Agro-forestry [India]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Unknown User
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Kaadu, Vilai, Thottam (Tamil)
technologies_1083 - India
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
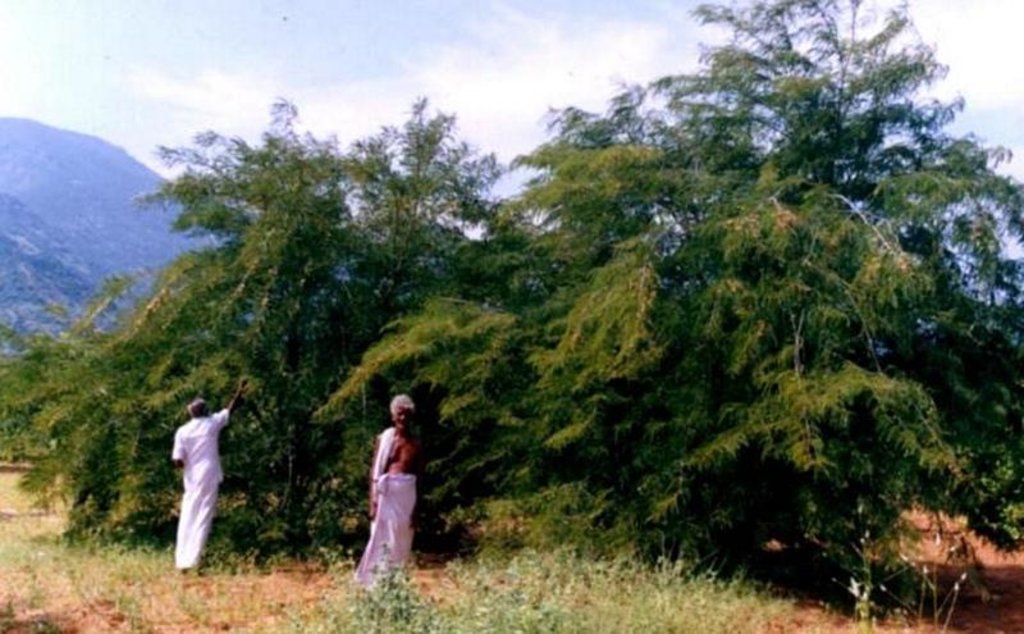
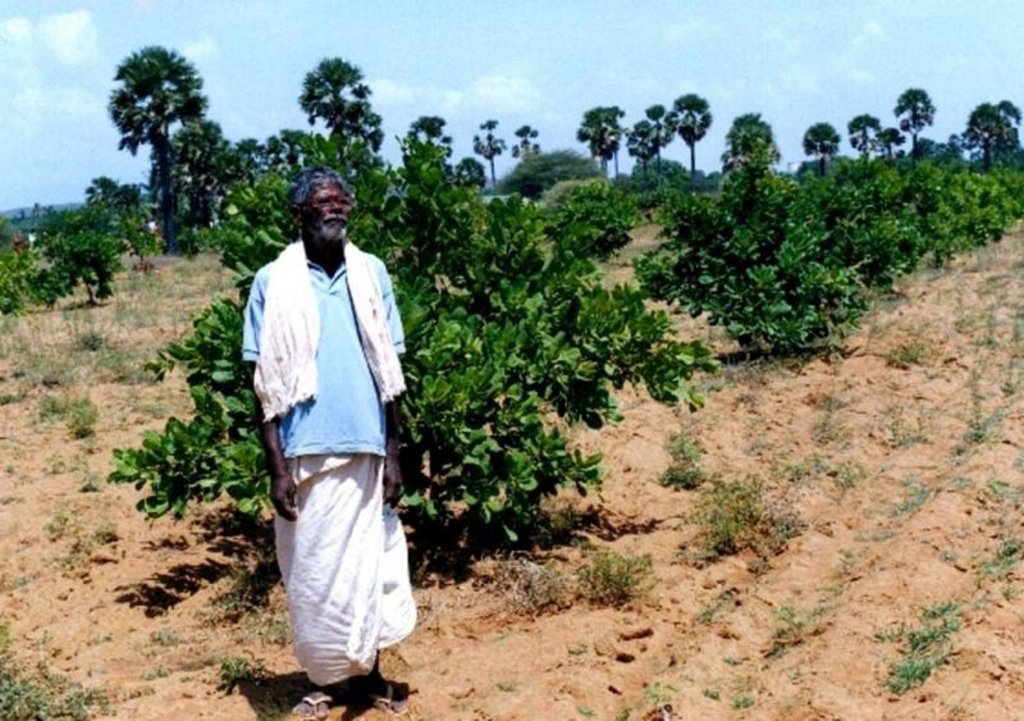
Development of degraded lands through plantation of productive tree species for long term benefit (conservation and economic) and cultivation of intercrop for short term benefit.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
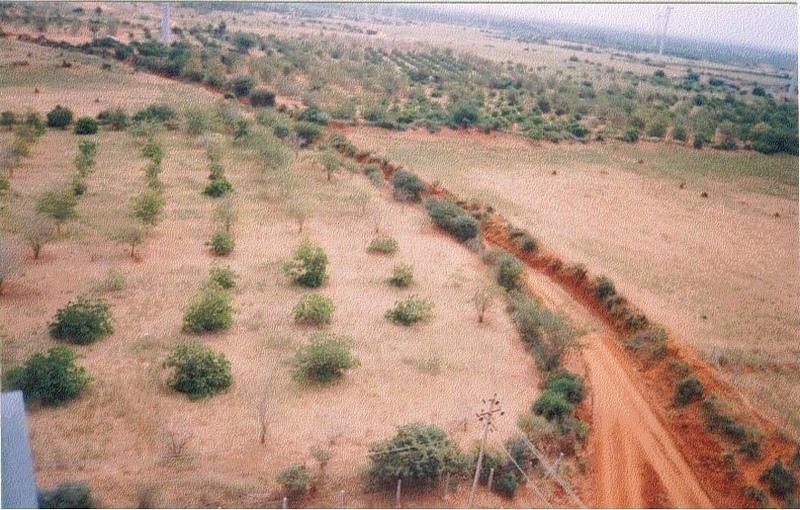
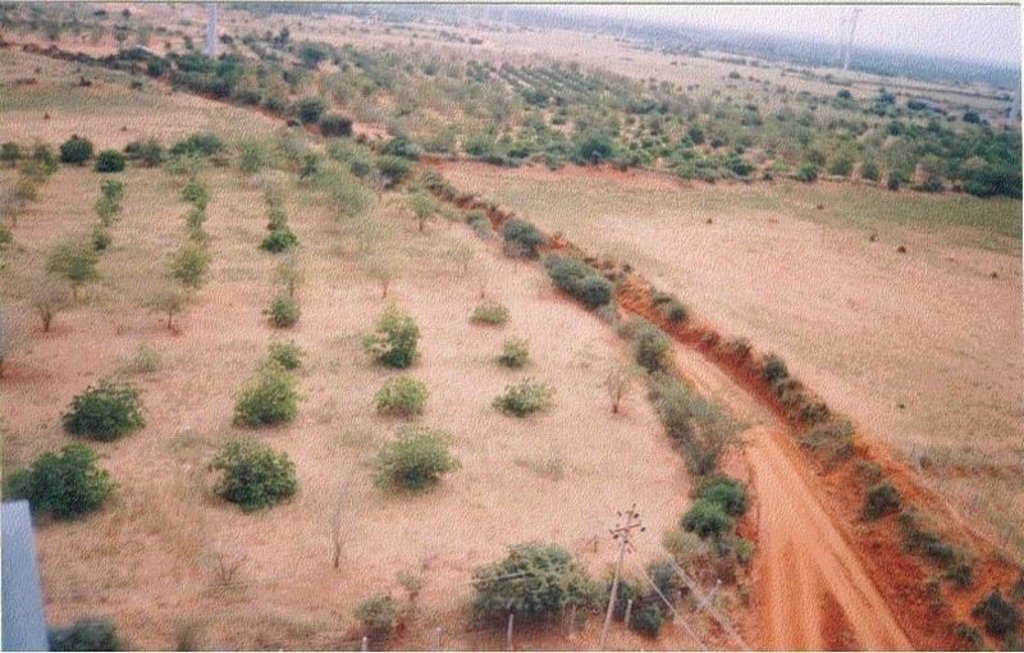
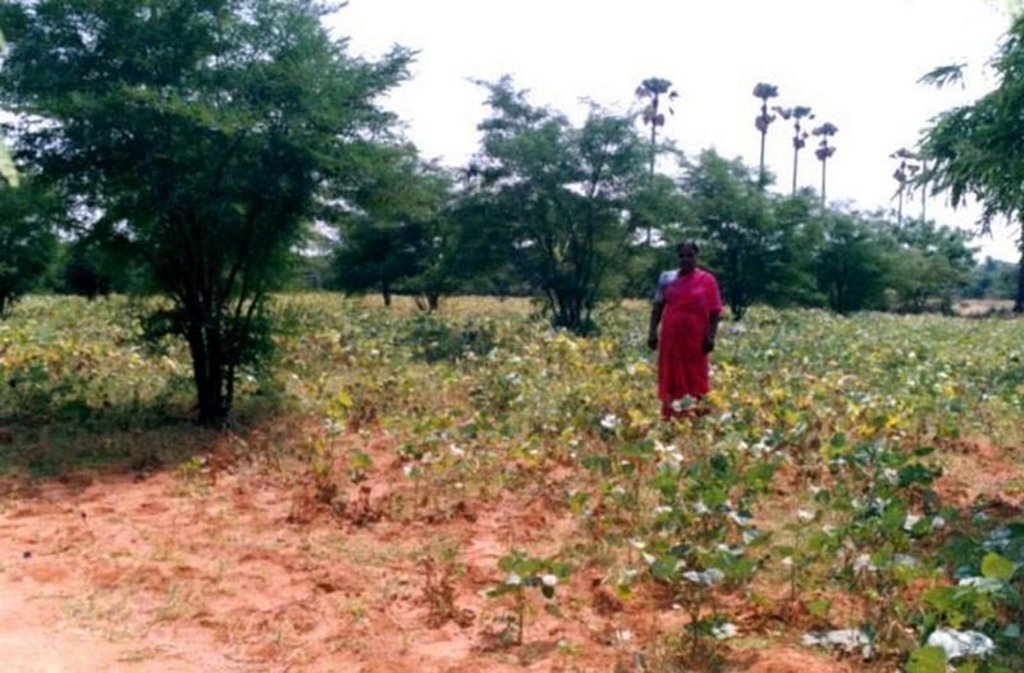
The technology can be described as a combination of tree cultivation ( mainly horticulture species) along with intercrop of pulse crops on degraded private lands, supported by in-situ measures for soil and water conservation. The supportive technology required is provision of water for protective irrigation during establishment phase.
Purpose of the Technology: the technology serves the folowing purposes 1. Short and long term economic benefits to land owners 2. Employment generation leading to reduced migration 3. Conservation of soil and water through vegetative and mechanical measures.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: 1. Community organisation, formation of Village Development Association, Identification and training of beneficiaries 2. Delineation of micro-watersheds and plantation blocks. 3. Establishment of farmers's nurseries 4. Land preparation, sinking bore-well, plantation and inter-cropping 5. Watch and ward.
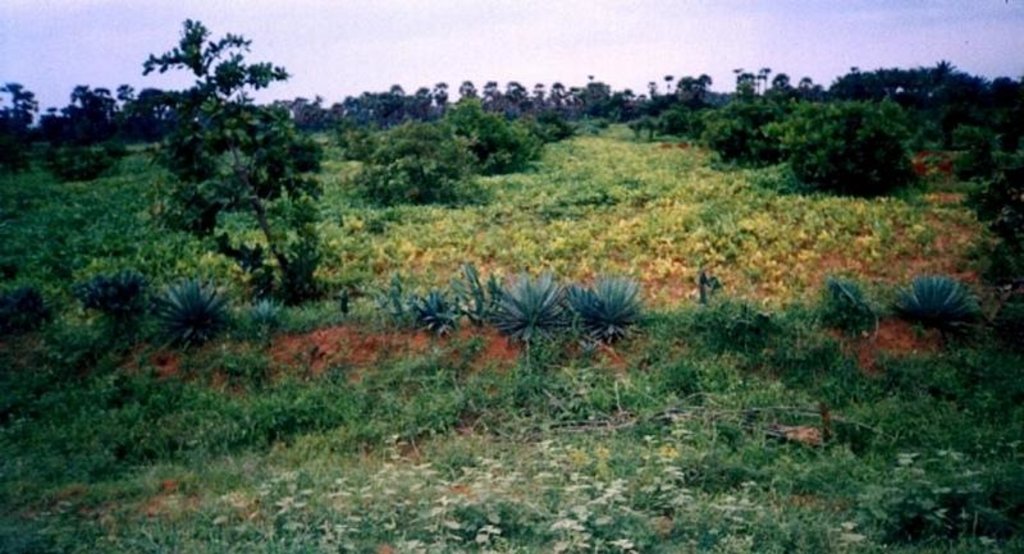
Natural / human environment: The environment is semi-arid, drought prone and subject to wind erosion. Soil depth is good.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
India
Region/ State/ Province:
Tamilnadu
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, specify area covered (in km2):
3.83
Comments:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 3.83 km2.
The area is predominantly degraded land affected by wind erosion. The annual rainfall is <600 mm, however distribution is erratic resulting in drought conditions. People are mostly small farmers engaged in rainfed agriculture, however large areas have been abandoned due to frequent crop failure. The technology has been applied in a gross area of over 300 sq.km.
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- more than 50 years ago (traditional)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through projects/ external interventions
Comments (type of project, etc.):
The technology evolved out farmers suggestions and project experiences while implementing the shelter programme to combat wind erosion.
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
Ja
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- Agroforestry

Cropland
- Annual cropping
- Tree and shrub cropping
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- legumes and pulses - beans
- legumes and pulses - other
- oilseed crops - groundnuts
- euphorbia sp.
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- cashew
- fruits, other
- mango, mangosteen, guava
- Tamarandus indicus, Emblica officianalis
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Specify:
Longest growing period in days: 100 Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Jan

Forest/ woodlands
Type of tree:
- Azadirachta indica
- Albizia lebeck
Comments:
Crop: agace, euphorbia sp.
Trees/ shrubs species: Azadirachta indica, Albizia lebeck
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Anacardium occidentale, Tamarandus indicus, Emblica officianalis, Mangifera incica
Other species: Phaseolus mungo, Arachis hypogea
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Uncontrolled grazing on un-cultivated lands, abandonment of fields by poor farmers due to recurrent crop failure as a result of drought.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Crop lands are not economocal to cultivate due to recurrent crop failure as a result of drought. This has lead to abandonment of fields and increase in numbers of small livestock which are left free to graze.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: The area is single cropped and hence only one food crop is taken per year.
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- mixed rainfed-irrigated
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- agroforestry
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
Comments:
Type of agronomic measures: better crop cover, mixed cropping / intercropping, mulching, pits, deep tillage / double digging
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion
- Wg: gully erosion/ gullying

soil erosion by wind
- Et: loss of topsoil
Comments:
Main type of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
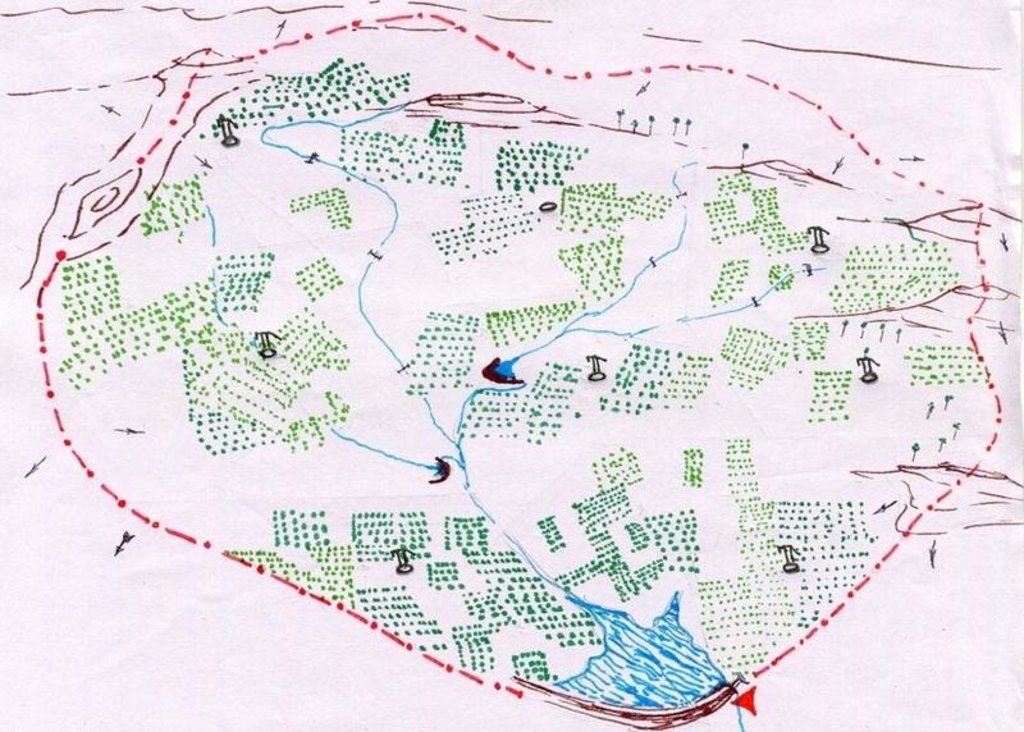
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
Technical Drawing Agro-forestry
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, reduction in wind speed
Better crop cover
Material/ species: trees + legume crops
Quantity/ density: 125 trees/
Remarks: Block plantation/ intercorp
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: trees + legume crops
Quantity/ density: 125 trees/
Remarks: Block plantation/ intercorp
Mulching
Material/ species: soil mulch
Quantity/ density: 125 basins
Remarks: 1 m. diameter basin per tree
Agronomic measure: vegetative hedges
Material/ species: agace, euphorbia sp.
Quantity/ density: 15 cm. Spa
Remarks: Along field boundries
Pits
Remarks: 125 pits/ha., 9 m. spacing. 45*45*45 cm for local species & 60*60*60 cm for grafts.
Deep tillage / double digging
Remarks: disc ploughing before pitting in first year, tiller ploughing annually at sowing of intercorp..
Trees/ shrubs species: Azadirachta indica, Albizia lebeck
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Anacardium occidentale, Tamarandus indicus, Emblica officianalis, Mangifera incica
Other species: Phaseolus mungo, Arachis hypogea
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 3.00%
Change of land use type: open grazing, cropping to agro-forestry
Change of land use practices / intensity level: open access to protected
Layout change according to natural and human environment: borewell blocks formed as per human environment but within watershed boundary.
Control / change of species composition: scrub clearance followed by plantation of agro-horticulture species.
Other type of management: VDA established - to manage all activities at village level
Author:
D. Samraj, Tiruneveli, Tamilna
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
other/ national currency (specify):
Indian Rupee
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
48.85
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
1.00
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Nursery raising | May - Nov |
| 2. | Planting in pits | Oct -Dec, onset of monsoon |
| 3. | Life watering | immediately after plantation |
| 4. | Planting of vegetative hedges | Oct - Dec |
| 5. | Sowing of intercrop (broadcasting, dibbling) | Premonsoon-groundnut, monsoon-legumes |
| 6. | Application of FYM to intercrop | September during tiller ploughing |
| 7. | Selection of village as per criteria | Mar/Apr, dry season |
| 8. | Rapport building, awareness generation | |
| 9. | VDA formation | April / May |
| 10. | Development of watershed plan including agroforestry | May / June |
| 11. | Trainings for VDA, farmers, nursery etc. | Jun - Aug |
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
Comments:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | scrub clearance | Sept/Oct,dry season / once before planting |
| 2. | deep ploughing | Oct/Nov,onset of monsoon / once before planting |
| 3. | pitting | Oct/Nov / once before planting |
| 4. | manuring | Oct/Nov / once before planting |
| 5. | filling pits, planting, forming basins | Nov / once before planting |
| 6. | life watering | Nov / after planting |
| 7. | tiller ploughing & sowing | Oct/Nov / annually after onset of monsoon |
| 8. | maintenance of tree basins | Oct / after annual tiller ploughing |
| 9. | Periodical watering | dry months 1st year /weekly |
| 10. | Weed removal | Nov / Dec /once during annual crop |
| 11. | Application of pesticides | Dec - Feb /as necessary |
| 12. | Pruning | Nov /annually |
| 13. | Casualty replacement | Nov /One year after plantation |
| 14. | Monitoring by VDA | - / monthly |
| 15. | Hand pump maintenance | / as required |
| 16. | Protection against animals | Year one / full time |
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
Comments:
- The costs were calculated for establishment of one block (average area 12.5 ha.) of horticulture plantation with project support. The agriculture component was implemented by farmer with project support for seeds during first monsoon and tiller ploughing during second monsoon.
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
- Establishment of the technology requires high labor input, specially for watering and watch & ward, which adds significantly to the cost. - Presence of hard pan necessiates deep ploughing with machinery. - Horticulture tree species were selected over forest species.
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
680 mm, however the rainfall over the past few years has been < 500 mm.
Agro-climatic zone
- semi-arid
Since past few years arid conditions prevail in the area
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Comments and further specifications on topography:
Landforms: Plateau/plains (level lands lying between hill slopes of Western mountain range & East coast of south India.)
Slopes on average: Flat (level land with some gullies passing through (originating in upper hilly area))
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
Soil depth on average: Moderately deep (ranked 1) and deep (ranked 2, patches of deep soil)
Soil texture: Medium (sandy loam)
Soil fertility: Medium (loss of top soil due to erosion)
Topsoil organic matter: Medium (originally low before agro-forestry)
Soil drainage/infiltration level: Medium (presence of hardpan below six inch depth. However, no waterlogging is observed due to runoff.)
Soil water storage capacity: Medium (has improved due to deep ploughing post treatment)
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Off-farm income:
- 10-50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- poor
- average
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
11% of the land users are rich and own 18% of the land (large holdings > 2 ha.).
50% of the land users are average wealthy and own 56% of the land (holdings of 1 to 2 ha.).
39% of the land users are poor and own 26% of the land (holdings < 1 ha.).
Off-farm income specification: Off farm sources are; poor - rolling beedis (locally made cigarettes), daily wage labor in fields and brick kilns. Average / rich; Business, livestock.
Level of mechanization: Manual labour (ranked 1, pitting, planting, watering, cultivating, watch and ward), mechanised (ranked 2, deep ploughing, tiller ploughing, drilling borewell) and animal traction (ranked 3, ploughing)
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- individual
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly negative
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly negative
Long-term returns:
very positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
Comments:
99% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
284 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
1% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
2 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Farmers are purchasing seedlings for plantation on their fields in small patches around existing water sources - Farmers who did not participate initially are now expressing a desire to treat their lands under the project.
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Review reports.
Available from where? Costs?
Chief Engineer, Agriculture Engineering Department, Anna Salai-439, Nandanam, Chennai-600035
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Project Implementation Plan. 2001.
Available from where? Costs?
Programme Coordinator, WDCU, 11/1 Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi-110016.
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Participatory Impact Evaluation. 2001.
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules