Снижения водопотрибление цитрусовых культур в типличных условиях [Tajikistan]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Rustam Kalandarov
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: Farrukh Nazarmavloev
Истифодаи самараноки об дар лимонхонахо.
technologies_3689 - Tajikistan
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
land user:
Сангинов Бахром бобоевич
917 956 763
республика Таджикистан. г. Душанбе, ул. Рудаки 17 а.
Tajikistan
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Environmental Land Management and Rural Livelihoods (ELMAR)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Youth Ecological Center, Tajikistan (Youth Ecological Center, Tajikistan) - Tajikistan1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
14/03/2018
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Nee
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
Nee
Comments:
Технология не приводит к деградации зхемли является природоохранным.
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
Дождевальная технология облегчает ручной труд фермера и улучшет процес фотосинтеза путем смывания с листьев пыля за счет этого рост и развитие растении цитрусовых культур.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
Одновременно повышается урожайность и качеств, плодов а также экономится вода при поливе и снижается эрозия почвы. Эта технология не применялась ранее в производстве оно находится в стадии доработки в опытном хозяйстве «Навбахор» Рудакинского района и дает хорошие результаты. Преимуществ заключается в том, что уменьшается объем рабочей силы, трудоемкая работа механизирована. Основной результат деятельности технологии в эконом воды промывке листьев и полива. Облегчается применение ядохимикатов во время опрыскивания также не происходит деградации почвы. Система дождевания в теплицах предназначен для полива растений сверху и применения препаратов против вредителей и болезней а также для внекорневой подкормки цитрусовых культур. Система используется специальными распылительными насадками, которые подключаются к шлангу, по которому подается вода. Для этой технологии необходимо применять трубы, дождевалки на каждые 2 метра, краники, фильтр, насос, емкость для воды (бочка). Одновременно можно установить капельное орошение, которое можно использовать в лимонариях.
Эта технология землепользователям нравится, поскольку одновременно с одним опрыскиванием можно провести четыре операции: промывку против пыли, внекорневую подкормку с применением минеральных удобрении опрыскиванием ядохимикатом против болезней и вредителей и полив.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Tajikistan
Region/ State/ Province:
РРП
Further specification of location:
Участок "Навбахор"
Comments:
Технология возделовалось на опытном участке "Навбахор" Не долек от центра столицы.
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
Indicate year of implementation:
2017
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- during experiments/ research
Comments (type of project, etc.):
Технология разработано на основе дождевания овощных культур. Как научная навизна оно еще не распространен, но научно обоснованно.
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- conserve ecosystem
- create beneficial economic impact
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Tree and shrub cropping
Main crops (cash and food crops):
Основным сельскохозяйственной культурой является цитрусовые культуры Лимон.
Comments:
Основным культурой является лимон и все цитрусовые культуры которые являются многолетные кустарниковые растения пользуются как сельхоз продукцией.
If land use has changed due to the implementation of the Technology, indicate land use before implementation of the Technology:
До применения технологии было также лимонная плантация.
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- full irrigation
Comments:
В основном лимоны выращиваются на поливных зонах земледелии в частности тепличных условиях.
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Specify:
Урожай получают один раз за вегетации.
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- improved ground/ vegetation cover
- minimal soil disturbance
- cross-slope measure
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- applied at specific points/ concentrated on a small area
Comments:
Технология новая распределения еще неразвитая разработывается но эффективная.
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A1: Vegetation/ soil cover

vegetative measures
- V1: Tree and shrub cover

structural measures
- S7: Water harvesting/ supply/ irrigation equipment
Comments:
Рамках технологии выполняется агрономическая растительность и инженерная установка насосы трубы, дождевальные и капельные устройства.
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion
Comments:
Основным решения проблем эконом поливного воды сокращения эрозии почвы.
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
Comments:
Технология является для экономно использования воды путем дождевания и капельного полива также сокращения деградации и эрозии почвы.
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
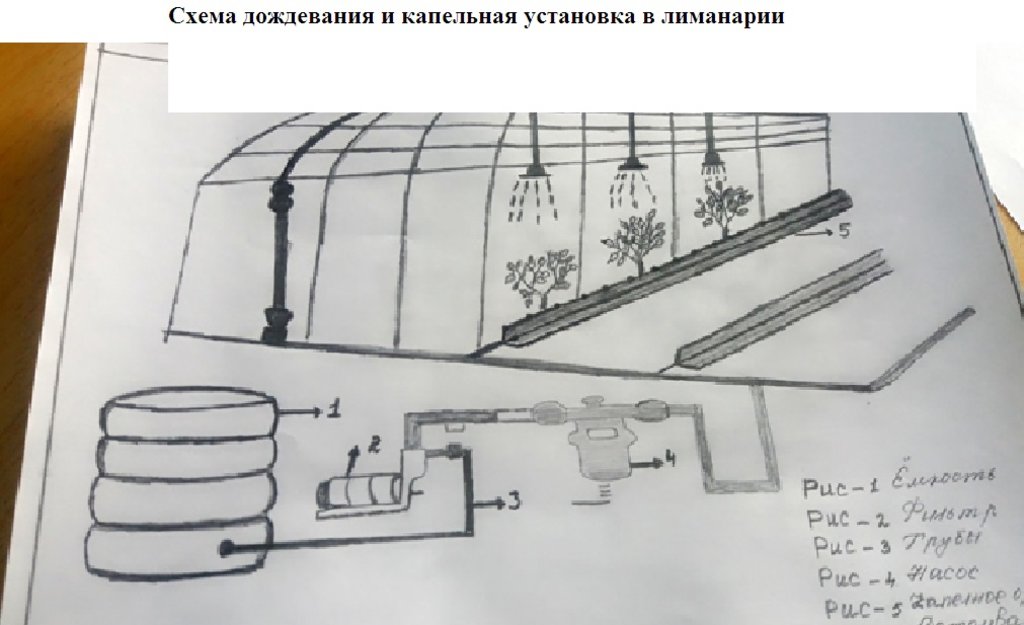
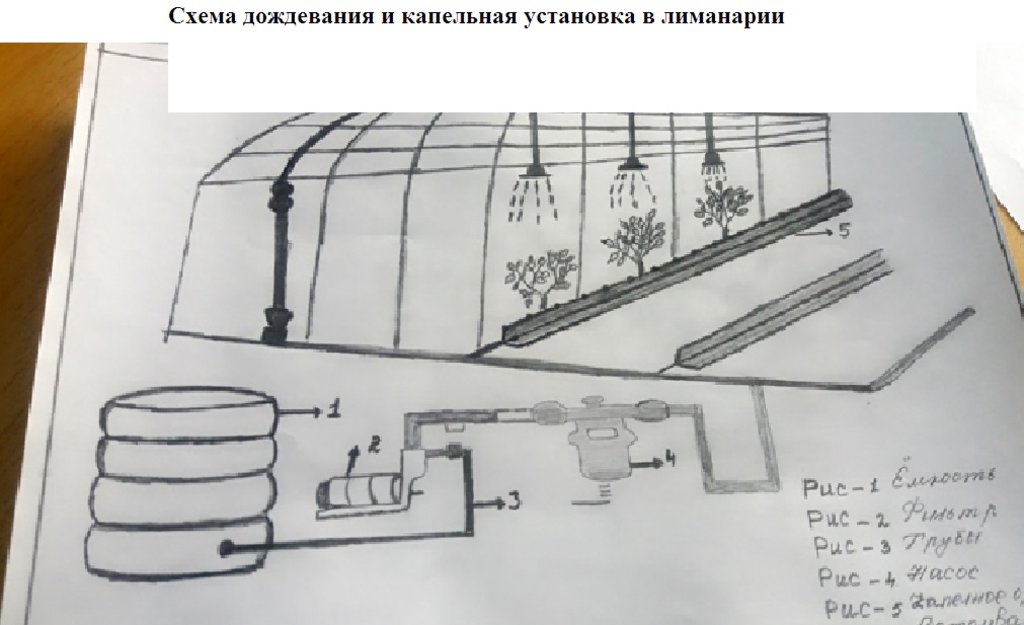
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
На схеме приведено данные по технологии возделывания дождевальной установки в лимонад. Основные материалы: Насос, емкость, шланг. шланг для капельного опрощения , дождевальные установка, фильтр, краники.
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology area
Indicate size and area unit:
На 1\га.
If using a local area unit, indicate conversion factor to one hectare:
10000 м. квадрат.
Specify currency used for cost calculations:
- US Dollars
Indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (if relevant): 1 USD =:
8.9
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
3.0
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | пласмассовые трубы | Structural | март |
| 2. | Муфта | Structural | март |
| 3. | Филтер | Structural | апрел |
| 4. | Насос | Structural | В течение установки |
| 5. | насадка | Structural | В течение установки |
| 6. | краники | Structural | во время установки |
| 7. | клапан | Structural | во время установки |
| 8. | Шланг для капельного орошения | Structural | Вовремя установки |
| 9. | Цистерна (Бочка для воды) | Structural | Вовремя установки. |
Comments:
Необходимые материалы для установки подготавливают до постройки дождевального системы на готовых лимонариях. Срок не иметь значения.
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Ручная работа | день | 20.0 | 5.5 | 110.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Труба ,шланг, филтер | 1.0 | 1080.0 | 1080.0 | 100.0 | |
| Plant material | саженцы лимона | шт | 133.0 | 3.3 | 438.9 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | Стойка трубы | день | 133.0 | 3.3 | 438.9 | 100.0 |
| Other | 510.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 2067.8 | |||||
If land user bore less than 100% of costs, indicate who covered the remaining costs:
Все затраты покрывается землепользователем
Comments:
Основная необходимые оборудования для дождевания расходы приведена по расчету в долларах.
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
Comments:
Необходимые материалы для установки подготавливают до постройки дождивального системы на готовых лимонариях. Срок не иметь значения.
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Ручная работа | день | 20.0 | 5.5 | 110.0 | 19.0 |
| Construction material | стойка трубы. и.т.д. | м | 30.0 | 3.1 | 93.0 | |
| Other | 510.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 203.0 | |||||
If land user bore less than 100% of costs, indicate who covered the remaining costs:
Все затраты покрывается землепользователем.
Comments:
основная необходимые оборудования для дождевания расходы приведена по расчету в долларах.
4.8 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
Наиболее значимые затраты это строй материалы, насос,труба, шланги , и.т.д.
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
осадка выпадает на долинных местах не очень много в основном где выращивается лимоны это Южная и восточная часть по этому осадка не очень играет важную роль
Indicate the name of the reference meteorological station considered:
ГМС, г.Душанбе.
Agro-climatic zone
- semi-arid
Зона выращиваемый лимона в основном засушливая жаркие регионы.
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- not relevant
Comments and further specifications on topography:
Лимонарники можно построит не зависимо от рельефа на любой подходящий землю, только надо траншея.
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
Данные по почвам нет
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
5-50 m
Availability of surface water:
medium
Water quality (untreated):
good drinking water
Is water salinity a problem?
Nee
Is flooding of the area occurring?
Nee
Comments and further specifications on water quality and quantity:
Вода доступная проточная, не соленная питьевая. Можно полить растений.
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- medium
Habitat diversity:
- medium
Comments and further specifications on biodiversity:
Биоразнообразия в сельском местности обычно древесно кустарниковые травянистые растительность.
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- subsistence (self-supply)
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- rich
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
Gender:
- men
Age of land users:
- middle-aged
- elderly
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Основной земле пользователи это домохозяйства, организации.
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- medium-scale
Comments:
Лимонарники обычно строят землепользователи на не более 0,5 га
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- state
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- communal (organized)
- individual
Water use rights:
- communal (organized)
Comments:
Землепользователи часто бывает собственность но с ограничением земли. арендная, или индивидуальная.
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Comments/ specify:
До применение технологии расход воды больше и много ручных работ после применения вся это сокрашается на 50 %
crop quality
Comments/ specify:
До применения качество намного хуже было после применения стало лучше на 60%
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
Comments regarding impact assessment:
Технология за пределами территории никаких влияние на природных ресурсов не имеет.
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | Type of climatic change/ extreme | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | well | |
| seasonal temperature | summer | increase | well |
| annual rainfall | decrease | well | |
| seasonal rainfall | winter | decrease | well |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| local hailstorm | well |
| local sandstorm/ duststorm | well |
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| heatwave | well |
| cold wave | moderately |
| extreme winter conditions | moderately |
| drought | well |
Comments:
Экстримальные явления погоды типа как жара засуха меньше влияет. Только зимные холода влияеи умерено из того что теплица обогревается.
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
Comments:
Полученные результаты сопоставим с текущем и расходами окупается.
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- 1-10%
If available, quantify (no. of households and/ or area covered):
Число домохозяйств под этим технологии пока нет это все научно исследовательская эксперимент который даёт уже хорошие результаты.
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
Comments:
Технология только запускается . Если кто может по своей инициативе может построит
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
Nee
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| Эконом воды, уменьшения ручных работ |
| Одновременно проведения обработки против вредителей и болезни и полив дождевания. |
| поддерживает дисбаланс растений. |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| эконом воды, уменьшения ручных работ |
| Одновременно проведения обработки против вредителей и болезни и полив дождевания |
| поддерживает дисбаланс растений. |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| дороговизна оборудования и материалы. |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| дороговизна оборудования и материалы. |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules