Orchard Rehabilitation [China]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Unknown User
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: David Streiff
Longan Rehabilitation
technologies_981 - China
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
26/12/1997
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches

Front Bank, Back Ditch on Contour Terraces [China]
Using contour principle, constructing terraces with the front bank and back ditch in order to control soil & water erosion.
- Compiler: Unknown User
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
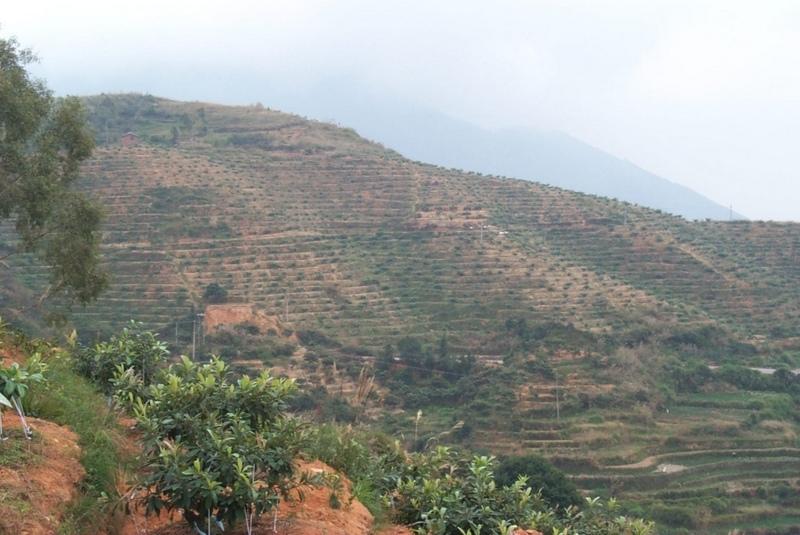
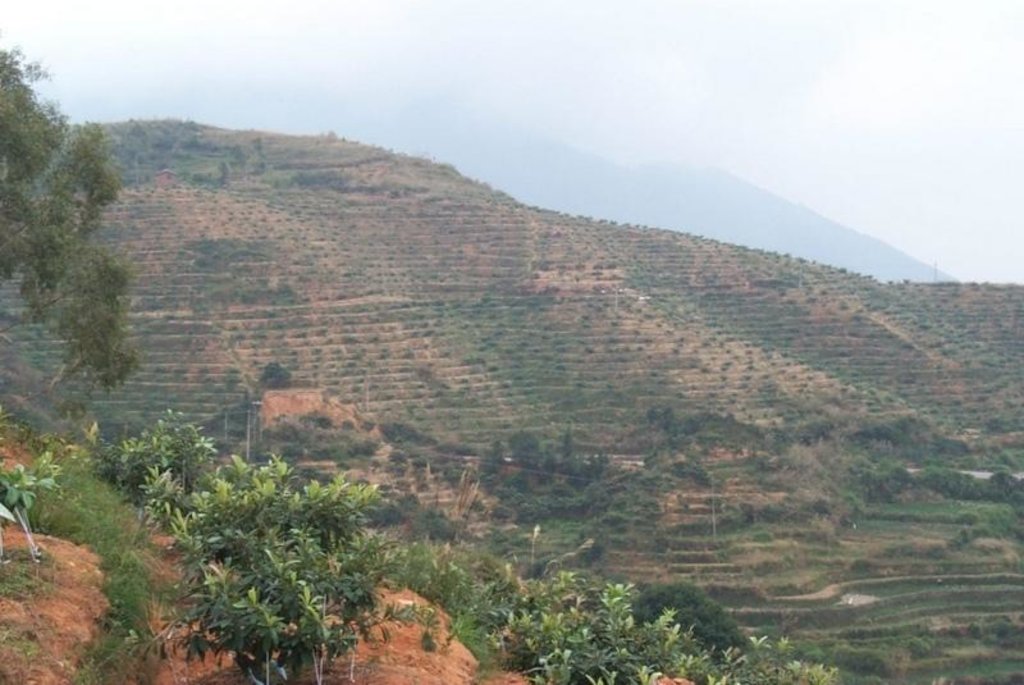
Contour terrace protection with front bank and three ditches in orchard rehabilitation.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
There is sufficient rainfall in this area and runoff often destroys the existing terraces causing much cost for maintaining. Sluice system on the terraces is important. This technology of the contour terrace protection is to build front bank and three ditches on terraces in order to solve this problem. The method is that building front bank on a terrace edge and digging a ditch on the back terrace as well as digging a ditch upright the terrace along a relatively low rill to induct overflow out.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
China
Region/ State/ Province:
Fujian
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- more than 50 years ago (traditional)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through projects/ external interventions
Comments (type of project, etc.):
Experiences from the farmers' over years practice.
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
- Perennial (non-woody) cropping
Main crops (cash and food crops):
perennial fruit trees. Rice-peanut-sweat potato etc.
Comments:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Lack of scientific planning, irrational development of the hilly and mountain areas causing serious soil loss and land degradation as well as yield decrease.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Low yield and much more input (fertilizer, pesticides etc.) needed to obtain the same production.
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- mixed rainfed-irrigated
Comments:
Water supply also rainfed
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 2
Specify:
Longest growing period in days: 365Longest growing period from month to month: Jan - Dec
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- cross-slope measure
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, indicate approximate area covered:
- 1-10 km2
Comments:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 2 m2.
This is a experimental and demonstrating area for applying the "Three Ditches on Terrace" technology.
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

vegetative measures
- V1: Tree and shrub cover
Comments:
Type of agronomic measures: mulching, contour tillage
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion

chemical soil deterioration
- Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content (not caused by erosion)
Comments:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify, education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge)
Secondary causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes), poverty / wealth (lack of captial)
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- reduce land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, Control / improvement of drainage
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, improvement of ground cover
Mulching
Material/ species: peanut and legume crop
Quantity/ density: 30 /m2
Remarks: layout
Contour tillage
Material/ species: layout
Fruit trees / shrubs species: longan trees
Perennial crops species: peanut
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 30.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 2.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 25.00%
Construction material (earth): easy to get, simple techniques, low prices, short life
Construction material (stone): trong enough, long life, and easy to construct
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 15.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 0.00%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 60.00%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:60.00
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify currency used for cost calculations:
- US Dollars
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
3.00
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | plant the fruit trees | Vegetative | spring |
| 2. | peanut | Vegetative | spring |
| 3. | flower and grass | Vegetative | spring |
| 4. | digging drainage ditch | Structural | spring |
| 5. | constructing front bank | Structural | spring |
| 6. | building contour terrace | Structural | spring |
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
Comments:
Duration of establishment phase: 72 month(s)
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | cultivation | Agronomic | dry and raining season / 2 times a year |
| 2. | harvest | Agronomic | summer and fall / 2 times a year |
| 3. | irrigation | Vegetative | spring /timely |
| 4. | control of pest and disease | Vegetative | spring /growing season |
| 5. | fertilization | Vegetative | spring /twice a year |
| 6. | weeding | Vegetative | spring /twice a year |
| 7. | maintaining the drainage ditch | Structural | free time/ |
| 8. | maintaining the front bank | Structural | free time/ |
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
Comments:
Area of the terraces.
4.8 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
Terrace sizes such as length, width, height etc.
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- humid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- not relevant
Comments and further specifications on topography:
slopes on average also steep
land forms also mountain slopes.
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- coarse/ light (sandy)
- fine/ heavy (clay)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
- low (<1%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
soil fertility is medium, low is ranked second highest and high is ranked as lowest.
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium - poor
Soil water storage capacity is medium - low
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Off-farm income:
- 10-50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
- rich
Level of mechanization:
- animal traction
- mechanized/ motorized
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
20% of the land users are rich and own 30% of the land.
80% of the land users are average wealthy and own 70% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Additional income increased from fruit trees and cash crops planted in the SWC area.
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- state
Land use rights:
- individual
Water use rights:
- individual
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
surface runoff
Quantity before SLM:
35
Quantity after SLM:
20
Soil
soil loss
Quantity before SLM:
15
Quantity after SLM:
5
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly negative
Long-term returns:
very positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
neutral/ balanced
Long-term returns:
very positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- more than 50%
If available, quantify (no. of households and/ or area covered):
43 households and 100 % of the area covered
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 50-90%
Comments:
65% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
27 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
35% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
16 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: More and more farmers are getting to know that the SWC technology can produce benefits.
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks

Front Bank, Back Ditch on Contour Terraces [China]
Using contour principle, constructing terraces with the front bank and back ditch in order to control soil & water erosion.
- Compiler: Unknown User
Modules
No modules