ប្រព័ន្ធបូមទឹកប្រើថាមពលព្រះអាទិត្យដើម្បីបន្ស៊ាំនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ [Cambodia]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Sok Pheak
- Editors: Sophea Tim, Navin Chea
- Reviewers: Nimul CHUN, Ursula Gaemperli
ប្រព័ន្ធសូឡាបូមទឹក
technologies_3214 - Cambodia
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
land user:
ម៉ៅ សារ៉ាត់
(+855) 88 829 10 97
កសិករ
ធម្មជាតិសម្ដេចតេជោ ហ៊ុន សែន ឃុំស្រអែម ស្រុកជាំខ្សាន្ត ខេត្តព្រះវិហារ
Cambodia
អ្នកផ្សព្វផ្សាយឃុំ:
ថុន ភារៈ
(+885) 97 46 100 66
មន្ត្រីផ្សព្វផ្សាយឃុំ
ធម្មជាតិសម្ដេចតេជោ ហ៊ុន សែន ឃុំស្រអែម ស្រុកជាំខ្សាន្ត ខេត្តព្រះវិហារ
Cambodia
មន្ត្រីការិយាល័យកសិកម្ម រុក្ខាប្រមាញ់ និងនេសាទស្រុកជាំក្សាន្ត:
ឆ្លាត ប្រាជ្ញ
(+855) 97 48 25 806
ការិយាល័យកសិកម្ម រុក្ខាប្រមាញ់ និងនេសាទស្រុកជាំក្សាន្ត
ភូមិជាំក្សាន្ត ឃុំជាំក្សាន្ត ស្រុកជាំក្សាន្ត ខេត្តព្រះវិហារ
Cambodia
ប្រធានការិយាល័យកសិកម្ម រុក្ខាប្រមាញ់ និងនេសាទស្រុកគូលែន:
ប្រធានការិយាល័យកសិកម្ម រុក្ខាប្រមាញ់ និងនេសាទស្រុករវៀង:
មន្ត្រីមន្ទីរកសិកម្ម រុក្ខាប្រមាញ់ និងនេសាទខេត្តព្រះវិហារ:
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Royal University of Agriculture (RUA) - Cambodia1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
06/05/2017
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
Nee
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
សូឡាបូមទឹកជាបច្ចេកទេសមួយដែលប្រើប្រាស់បន្ទះសូឡាសម្រាប់ទាញយកប្រភពថាមពលពីព្រះអាទិត្យ ហើយបំលែងជាថាមពលអគ្គិសនីដើម្បីដំណើរការម៉ូទ័រសម្រាប់បូមទឹកពីប្រភពនានារួមទាំងប្រភពទឹកក្រោមដីផងដែរ។ សូឡាបូមទឹកអាចកាត់បន្ថយការចំណាយ និងមិនមានបញ្ចេញឧស្ម័ន (CO2) ដែលជាជម្រើសល្អនៃការបង្កើនភាពធន់ទ្រាំ និងរួមចំណែកការកាត់បន្ថយការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ។
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
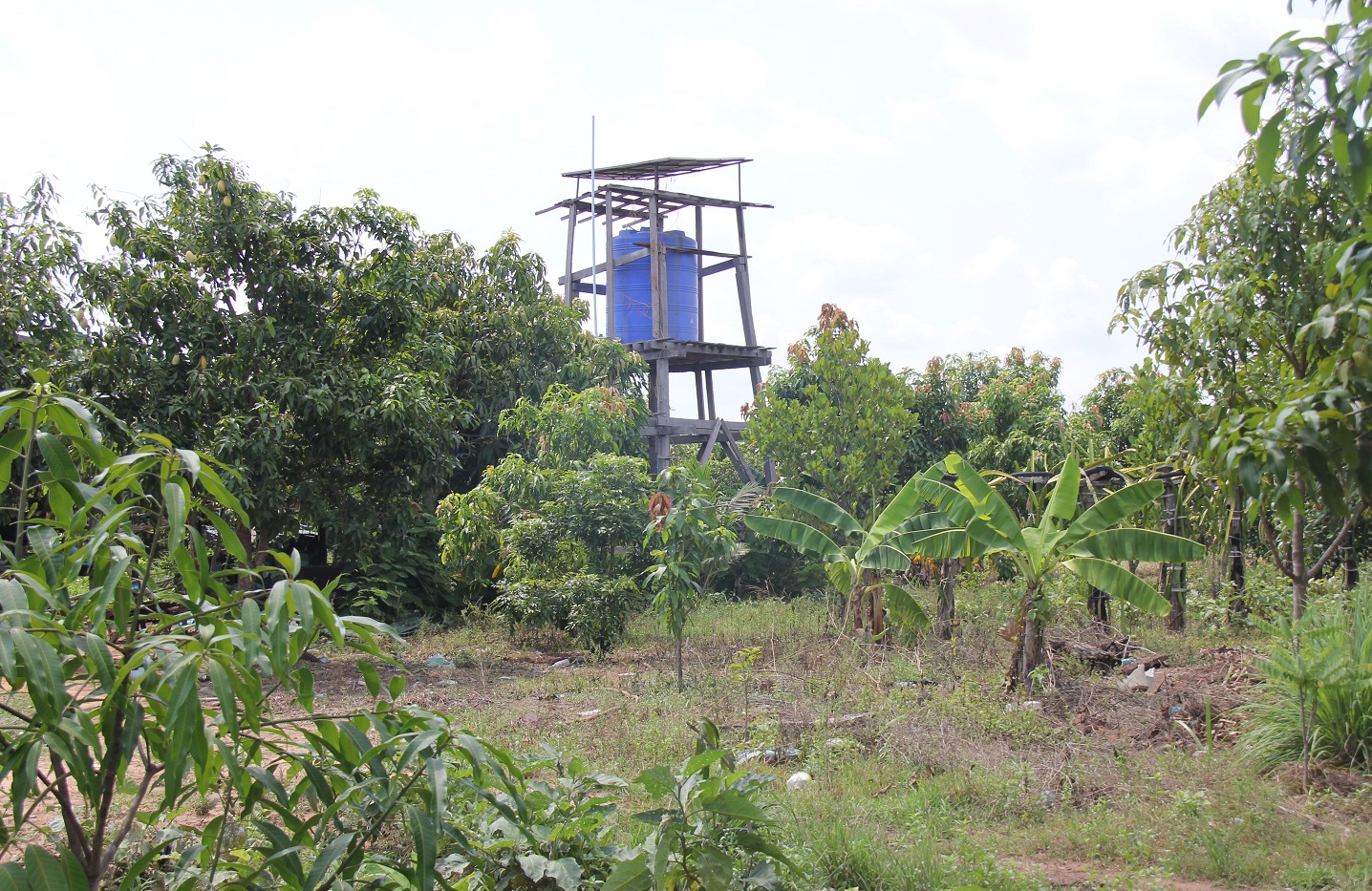
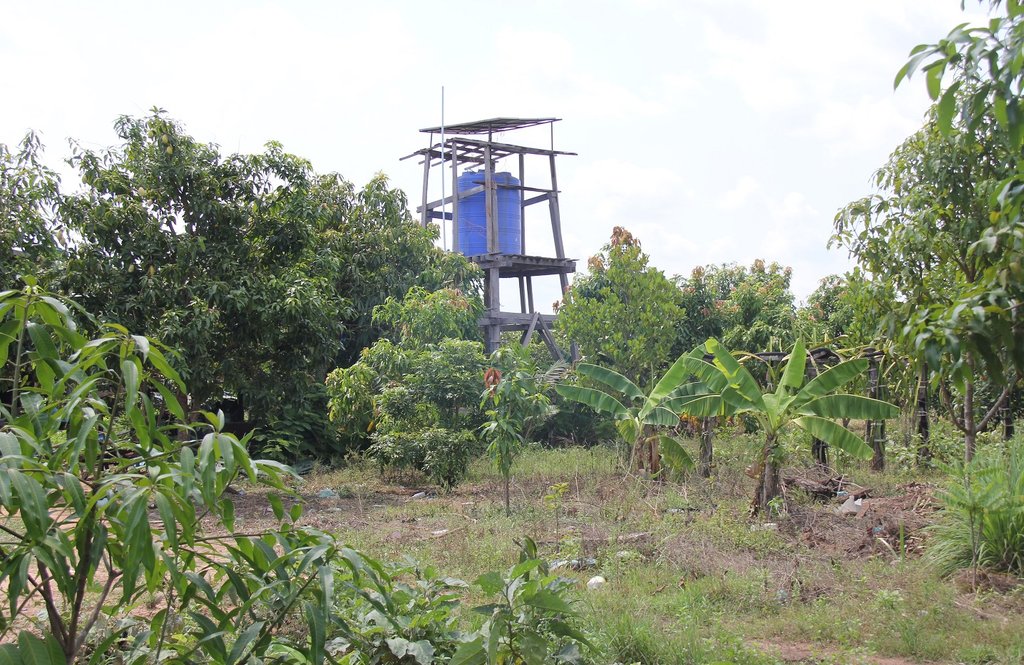
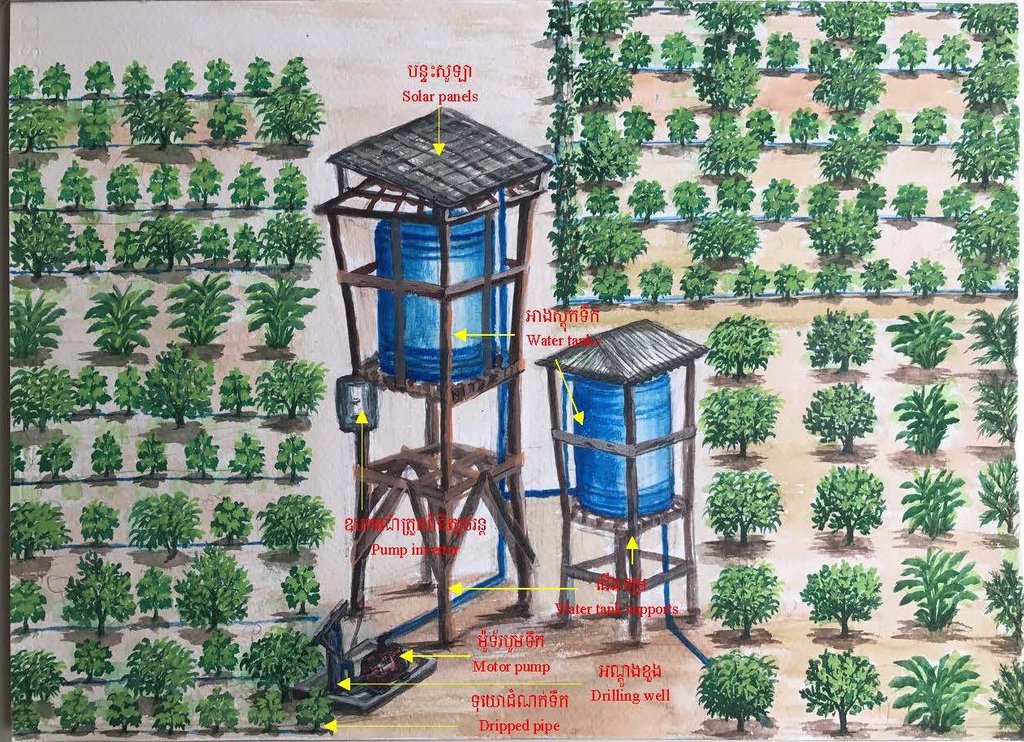
ប្រព័ន្ធបូមទឹកដោយប្រើថាមពលព្រះអាទិត្យ គឺជាការស្រាវជ្រាវមួយដោយប្រើប្រាស់បន្ទះសូឡាសម្រាប់ទាញយកពន្លឺព្រះអាទិត្យបង្កើតជាថាមពេលអគ្គិសនីសម្រាប់បូមទឹក។ ការប្រើសូឡាបូមទឹកជាជម្រើសដ៏ល្អមួយដើម្បីចូលរួមកាត់បន្ថយការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ។ កសិករនៅភូមិធម្មជាតិសម្តេចតេជោ ហ៊ុន សែន ឃុំស្រអែម ស្រុកជាំក្សាន្ត ខេត្តព្រះវិហារ ពីមុនបានប្រើប្រាស់ទឹកស្រះជាប្រភពសម្រាប់ស្រោចស្រពដំណាំរបស់គាត់ ប៉ុន្តែការប្រើប្រាស់មិនបានផ្តល់ទឹកគ្រប់គ្រាន់ទៅតាមតម្រូវការទេ។ ដោយឃើញពីបញ្ហាកង្វះខាតនេះទើបមានអង្គការសេដាក (CEDAC) បានអនុវត្តន៍គម្រោងមួយនៅក្នុងតំបន់ហើយក៏បានផ្តល់អណ្តូងទឹកមួយដល់ប្រជាកសិករនៅក្នុងឃុំនេះនៅឆ្នាំ ២០១១ ដើម្បីដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាខ្វះខាតទឹក។ ក្រោយមកនៅឆ្នាំ ២០១៤ មន្ទីរកសិកម្ម រុក្ខាប្រមាញ់ និងនេសាទខេត្តព្រះវិហារបានផ្តល់សូឡាបូមទឹកមួយឈុតសម្រាប់ដាំបន្លែក្រោមជំនួយឧបត្ថម្ភរបស់កម្មវិធីសកម្មភាពបន្ស៊ាំនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុដំណាក់កាលទី ២ ដែលបានអនុវត្តនៅក្នុងឃុំនេះ។ គម្រោងបានផ្តល់ប្រព័ន្ធសូឡាបូមទឹកប្រើថាមពលព្រះអាទិត្យចំនួន ៧ កន្លែង នៅក្នុងភូមិធម្មជាតិសម្តេចតេជោ ហ៊ុន សែន ហើយគម្រោងក៏បានតម្លើងប្រព័ន្ធសូឡាបូមទឹកមួយកន្លែងមានទីតាំងនៅផ្ទះរបស់ លោក ម៉ៅ សារ៉ាត់សម្រាប់ប្រើប្រាស់ទឹកដាំបន្លែ។ អណ្តូងស្នប់នេះមានលក្ខណៈពិសេសមួយដែលអាចដំណើរការបានបើទោះជាថាមពលរបស់វាមានការប្រែប្រួលក៏ដោយ។
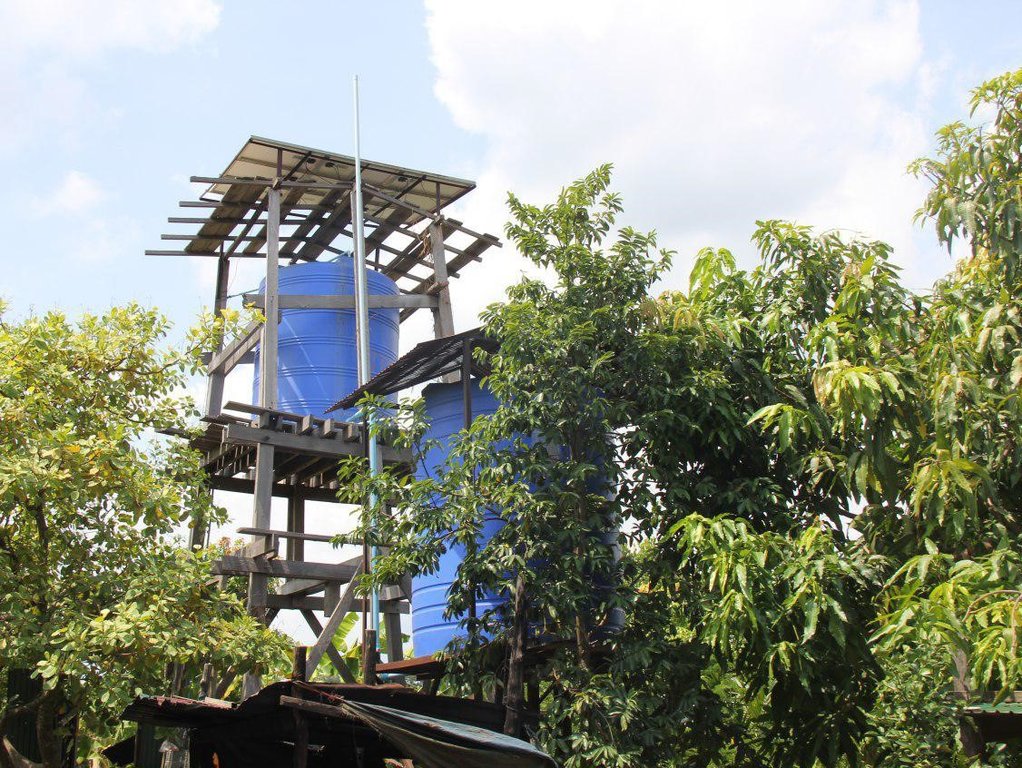
ដើម្បីដំណើរការប្រព័ន្ធសូឡាបូមទឹកនេះត្រូវមានឧបករណ៏ជាធាតុផ្សំសំខាន់ៗមួយចំនួនដូចជា៖បន្ទះសូឡាដែលបានដាក់នៅខាងលើជើងទម្រឈើ ម៉ូទ័របូមទឹក ឧបករណ៍ត្រួតពិនិត្យចរន្ត អាងស្តុកទឹកដែលមានជើងទម្រ និងខ្សែភ្លើង។ ចំពោះការតម្លើងប្រព័ន្ធសូឡាបូមទឹកនេះ ជាដំបូងត្រូវខួងអណ្តូងទឹក ហើយដាក់ម៉ូទ័របូមទឹកចូលក្នុងអណ្តូង និងរៀបចំទុយោចែកចាយ។ បន្ទាប់មកទៀតត្រូវរៀបចំជើងទម្រសម្រាប់ដាក់អាងស្តុកទឹកចំនួន ២ ដែលមានកម្ពស់ ៤,៨ ម៉ែត្រ និង ២,០៤ ម៉ែត្រ រួចតម្លើងអាងស្តុកទឹក និងម៉ូទ័របូមសម្រាប់បូមទឹកមកស្តុកទុកក្នុងអាងស្តុកទឹក។ គាត់តម្លើងបន្ទះសូឡាចំនួន៩ដោយដាក់លើជើងទម្រខាងលើប្រអប់បញ្ជាម៉ូទ័របូមទឹកដើម្បីទាញយកថាមពលពន្លឺព្រះអាទិត្យមកប្រើប្រាស់ និងត្រួតពិនិត្យកម្ពស់ក្នុងអាងស្តុកទឹកដើម្បីចែកចាយទឹកដល់ដំណាំ និងប្រើប្រាស់ក្នុងគ្រួសារ។ អាងស្តុកទឹកមានចំណុះ៥០០០លីត្រចំនួន ២ ដែលប្រើប្រាស់សម្រាប់ដំណាំក្នុងសួនបន្លែ និងផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកតាមផ្ទះចំនួន ៣ គ្រួសារនៅក្នុងភូមិផងដែរ។ ដោយសារតែមានឧបករណ៍ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកដែលធន់ទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងជួយកាត់បន្ថយការចំណាកស្រុកដោយកសិករងាកមកធ្វើកសិកម្មវិញ។
ប្រព័ន្ធសូឡាបូមទឹក គឺជាបច្ចេកទេសបូមទឹកដោយស្វ័យប្រវត្តិដែលទាញយកថាមពលព្រះអាទិត្យមកប្រើប្រាស់ដែលអាចចំណេញកម្លាំងពលកម្ម និងពេលវេលា កាត់បន្ថយការបំភាយឧស្ម័នទៅក្នុងបរិយាកាស និងអាចចែកចាយទឹកទៅតាមតំបន់ឆ្ងាយ។ នៅពេលគម្រោងបញ្ចប់បានបន្សល់ទុកប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភចំនួន ២,០០០ ដុល្លា ទុកសម្រាប់ជុសជុលប្រព័ន្ទសូឡាបូមទឹក។ សហគមន៍ កសិកម្មធម្មជាតិនិងអភិវឌ្ឍន៍ជាយដែនបានគ្រប់គ្រង់ថវិកាដែលបានផ្តល់ជូនដោយប្រើប្រាស់ថវិកាបង្កើតជាឥណទានសម្រាប់សមាជិកសហគមន៍មានអាត្រាការប្រាក់២%ក្នុង១ខែហើយនៅពេល ដែលជុសជុលសហគមន៍បានបង្វិលថវិកាមកវិញ។ ម្យ៉ាងវិញទៀត បន្ទាប់ពីបានតម្លើងសូឡាបូមទឹកបានរយៈពេល ១ ឆ្នាំ លោក ម៉ៅ សារ៉ាត់ បានលក់ទឹកឱ្យកសិករផ្សេងៗក្រៅពី ៣ គ្រួសារដែលចែកចាយទឹកទៅដល់ក្នុងតម្លៃ១៥០០ រៀល ក្នុង១ម៉ែត្រគួបនៅរដូវប្រាំង ឫពេលរាំងស្ងួត ប៉ុន្តែមកដល់ពេលនេះគាត់មិនអាចលក់ទឹកបានទៀតទេដោយសារគ្រួសារភាគច្រើននៅក្នុងភូមិមានទឹកអណ្តូងនិងស្រះទឹករៀងៗខ្លួនប្រើប្រាស់គាំទ្រដោយអង្គការក្រៅរដ្ឋាភិបាល។
សរុបសេចក្តីមក ប្រព័ន្ធសូឡាបូមទឹកគឺជាបច្ចេកវិទ្យាមួយទាញយកថាមពលពន្លឺព្រះអាទិត្យមកដំណើរការម៉ូទ័របូមទឹកជំនួសឱ្យម៉ូទ័រដើរដោយឥន្ទនៈដែលប៉ះពាល់ដល់បរិស្ថានយ៉ាងខ្លាំង។ក្រៅពីប្រើប្រាស់ទឹកសម្រាប់សួនបន្លែប្រព័ន្ធបូមទឹកដោយថាមពលពន្លឺព្រះអាទិត្យក៏អាចប្រើប្រាស់ទឹកសម្រាប់ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកតាមផ្ទះនៅក្នុងភូមិផងដែរ។ ដើម្បីជំនួសឱ្យការជីកអណ្តូងច្រើននៅកន្លែងខុសៗគ្នាក្នុងភូមិកសិករមានទឹកនៅក្នុងផ្ទះដោយជីកអណ្តូងមួយបំពាក់ដោយប្រព័ន្ធថាមពលពន្លឺព្រះអាទិត្យជាមួយអាងទឹកនៅទីខ្ពស់ និងប្រព័ន្ធទុយោបង្ហូរទឹកទៅតាមផ្ទះនីមួយៗនៅក្នុងភូមិមានលក្ខណៈងាយស្រួល។
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Cambodia
Region/ State/ Province:
ភូមិធម្មជាតិសម្តេចតេជជោ ហ៊ុន សែន ឃុំស្រអែម ស្រុកជាំខ្សាន ខេត្តព្រះវិហារ
Further specification of location:
តំបន់ជនបទ
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
Indicate year of implementation:
2012
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through projects/ external interventions
Comments (type of project, etc.):
កម្មវិធីសកម្មភាពបន្សុំនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុដំណាក់កាលទី ២។
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- reduce risk of disasters
- adapt to climate change/ extremes and its impacts
- mitigate climate change and its impacts
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Perennial (non-woody) cropping
Main crops (cash and food crops):
មានដំណាំដូចជា៖ ស្វាយ ខ្នុរ ត្រប និងននោង។
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- full irrigation
Comments:
កសិករបានប្រើប្រាស់ថាមពលពន្លឺព្រះអាទិត្យ និងស្រះទឹកសម្រាប់ស្រោចស្រពដំណាំ។
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 3
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- water harvesting
- irrigation management (incl. water supply, drainage)
- water diversion and drainage
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- applied at specific points/ concentrated on a small area
Comments:
ប្រសិនបើមិនមានជំនួយពីអង្គការក្រៅរដ្ឋាភិបាល កសិករមិនអាចចំណាយថវិកាដើម្បីសូឡាបូមទឹកបាននោះទេដោយសារតែមានតម្លៃខ្ពស់។
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

structural measures
- S7: Water harvesting/ supply/ irrigation equipment
- S10: Energy saving measures
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

water degradation
- Ha: aridification
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
- reduce land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
ដើម្បីដំណើរប្រព័ន្ធសូឡាបូមទឹកនេះបានត្រូវមានឧបករណ៍ជាធាតុផ្សំសំខាន់ៗ៖ បន្ទះសូឡាដែលបានដាក់នៅខាងលើជើងទម្រឈើ ម៉ូទ័របូមទឹក ឧបករណ៍ត្រួតពិនិត្យចរន្ត អាងស្តុកទឹកដែលមានជើងទម្រ និងខ្សែភ្លើង។ ត្រូវមានអណ្តូងស្នប់ជម្រៅ ២៩ ម៉ែត្រ មុខកាត់ទំហំ ០,០៨ ម៉ែត្រ ក្រោយពីខួងអណ្តួងរួចត្រូវតម្លើងម៉ូទ័របូមទឹក។ ជើងទម្រសម្រាប់អាងស្តុកទឹកត្រូវមានពីរកម្ពស់ ២.០៤ ម៉ែត្រ និង២,៨ ម៉ែត្រដែល
មានចំណុះ ៥០០០ លីត្រ។ សូឡាបូមទឹកមួយថ្ងៃអាចបូមបានពី៦ ទៅ ៧ ម៉ែត្រគួបប្រសិនបើមានពន្លឺព្រះអាទិត្យល្អអាចបូមបាន ៨ ម៉ែត្រគួបក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ។
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology unit
Specify unit:
សូឡាបូមទឹកអាចដំណើរការបានអាងស្តុកទឺកពីរដែលមានចំណុះ ៥០០០ លីត្រ
Specify volume, length, etc. (if relevant):
មាឌអាងស្តុកទឹក១មានចំណុះ ៥០០០ លីត្រ
other/ national currency (specify):
រៀល
Indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (if relevant): 1 USD =:
4000.0
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
២០០០០ រៀល
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | បុកអណ្តូងទឹក | Structural | កុម្ភះ |
| 2. | ធ្វើជើងទម្រ | Structural | ឧសភា |
| 3. | ទិញធុងសាទែនទឹក (គម្រោងអ្នកចេញ) | Structural | ឧសភា |
| 4. | តម្លើងប្រព័ន្ធសូឡា | Structural | ឧសភា |
| 5. | ម៉ូទ័របូមទឹក | Structural | ឧសភា |
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | បុកអណ្តូង | ឈុត | 1.0 | 1600000.0 | 1600000.0 | |
| Labour | ធ្វើជើងទម្រ | ឈុត | 1.0 | 800000.0 | 800000.0 | |
| Equipment | ធុងសាទែនទឹក | ដុំ | 2.0 | 2000000.0 | 4000000.0 | |
| Equipment | ឧបករណ៍ត្រួតពិនិត្យចរន្ត | ដុំ | 1.0 | 4000000.0 | 4000000.0 | |
| Equipment | ម៉ូទ័របូមទឹករួមបញ្ជូលបន្ទះសូឡា | ឈុត | 1.0 | 8000000.0 | 8000000.0 | |
| Construction material | ជើងទម្រសម្រាប់ដាក់សាទែនទឹក | ចំនួន | 2.0 | 800000.0 | 1600000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 20000000.0 | |||||
If land user bore less than 100% of costs, indicate who covered the remaining costs:
កម្មវិធីសកម្មភាពបន្សុំនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុដំណាក់កាលទី ២ បានចំណាយថ្លៃប្រព័ន្ធសូឡាបូមទឹក និង CEDAC ចំណាយថ្លៃអណ្តូងទឹក។
Comments:
ចំពោះប្រព័ន្ធសូឡាបូមទឹក ១ ឈុតមានតម្លៃ ២០,០០០,០០០ រៀល។
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | ត្រួតពិនិត្យមើលកម្រិតទឹក និងការតម្លើងម៉ូទ័រ | Structural | រដូវប្រាំង |
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | ជុសជុលម៉ូទ័របូមទឹក | ចំនួន | 1.0 | 400000.0 | 400000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 400000.0 | |||||
If land user bore less than 100% of costs, indicate who covered the remaining costs:
កម្មវិធីសកម្មភាពបន្សុំនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុដំណាក់កាលទី ២។
Comments:
ជុសជុលម៉ូទ័របូមទឹកនៅពេលដែលមានតម្រូវថែទាំដោយសារតែគម្រោងបានបន្សល់ទុកថវិកាចំនួន ២០០០ដុល្លាសម្រាប់សេវាកម្មជុសជុល។
4.8 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
តម្លៃប្រព័ន្ធសូឡាមានតម្លៃថ្លៃទើបជះឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយរបស់កសិករ។
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
នៅឆ្នាំ២០១៥ កម្ពស់ទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ ១៤២៩.៣ មម
នៅឆ្នាំ២០១៤ កម្ពស់ទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ ១៦៤៧.៣ មម
Indicate the name of the reference meteorological station considered:
ក្រសួងធនធានទឹក និងឧត្តុនិយម (២០១៥)
Agro-climatic zone
- semi-arid
អាកាសធាតុក្ដៅ សើម ដែលបង្កឱ្យមាន ២ រដូវ គឺរដូវប្រាំង និងវស្សា។
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- not relevant
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- high (>3%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
ដីស្រទាប់លើមានជីជាតិល្អដោយកសិករប្រើលាមកគោលើដំណាំ។
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
5-50 m
Availability of surface water:
medium
Water quality (untreated):
for agricultural use only (irrigation)
Is water salinity a problem?
Nee
Is flooding of the area occurring?
Nee
Comments and further specifications on water quality and quantity:
ការប្រើប្រាស់ទឹកមានជាតិកំបោរ ដូច្នេះពេលបរិភោគត្រូវដាំទឹកក្តៅ តែមិនប៉ះពាល់ដល់ដំណាំនោះទេ។
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- low
Habitat diversity:
- low
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
- mechanized/ motorized
Gender:
- men
Age of land users:
- elderly
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
កសិករមានដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសនេះមានអាយុ ៦០ឆ្នាំ ។
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- small-scale
Comments:
កសិករមានដីសម្រាប់ដាំបន្លែចំនួន ១ ហិកតា និង ១,៥ ហិកតាជាដីស្រែសុំគេធ្វើ ដាំពោត សណ្តែក។
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- leased
- individual
Water use rights:
- open access (unorganized)
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Quantity before SLM:
៣០%
Quantity after SLM:
៦០%
Water availability and quality
drinking water availability
Comments/ specify:
កសិករអាចប្រើប្រាស់ទឹកសម្រាប់ស្រោចស្រពដំណាំ និងចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ។
drinking water quality
Comments/ specify:
គុណភាពទឹកសម្រាប់បរិភោគនៅមានការកើនឡើងតិចតូច ប៉ុន្តែកសិករអាចបរិភោគបានដោយដាំទឹកក្តៅជាមុនសិន។
irrigation water availability
Comments/ specify:
ក្រោយពីបានតម្លើងប្រព័ន្ធបូមទឹកកសិករអាចយកទឹកប្រើប្រាស់ស្រោចស្រពដំណាំគ្រប់រដូវកាលដាំដុះ។
irrigation water quality
Comments/ specify:
គុណភាពទឹកស្រោចស្រពមានលក្ខណៈល្អគ្រាន់ បើទោះបីជាមានជាតិកំបោរ ប៉ុន្តែមិនប៉ះពាល់ដល់ដំណាំ។
demand for irrigation water
Quantity before SLM:
៣០%
Quantity after SLM:
៦០%
Income and costs
expenses on agricultural inputs
Comments/ specify:
កសិករពុំបានចំណាយច្រើនដោយសារមានគម្រោងជួយគាំទ្រ។
farm income
Comments/ specify:
ពីមុនកសិករទទួលបានចំណូលតិចតួចដោយសារកសិករទទួលបានទិន្នផលបន្លែទាប តែបច្ចុប្បន្នគាត់ទទួលបានចំណូលកើនឡើង ដោយសារមានទឹកស្រោចស្រពគ្រប់គ្រាន់។
workload
Comments/ specify:
កសិករមានពេលវេលាច្រើនធ្វើការងារផ្សេងទៀតដោយសារគាត់មានប្រព័ន្ធបូបទឹកដោយថាមពលពន្លឺព្រះអាទិត្យជួយលើការងារ ស្រោចស្រពដំណាំ។
Socio-cultural impacts
land use/ water rights
Comments/ specify:
កសិករមានដីផ្ទាល់ខ្លួនសម្រាប់ប្រើប្រាស់ និងទឹកស្រោចស្រពដំណាំបន្លែ។
SLM/ land degradation knowledge
Comments/ specify:
ជួយកាត់បន្ថយការហូរច្រោះដីដោយប្រព័ន្ធទុយោទឹកស្រោចស្រពដំណាំ និងចូលរួមការពារបរិស្ថាន តាមរយៈការមិនប្រើប្រាស់ប្រេងឥន្ធនៈលើម៉ាស៊ីនបូមទឹក។
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
water quantity
Comments/ specify:
សូឡាបូមទឹកត្រូវការថាមពលពន្លឺព្រះអាទិត្យដើម្បីបង្កើតអគ្គិសនីដូចនេះវាអាស្រ័យទៅលើថាមពលពន្លឺព្រះអាទិត្យ ដែលអាចទាញយកទឹកបាន។
Climate and disaster risk reduction
emission of carbon and greenhouse gases
Comments/ specify:
ដោយសារបន្ទះសូឡាចាប់យកថាមពលពន្លឺព្រះអាទិត្យដើម្បីទាញយកទឹកប្រើប្រាស់។
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
impact of greenhouse gases
Comments/ specify:
ដោយសារបន្ទះសូឡាចាប់យកថាមពលពន្លឺព្រះអាទិត្យដើម្បីទាញយកទឹកប្រើប្រាស់ក្នុងគ្រួសារ និងស្រោចស្រព។
Comments/ specify:
កសិករអាចចែកចាយទឹកទៅឱ្យអ្នកជិតខាងប្រើប្រាស់បាននៅពេលខ្វះខាតទឹកនៅរដូវប្រាំង។
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | Type of climatic change/ extreme | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | decrease | moderately | |
| seasonal temperature | wet/ rainy season | increase | moderately |
| annual rainfall | decrease | well | |
| seasonal rainfall | wet/ rainy season | decrease | well |
Other climate-related consequences
Other climate-related consequences
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| extended growing period | well |
Comments:
នៅតំបន់ខ្លស់កសិករមានការលំបាកក្នុងការទទួលយកទឹកមកប្រើប្រាស់នៅរដូវប្រាំង ជាពិសេសពេលមានគ្រោះរាំងស្ងួត។ ទោះបីជាយ៉ាងណាក៏ដោយ វាក៏អាចអូសបន្លាយពេលដំាដុះខណៈពេលដែលយើង អាចបន្តយកទឹកមកប្រើប្រាស់ និងដំាដំណាំ។
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- 1-10%
If available, quantify (no. of households and/ or area covered):
មាន ៧ គ្រួសារនៅក្នុងភូមិធម្មជាតិសម្តេចតេជោ ហ៊ុន សែន បានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសនេះ (រួមបញ្ចូលអ្នកបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសនេះ)
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
Comments:
មិនទាន់មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯងដោយសារកសិករភាគច្រើនបើគ្មានជំនួយពីក្រសួង ស្ថាប័នពាក់ ឬអង្កការក្រៅរដ្ឋាភិបាលទេកសិករមិនហ៊ានចំណាយលុយធ្វើនោះទេព្រោះត្រូវចំណាយថ្លៃ
លើការទិញសម្ភារ។
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
Nee
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| អាចយកទឹកដាំដំណាំ និងប្រើប្រាស់មិនបាច់ប្រើម៉ាស៊ីនបូមទឹក។ |
| បង្កើនសេដ្ឋកិច្ចដោយមិនបាច់ទិញប្រេងដោយមានសូឡាបូមទឹក |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| បន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ |
| កាត់បន្ថយការបំភាយ GHG ទៅក្នុងបរិយាកាស |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| ចំណាយថវិកាច្រើន។ | មានបណ្តាអង្កការជួយ និងចូលរួមអនុវត្ត។ |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
៣ នាក់
- interviews with land users
១ នាក់
- ភ្នាក់ងារផ្សពផ្សាយឃុំ
១ នាក់
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Abrams, J. H. (2015). Climate Resilient Irrigation Training Manual. Phnom Penh: Project Support Unit, Ministry of Agriculure, Forestry, and Fisheries (MAFF-PSU).
Available from where? Costs?
MAFF, Free available.
7.3 Links to relevant information which is available online
Title/ description:
SGE. (2015). Soalr water pump with sun tracker. Retrieved February 7, 2018, from
URL:
http://www.solarcambodia.com/index.php?lang=en&p=products-system&id=10
Title/ description:
CDD. (2014). NAPA Follow-UP-Cambodia's Official Climate Change Website. Retrieved February 7, 2018, from
URL:
http://www.camclimate.org.kh/en/activities/napa-follow-up.html
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules