜັກ ຂອງຊາວກະສິກອນ ໃນເມືອງດາກຈຶງ ໃສ່ພື້ນທ່ີ ດິນຄອ້ຍຊັນ ເປັນພັກຄັນໃດ ແມ່ນເຄີຍໄດ້ປະຕິບັດມາ ເປັນເວລາດົນນານແລ້ວ. ເຖິງຢ່າງໃດກໍ່ຕາມ, ການປຸກຜັກ ຢູ່ດິນຄອ້ຍຊັນ (ສະເລ່ຍ ຄວາມຄອ້ຍຊັນ 11-15%) ມີຄວາມສ່ຽງຫຼາຍ ແລະ ເປັນຂໍ້ຈຳກັດ. ດັ່ງທ່ີກ່າວມານັ້ນ ຊາວກະສິກອນ ຈ່ຶງໄດ້ປະດິດສ້າງ (ໃຊພູມປັນຍາ ຂອງຊາວບາ້ນ) ປູກຜັກ ໃນພື້ນທ່ີ ດິນຄອ້ຍຊັນ ເພື່ອບໍລິໂພກ ແລະ ຂາຍຕະຫຼອດປີ. ຜັກ ທ່ີຊາວກະສິກອນ ປູກສ່ວນຫຼາຍ ແມ່ນຜັກ ຫອມປ້ອມ, ຜັກບົ້ງ, ຜັກກາດຂາວ, ຜັກກາດດອກ ແລະ ຜັກ ກາດຕີນໝີ. ໃນປີ 2000, ຊາວກະສິກອນ ໄດ້ຂະຫຍາຍພື້ນທີ ການປູກຜັກ ໃນພື້ນທ່ີ ດິນຄ້ອຍຊັນ ໂດຍນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກນິກການຂຸດ ເປັນພັກດິນ. ເຕັກນິກ ແລະ ວິທີ ການກຽມພື້ນທ່ີ ແມ່ນເລ່ີມຈາກການຄັດເລືອກ ພື້ນທ່ີດິນ ທ່ີຢູ່ລຽບຕາມຫ້ວຍ (ຫ່າງຈາກຫ້ວຍ ຫາ ຫນານຜັກ ປະມານ 5-10 ແມັດ). ກ່ອນອ່ືນຫມົດ ກ່ໍຈະເສຍຫຍາ້ ອອກໃຫ້ກຽ້ງ ລະອຽດດີ ຫັຼງຈາກນັ້ນ ເປັນການຂຸດດິນ ຈາກດິນສ່ວນທາງເທິງ ຂອງຫນ້າດິນ ທ່ີສູງກວ່າ ມາຖົມດິນ ຢູ່ສ່ວນລຸ່ມ ທ່ີຕ່ໍາກ່ວາ ເພື່ອປັບໃຫ້ຫນ້າດີນ ໃຫ້ພຽງ ສະຫມໍ່າສະເຫມີກັນ ຊ່ຶງໃຊ້ເວລາດົນ (ປະມານ 3 ຫືຼ 4 ອາທິດ) ໃນການຂຸດຫນານປູກຜັກ, ໃຊ້ແຮງງານ ປະມານ 2-3 ຄົນ ຊ່ຶງເປັນແຮງງານ ພາຍໃນຄອບຄົວ. ເຕັກນິກ ວິທີການຂຸດ ປັບພື້ືນທ່ີ ຢູ່ເຂດຄອ້ຍຊັນ ມີຂໍ້ຈຳກັດຄື: ຫນ້າດິນສ່ວນເທິງ ກ່ໍຄືຊັ້ນດິນທໍາອິດ ຈະຖືກຕັດອອກໄປ ເຫືຼອແຕ່ດິນຊັ້ນລຸ່ມ ທ່ີມີຄວາມອຸດົມສົມບູນ, ທາດອາຫານ ໃນດິນ ຈະຕ່ຳ ຊື່ງສົ່ງຜົນ ເຮັດໃຫ້ ການຈະເລີນເຕີບໂຕ ຂອງພືດຜັກ ໃນໄລຍະປູກຜັກ ທຳອີດ ບໍ່ງາມເທົ່າທີ່ຄວນ. ສ່ວນໜ້າດິນ ທ່ີຖືກຕັດອອກໄປ ຈະຖືກນໍາເອົາໄປຖົມ ໃນສ່ວນຂອງດິນຊັ້ນລຸ່ມ ເພື່ອປັບເປັນຄັນນາ ຫືຼ ເປັນພັກ ເປັນຊັ້ນ ທ່ີຄາ້ຍຄື ກັບຄັນໃດ. ຈ່ືງເຮັດໃຫ້ຜັກທ່ີປູກ ໃນພື້ນທ່ີ ສ່ວນລຸ່ມ ຈະເລີນເຕີບໂຕໄດດີ ກວ່າຫນານປູກຜັກຊັ້ນເທິງ ຍອ້ນວ່າຫນ້າດິນຊັ້ນເທິງ ມີທາດອານຫານ ແລະ ອີນຊີວັດຖຸຫຼາຍກວ່າ ການແກ້ບັນຫາຂອງຊາວກະສິກອນ ໃນເບ້ືອງຕົ້ນ ແມ່ນສາມາດ ຂຸດເອົາດິນຊັ້ນເທິງ ຂອງຫນານປູກຜັກ ທ່ີຢູ່ເທິງ ຂ້ືນໄປໃສ່ແປງຜັກ ທ່ີຢູ່ດ້ານລຸ່ມ ປັບລະດັບ ໃຫ້ສະຫມ່ໍາສະເຫມີ. ໂດຍສະເລ່ຍ ເນ້ືອທ່ີ ໃນການເຮັດຫນານຜັກ ປະມານ 0,01 ເຮັກຕາ (ປະມານ 7-8 ຫນານ/ຄອບຄົວ), ແຕ່ລະຫນານ ມີຄວາມກວ້າງ ປະມານ 60-80 ຊັງຕີ ແມັດ, ຍາວ 2-3 ແມັດ, ຄວາມເລິກ ລະຫວ່າງ ພັກຊັ້ນລຸ່ມ ຫາຊັ້ນເທິງ ປະມານ 30 ຊັງຕີແມັດ. ຫ້ັຼງຈາກ ການປັບລະດັບ ຫນ້າດິນແລ້ວ ຊາວກະສິກອນ ກ່ໍຈະຂຸດດິນ ເປັນຫນານ ຕາກແດດ ປະມານ 5-7 ມື້ ແລ້ວກໍ່ແປງຫນານປູກຜັກ ເອົາໄມ້ກົມ ຫືຼ ໄມ້ ສີແປດ ທຸບດິນໃຫ້ຫມຸ່ນ ແລະ ເອົາຄາດ ມາຄາດດີນ ເພື່ອປັບໜ້າດິນ ໃຫ້ພຽງ ສະຫມ່ໍາສະເຫມີກັນ ແລ້ວກ່ໍໃຊໄມ້ແປ້ນ ມາຂັ້ນເປັນພັກ ເພື່ອປ້ອງກັນ ບ່ໍໃຫ້ດິນເຈ່ືອນ (ສູງປະມານ 10 ຊັງຕີແມັດ). ກ່ອນການປູກຜັກ ແມ່ນຕ້ອງໄດ້ມີ ການລອ້ມຮົ້ວ ເພື່ອປ້ອງກັນສັດບຸກລຸກເຂົ້າ ໄປສວນຜັກ. ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ ທ່ີຊາວກະສິກອນ ໄດ້ຮັບຈາກເຕັກນິກດັ່ງກ່າວ ແມ່ນສາມາດ ປຸກຜັກແຄມນໍາ້ໄດ້ ແລະ ມີຜັກໄວ້ກິນ ພາຍໃນຄອບຄົວ. ພອ້ມທັງ ເປັນການນໍາໃຊ້ ທ່ີດິນຄອ້ຍຊັນ ໃຫ້ເກິດປະໂຫຍດ ທັງເປັນການປ້ອງກັນ ດິນແຄມນໍາ້ ເຊາະເຈ່ຶອນ. ເຖິງຢ່າງໃດກໍ່ຕາມ, ການເຮັດເຕັກນິກດັ່ງກ່າວ ກໍ່ມີອຸປະສັກ ເປັນຕົ້ນ ແມ່ນການກະກຽມພື້ນທ່ີ ເພາະເປັນພື້ນທ່ີ ເນີນສູງ, ຍາກໃນການປັບຫນ້້າດິນ ເພື່ອໃຫ້ດິນພຽງສະຫມ່ໍາສະເຫມີ ໂດຍສະເພາະ ການຂຸດດິນ ຈາກເປ້ີນເທິງລົງມາລຸ່ມ, ຂຸດດິນ ເປັນຊັ້ນໆ, ເປັນພັກຄາ້ຍຄືຄັນໃດ.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Lao People's Democratic Republic
Region/ State/ Province:
ແຂວງເຊກອງ
Further specification of location:
ເມືອງດາກຈຶງ
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- 10-50 years ago
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- as part of a traditional system (> 50 years)
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
Main crops (cash and food crops):
ປູກຜັກກາດ ແລະ ກາລຳປີ
3.3 Further information about land use
other (e.g. post-flooding):
- ນ້ຳຈາກຫ້ວຍ
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 3
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- improved ground/ vegetation cover
- cross-slope measure
- home gardens
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A1: Vegetation/ soil cover

structural measures
- S1: Terraces
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion
- Wg: gully erosion/ gullying

biological degradation
- Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
ສະເລ່ຍ ຄວາມຄອ້ຍຊັນ ປະມານ 10-15% ໃນການເຮັດ ເຕັກນິກ ປູກຜັກ ເຂດຄ້ອຍຊັນ, ໄລຍະຫ່າງ ຈາກແຄມຫ້ວຍ ຫາ ພື້ນທ່ີຫນານປູກຜັກ ປະມານ 5 ແມັດ, ຄວາມກວ້າງ ຂອງຫນານຜັກ ປະມານ 60-80 ຊັງຕີແມັດ, ຄວາມຍາວ ປະມານ 2-3 ແມັດ ແລະ ຄວາມເລິກ ລະຫວ່າງພັກຊັ້ນເທິງ ປະມານ 30 ຊັງຕີແມັດ. ການລອ້ມຮົ້ວ ສວນປູກຜັກ ແມ່ນມີຄວາມຈໍາເປັນຫຼາຍ ທີ່ຕອ້ງໄດ້ເຮັດ ເນ່ືອງຈາກເປັນການປ້ອງກັນ ສັດລຽ້ງ (ງົວ ແລະ ແບ້) ເຂົ້າໄປທໍາລາຍຜົນຜະລິດ.
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology area
Indicate size and area unit:
200 ແມັດກະເລ້
If using a local area unit, indicate conversion factor to one hectare:
0,02 ເຮັກຕາ
other/ national currency (specify):
ກີບ
Indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (if relevant): 1 USD =:
8000.0
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
30000
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | ການກະກຽມດິນ (ຂຸດ ແລະ ປັບໜ້າດິນ) | Management | ກ່ອນລະດູຝົນ |
| 2. | ການລ້ອມຮົ້ວ | Structural | ກ່ອນປູກຜັກ |
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | ແຮງານ ກະກຽມດິນ ແລະ ປັບໜ້າດິນ | ວັນງານ | 21.0 | 30000.0 | 630000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | ແຮງງານ ລ້ອມຮົ້ວ | ວັນງານ | 4.0 | 30000.0 | 120000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | ຈົກ | ດວງ | 2.0 | 100000.0 | 200000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | ຊວານ | ດວງ | 2.0 | 100000.0 | 200000.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | ເຫຼັກຕະປູ | None | 2.0 | 10000.0 | 20000.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | ໜາມໝາກຈັບ | None | 2.0 | 60000.0 | 120000.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | ເສົາຫຼັກຮົ້ວ | None | 80.0 | 5000.0 | 400000.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | ໄມ້ແປ້ນ | None | 20.0 | 5000.0 | 100000.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | ໄມ້ໃຜ່ | None | 300.0 | 2000.0 | 600000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 2390000.0 | |||||
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | ການປັບຄັນຄູ | Structural | ພາຍຫຼັງ ເກັບກ່ຽວ |
| 2. | ປູກຜັກ | Agronomic | ພາຍຫຼັງ ສຳເລັດ ການກະກຽມດິນ |
| 3. | ເສຍຫຍ້າ | Management | ເປັນປະຈຳ |
| 4. | ໃສ່ຝຸ່ນຄອກ | Management | ເປັນປະຈຳ |
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | ແຮງງານ ໃນການປັບດິນ ໜານຜັກ | ວັນງານ | 4.0 | 30000.0 | 120000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | ແຮງງານ ເສຍຫຍ້າ | ວັນງານ | 3.0 | 30000.0 | 90000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | ແຮງງານ ໃສ່ຝຸ່ນຄອກ | ວັນງານ | 1.0 | 30000.0 | 30000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | ແຮງງານ ປູກຜັກ | ວັນງານ | 3.0 | 30000.0 | 90000.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | ແນວພັນຜັກ/ແກ່ນຜັກ | ຸຖົງ | 4.0 | 5000.0 | 20000.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | ຝຸ່ນຄອກ | ກິໂລ | 30.0 | 5000.0 | 150000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 500000.0 | |||||
4.8 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
ແຮງງານ ໃນການປັບຫນ້າດິນ ແມ່ນສົ່ງຜົນ ຕ່ໍຕົ້ນທືນ ໃນການເຮັດເຕັກນິກນ້ີ ເພາະຕອ້ງໄດ້ໃຊ້ ເວລາປະມານ 3-4 ອາທິດ ຈ່ຶງສໍາເລັດ.
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Indicate the name of the reference meteorological station considered:
ຫ້ອງການ ອຸຕຸນິຍົມ ເມືອງດາກຈຶງ
Agro-climatic zone
- humid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- convex situations
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- coarse/ light (sandy)
- medium (loamy, silty)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
< 5 m
Availability of surface water:
good
Water quality (untreated):
for agricultural use only (irrigation)
Is water salinity a problem?
Nee
Is flooding of the area occurring?
Nee
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- medium
Habitat diversity:
- medium
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
Gender:
- women
Age of land users:
- youth
- middle-aged
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- small-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- open access (unorganized)
Water use rights:
- open access (unorganized)
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Comments/ specify:
ເພີ່ມຜົນຜະລິດສູງຂຶ້ນ
risk of production failure
Comments/ specify:
ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກບັນຫາ ນ້ຳຖ້ວມ ເນື່ອງຈາກຢູ່ພື້ນທີ່ສູງ ເມື່ອສົມທຽບ ໃສ່ບ່ອນ ທີ່ເຮັດສວນຜັກ ແຄມນານ້ຳຢູ່ ພື້ນທີ່ຕ່ຳ.
product diversity
Comments/ specify:
ຊາວກະສິກອນ ສາມາດ ເພີ່ມຜົນຜະລິດ ແລະ ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ຂອງຜັກ ໃນສວນຄົວ ເນື່ອງຈາກ ພື້ນທີ່ປູກຜັກ ເພີ່ມຂຶ້ນ.
production area
Quantity before SLM:
0.02 ເຮັກຕາ
Quantity after SLM:
0.04 ເຮັກຕາ
land management
Comments/ specify:
ຊາວກະສິກອນ ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ຄ້ອຍຊັນ ຢູ່ລຽບຕາມຫ້ວຍໃກ້ບ້ານ ໂດຍການປັບໜ້າດິນ ເຮັດເປັນພັກຄັນໃດ ເພື່ອປູກຜັກສວນຄົວ ຊຶ່ງເປັນວິທີ ທີ່ງ່າຍດາຍ ແລະ ເປັນພື້ນຖານ ສົມທຽບກັບ ເມື່ອກ່ອນ ປະຊາຊົນ ແມ່ນເຂົ້າປ່າ ທີ່ໃກຈາກບ້ານ ເພື່ອໄປເກັບຜັກປ່າມາກິນ.
Income and costs
farm income
Comments/ specify:
ໃນເມື່ອກ່ອນ ຊາວກະສິກອນ ປູກຜັກໄວ້ກິນ ພາຍໃນຄອບຄົວ ແຕ່ປະຈຸບັນ ມີຜັກຫຼາຍ ສາມາດ ຂາຍເປັນສິນຄ້າ.
diversity of income sources
Comments/ specify:
ການປູກຜັກ ເປັນອີກທາງເລືອກໜື່ງ ທີ່ເຮັດໃຫ້ ຊາວກະສິກອນ ສາມາດ ເພີ່ມແຫຼ່ງລາຍຮັບໄດ້ເປັນຢ່າງດີ.
workload
Comments/ specify:
ສາມາດ ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ວຽກແມ່ຍິງ ໃນການໄປຊອກເກັບຜັກຢູ່ປ່າ ແລະ ຢູ່ໄຮ່ ມາກິນ ພາຍໃນຄອບຄົວ.
Socio-cultural impacts
situation of socially and economically disadvantaged groups
Comments/ specify:
ເປັນກິດຈະກຳ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນດີ ໃຫ້ແກ່ແມ່ຍິງ ເນື່ອງຈາກສາມາດ ຊ່ວຍຫຼຸດຜ່ອນວຽກ ແລະ ປະຢັດເວລາ ໃນການໄປຊອກຫາ ຜັກຢູ່ປ່າ ແລະ ຢູ່ໄຮ່ ມາກິນ ພາຍໃນຄອບຄົວ.
Ecological impacts
Soil
soil loss
Comments/ specify:
ສາມາດ ປ້ອງກັນ ດິນແຄມຫ້ວຍ ເຊາະເຈ່ືອນ ໃນເວລາ ທີ່ຝົນຕົກແຮງ.
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
Vegetation cover
Comments/ specify:
ເພິ່ມເນື້ອທີ່ປູກຜັກ ໃສ່ດິນຄ້ອຍຊັນ ໃຫເກີດປະໂຫຍດ ເນື່ອງຈາກໃນເມື່ອກ່ອນ ເຄີຍເປັນປ່າຫຍ້າຮົກເຮື້ອ.
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
buffering/ filtering capacity
Comments/ specify:
ຫຸຼດຜ່ອນ ບັນຫາ ການຕົກຕະກອນ ຈາກການເຊາະໄຫຼຂອງນໍາ້ ພອ້ມດຽວກັນນັ້ນ ກ່ໍປັບປຸງພືດພັນ ຢູ່ຫນ້າດິນ ໃຫ້ມີຄວາມອຸດົມສົມບູນ ຢູ່ເຂດຄອ້ຍຊັນ.
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
neutral/ balanced
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
neutral/ balanced
Long-term returns:
positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- 10-50%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 90-100%
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
Nee
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| ນໍາ້ ບ່ໍຖ້ວມ ພື້ນທ່ີ ການຜະລິດ ເນື່ອງຈາກປູກຜັກຢູ່ພື້ນທີ່ສູງ ເມ່ືອທຽບໃສ່ ພື້ນທ່ີ ປູກຜັກ ແຄມນໍາ້ ຢູ່ພື້ນທ່ີຕ່ຳ. |
| ກິດຈະກໍາ ປູກພືດຜັກ ສວນຄົວ ສາມາດ ສ້າງລາຍຮັບ ໃຫ້ຄອບຄົວ ແລະ ທັງປະກອບສ່ວນ ເປັນອາຫານ ໃຫ້ແກ່ ຄອບຄົວ. |
| ເປັນກິດຈະກໍາ ທ່ີສົ່ງຜົນດີ ແລະ ເປັນປະໂຫຍດ ໃຫ້ແກ່ແມ່ຍິງ ພາຍໃນຊຸມຊົນ ທີ່ສາມາດ ປະກອບສ່ວນ ໄດ້ເປັນຢ່າງດີ. |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| ກິດຈະກໍາ ປູກຜັກ ສວນຄົວ ແມ່ນຕອ້ງໄດ້ ເອົາໃຈໃສ່ ໃນການໃສ່ຝຸນ ຫຼາຍຄັ້ງ ເພື່ືອຍົກສະມັດຕະພາບ ຜົນຜະລິດ ໃຫ້ສູງຂື້ນ. | ຊອກຫາໄມ້ ມາເຮັດຂັ້ນໃຫ້ສູງ ຫືຼ ປ້ານຄັນຄູ ໃຫ້ສູງຂ້ຶນ ເພື່ອສາມາດ ຮອງຮັບ ຝຸ່ນທ່ີໃສ່ ໃນແຕ່ລະຄັ້ງ. |
| ສ້ີນເປືອງ ເວລາ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ແລະ ບົວລະບັດ ຮັກສາຕົ້ນ ເປັນຕົ້ນແມ່ນ ກິດຈະກໍາປັບດິນ, ແປງຫນານ, ໃສ່ຝຸນ, ລອ້ມຮົ້ວ ເພື່ອປ້ອງກັນສັດລຽ້ງ. | ຕອ້ງໄດ້ ເອົາໃຈໃສ່ ໃນການບົວລະບັດ ໃຊ້ວັດສະດຸ ທ່ີແຫນ້ນຫນາ ເພື່ືຶອສາມາດ ຮັບປະກັນ ບໍ່ໃຫ້ຮົ້ວເປເພໄວ. |
| ພື້ນທ່ີ ທ່ີເຫມາະສົມ ໃນການເຮັດເຕັກນິກ ແມ່ນມີຈຳກັດ ເນ່ືອງຈາກ ລັກສະນະ ພູມສັນຖານ ແມ່ນເປັນເຂດຄອ້ຍຊັນ. |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| ວິທີການ ໃນການຄັດເລືອກພື້ນທ່ີ ທີ່ມີຄວາມເໝາະສົມ ໃນການເຮັດເຕັກນີກນີ້ ແມ່ນເປັນສິ່ງທ້າທາຍ. | ການເຮັດ ເຕັກນີກນ້ີ ຕອ້ງເລືອກພື້ນທ່ີ ທ່ີມີຄວາມຄອ້ຍຊັນ ຕໍາ່ກວ່າ 15% ແລະ ຕອ້ງຂຸດ ຫ່າງຈາກຫ້ວຍ ໃກກ່ອນ 5 ແມັດ ເພື່ອ ຫີຼກລ່ຽງ ບັນຫາດິນ ເຈືອນ. |
| ວິທີ ການຂຸດຫນານຜັກ ແມ່ນຈະຂຸດ ຈາກສ່ວນເທີງ ລົງລຸ່ມ ເຮັດໃຫ້ດິນ ທ່ີຂຸດຢູ່ເທີງ ຈະເລ່ືອນ ລົງມາທັບຖົມດິນ ທ່ີຢູ່ລຸ່ມ. | ຜູ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ຄວນຈະຂຸດ ສະສົມດິນ ຊັ້ນໜ້າໄວ້ບ່ອນໃດບ່ອນຫນ່ືງກ່ອນ ເພື່ອນໍາມາກອງ ໃສ່ໜານທ່ີຂຸດແລວ້ ຕາມພາຍຫັຼງ ເນ່ືອງຈາກດິນຊັ້ນໜ້າ ຈະມີຄວາມອຸດົມສົມບູນ ເປັນເນ້ືອດິນ ທ່ີປະປົນກັບອິນຊີວັດຖຸ. |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
1 ຄັ້ງ
- interviews with land users
1 ທ່ານ
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules