Mise en défens [Madagascar]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Harifidy RAKOTO RATSIMBA
- Editors: Felana Nantenaina RAMALASON, Dimby RAHERINJATOVOARISON, Siagbé Golli, Tahiry Ravivonandrasana, Natacha Rabeary, Tabitha Nekesa, Ahmadou Gaye
- Reviewers: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Kirihitrala arovana, Kirihitr'ala arovana ka tsy kitihana
technologies_6473 - Madagascar
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
land user:
RAZANIZAKASON Albert Ferdinand
Madagascar
land user:
RAZAFINIRINA Nomenjanahary Daniel (ZAFY)
Madagascar
land user:
ANGELINE
Madagascar
land user:
FIADANA
Madagascar
land user:
VILISOA
Madagascar
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
Nee
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
La mise en défens consiste à sanctuariser une zone que le ou les propriétaires et la population aux alentours acceptent de ne plus cultiver ni exploiter en optant pour la régénération naturelle du milieu (mise en défens passive) ou à l'enrichissement de l’espace notamment avec des essences forestières (mise en défens active). C'est une mesure de conservation qui nécessite l’implication de la collectivité dans la protection de la zone de mise en défens contre les passages de feu et la divagation du bétail.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
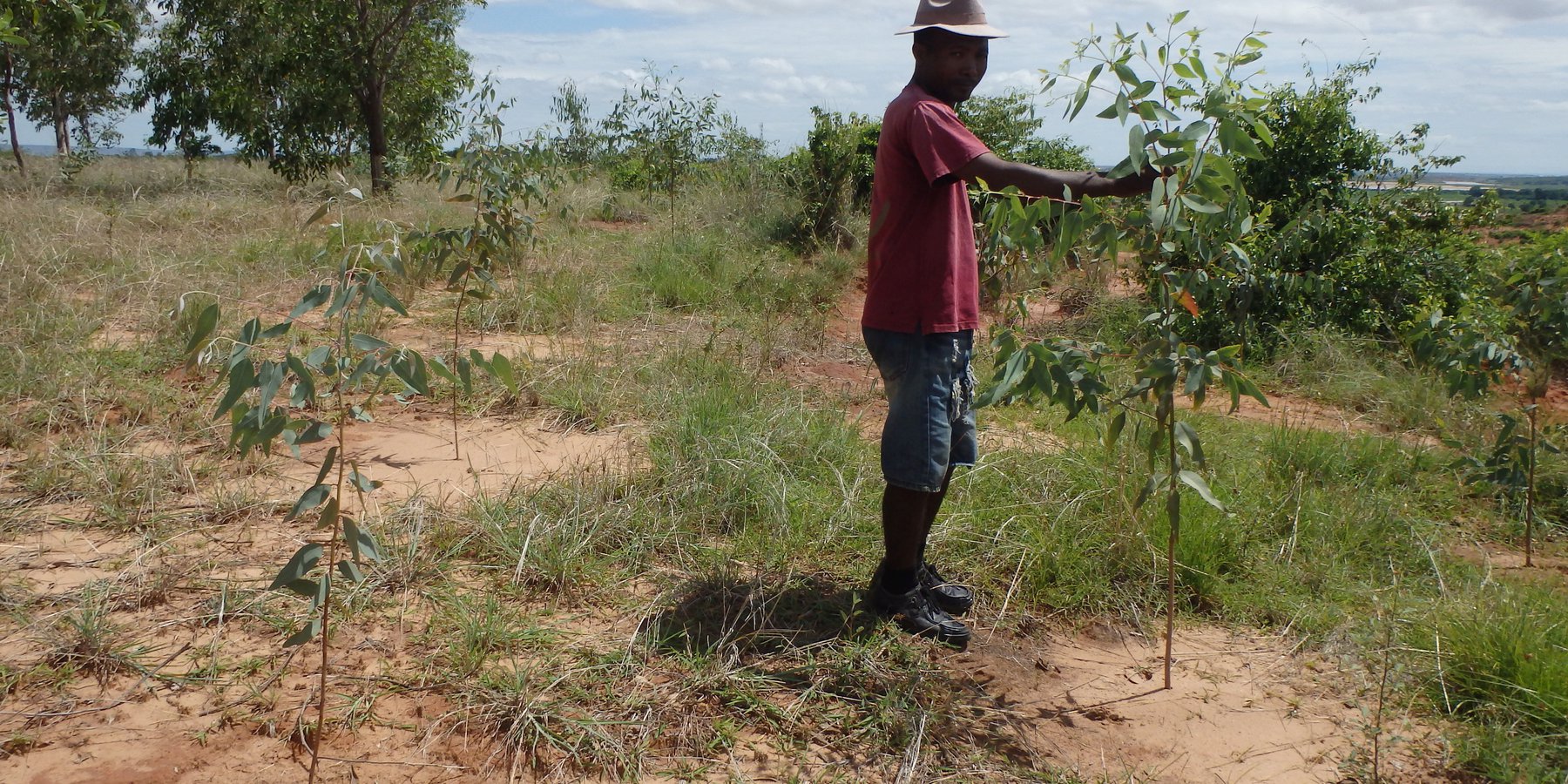
La mise en défens se pratique sur les parties sommitales et les pentes fortes où il est déconseillé de cultiver en raison de risques d’érosion. La mise en défens passive consiste à ne pas exploiter une zone forestière et à favoriser la régénération naturelle du milieu tout en le protégeant des passages de feu et de la divagation du bétail. Tandis que la mise en défens active consiste à accompagner la régénération naturelle avec des restaurations (enrichissement et reboisement) ; pour l’application de cette technologie, il faut privilégier les espèces autochtones (Harungana madagascariensis, Albizzia lebbeck, etc.) aux espèces à croissance rapide (Eucalyptus, Acacias) pour maintenir la diversité biologique du milieu.
Que ce soit pour la mise en défens passive ou celle active, les différentes étapes de sa mise en place sont :
- l'organisation d'une assemblée générale d'information pour sensibiliser et collecter les préoccupations de la population environnante
- la délimitation participative de la zone à mettre en défens (autorités locales, propriétaires et usagers concernés...),
- la création d'un comité de gestion,
- l'élaboration d'un projet de plan(s) de mise en défens et d'une convention locale,
- la consultation publique des projets et leur validation,
- la formalisation au niveau du Fokontany et de la commune,
- la mise en œuvre.
L'aménagement des zones environnantes et la mise en place de fascines en cas de ravinement peuvent faire partie aussi de la mise en défens suivant la convention locale établie. La mise en défens permet de protéger les cultures en aval contre l'ensablement, de conserver la fertilité du sol et de régénérer les terres dégradées. Elle améliore aussi l'infiltration et réduit l'érosion ainsi que les pertes en terre. Une exploitation raisonnée des branches d'arbres issues des régénérations est envisageable en fonction des besoins (fourrages, bois, matière organique pour le mulch...). L'exploitation de produits non ligneux sur ces parcelles aussi peut se faire (apiculture, plantes médicinales, espèces utilisées pour la fabrication de produits à base de connaissance traditionnelle ou "ady gasy").
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Madagascar
Region/ State/ Province:
Boeny
Further specification of location:
Tsaramandroso, Antanambao Andranolava, Marovoay Banlieue, Manerinerina
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
Nee
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
Indicate year of implementation:
2020
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through projects/ external interventions
Comments (type of project, etc.):
Projet ProSol GIZ Madagascar
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- conserve ecosystem
- protect a watershed/ downstream areas – in combination with other Technologies
- preserve/ improve biodiversity
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
Nee

Forest/ woodlands
- Tree plantation, afforestation
Tree plantation, afforestation: Specify origin and composition of species:
- Monoculture exotic variety
- Mixed varieties
Type of tree plantation, afforestation:
- tropical shrubland plantation - Eucalyptus spp.
- tropical shrubland plantation - broadleaf
- Eucalyptus, Acacia, Albizia lebbeck
Are the trees specified above deciduous or evergreen?
- deciduous
Products and services:
- Timber
- Fuelwood

Unproductive land
Specify:
Terre où il est impossible de cultiver ou constituer une menace aux cultures en aval
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- Yes (Please fill out the questions below with regard to the land use before implementation of the Technology)
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
Nee

Cropland
- Perennial (non-woody) cropping
Perennial (non-woody) cropping - Specify crops:
- banana/plantain/abaca
- sugar cane

Forest/ woodlands
- (Semi-)natural forests/ woodlands
(Semi-)natural forests/ woodlands: Specify management type:
- Clear felling
Are the trees specified above deciduous or evergreen?
- deciduous
Products and services:
- Fuelwood

Unproductive land
Specify:
Acacia
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- forest plantation management
- improved ground/ vegetation cover
- integrated soil fertility management
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

vegetative measures
- V1: Tree and shrub cover

management measures
- M1: Change of land use type
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion
- Wg: gully erosion/ gullying

biological degradation
- Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
- Bh: loss of habitats
- Bq: quantity/ biomass decline
- Bs: quality and species composition/ diversity decline
- Bl: loss of soil life
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- reduce land degradation
- restore/ rehabilitate severely degraded land
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
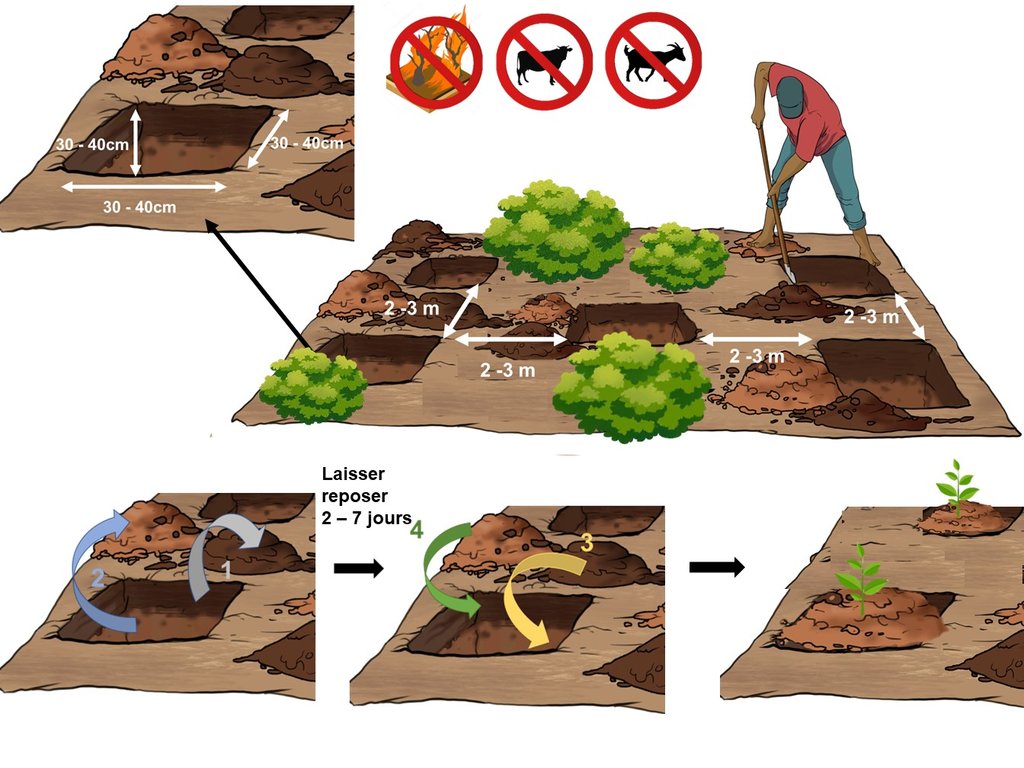
La mise en défens est avant tout une zone de conservation dont la réussite dépend fortement de la réponse aux préoccupations de la population et des usagers des terres. Ces acteurs doivent se concerter pour aboutir à une convention qui sera acceptée et bien respectée (zone de conservation, délimitation de la zone de mise en défens, protection de la zone aux feux de brousse et à la divagation du bétail,...)
Dans le cas où l'enrichissement est nécessaire (mise en défens active), les spécifications techniques suivantes doivent être considérées :
- les trous sont de 30 à 40 cm de longueur et de largeur avec une profondeur de 30 à 40 cm;
- les trous sont disposés en quinconce écartés de 2 à 3 m;
- la couche superficielle et la couche inférieure du trou doivent être bien séparées. Le trou va être ensuite laissé à l'air libre durant 2 à 7 jours avant de remettre la terre : la couche supérieure initiale va être remise au fond du trou tandis que la couche inférieure initiale sera mise en surface ;
- les jeunes plants sont mis en terre et recouverts de matières végétales sèches afin de garder l'humidité au collet des jeunes plants ;
- des indications d'interdiction de pâturage et de passage de feu seront ensuite mises en place sans oublier les pare-feux.
Author:
GIZ Prosol Madagascar
Date:
02/24/2023
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology area
Indicate size and area unit:
1 hectare
other/ national currency (specify):
Ariary
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
4300.0
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
5000
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Délimitation de la zone de mise en défens | |
| 2. | Trouaison | Janvier - Mars |
| 3. | Mise à terre des jeunes plants | au plus tard 1 semaine après la trouaison |
| 4. | None | |
| 5. | None | |
| 6. | None | |
| 7. | None | None |
| 8. | None | None |
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Trouaison et mise à terre des jeunes plants | jours-personne | 6.0 | 5000.0 | 30000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Jeunes plants | nombre | 100.0 | 700.0 | 70000.0 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 100000.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 23.26 | |||||
If land user bore less than 100% of costs, indicate who covered the remaining costs:
Les jeunes plants ont été pris en charge par le projet GIZ Prosol.
Comments:
Les coûts énumérés sont relatifs à la mise en défens active, du fait que la mise en défens passive consiste seulement à conserver le milieu de la divagation du bétail et des passages de feu.
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Désherbage du pare-feu (facultatif selon la menace du feu de la zone de mise en défens) | avant la saison de pluie, 1 à 2 fois par an |
| 2. | Protection contre le pâturage du bétail (facultatif) | Toute l'année |
| 3. | Regarnissage | Période de pluie de l'année suivante |
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Création et entretien pare-feu | jours-personne | 26.0 | 5000.0 | 130000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | Elagage | jours-personne | 22.0 | 10000.0 | 220000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 350000.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 81.4 | |||||
Comments:
Le coût de la main d'œuvre journalier est de 5000 Ariary par jour pour une demi-journée et de 10000 Ariary pour une journée toute entière.
Les coûts d'entretien sont valables pour les deux types de mise en défens.
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specify average annual rainfall (if known), in mm:
1400.00
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- not relevant
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- fine/ heavy (clay)
Topsoil organic matter:
- low (<1%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
5-50 m
Availability of surface water:
good
Water quality (untreated):
poor drinking water (treatment required)
Water quality refers to:
ground water
Is water salinity a problem?
Nee
Is flooding of the area occurring?
Nee
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- medium
Habitat diversity:
- medium
Comments and further specifications on biodiversity:
Plusieurs espèces faunistiques et floristiques sont présentes dans cette Région, certaines sont même endémiques. La mise en défens permet de constituer un habitat pour la faune aérienne et souterraine.
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- poor
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
- groups/ community
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
- animal traction
Gender:
- women
- men
Age of land users:
- youth
- middle-aged
- elderly
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- small-scale
- medium-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, not titled
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- leased
- individual
Water use rights:
- open access (unorganized)
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
Ja
Specify:
Les habitants du village reconnaissent tous les propriétaires des parcelles au sein du village
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
wood production
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
surface runoff
Soil
soil moisture
soil loss
Specify assessment of on-site impacts (measurements):
Il s'agit des estimations des exploitants enquêtés.
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
downstream siltation
damage on neighbours' fields
Specify assessment of off-site impacts (measurements):
Il s'agit des estimations des exploitants enquêtés.
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | increase or decrease | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual rainfall | decrease | not well |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
negative
Long-term returns:
slightly positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly negative
Long-term returns:
positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- single cases/ experimental
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
Nee
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| Restauration de la fertilité du sol. |
| Production sur les terres infertiles. |
| Protection des terrains de culture en aval contre l'ensablement. |
| Production de bois. |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Charge de travail et dépenses élevées à la première année d'installation dans le cas de la mise en défens active. | |
| Pâturage du bétail. | Surveillance de la zone mise en défens. |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
5 terrains visités
- interviews with land users
5 exploitants enquêtés
- compilation from reports and other existing documentation
Fiche technique de GIZ Prosol Madagascar
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
02/06/2023
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Région Boeny, 2016, "Schéma Régional d’Aménagement du Territoire de la Région Boeny"
Available from where? Costs?
Hotel de la Région Boeny
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Raharinaivo S., 2008, "Les techniques de correction des ravines et de stabilisations des Lavaka", tirés des acquis du PLAE Marovoay
Available from where? Costs?
PLAE Marovoay, https://wocatpedia.net/wiki/File:Solofo_Raharinaivo_(2008)_-_Les_techniques_de_Correction_des_ravines_et_de_Stabilisation_des_Lavaka_.pdf
Title, author, year, ISBN:
GRET, 2015, "Pratiques agroécologiques et agroforestières en zone tropicale humide", Fiche N°20 Régénération naturelle assistée
Available from where? Costs?
GRET, https://gret.org/publication/pratiques-agroecologiques-et-agroforestieres-en-zone-tropicale-humide/
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules