Эффективная использования земель под интенсивный садоводства [Tajikistan]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Rustam Kalandarov
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: Farrukh Nazarmavloev
Самаранок истифодабарии заминхо барои бунёди богхои интенсиви.………………………………………………………………………
technologies_3677 - Tajikistan
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
land user:
Рахимов Тагаймурод
93 552 30 30
Фермерская хозяйство " Асадулло"
Хуросонский район. хозяйства " Асадулло"
Tajikistan
Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Youth Ecological Center, Tajikistan (Youth Ecological Center, Tajikistan) - Tajikistan1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
Nee
Comments:
Технология является природоохранным проблемы деградации и эрозии земли не приводит.
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
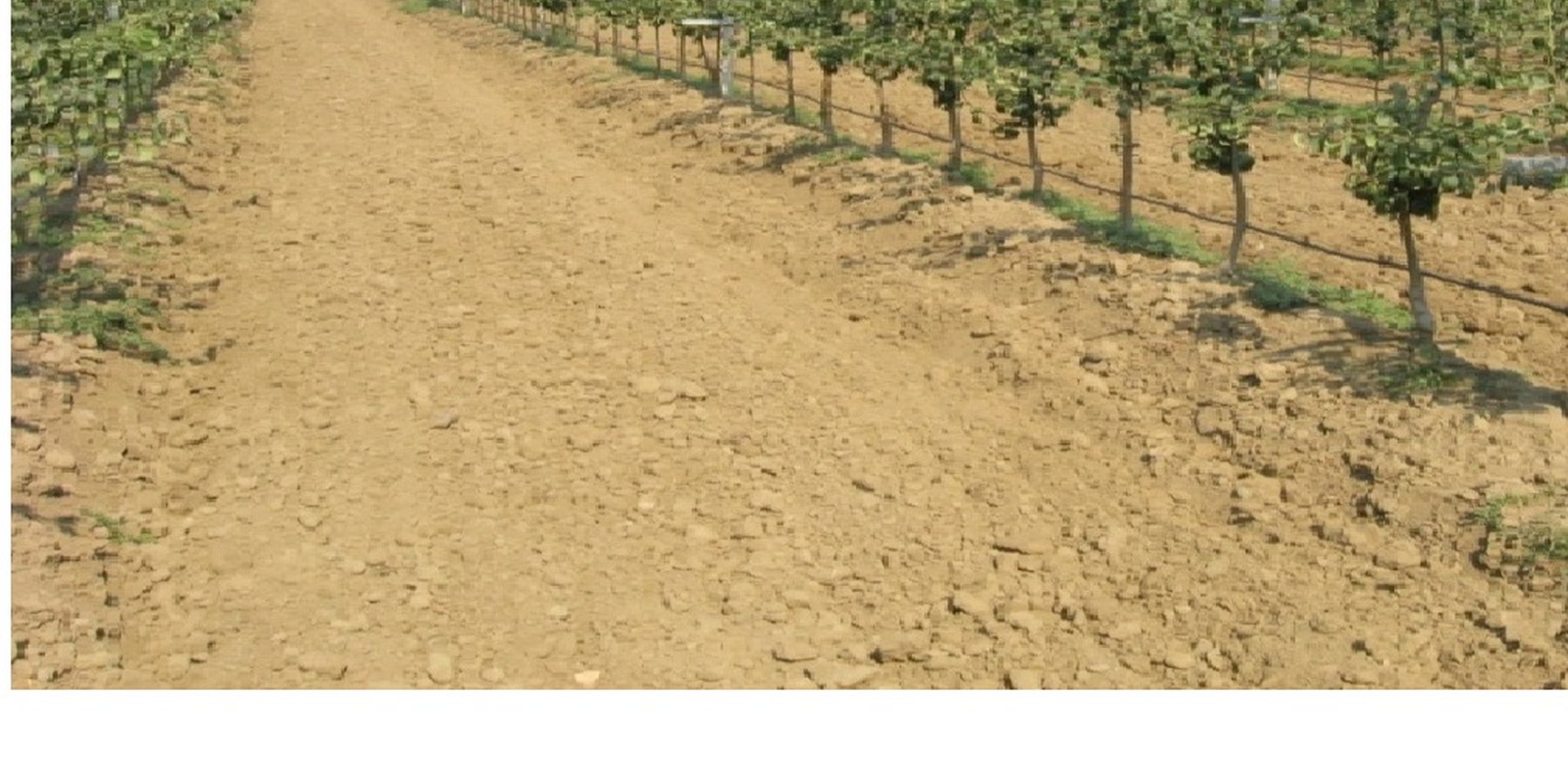
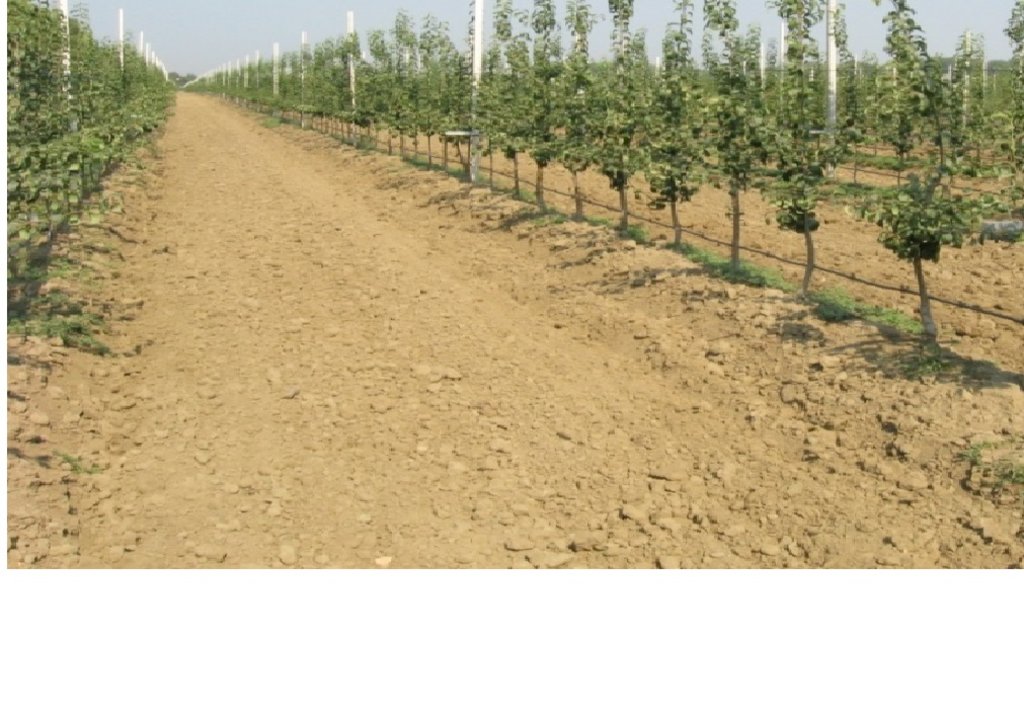
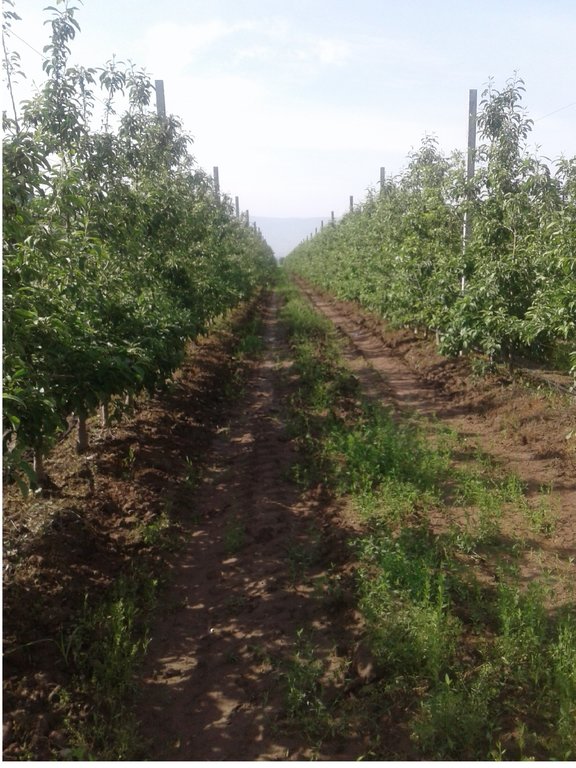
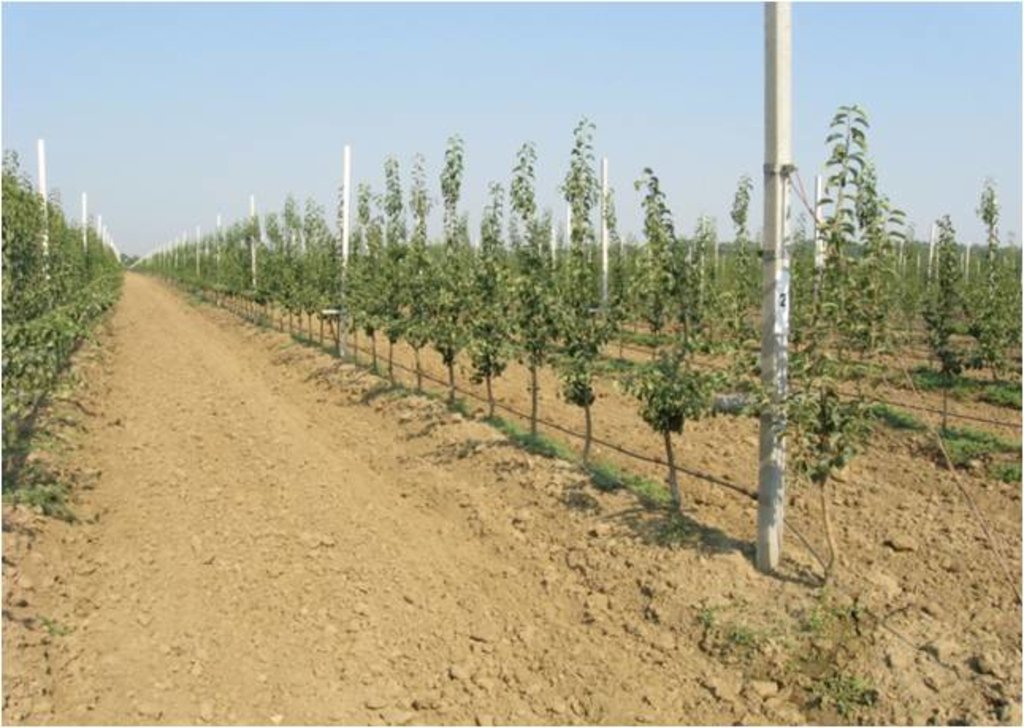
В технологии приводятся данные по эффективному использованию земель под сады путем посадки на 1 га 2083 -2500 шт. саженцев по схеме 4,0 х 1,2м. 4,0 х 1.0 м. и получить от 30 до 40 тонн урожая с сохраняя экосистемы. Технология применялась в фермерском хозяйстве «Асадулло» на площади более 150 га. Природные условия богарные и поливные под капельным орошением сады и виноградники. Землепользователи занимаются в основном садоводствам и виноградарством, от которых получают хорошие доходы.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
Прежде чем начать эту технологию, надо предусмотреть следующие правила: необходимо подобрать участок, исходя из биологических особенностей сорта и подвоя провести тщательно подготовку почвы. Выбранный участок должен соответствовать требованиям культуры и сорта. Уровень грунтовых вод не должен быть выше 1,5-2 м. При определении и выбора участка под закладку интенсивного сада, наличие источника воды для капельного орошения считается самым важным условием. В зависимости от рельефа местности, определяется уровень высоты расположения участка. Интенсивные сады закладывают двумя путями:- на равнинных землях и на гребнях В обоих случаях согласно плану определяют направления рядов. Для лучшего освещения деревьев рекомендуется направить ряды с севера на юг. После определения рядов в первую очередь определяют места столбиков- опор и устанавливают их. Расстояние между столбиками в ряду до 10 м, длина столбика 4 м, а столбиков-упоров в начале и конце ряда должно быть 4,2 м. Столбики изготавливаются из железобетона или из железных труб. В условиях Республики в зависимости от расположения местности над уровнем моря, посадка деревьев проводится в два периода: осенью и весной. В долинах на высотах до 1000-1200 м н.у.м. лучшим для посадки считается осенний период после листопада. Весенняя посадка до распускания почек соответствует поставленной цели. План посадки в интенсивных садах определяется в зависимости от степени роста и развития деревьев. Расстояние между рядами от 2,5 до 4 м, расстояние деревьев в ряду от 0,7 до 1,5 м. До установки столбиков при помощи механического канавокопателя роют канавку для посадки саженцев или после установки столбиков эту работу нужно проводить с одной стороны ряда. Затем по выбранной схеме высаживают деревья. Первое окучивание производится вручную при помощи лопаты, почва утрамбовывается вплотную к корневой системе. Затем саженцы обильно поливаются для обеспечения плотного прилегания почвы к корням и полного обеспечения растений влагой. После посадки саженце, в в зависимости от выбранного типа формы кроны, приступают к их формировке. В интенсивных садах приемлемы следующие типы формировок деревьев: последовательно располагать основные ветви вокруг ствола путем длинной обрезки. Вокруг ствола последовательно располагать основные ветви путем короткой обрезки. Бибаум - последовательное расположение ветвей вокруг проводников. Ежегодно проводится две обрезки весенняя и летняя. Полив проводится капельным орошением. Принцип капельного орошения состоит в формировании луковицы увлажнения в прикорневой зоне дерева, позволяющей системе регулярно поглощать воду и питательные элементы в достаточном количестве. Естественно, оборудование и методика полива должны быть адаптированы типу почвы. В зависимости от типа почвы для формирования луковицы увлажнения рекомендуется проложить две капельных линии или повысить расход капельниц. Для капельного орошения фермерам необходимо иметь оборудование, в том числе водяной насос, фильтры, пластиковые трубы диаметром 50 мм, толщиной 2 мм, пластиковые трубочки диаметром 15 мм. Исследованиями установлено, что при капельном орошении через капельницы для потребности одного дерева расходуется от 5 до 8 литров воды. Урожайность очень высокая можно получить от 30 до 60 тонн плодов. Основная цель сокращение земельной площади. Преимущество в том, что на 1 га размешается от 2000 до 2500 саженцев на против обычной технологии, где на 1 га сажают 270 - 350 саженцев , почти на 80 % получали меньше урожая. Сбор урожая вручную очень удобен. Полив проводится экономно, только капельной системой. Сохраняется экосистема. Сокращается эрозия почвы. Землепользователям технология приемлема подходит для них . Затраты несколько больше зато они в 2-4 раза окупаются пору плодоношения.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
General remarks regarding photos:
Интенсивный сад с использованием карликовых саженцев для эффективного использование земель. Дает очень хорошие результаты.
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Tajikistan
Region/ State/ Province:
Хуросонский район, РРП
Further specification of location:
Участок Фахрабад хозяйство "Асадулло"
Comments:
Участок где применяется технология находится на Юге Таджикистана не далеко от столицы 35 км.
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- 10-50 years ago
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- during experiments/ research
Comments (type of project, etc.):
Научно обоснованная технология применяется эффективна в Таджикистане.
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- conserve ecosystem
- create beneficial economic impact
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Tree and shrub cropping
Main crops (cash and food crops):
Основным культурой является плодоносящий интенсивный сад
Comments:
культурой служит интенсивный карликовые сад которое в настоящем времени интенсивно пользуют в Таджикистане.
If land use has changed due to the implementation of the Technology, indicate land use before implementation of the Technology:
Тип землепользование было зернобобовые культуры. Старые сады и виноградники.
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- full irrigation
Comments:
Технология пользуется на поливных капельном орошение.
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Specify:
Урожай за вегетацию один раз получает.
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- improved ground/ vegetation cover
- improved plant varieties/ animal breeds
- irrigation management (incl. water supply, drainage)
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, indicate approximate area covered:
- 10-100 km2
Comments:
Технология пользуется по все местно по одельным и массивным
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A1: Vegetation/ soil cover
- A3: Soil surface treatment

vegetative measures
- V1: Tree and shrub cover
Comments:
Использованием является древесный многолетние растительности.
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion
Comments:
Использованием капельного орощения предотврашается эрозия почвы.
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
- reduce land degradation
Comments:
Технология предотвращает деградацию почвы.
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
Приведено схема посадка расстояние между кустами 4 х 1.5 м количество наятяжка проволок 4 ряда. формировка саженца.Шланг для капельного орошения. Стойки вставляется каждый 10 м.
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology area
Indicate size and area unit:
Размер плошади расчитовалис на 1га.
If using a local area unit, indicate conversion factor to one hectare:
10000 м. квадрат
Specify currency used for cost calculations:
- US Dollars
Indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (if relevant): 1 USD =:
8.9
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
3,0
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Подготовка земель | Agronomic | осень |
| 2. | Разбивка участок | Agronomic | весна |
| 3. | Копка лунки для посадки саженцев | Agronomic | весна |
| 4. | Посадка саженцев | Agronomic | весна |
| 5. | Установка стойки и натяжки проволок | Agronomic | весна |
| 6. | Агроуход | Agronomic | постоянно |
Comments:
Все расчеты выбрано по тех карте
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Механическая работа | день | 50.0 | 22.2 | 1110.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | Ручная работа | день | 30.0 | 4.5 | 135.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Капельная орощения | 1.0 | 3500.0 | 3500.0 | 100.0 | |
| Plant material | саженцы | шт | 2083.0 | 2.7 | 5624.1 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | Шпалер (стойки) | шт | 250.0 | 2.44 | 610.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | проволоки | м | 2000.0 | 0.54 | 1080.0 | 100.0 |
| Other | 2915.6 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 12059.1 | |||||
If land user bore less than 100% of costs, indicate who covered the remaining costs:
Все затраты покрывается землепользователем
Comments:
Все расчеты приведено рыночным ценами в долларах США.
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Агроуход | Agronomic | постоянно |
Comments:
Все расчеты выбрано по тех карте
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Ручная работа | чел | 15.0 | 4.5 | 67.5 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 67.5 | |||||
If land user bore less than 100% of costs, indicate who covered the remaining costs:
Покрывается землепользоватеоем
4.8 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
Покупка саженцы, установка капельного орошения
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
Осадка выпадает в основном осенью ,зимой и весной.
Indicate the name of the reference meteorological station considered:
ГМС Душанбе
Agro-climatic zone
- semi-arid
Местность полузасушливая поливная зона
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- convex situations
Comments and further specifications on topography:
Рельеф равнина также полу склоны
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
Данных нет
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
> 50 m
Availability of surface water:
medium
Water quality (untreated):
good drinking water
Is water salinity a problem?
Nee
Is flooding of the area occurring?
Nee
Comments and further specifications on water quality and quantity:
Поливная вода Артизианская
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- medium
Habitat diversity:
- medium
Comments and further specifications on biodiversity:
По биоразнообразии встречается древесна кустарничные растительность мендальники , боярки, шиповники травянистые растения полукустарники.
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- subsistence (self-supply)
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- rich
Individuals or groups:
- groups/ community
- employee (company, government)
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
- mechanized/ motorized
Gender:
- men
Age of land users:
- youth
- middle-aged
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Землепользователи иногда пользуют наёмных сил.
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- large-scale
Comments:
Хозяйство является крупным.
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- company
Land use rights:
- open access (unorganized)
Water use rights:
- open access (unorganized)
Comments:
Хозяйство является частным компаниям.
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Comments/ specify:
После применения технологии
crop quality
Comments/ specify:
Улучшилось
Water availability and quality
drinking water availability
Comments/ specify:
Для поливного сооружения стало лучше
drinking water quality
Comments/ specify:
Улучшилось
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
water availability
Comments/ specify:
Накопления воды для полива улучшилось
damage on neighbours' fields
Comments/ specify:
Сократилось
Comments regarding impact assessment:
Технология не влияет на окружность
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | Type of climatic change/ extreme | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | well | |
| seasonal temperature | summer | increase | well |
| annual rainfall | decrease | well | |
| seasonal rainfall | winter | decrease | well |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| local hailstorm | moderately |
| local sandstorm/ duststorm | well |
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| heatwave | well |
| cold wave | well |
| extreme winter conditions | well |
| drought | well |
Comments:
Все связанные с климатом технология успешно справляется
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
Comments:
Получаемые результаты успешно покрывается всеми затратами.
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- 1-10%
If available, quantify (no. of households and/ or area covered):
Частная хозяйства площадь пока более 150 га
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 10-50%
Comments:
Технологию применяют фермеры, которые сильно заинтересованные.
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
Nee
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| Эффективна использование земель. Снижения затраты поливного воды через капельный орошения. |
| За счет количество кустов на 1\га увеличивается урожай |
| Удобно собирать Удобно обрезку и проводить агротехнические работы |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| Снижения затраты |
| увеличивается урожай |
| Удобно собирать, проводить агротехнические работы |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| срок эксплуатации 15-20 лет |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
число 5
- interviews with land users
5
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Рекомендации по закладке интенсивных садов с использованием капельного орошения. Ахмедов Т.А., Гулов С.М., Камолов Н., Сафаралиев Х.
Available from where? Costs?
0.5 USD
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules