Borana Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles [Kenya]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Michael Herger
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_2972 - Kenya
- Full summary as PDF
- Full summary as PDF for print
- Full summary in the browser
- Full summary (unformatted)
- Borana Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: Sept. 3, 2018 (inactive)
- Borana Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: Mei 6, 2019 (inactive)
- Borana Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: Nov. 2, 2021 (public)
- Borana Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: Feb. 22, 2018 (inactive)
- Borana Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: Feb. 1, 2018 (inactive)
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
land user:
Sora Abdi
+254 728 391 823
sora@borana.co.ke
Borana Ranch ltd. and Borana Conservancy ltd.
Borana Ranch ltd. and Borana Conservancy ltd. P O Box 137, Nanyuki 10400, Laikipia, Kenya
Kenya
1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
22/01/2017
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
Nee
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
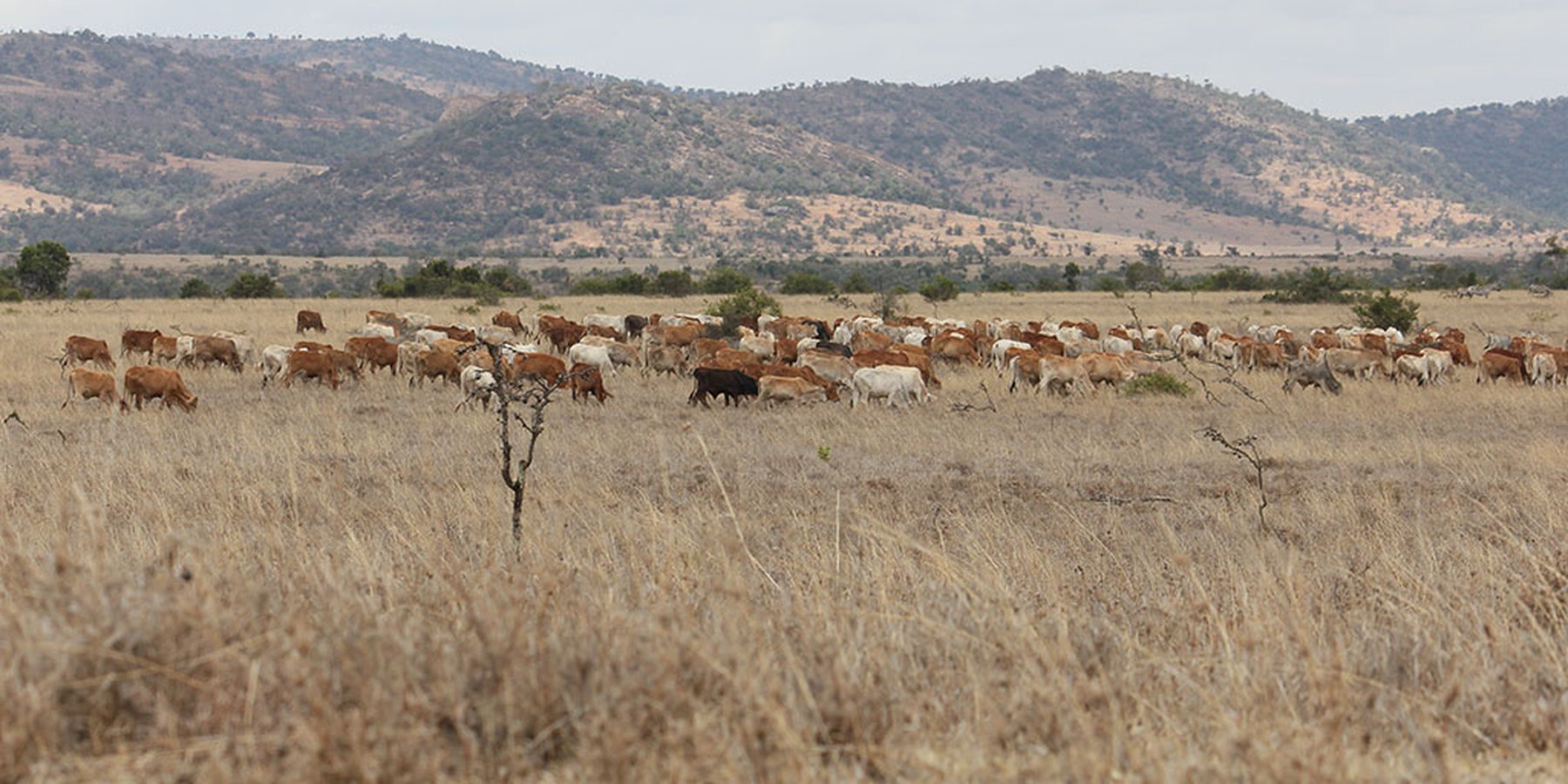
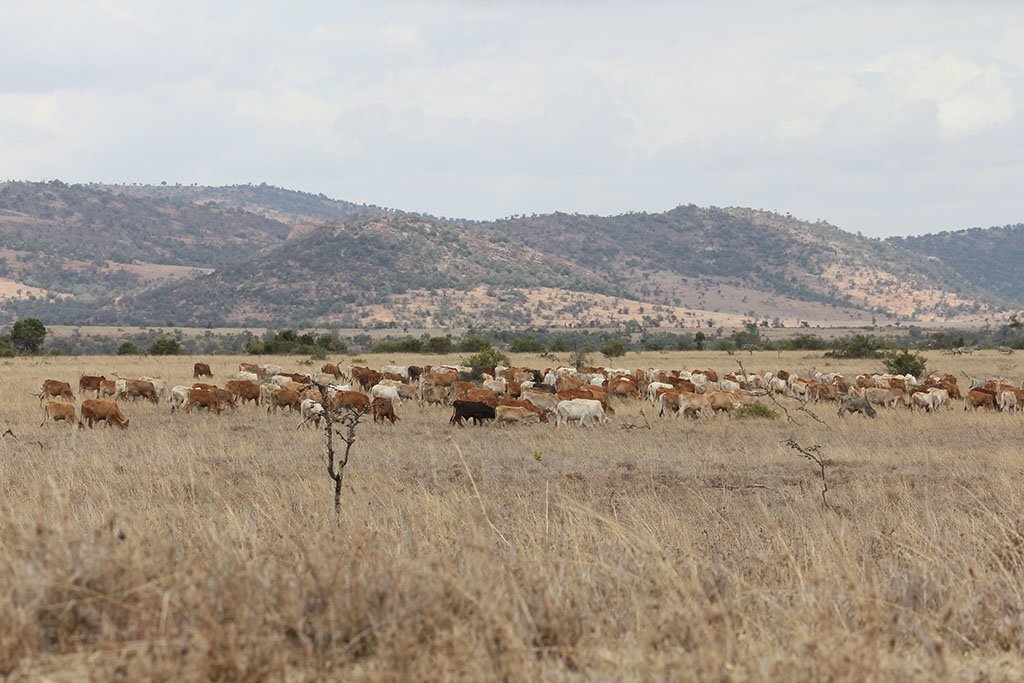
Borana is a private ranch which combines livestock production with conservation and tourism. "Holistic Management" is applied as a principle for livestock on semi-arid lands with limited water resources. Grazing comprises “bunching” and rotational movement of all animals in herds.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
Livestock production on Borana ranch is carried out under extensive grazing for beef, dairy, and sheep production. There is strategic fattening and offtake for sales in harmony with conservation principles. The Borana Conservancy is a non-profit organisation, also belonging to the ranch – on the same land - dedicated to the sustainable conservation of critical habitat and wildlife. Ranching contributes financially to the running of the conservancy.
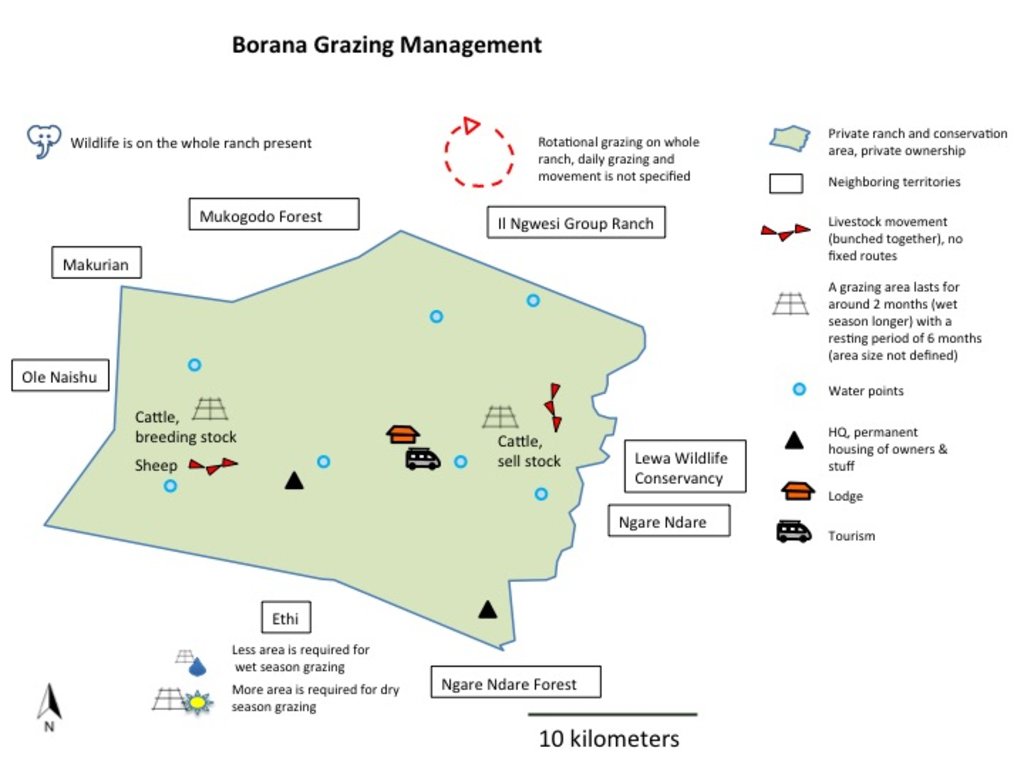
“Holistic Management” (HM) as described by Allan Savory (1988) and promoted by Laikipia Wildlife Forum in Laikipia, is a method that integrates decision-making, planning, and livestock keeping. On the land, this means bunching of all livestock close together in order to act as a "plough" and break the soil to help incorporate seeds and nutrients. Water also infiltrates better. The aim is to improve plant growth and thus soil. Furthermore, it means moving the animals together from block to block, by planned rotational grazing with resting periods. HM aims at managing high numbers of livestock and simultaneously restoring degraded land. However, Holistic Management principles remain controversial.
Livestock herders employed by Borana move different herds of animals rotationally from one grazing area to the next. A defined grazing area lasts for around two months, with a resting period of six months. However, the grazing area and period vary a lot depending on rainfall. During the wet season, livestock usually spend more than two months within the same block. Cattle herds are split depending on their function as offtake for sales, or as breeding stock. The selling stock is located on the eastern side of Borana (currently 600 Head of cattle), while the breeding stock is on the western side (currently 1,800 Head of cattle). Sheep are grazed on the western side too (currently 1,200 Head of cattle).
A calf stays with its mother until it is about six months old. Then a few males are selected as bulls, and all others castrated. At the same time females are selected for breeding to rebuild stock. Only one bull was purchased from outside, in 2013 which was a rare exception.
Livestock are sold to butchers in local centres (e.g. Nanyuki, about 50 km distance), in the capital Nairobi (about 300 km away), and to the son of the owner, who runs a business nearby. Usually, only old and disabled cows are selected for selling.
Borana helps neighbouring group ranches with improved genetics - and access to their land for fattening purpose. It also acts as a grass bank during droughts. According to Borana management, boundaries between Borana and community ranches, which once clearly defined the difference between managed and over-grazed lands, are becoming less clear.
Typical of private ranches in Laikipia, Borana supports some of the highest densities of wildlife in Kenya. The wild herbivore biomass density on private ranches is estimated by Georgiadis (2007) at 14 ha /TLU.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
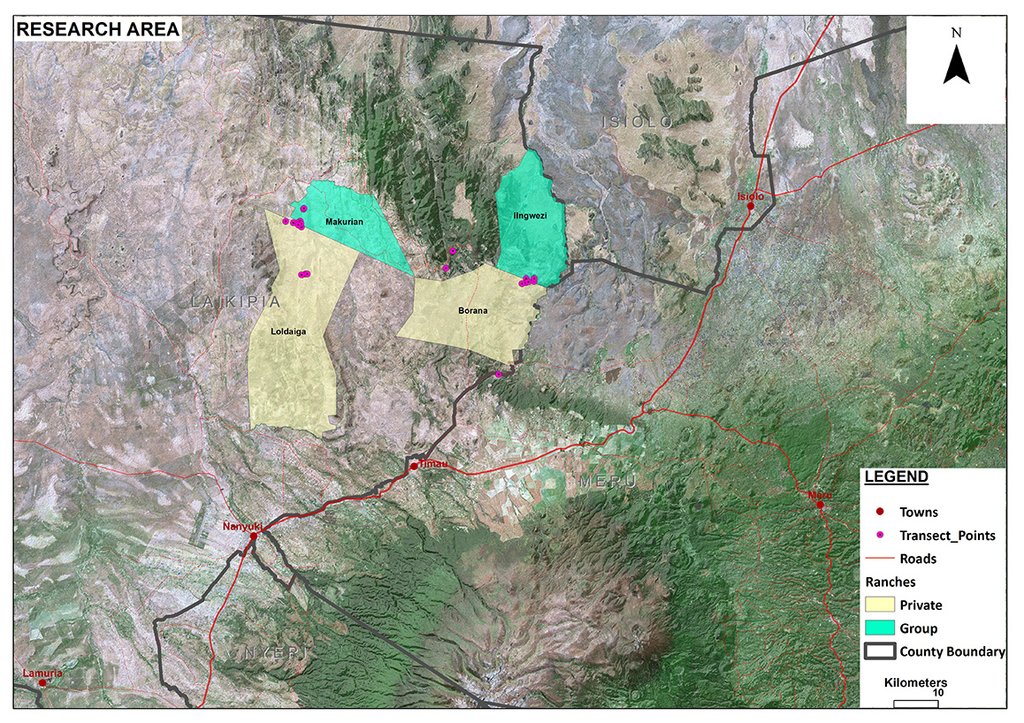
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Kenya
Region/ State/ Province:
Laikipia
Further specification of location:
Mukogodo District
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
Indicate year of implementation:
2008
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through projects/ external interventions
Comments (type of project, etc.):
Holistic Management approach by Allan Savory.
In Laikipia, it was introduced by Richard Hartfield, Laikipia Wildlife Forum and funded by Laikipia Wildlife Forum (LWF), Lewa Conservancy and Northern Rangeland Trust (NRT). Borana beared costs themselves.
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- conserve ecosystem
- preserve/ improve biodiversity
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Grazing land
Extensive grazing land:
- Ranching
Main animal species and products:
Extensive grazing land: Ranching
Main animal species and products: Livestock: Cattle, sheep, chicken, pigs. Milk, beef and sheep production (a few chicken and pigs). Some organic farming (herbs, vegetables). Local (30%), national and partly international distribution (both 70%). Livestock: 1,780 TLU; Stocking rate: 7.3 ha/TLU Pressure on land including wildlife: 4.8 ha/TLU Livestock numbers: 2,400 cattle, 1,000 sheep Sales: Cattle 10% sales, Sheep 25%. Assisting community grazing: 500-1,000 Head of cattle during droughts until it rains. Wildlife: giraffe, antelope/gazelle (e.g. gerenuk, eland, waterbuck, impala, Thomson's gazelle), baboon, zebra, dikdik, hare, rhino, elephant, predators and others. There is more wildlife than on group ranches.

Settlements, infrastructure
- Settlements, buildings
Remarks:
Lodge for Tourism.
Headquarter.
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 2
Specify:
Short rains in November and December. Long rains in April and May. Rains from (October) November to December are usually better in this area. Rainfalls with strong local variations and changing regimes.
Livestock density (if relevant):
Livestock: 1780 TLU; Stocking rate: 7.3 ha/TLU livestock but overall pressure on land including wildlife: 4.8 ha/TLU
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- pastoralism and grazing land management
- improved ground/ vegetation cover
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, indicate approximate area covered:
- 100-1,000 km2
Comments:
Borana has an area size of 130 km2. The technology is also applied on other ranches (e.g. neighbouring group ranch, see documentation for "Il Ngwesi") in Laikipia.
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

management measures
- M2: Change of management/ intensity level
- M4: Major change in timing of activities
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion
- Wg: gully erosion/ gullying

soil erosion by wind
- Et: loss of topsoil

physical soil deterioration
- Pc: compaction
- Pk: slaking and crusting
- Pi: soil sealing

biological degradation
- Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
- Bh: loss of habitats
- Bq: quantity/ biomass decline
- Bs: quality and species composition/ diversity decline
- Bl: loss of soil life
Comments:
Across the grasslands and rangelands, an increase in bare land and bush has been a clear trend all over Laikipia for many years, both on community-owned lands and private ranches. Major identified ecological problems (partly) caused by livestock production are: bare ground, low contents of soil organic carbon and plant-available nutrients, soil erosion (sealing, crusting, rills and gullies, water flow patterns, sheet erosion, pedestals), poor soil properties, undesirable species, and (increasing) woody and invasive species. The technology aims at improving vegetation cover of the land and thereby reducing further degradation and restoring degraded land. Borana is clearly not as much affected by the degradation of the land (compare Herger 2018), however, they use and support ranching with Holistic Management as a tool to enhance the quality of the grazing and prevent degradation. According to Borana management, cattle grazing reduces the moribund grass biomass, promotes seed dispersal, increases the nutritional value of the grass, and decreases the risk of bush fires. Even more crucial: The introduction of planned grazing (as Holistic Management) to Group Ranches in the area prevents conflicts (e.g. invading of private ranches), livestock diseases and deaths.
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
- reduce land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology unit
Specify unit:
Only livestock production related; for the whole farm: Herders, animals treatment
Specify currency used for cost calculations:
- US Dollars
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
4
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Training of employees | Management | |
| 2. | Grazing planning | Management |
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
Comments:
No figures on this, costs for implementation are estimated low, because ranching with the former grazing system was not that different before.
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Herders, supervisors, watchmen etc | Management | |
| 2. | Animal treatments (vaccination, spraying, injections) | Agronomic |
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Herders/employees | Person*days | 16200.0 | 4.0 | 64800.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | Insurance | Unknown quantity | 1.0 | 3900.0 | 3900.0 | |
| Equipment | Vehicle | Unknown quantity | 1.0 | 3700.0 | 3700.0 | |
| Other | Animals treatments | Per TLU | 1780.0 | 11.0 | 19580.0 | |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 91980.0 | |||||
4.8 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
Labor
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specify average annual rainfall (if known), in mm:
497.00
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
Rainfall gauge Borana HQ average from 2013-2016. Strong local (and temporal) variation, changing rainfall regimes.
Indicate the name of the reference meteorological station considered:
Rainfall gauge Borana HQ
Agro-climatic zone
- semi-arid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- not relevant
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- coarse/ light (sandy)
- medium (loamy, silty)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- coarse/ light (sandy)
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
Red and brown sandy soils. Black cotton soil. Luvisol, Regosol, Vertisol
SOC 2 %
pH: 6.4
Clay: 8%
Silt: 53%
Sand: 39%
Further data on rangeland health compare Herger (2018)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
> 50 m
Availability of surface water:
medium
Water quality (untreated):
poor drinking water (treatment required)
Is water salinity a problem?
Nee
Is flooding of the area occurring?
Nee
Comments and further specifications on water quality and quantity:
Waterpoints provided by waterpipes (sometimes destroyed by elephants)
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- high
Habitat diversity:
- high
Comments and further specifications on biodiversity:
Grassed acacia bushland. Little bare ground. Dominant grasses: Eragrostis species, Cynadon species, Hyparrhenia species, Kelenger species. Dominant shrubs: Grewia tembensis, Hibiscus aponeurus, Rhus natalensis, Scutia myrtina. Dominant trees: Acacia tortilis, Acacia mellifera, Euclea divinorum, Boscia angustifolia. Detailed list of all species (also wildlife) available (Herger 2018)
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- commercial/ market
Off-farm income:
- 10-50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- very rich
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
Gender:
- women
- men
Age of land users:
- middle-aged
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- large-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- individual
Water use rights:
- individual
Comments:
Masai in the area have claimed that land leases of white settlers have expired and the land belongs to them. Government states the land belongs to the private ranchers, but the future development is unknown. There have already been conflicts and are likely to happen again. On the other hand, cooperation with group ranches has increased.
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
fodder production
Comments/ specify:
Quality of pasture
animal production
Comments/ specify:
Better quality of animals
land management
Water availability and quality
water availability for livestock
water quality for livestock
Income and costs
workload
Socio-cultural impacts
land use/ water rights
Comments/ specify:
Cooperation with Group Ranches
SLM/ land degradation knowledge
conflict mitigation
Comments/ specify:
Good: Cooperation with Group Ranches. But still danger of invaders. Good pasture attracts herders in distress (e.g. pastoralists from further north)
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
water quantity
water quality
surface runoff
evaporation
Soil
soil moisture
soil cover
soil loss
soil organic matter/ below ground C
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
Vegetation cover
biomass/ above ground C
plant diversity
animal diversity
habitat diversity
Climate and disaster risk reduction
drought impacts
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
neutral/ balanced
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- 10-50%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 10-50%
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
Nee
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| Method leaves grass time to grow/rest |
| One can manage resources properly (water and pasture) |
| To keep all animals in one place makes vaccinations /disease prevention easier |
| “Ploughing effect” by the concentrated / bunched animals in one herd (new grass stimulated) |
| Tick population kept under control |
| In general for the whole area if many Group Ranches implement Holistic Management: More secure financial future and less stress during times of drought for pastoralists’ livestock. For Borana, this means less pressure from surrounding pastoralists when pasture is scarce. |
| Enhance the quality of grazing. Cattle grazing reduces the moribund grass biomass, promotes seed dispersal, increases the nutritional value of the grass and decreases the risk of bush fires. |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| The listed advantages from Abdi Sora, land user, are for the most part shared by the compiler's view. Regarding Holistic Management (HM) principles and land recovery there remain some uncertainties. On the one hand it is generally questionable to state as in HM that: “the more animals the better” (as long as they are managed properly they can even recover degraded land), but this seems dangerous in areas with such high livestock numbers and cultural value of livestock keeping - without scientific proof of the principles in similar ecological conditions. Since Borana has relatively low stocking rates and good management the rangeland is in good condition anyway. The effects of Holistic Management principles on their own are difficult to estimate. |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| More work (a lot of supervision, monitoring etc) | |
| More costs (a lot of supervision, monitoring etc) | |
| Danger of disease outbreak in a big herd |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
4 field visits with included "rangeland health assessment" in different parts of Borana (mainly next to gate to Il Ngwesi) where I could see the condition of the land as well as several other visits of the area.
- interviews with land users
Several meetings with the general manager and a short meeting with the owner of the ranch.
- interviews with SLM specialists/ experts
Truman Young
Dan Rubenstein
Dino Martins
John Letai
Samali Letai
Peter Hetz
Dominic Maringa
Joseph Putunoi
Patrick Ekodere
- compilation from reports and other existing documentation
Scientific papers, LWF reports etc.
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Georgiadis, N.J., Olivero, I.N., Romanach, S.S. (2007). Savanna herbivore dynamics in a livestock-dominated landscape: I. Dependence on land use, rainfall, density, and time. Biology Conservation 137(3): 461-472.
Available from where? Costs?
Online
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Herger, M.B. (2018). Environmental Impacts of Red Meat Production. MSc Thesis. University of Bern.
Available from where? Costs?
University of Bern
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Savory, A (1988). Holistic Resource Management. Gilmour Publishing, Harare, Zimbabwe
Available from where? Costs?
Online
Title, author, year, ISBN:
• Carter, J., Jones, A., O’Brien, M., Ratner, J., Wuerthner, G. (2014). Holistic Management: Misinformation on the Science of Grazed Ecosystems.
Available from where? Costs?
International Journal of Biodiversity.
Title, author, year, ISBN:
• Briske, D.D., Ash, A.J., Derner, J.D., Huntsinger, L. (2014). Commentary: A critical assessment of the policy endorsement for holistic management. Agricultural Systems 125:50-53.
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules