This is an outdated, inactive version of this case.
Go to the current version.
Technologies
Inactive
New SLM Technology [Tajikistan]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: MIZROBSHO AMIRBEKOV
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: Farrukh Nazarmavloev
technologies_3701 - Tajikistan
View sections
Expand all Collapse all
Completeness: 76%
1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
SLM specialist:
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Mountain Societies Development Support Programme, TajikistanName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (GIZ) - Germany1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
Nee
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches

Soil management initiative [United Kingdom]
An independent organisation that promotes the adoption of appropriate soil management practices, especially conservation agriculture, within England.
- Compiler: Alastaire Leake
2. Description of the SLM Technology
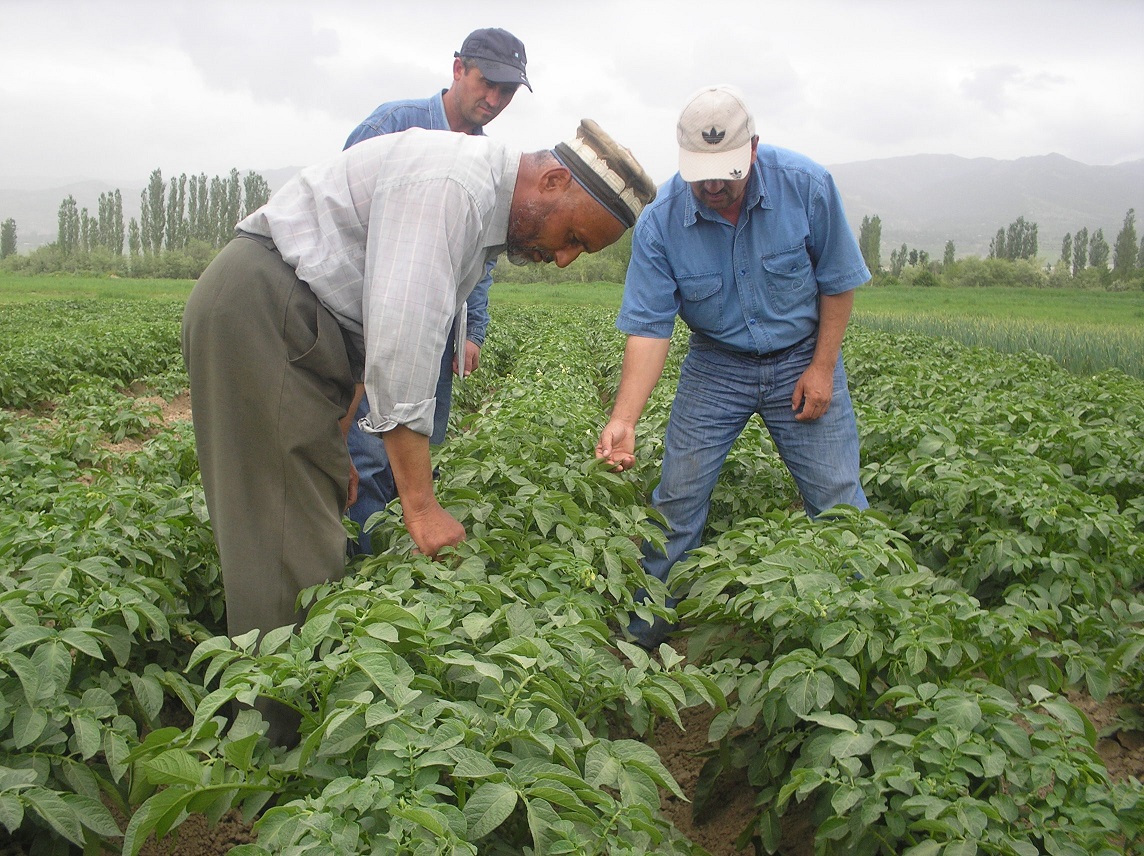
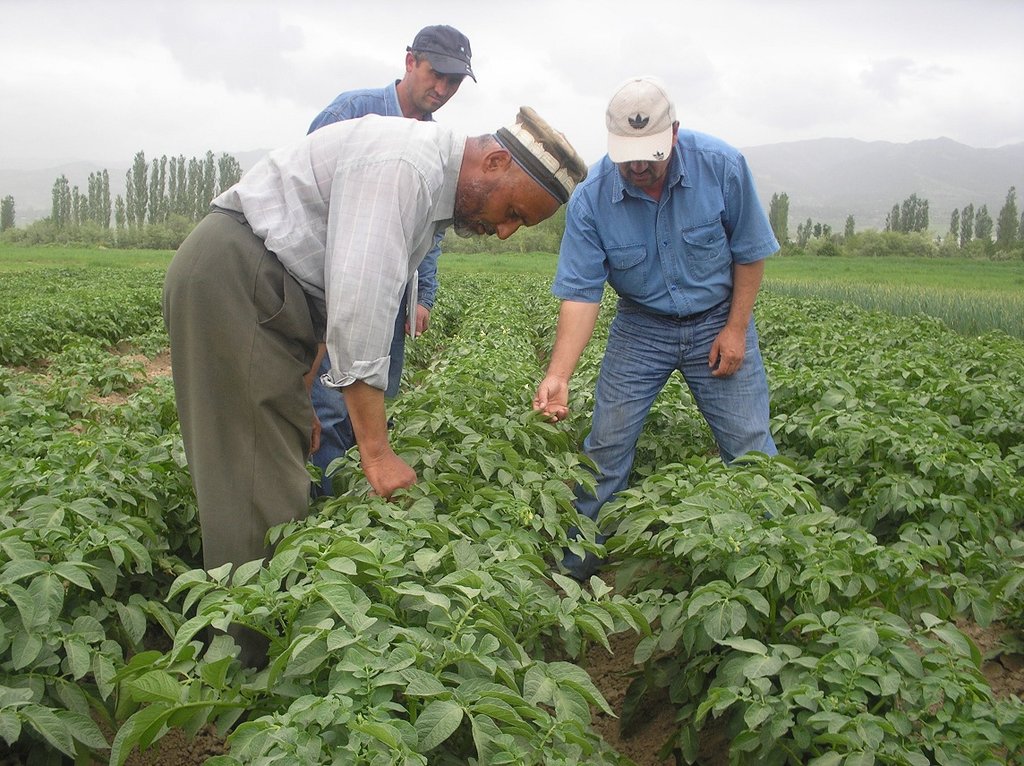
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Tajikistan
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through projects/ external interventions
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- conserve ecosystem
- preserve/ improve biodiversity
- adapt to climate change/ extremes and its impacts
- create beneficial economic impact
- create beneficial social impact
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
- Perennial (non-woody) cropping
- Tree and shrub cropping
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- full irrigation
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- rotational systems (crop rotation, fallows, shifting cultivation)
- integrated crop-livestock management
- improved ground/ vegetation cover
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- applied at specific points/ concentrated on a small area
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A1: Vegetation/ soil cover
- A2: Organic matter/ soil fertility

management measures
- M1: Change of land use type
- M2: Change of management/ intensity level
- M3: Layout according to natural and human environment
- M4: Major change in timing of activities
- M5: Control/ change of species composition
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

chemical soil deterioration
- Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content (not caused by erosion)
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- reduce land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology unit
Specify currency used for cost calculations:
- US Dollars
Indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (if relevant): 1 USD =:
8.94
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | None | Agronomic | None |
| 2. | None | Agronomic | None |
| 3. | None | Agronomic | None |
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | None | None | 3500.0 | 0.2 | 700.0 | 24.0 |
| Labour | None | None | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 0.7 |
| Labour | None | None | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 0.7 |
| Equipment | None | None | 6.0 | 10.0 | 60.0 | |
| Plant material | None | None | 3500.0 | 0.55 | 1925.0 | 66.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | None | None | 250.0 | 0.45 | 112.5 | 3.8 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | None | None | 150.0 | 0.45 | 67.5 | 2.3 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 2905.0 | |||||
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | None | Agronomic | None |
| 2. | None | Agronomic | None |
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | None | None | 5.0 | 10.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | None | None | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | None | None | 6.0 | 25.0 | 150.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 250.0 | |||||
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- not relevant
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- medium (loamy, silty)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
5-50 m
Availability of surface water:
good
Water quality (untreated):
good drinking water
Is water salinity a problem?
Nee
Is flooding of the area occurring?
Nee
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- high
Habitat diversity:
- high
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial
Off-farm income:
- 10-50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
- mechanized/ motorized
Gender:
- women
- men
Age of land users:
- middle-aged
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- medium-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- state
Land use rights:
- leased
Water use rights:
- communal (organized)
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop quality
decreased
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
very positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- 1-10%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 10-50%
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
Nee
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
- interviews with land users
- interviews with SLM specialists/ experts
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks

Soil management initiative [United Kingdom]
An independent organisation that promotes the adoption of appropriate soil management practices, especially conservation agriculture, within England.
- Compiler: Alastaire Leake
Modules
No modules