Digue anti-sel et de retenue des eaux de ruissellement [Senegal]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Julie Zähringer
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
O Pang
technologies_1748 - Senegal
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
SLM specialist:
Babacar Ibrahima Birham Bass
ADAF / YUNGAR
Senegal
SLM specialist:
Baboucar Gning
République du sénégal - Ministère des Ecovillages, des Bassins de Rétention, des Lacs artificiels et de la Pisciculture - Projet d'appui à la petite irrigation locale (PAPIL)
Senegal
Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - SwitzerlandName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Ministère des Ecovillages, des Bassins de Rétention, des Lacs artificiels et de la Pisciculture - Projet d'appui à la petite irrigation locale (PAPIL) - SenegalName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
ADAF / YUNGAR Consultants agricoles - Senegal1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
Une technologie permettant de retenir les eaux de ruissellement et de reduire la salinité des terres.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
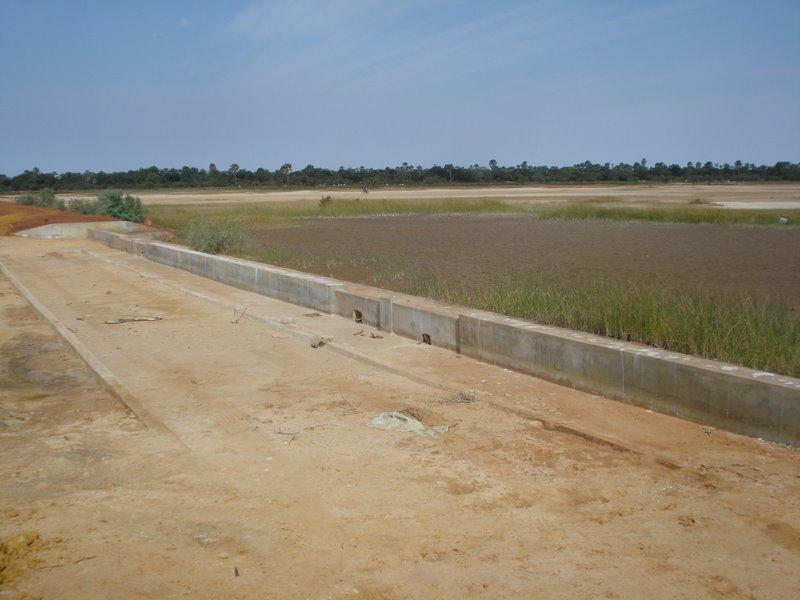
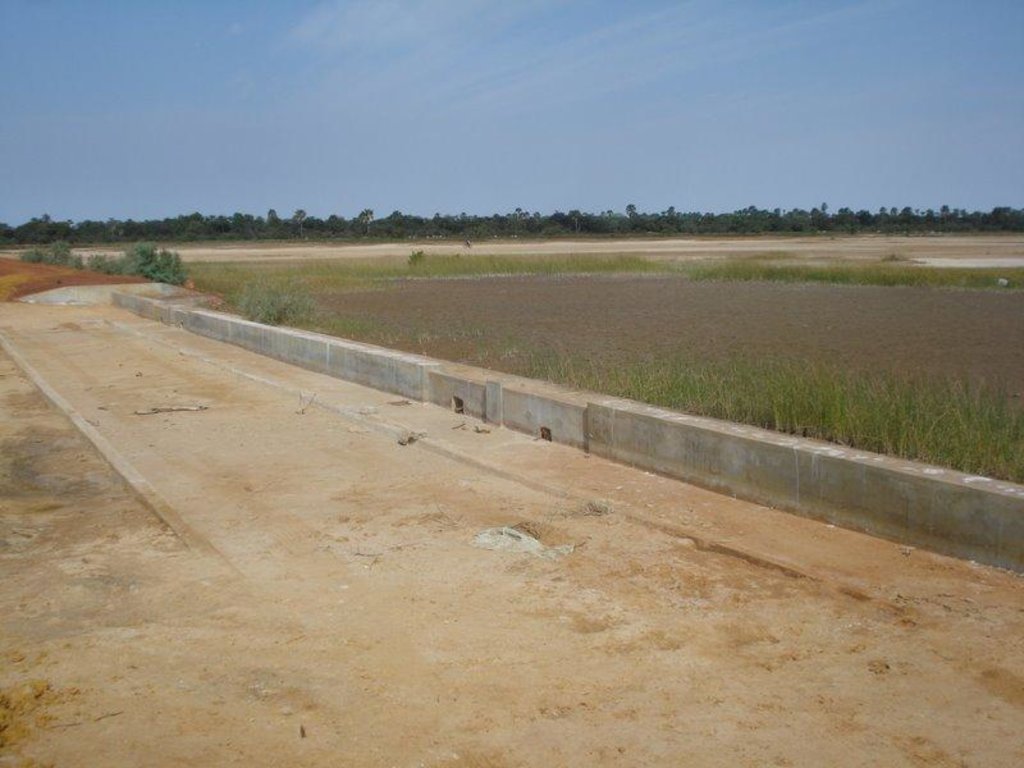
Ouvrage constitué d un déversoir central en beton armé de 30 m et d'une digue en terre de 400 m.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Senegal
Region/ State/ Province:
Région de Fatick, Département de Fatick
Further specification of location:
Arrondissement de Fimela, Communauté rurale de Fimela
Comments:
La superficie totale couverte par la technologie SLM est de 1 km2.
Superficie sous influence de la digue
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through projects/ external interventions
Comments (type of project, etc.):
2009
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
Ja
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- Agro-silvopastoralism

Cropland

Grazing land

Forest/ woodlands
Comments:
Principaux problèmes d'utilisation des sols (perception des utilisateurs fonciers): absence d'activités agricoles et de patures à cause d'une forte salinisation des sols et de la nappe
Usage futur (final) de la terre (après la mise en œuvre de la technologie SLM): Mélangé: Mp: Agro-pastoralisme
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- Yes (Please fill out the questions below with regard to the land use before implementation of the Technology)
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
Ja
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- Agro-silvopastoralism

Cropland

Grazing land

Forest/ woodlands
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- cross-slope measure
- Digue anti-sel
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

structural measures
- S5: Dams, pans, ponds
Comments:
Principales mesures: Structures physiques
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

chemical soil deterioration
- Cs: salinization/ alkalinization

biological degradation
- Bc: reduction of vegetation cover

water degradation
- Hg: change in groundwater/aquifer level
Comments:
Type principal de dégradation adressée: Cs: salinisation / alcalinisation
Types de dégradation secondaires abordés: Bc: réduction de la couverture végétale, Hg: modification dans les nappes phréatiques et aquifères
Principales causes de dégradation: déforestation / disparition de la végétation naturelle (inclusive les feux de forêts), la surexploitation de la végétation pour l'usage domestique (surexploitation liée à la pauvreté), sécheresses, autres Causes naturelles (avalanches, éruptions volcaniques, topographie extrême, coulée de boue, etc.) Spécifier. (Intrusion de l'eau salée)
Causes secondaires de la dégradation: pression de la population, pauvreté / santé, gouvernance / institutionnel (absence de conventions en rapport avec l'utilisation des ressources naturelles et octroi de permis aux allochthones)
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- restore/ rehabilitate severely degraded land
Comments:
Objectifs secondaires: prévention de la dégradation des terres, atténuation / réduction de la dégradation des sols
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
Principales fonctions techniques: contrôle du ruissellement en nappe: rétention / capture, récupération de l'eau / augmentation des réserves d'eau, amélioration de la qualité de l'eau, eau filtrée / solution tampon
Fonctions techniques secondaires: contrôle de la battance ('splash'), augmentation du niveau / recharge de la nappe phréatique
Barrage / poêle / étang
Longueur des bunds / banques / autres (m): 430.00
Matériaux de construction (autre): 30 m de béton + 200 m en terre (latérite) de chaque côté
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Fondation |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules