ການຫັນປ່ຽນ ພື້ນທ່ີດິນ ທ່ີມີຫີນຂ້ີໝ້ຽງຫຼາຍ ໃຫ້ກາຍເປັນດິນປູກຫຍ້າ ເພື່ອເປັນອາຫານສັດ [Lao People's Democratic Republic]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: kang phanvongsa
- Editors: sinnilong vongkhamchanh, Bounthanom Bouahom
- Reviewers: Nicole Harari, Stephanie Jaquet, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_2891 - Lao People's Democratic Republic
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
land user:
ແກ້ວສີມົນກອງ ຄຳທີ
Lao People's Democratic Republic
SLM specialist:
ຈະເລີນສັກ ອຳພອນ
ຫ້ອງການກະສີກຳ ແລະ ປ່າໄມ້
Lao People's Democratic Republic
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
National Agriculture and Forestry Research Institute (NAFRI) - Lao People's Democratic Republic1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
Nee
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
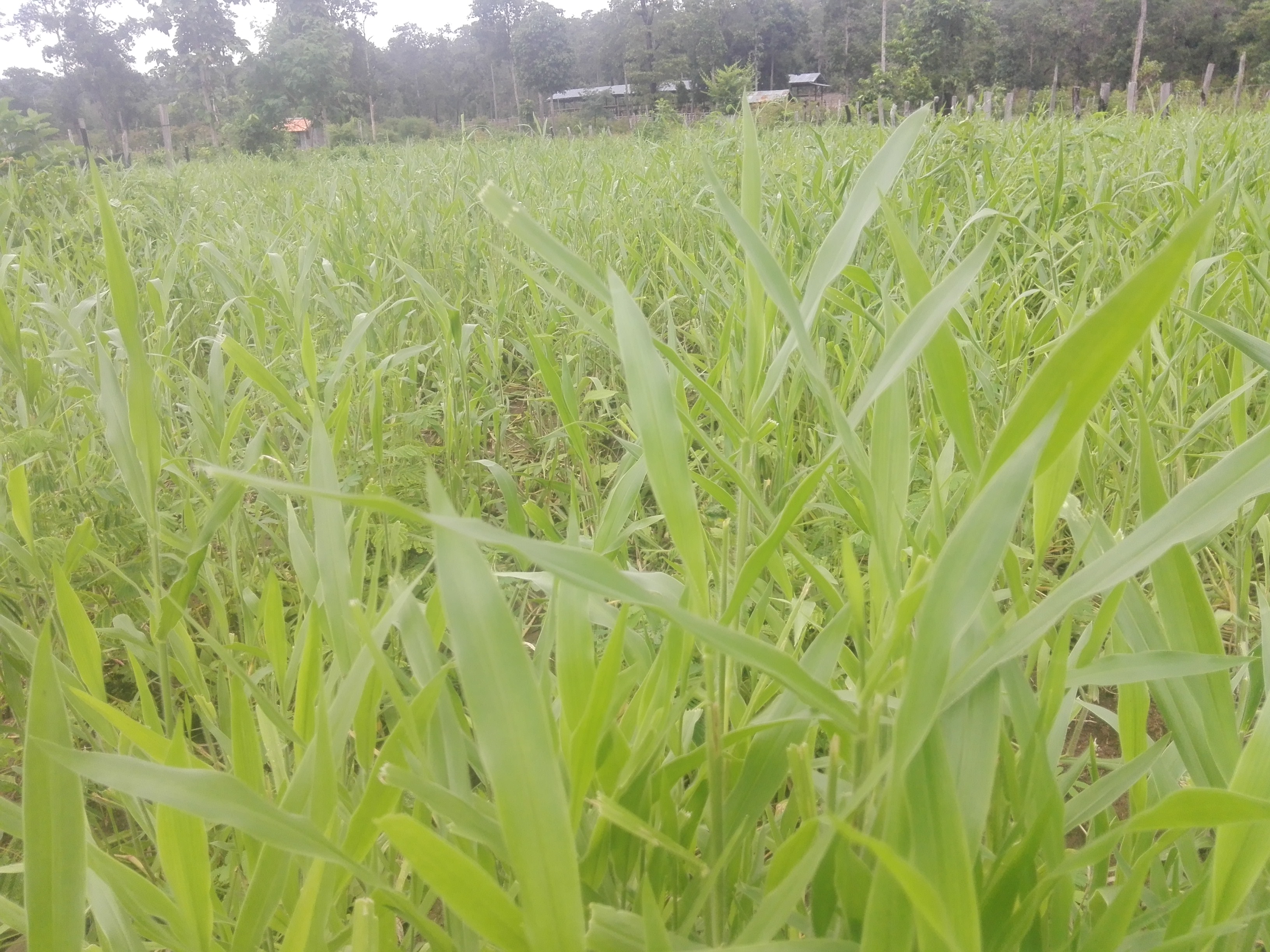
ເຕັກນິກ ການຫັນປ່ຽນ ພື້ນທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ເປັນຫີນຂີ້ໝ້ຽງ ເນື່ອງຈາກການເຊາະລ້າງ ໃນເວລາຝົນຕົກ ເຮັດໃຫ້ ດິນເຊາະລ້າງ ມາຈາກເທີງພູ ໄຫຼມາໃສ່ດິນ ເຂດພູພຽງ ເຮັດໃຫ້ດິນບໍລິເວນ ດັ່ງກ່າວ ບໍ່ສາມາດທຳການຜະລິດໄດ້.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
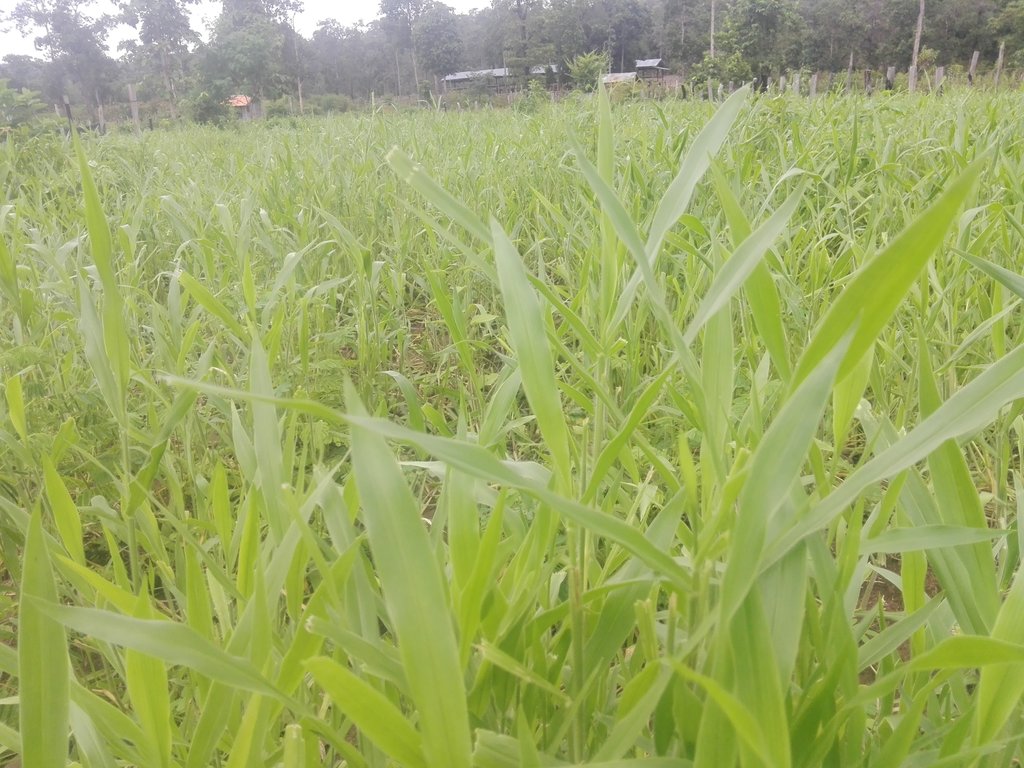
ບັນຫາ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງດິນ ໂດຍສະເພາະ ແມ່ນບັນຫາ ດິນຫິນຂີ້ ໝ້ຽງ ເນ້ືອດິນ ເປັນດິນດາກ ແກມດິນຊາຍ ແລະ ມີຫິນ ກ້ອນນ້ອຍໆ ແລະ ໄຫ່ຍປະປົນຢູ່ນາໍ ຊື່ງເກີດຂ້ືນເອງຕາມ ທາໍມະຊາດ ຊື່ງເປັນບັນຫາ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ການຜະລິດ ຂອງຊາວກະສິກອນ. ສາເຫດ ທີ່ເຮັດໃຫ້ເກີດ ດິນເຊື່ອມໂຊມດັ່ງກ່າວ ແມ່ນເກີດຈາກການເຊາະລ້າງ ຂອງນໍ້າຝົນ ທີ່ຕົກແຮງໄດ້ໄຫຼ ພັດເອົາຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ ທີ່ມີອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ໄປເຮັດໃຫ້ຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ ຍັງເຫຼືອໄວ້ແຕ່ຫິນຂີ້ ໝ້ຽງ ແລະ ດິນດາກ ທີ່ໄຫຼພັດໄປຕາມກະແສນ້ຳຝົນ ປະມານ 20% ເປັນເວລາຫຼາຍປີ. ໃນປີ 2009, ທາງໂຄງການ ADB ໄດ້ເຂົ້າມາຊຸກຍູ້ ສົ່ງເສີມປະຊາຊົນ ລ້ຽງງົວ ແລະ ປູກຫຍ້າ ເປັນອາຫານສັດ ໂດຍໄດ້ມີ ການສ້າງຕັ້ງກຸ່ມລ້ຽງງົວ ຈໍານວນ 10 ກຸ່ມ ຢູ່ໃນໝູ່ບ້ານ ມີທັງໝົດ ຈາໍນວນ 80 ຄອບຄົວ ທາງໂຄງການ ໄດ້ມອບງົວ ຈາໍນວນ 4 ໂຕ/ຄອບຄົວ, ນອກຈາກແນວພັນງົວແລ້ວ ທາງໂຄງການ ຍັງໄດ້ສະໜອງ ແນວພັນແກ່ນຫຍ້າ, ຈົກ, ສຽມ ແລະ ອຸປະກອນ ສ້າງລະບົບນ້ຳລິນເພ່ືອຫົດສວນຫຍ້າ ແລະ ໃຫ້ສັດລ້ຽງກີນ. ຊື່ງໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງກັນເປັນກຸ່ມ ແລະ ນາໍໃຊ້ດິນລວມຂອງບ້ານ ພາຍໃນ ເນື້ອທີ ່ 15 ເຮັກຕາ. ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງກັນເປັນກຸ່ມ ແມ່ນສະມາຊິກ ທຸກຄົນ ຕ້ອງໄດ້ປ່ຽນຜຽນກັນໄປເຝົ້າງົວ ແລະ ໄປຕັດຫຍ້າ ມາເກືອສັດ ຫຼື ໄປປ່ອຍສັດ ເຂົ້າໄປກີນຫຍ້າເອງເລີຍ ໃນທົ່ງຫຍ້າທີ່ພວກເຂົາປູກ. ພາຍຫຼັງ, ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດມາໄດ້ 4 ປີ ທີ ່ ປະຊາຊົນ ເຮັດເປັນກຸ່ມ ປະຊາຊົນ ກໍ່ພົບບັນຫາ ໃນການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ສັດລ້ຽງ ພາຍໃນກຸ່ມ ເນື່ອງຈາກ ວ່າມີ ສະມາຊິກ ຈາໍນວນໜື່ງ ພາຍໃນກູ່ມ ກໍ່ປ່ອຍປະລະເລີຍ ໜ້າທີ່ຄວາມຮັບຜິດຊອບ ພາຍໃນກຸ່ມ, ຂາດຄວາມສາມັກ ຄີດັ່ງນັ້ນ ຈ່ືງເປັນສາເຫດເຮັດໃຫ້ເກີດມີຊ່ອງຫວ່າງ ໃຫ້ກຸ່ມຄົນບ່ໍດີ ມາລັກເອົາໜາມໝາກຈັບທີ່ ກຸ່ມບ້ານໄດ້ເຮັດຮົ້ວ ລ້ອມ ທົ່ງຫຍ້າສັດໄວ້ ແລະ ສາຍຢາງຕໍ່ນ້ຳ ເຮັດສັບສີນເສຍຫາຍ. ຕົກມາເຖິງປີ 2012 ສວນປູກຫຍ້າ ກໍ່ເກີດໄຟໄໝ້ ສາເຫດຍ້ອນ ປະຊາຊົນ ຈູດປ່າເຮັດໄຮ່ ເຊີ່ງ ເຮັດໃຫ້ ສວນປູກຫຍ້າ ໄດ້ຮັບຄວາມເສຍຫາຍທັງໝົດ 15 ເຮັກຕາ ຂອງພື້ນທີ ່ ປູກຫຍ້າທັງໝົດ. ດັ່ງນັ້ນ, ຈື່ງເຮັດໃຫ້ເຈົ້າຂອງງົວ ຈາໍນວນໜ່ືງ ກ່ໍເອົາງົວ ມາລ້ຽງເອງ ພໍໃຜພໍລາວ ແລະ ໃນທີ່ສຸດ ກຸ່ມດັ່ງກ່າວ ກໍ່ບໍ່ສາມາດສືບຕໍ່ໄປໄດ້. ໃນທ້າຍປີ 2014 ມີຄອບຄົວຊາວກະສິກອນ ຄອບຄົວໜື່ງ ທີ່ເຄີຍເປັນສະມາຊິກ ພາຍໃນກຸ່ມ ມີຄວາມຄິດສົນໃຈ ແລະ ຕ້ອງການຢາກລ້ຽງງົວ ເປັນສິນຄ້າ ຈີ່ງໄດ້ໄປ ປຶກສາຫາລື ກັບອາໍນາດການປົກຄອງບ້ານ ເພື່ອຕ້ອງການ ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ດັ່ງກ່າວ ໂດຍບໍ່ໄດ້ເສຍຄ່າເຊົ່າດິນ. ປະຈຸບັນ ເນື້ອທີ່ທັງໝົດ ໃນການປູກຫຍ້າ ລ້ຽງສັດ 15 ເຮັກຕາ ແລະ ມີງົວ ຈາໍນວນ 130 ໂຕ. ສໍາລັບຫຍ້າ ທີ່ເອົາມາປູກໃນເບື້ອງຕົ້ນ ແມ່ນເອົາມາແຕ່ສວນຫຍ້າເກົ່າ ທີ່ທາງໂຄງການສະໜອງໃຫ້ເມ່ືອກ່ອນ ໂດຍການຄັດເລືອກ ເອົາເຫົ້ງາ ທີ່ແຂງແຮງ ສົມບູນດີ ມາປູກ. ຊະນິດພັນຫຍ້າ ທີ່ນໍາມາປູກ ມີ 2 ຊະນິດພັນຄື: ຫຍ້າກີນີ ແລະ ຫຍ້າປັດສະປາລອມ (Paspalum Grass) ປູກ ເປັນແຖວໃນພື້ນທີ່ດຽວກັນ, ການກະກຽມພ້ືນທີ່ ແມ່ນໄດ້ໄຊ້ລົດໄຖ ຄູໂບຕາ 4,000 ແຮງມ້າ ແລະ ການນໍາໄຊ້ແຮງງານປູກ ປະມານ 50 ແຮງງານ ພາຍໃນ 30 ວັນ, ໃຊ້ແຮງງານ ໃນການໄປຂຸດເຫງົ້າ ຈາໍນວນ 10 ແຮງງານ ພາຍໃນເວລາ 5 ວັນສໍາເລັດ. ພາຍຫຼັງ ປູກແລ້ວ ກໍ່ມີການບົວລະບັດຮັກສາ 2 ຄັ້ງ/ປີ ໃນລະຫວ່າງ ເດືອນ 5 – 12. ລະດູການປູກ ທີ່ເໝາະສົມ ແມ່ນໃນຊ່ວງກາງເດືອນ 5 ເນື່ອງຈາກ ມີຝົນຝອຍ, ປະມານວັນທີ 12 ແມ່ນໄດ້ເລີ່ມບຸກເບີກພື້ນທີ່ ແລະ ໄຖດິນ ຕາກແດດໄວ້ປະມານ 15 ວັນ ເພື່ອໃຫ້ເສດຫຍ້າ ແລະ ວັດສະພືດ ທີ ່ ບໍ່ຕ້ອງ ການນັ້ນຕາຍ, ເໜົ່າເປື່ອຍ ກາຍເປັນຝຸ່ນ ອີນຊີ ເພີ ່ ມລົງໃນດິນ, ທັງເຮັດໃຫ້ໂຄງສ້າງ ຂອງເນ້ືອດິນ ແໜ້ນແຂງແຕ່ກໂຕ, ອັນເປັນຜົນເຮັດໃຫ້ ພືດທີ່ເກີດໃໝ່ ສາມາດຈະເລີນເຕີບໂຕຂ້ືນ ຈາກໜ້າດິນ ແລະ ຂະຫຍາຍ ຮາກໄດ້ດີ. ໃນຊ່ວງ 15 ວັນ ທີ່ໄດ້ຕາກກ້ອນຫີນໄຖຢູ່ນັ້ນ ແມ່ນໄດ້ເຮັດຮົ້ວອ້ອມສວນ (ທັງຂຸດຂຸມ, ຝັງຫຼັກ ຮົ້ວ, ຕອກເຫຼັກໝາກຈັບ) ອ້ອມທັງ 15 ເຮັກຕາ ແລະ ໃສ່ຝຸ່ນຄອກຈຳນວນ 40 ໂຕນ, ໂດຍນຳໃຊ້ລົດຕ໋ອກໆ ແກ່ຝຸ່ນເຂົ້າໄປໃນສວນແລ້ວ ໃຊ້ຊ້ວນ ຕັກລົງໃສ່ໜ້າດີິນ ເປັນກອງໆ (ກອງລະ 20-30 ຊ້ວນ), ແຕ່ລະກອງ ຫ່າງກັນ ປະມານ 5x5 ແມັດ, ເມື່ອຮອດວັນທີ 24/5 ກໍ່ໄດ້ໄຖຄົ້ນຄ້ືນ ອີກເທ່ືອໜ່ືງ ເພື່ອເປັນການປະສົມຝຸ່ນຄອກ ທີ່ໃສ່ລົງໄປໃນສວນນັ້ນ ໃຫ້ປົນກັບເນ້ືອດີນໄດ້ດີ ແລະ ຍັງເປັນການກຳຈັດ ວັດສະພືດ ອີກຄັ້ງ. ເມື່ອວັນທີ 1/6 ກໍ່ໄດ້ລົງມືການປູກ ແມ່ນໄດ້ໃຊ້ວິທີການຂຸດເປັນແຖວ ເອົາເຫົ້ງາ ມາຝັງລົງດິນເລີກປະມານ 5 ເຊັນຕິແມັດ ແລ້ວຖົມທັນທີ, ໄລຍະຫ່າງຂອງຕົ້ນປະມານ 50x50 ເຊັນຕິແມັດ, ລະຫວ່າງແຖວ 80 ເຊັນຕີແມັດ ຫຼັງຈາກປູກແລ້ວ ແມ່ນບໍ່ໄດ້ຫົດນໍ້າ ມີແຕ່ອາໃສນໍ້າຝົນ ເພາະປູກ ໃນຕົ້ນ ເດືອນ 6 ພໍດີມີຝົນຝອຍຕົກລົງມາ ແຕ່ໃນບາງຊ້ວງ ທີ່ຝົນບໍ່ຕົກ (ພາຍຫຼັງ ປູກແລ້ວ) ກໍ່ສາມາດ ໃຊ້ນາໍ້ລິນ ທີ່ທາງໂຄງການ ໄດ້ຕິດຕັ້ງໄວ້ໃຫ້ ແລະ ຫົດ ໃນລະດູແລ້ງ ພ້ອມເກັບກັກນາໍ້ ໄວ້ໄຫ້ສັດກິນ. ສ່ວນການເກັບກູ້ ແມ່ນນັບແຕ່ມື້ທີ່ປູກ ປະມານ 90-100 ວັນ ກໍ່ສາມາດຕັດຫຍ້າ ມາໃຫ້ສັດກິນໄດ້. ຊື່ງມີ 2 ຮູບແບບການເກືອສັດ ເຊັ່ນຮູບແບບທາໍອີດ ແມ່ນໄດ້ນາໍໃຊ້ແຮງງານຄົນ ໄປຕັດຫຍ້າ ທີ່ປູກ ເປັນແຖວ ໃນສວນດຽວ ແລ້ວເກັບໃສ່ກະສອບ ເພື່ອມາໄຫ້ງົວກິນ ສາໍລັບ ຮູບແບບທີສອງ ແມ່ນຮູບແບບ ການປ່ອຍງົວ ເຂົ້າໄປກິນຫຍ້າ ຢູ່ສວນເລີຍ ເມ່ືອຫຍ້າ ອາຍຸ ໄດ້ປະມານ 6 ເດືອນ ໂດຍປ່ອຍ ເປັນອາທິດ ໝູນວຽນ ກັນໄປ ແລະ ໃນຊ່ວງເວລາທີ ່ ຕັດເອົາຫຍ້າໄປລ້ຽງງົວນັ້ນ ແມ່ນຈະໄດ້ ອານາໄມ ວັດສະພືດໄປພ້ອມ, ໃນທຸກໆປີ ແມ່ນຈະໄດ້ ໃສ່ຝຸ່ນຄອກ ເປັນປະຈຳ ພາຍຫຼັງທີ່ຕັດ ຫຼື ເກັບກູ້ຫຍ້າໄປໃຫ້ງົວກິນ ແລະ ໃນບາງປີກໍ່ ມີການສ້ອມແຊມຮົ້ວ ຫາກມີການເປ້ເພ ເສຍຫາຍ.
ຈຸດດີຈາກເຕັກນິກນີ້ - ດິນບ່ໍເຈ່ືອນໃນເວລາຝົນຕົກແຮງ (ຮາກຂອງຫຍ້າຍືດເກາະດິນໄດ້ດີ) ໝາຍຄວາມວ່າເຕັກນິກການປູກຫຍ້ານີ້ ສາມາດປ້ອງກັນການເຊາະລ້າງທາດອາຫານໃນດິນ, ເທີງໜ້າດິນໃນເວລາຝົນຕົກແຮງ ແລະ ບໍ່ເຮັດໃຫ້ດິນແໜ້ນ,ບໍ່ເຮັດໃຫ້ດິນແຂງ - ຈຸລິນຊີເພີ່ມຂ້ືນ (ຍ້ອນໃບຮາກທີ່ຕາຍໄປທັບຖົມກັນແລ້ວເນົ່າເປື່ອຍ ) - ດີນງອກງາມຂື້ນ (ຍ້ອນໃບຮາກຫຍ້າທີ່ຕາຍ ໄປທັບຖົມກັນ ແລ້ວເນົ່າເປື່ອຍ ກາຍເປັນຝຸ່ນໃຫ້ດິນ, ການຖ່າຍເທມູນສັດ ທີ່ປ່ອຍງົວເຂົ້າໄປກິນຫຍ້າ) - ສໍາລັບ ສັດລ້ຽງ ແມ່ນໄຫ່ຍໄວ ແຂງແຮງດີ - ຫຸຼດຜ່ອນ ອັດຕາການເກີດພະຍາດຫຼາຍຂ້ືນ, ສັດບ່ໍເສຍຫາຍ - ຊາວກະສິກອນ ມີລາຍໄດ້ເພີ່ມຂ້ືນຈາກການຂາຍສັດ (ສາມາດ ສ້າງລາຍໄດ້ 80,000,000 ກີບ/ປີ) - ມີເວລາຫວ່າງ ພຽງພໍ ໃນການເຮັດກີດຈະກາໍ ການຜະລິດອ່ືນໆ ພາຍໃນຄອບຄົວ.
ຈຸດອ່ອນ - ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ຂອງຊິວະນາໆພັນຫຼຸດລົງເຊັ່ນ: ແມງໄມ້ທີ ່ ເປັນປະໂຫຍດຫຼຸດລົງ (ຈີ່ນາຍ,ຈິ່ຫຼໍ່) - ຈາໍນວນ ແລະ ປະເພດ ເຄື່ອງປ່າຂອງດົງຫຼຸດລົງ ເປັນຕົ້ນ ແມ່ນເຫັດລະໂງກ, ເຫັດຂ່າ, ເຫັດດີນ, ຂີ້ຊີ, ແຂມ, ຫວາຍ - ຈາໍນວນສັດປ່າ ກໍ່ຫຼຸດລົງ ຈາກເມື່ອກ່ອນ ເຄີຍພົບເຫັນ ກວາງ, ຟານ, ກະຮອກ, ກະແຕ ຢູ່ພື້ນທີ່ດັ່ງກ່າວ. - ຈາໍກັດ ແຮງງານ ພາຍໃນຄອບຄົວ ເພື່ອປະກອບເຂົ້າໃນກິດຈະກາໍສ້ອມແປງຮົ້ວ ແລະ ປູກຫຍ້າ. - ຄ່າຈ້າງ ແຮງງານແພງ ວັນລະ 50,000 ກີບ/ວັນ ໃນກິດຈະກາໍ ບົວລະບັດຮັກສາ ສວນຫຍ້າ. - ມີຄວາມຫຍຸ້ງຍາກ ໃນການບົວລະບັດ ກໍາຈັດວັດສະພືດ ເຊັ່ນ ຫຍ້າໜາມແກ້ວ ເກີດຂື້ນຫຼາຍ. - ປະຢັດຕົ້ນທືນ ໃນການຊື້ແກ່ນຫຍ້າ ເພາະປະຊາຊົນ ສາມາດ ໄປຂຸດເອົາເຫງົ້າ ໄດ້ຢູ່ຕາມພື້ນທີ່ໆ ເຄີຍປູກຫຍ້າ ຜ່ານມາຂອງໂຄງການ.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Lao People's Democratic Republic
Region/ State/ Province:
ແຂວງ ອັດຕະປື
Further specification of location:
ບ້ານຕາດແສງ, ເມືືອງຊານໄຊ
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 0.1-1 km2
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
Indicate year of implementation:
2011
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through land users' innovation
- through projects/ external interventions
Comments (type of project, etc.):
ເຕັກນິກດັ່ງກ່າວ ແມ່ນໄດ້ຮັບການສະໜັບສະໜູນຈາກໂຄງການ ADB (ທືນພັດທະນາ ກະສິກຳ)
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- create beneficial economic impact
- create beneficial social impact
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Grazing land
Extensive grazing:
- Ranching
Intensive grazing/ fodder production:
- Improved pastures
Comments:
ຈໍານວນ ລະດູການ ປູກໃນປີໜຶ່ງ: 1
ຄວາມໜາແໜ້ນ ຂອງສັດລ້ຽງ (ຖ້າຫາກວ່າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ): 130ໂຕ/15ເຮັກຕາ
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- mixed rainfed-irrigated
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- pastoralism and grazing land management
- improved ground/ vegetation cover
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

management measures
- M2: Change of management/ intensity level
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

physical soil deterioration
- Pc: compaction

biological degradation
- Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
- Bf: detrimental effects of fires

water degradation
- Ha: aridification
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- restore/ rehabilitate severely degraded land
- adapt to land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
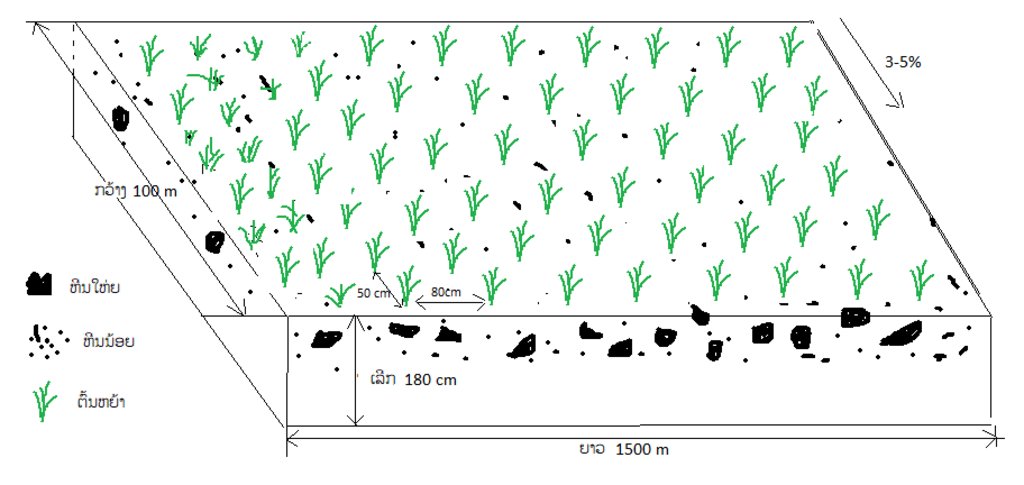
ການກະກຽມພ້ືນທີ ແມ່ນໄດ້ໄຊ້ລົດໄຖ ຄູໂບຕາ 4,000 ແຮງມ້າ
ຊະນິດພັນທີ ່ ໃຊ້ ແມ່ນ ຫຍ້າກີນີ ແລະ ປັດສະປາລອນ ໂດຍການປູກ ເປັນແຖວໃນພື້ນທີ ່ ດຽວກັນ
ຄວາມໜ້າແໜ້ນຂອງພືດ ທີ ່ ປູກແມ່ນ 37 000 ຕົ້ນ/ຮຕ
ພື້ນທີ ່ ການປູກຫຍ້າ ກວ້າງ 100 ແມັດ, ຍາວ 1500 ແມັດ
ການປູກຫຍ້າ ແມ່ນ ຂຸດຂຸມ ປູກ ຫ່າງກັນ 50 X 50 ຊັງຕີແມັດ
ໄລຍະຫ່າງ ລະຫວ່າງແຖວ ແມ່ນ 80 ຊັງຕີແມັດ
ພື້ນທີ ່ ການປູກຫຍ້າ ແມ່ນຢູ່ລຸ່ມຕີນພູ ມີຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ ປະມານ 3-5%
ພາຍຫຼັງ ປູກແລ້ວ ກໍ່ມີການບົວລະບັດຮັກສາ 2 ຄັ້ງ/ປີ ໃນລະຫວ່າງ ເດືອນ 5 – 12.
ສ່ວນການເກັບກູ້ ແມ່ນນັບແຕ່ມື້ທີ ່ ປູກ ປະມານ 90-100 ວັນ ກໍ່ສາມາດຕັດຫຍ້າ ມາໃຫ້ສັດກິນໄດ້.
Author:
ສິນນິລົງ ວົງຄຳຈັນ
Date:
03/07/2017
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology area
Indicate size and area unit:
ເຮັກຕາ
If using a local area unit, indicate conversion factor to one hectare (e.g. 1 ha = 2.47 acres): 1 ha =:
15
other/ national currency (specify):
ກີບ
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
8000.0
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
50000
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | ລົງສຳຫຼວດຄວາມເໝາະສົມຂອງພື້ນທີ່ | ເດືອນ 1-2 |
| 2. | ການບຸກເບີກພື້ນທີ່ | |
| 3. | ການປູກ(ການຢອດເມັດ) | |
| 4. | ການບົວລະບັດສາ ແລະ ການໃສ່ຝຸ່ນ | |
| 5. | ການເຮັດຮົ້ວອ້ອມສວນ |
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | ແຮງງານປູກຫຼື ຢອດເມັດ | ຄົນ | 20.0 | 50000.0 | 1000000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | ແຮງງານເຮັດຮົ້ວ | ຄົນ | 30.0 | 50000.0 | 1500000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | ແຮງງານໃສ່ຝຸ່ນ | ຄົນ | 60.0 | 50000.0 | 3000000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | ຄ້ອນຕີ | ດວງ | 6.0 | 35000.0 | 210000.0 | |
| Equipment | ເຫຼັກຫງັດ | ດ້າມ | 3.0 | 170000.0 | 510000.0 | |
| Equipment | ຂົນຝຸ່ນເຂົ້າໃນສວນ | ທ້ຽວ | 60.0 | 35000.0 | 2100000.0 | |
| Equipment | ເຄ່ືອງອັດຫຍ້າ | ເຄ່ືອງ | 3.0 | 1500000.0 | 4500000.0 | |
| Plant material | ແກ່ນຫຍ້າລູຊີ | ກິໂລກຣາມ | 55.0 | 50000.0 | 2750000.0 | |
| Plant material | ແກ່ນຫຍ້າກິນີ | ກິໂລກຣາມ | 40.0 | 50000.0 | 2000000.0 | |
| Plant material | ຫຍ້າມູລາໂຕ | ກິໂລກຣາມ | 35.0 | 50000.0 | 1750000.0 | |
| Fertilizers and biocides | ຝຸ່ນຄອກ | ໂຕນ | 40.0 | 200000.0 | 8000000.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | ຕະປູ | ແກັດ | 1.0 | 80000.0 | 80000.0 | |
| Construction material | ເຫລັກໝາກຈັບ | ໂຄ້ງ | 48.0 | 250000.0 | 12000000.0 | |
| Construction material | ຫຼັກຮົ້ວ | ຫຼັກ | 1600.0 | 10000.0 | 16000000.0 | |
| Construction material | ຂຸມຫຼັກຮົ້ວ | ຂຸມ | 1600.0 | 3000.0 | 4800000.0 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 60200000.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 7525.0 | |||||
If you are unable to break down the costs in the table above, give an estimation of the total costs of establishing the Technology:
61878000.0
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | ການໃສ່ຝຸ່ນຄອກ | None |
| 2. | ການຕັດຫຍ້າມາໃຫ້ສັດກິນ | None |
| 3. | ການອະນະໄມວັດສະພືດຫຼັງການຕັດຫຍ້າ | None |
| 4. | ການສ້ອມແຊມແປງຮົ້ວຮາວ | None |
Comments:
ດ້ານການບຳລຸງຮັກສາແມ່ນຈະບໍ່ຄ່ອຍມີກິດຈະກຳຫຼາຍ ຈະເປັນກິດຈະກຳທີ່ ຕ້ອງປະຕິບັດພຽງຄັ້ງດຽວຕໍ່ປີເທົ່ານັ້ນ.
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | ແຮງງານ | ຄົນ | 50.0 | 30000.0 | 1500000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | ຈົກ | ດວງ | 25.0 | 30000.0 | 750000.0 | |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 2250000.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 281.25 | |||||
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
ອຸປະກອນ ທີ່ໃຊ້ເຂົ້າ ໃນການເຮັດນ້ຳລິນ (ທໍ່, ອ່າງເກັບນ້ຳ) ແລະ ອຸປະກອນ ເຮັດຮົ້ວ ເພື່ອປ້ອງກັນບໍ່ໃຫ້ສັດເຂົ້າພື້ນທີ່
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specify average annual rainfall (if known), in mm:
2500.00
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
ມີຝົນເລີ່ມຕົກນັບແຕ່ກາງເດືອນ5-6, ຝົນຕົກແຮງແມ່ນໃນຊ່ວງເດືອນ 8-9-ຕົ້ນເດືອນ10. ສະເພາະການຕົກຂອງຝົນໃນພື້ນທີ່ດັ່ງກ່າວແມ່ນເລີ່ມຕົກແຕ່ ເດືອນ 6-11
Indicate the name of the reference meteorological station considered:
ຫ້ອງການຊັບພະຍາກອນທຳມະຊາດ ແລະ ສິ່ງແວດລ້ອມ
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
ສະເພາະການຕົກຂອງຝົນໃນເຂດພື້ນທີ່ດັ່ງກ່າວແມ່ນເລີ່ມຕົກແຕ່ ກາງເດືອນ5 -11
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- not relevant
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
5-50 m
Availability of surface water:
medium
Water quality (untreated):
for agricultural use only (irrigation)
Is water salinity a problem?
Nee
Is flooding of the area occurring?
Nee
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- medium
Habitat diversity:
- medium
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- commercial/ market
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
- rich
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- mechanized/ motorized
Gender:
- men
Age of land users:
- middle-aged
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- large-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- communal/ village
Land use rights:
- individual
Water use rights:
- individual
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Comments/ specify:
ກ່ອນຫນ້ານີ້ ດິນໄດ້ຖືກປະສົມກັບກ້ອນຫີນນ້ອຍໃຫຍ່, ດັ່ງນັ້ນມັນຍາກສໍາລັບການປູກ. ໂດຍການນໍາໃຊ້ວິທີການປູກຫຍ້າ ແມ່ນ ຄ່ອຍໆເອົາກ້ອນຫີນເຫຼົ່ານັ້ນອອກ ແລະ ການຜະລິດການປູກພືດກໍ່ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ.
fodder production
Comments/ specify:
ກ່ອນທີ່ຜູ້ໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນຈະປ່ອຍໃຫ້ສັດຂອງຕົນ ກີນຫຍ້າຕາມທໍາມະຊາດ. ຫຼັງຈາກນັ້ນ, ໂດຍການປູກແນວພັນຫຍ້າທີ່ແຕກຕ່າງກັນໃນເຂດພື້ນທີ່ຂະຫນາດໃຫຍ່, ການຜະລິດອາຫານສັດໄດ້ເພີ່ມຂື້ນຢ່າງຫຼວງຫຼາຍ
fodder quality
Comments/ specify:
ຫຍ້າທໍາມະຊາດມີທາດອາຫານ ແລະ ທາດໂປຼຕີນຕໍ່າ ທີ່ຈໍາເປັນສໍາລັບການເຕີບໂຕຂອງສັດລ້ຽງ ເມື່ອທຽບກັບແນວພັນທີ່ມີໂປຼຕີນສູງ ທີ່ປູກໂດຍຊາວກະສິກອນ
animal production
Comments/ specify:
ກ່ອນຫນ້ານີ້ ການຂາດແຄນອາຫານສໍາລັບ ການລ້ຽງສັດໄດ້ເຮັດໃຫ້ການຜະລິດສັດຕົກຕໍ່າ. ປັດຈຸບັນຊາວກະສິກອນສາມາດ ນຳເອົາອາຫານສັດຈາກທົ່ງຫຍ້າຂອງລາວຢ່າງພຽງພໍ, ການຜະລິດສັດເພີ່ມຂື້ນຢ່າງຫຼວງຫຼາຍ.
risk of production failure
Comments/ specify:
ເນື່ອງຈາກວ່າອາຫານສັດມີຈໍາກັດ ໂດຍສະເພາະແມ່ນໃນລະດູແລ້ງ, ຄວາມລົ້ມເຫຼວຂອງການຜະລິດສັດແມ່ນມີບັນຫາ. ປັດຈຸບັນ ລາວສາມາດຜະລິດອາຫານສັດທີ່ມີຄຸນຄ່າສູງ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ຂະຫນາດໃຫຍ່, ຄວາມສ່ຽງຂອງການຜະລິດຫຼຸດລົງບາງລະດັບ.
product diversity
Comments/ specify:
ເມື່ອກ່ອນ ທີ່ຊາວກະສິກອນ ມີພຽງແຕ່ຫຍ້າທໍາມະຊາດຈາກທຳມະຊາດ, ແຕ່ວ່າໃນປັດຈຸບັນເຂົາຜະລິດຫຍ້າ Napier, ຫຍ້າ ກີນີ, ຫຍ້າ Paspalum ໂດຍຕົນເອງ
production area
Comments/ specify:
ເມື່ອກ່ອນ ການລ້ຽງສັດ ແມ່ນ ຂື້ນກັບປ່າທໍາມະຊາດ ແລະ ຈາກທົ່ງນາ. ຫຼັງຈາກຊາວກະສິກອນສາມາດຂະຫຍາຍພື້ນທີ່ຜະລິດໄດ້ 15 ຕາແມັດ.
land management
Comments/ specify:
ເມື່ອກ່ອນ ສັດຈະກີນຫຍ້າຢູ່ຕາມບ້ານ, ແລະຊາວກະສິກອນຕ້ອງປອ້ງສັດ. ຫລັງຈາກການປູກຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ຫຍ້າທີ່ມີຮົ້ວ ສາມາດປ່ອຍງົວໄດ້ ສອງອາທິດ. ໃນອະນາຄົດ ງົວສາມາດໄດ້ຮັບອາຫານໂດຍການຕັດ ຫຍ້າສົດ ຫຼື ຫຍ້າອາຫານແຫ້ງ.
Income and costs
expenses on agricultural inputs
Comments/ specify:
ເຂດພື້ນທີ່ຂະຫຍາຍຕົວ ໄດ້ຮຽກຮ້ອງໃຫ້ມີການປະກອບສ່ວນທາງດ້ານການເງິນເພີ່ມເຕີມເພື່ອສ້າງກະສິກໍາລ້ຽງສັດ ແລະ ການປູກ 15 ເຮັກຕາເພີ່ມເຕີມ (ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃຫມ່: ທີ່ພັກອາໄສສັດລ້ຽງ, ຮົ້ວ, ແນວພັນຫຍ້າ ແລະ ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງກະສິກໍາ).
farm income
Quantity after SLM:
80,000,000 kip/annualຂື້ນ
Comments/ specify:
ການພີ່ມຂື້ນຂອງລາຍຮັບ ອີງໃສ່ຄວາມຈິງ, ວ່າໃນປັດຈຸບັນ ຊາວກະສິກອນສາມາດຂາຍງົວທີ່ມີສຸຂະພາບແຂງແຮງ ແລະ ລາຄາທີ່ດີ. ຕົວຈິງແລ້ວ, ລາວຜະລິດງົວ ແມ່ນສົ່ງອອກໄປເຖີງຫວຽດນາມ.
diversity of income sources
Comments/ specify:
ເມື່ອກ່ອນ ງົວໄດ້ຂາຍຈໍານວນຫນ້ອຍ. ຫຼັງຈາກການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ຊາວກະສິກອນກໍ່ໄດ້ລ້ຽງງົວ, ຫມູ, ສັດປີກໃຫ້ແກ່ຕະຫຼາດ. ນອກຈາກນັ້ນ, ລາວຍັງສາມາດຂາຍແນວພັນຫຍ້າຕ່າງໆ.
workload
Comments/ specify:
ການລ້ຽງສັດທີ່ຜ່ານມາ ໂດຍອີງໃສ່ ການລ້ຽງສັດແບບປ່ອຍຕາມໝູ່ບ້ານ. ການສ້າງ ແລະ ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາພື້ນທີ່ທົ່ງຫຍ້າໃຫມ່ ແລະ ການລ້ຽງງົວອື່ນໆ ທີ່ເພີ່ມຂື້ນໄດ້ເຮັດໃຫ້ວຽກງານເພີ່ມຂື້ນ
Ecological impacts
Soil
soil cover
Comments/ specify:
ການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງດິນໄດ້ເພີ່ມຂື້ນຢ່າງຫຼວງຫຼາຍ ເນື່ອງຈາກວ່າການປູກແນວພັນຫຍ້າທີ່ໜາແໜ້ນ.
soil loss
Comments/ specify:
ດິນສາມາດໄດ້ຮັບການແກ້ໄຂດ້ວຍຮາກທີ່ຂະຫຍາຍ ແລະ ລືກຂອງແນວພັນຫຍ້າທີ່ແຕກຕ່າງກັນ. ນອກຈາກນັ້ນ, ເສດຫຍ້າກໍ່ສະຫນັບສະຫນູນການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງດິນທີ່ດີ ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການສູນເສຍດິນໂດຍການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຂອງນ້ໍາ.
soil accumulation
Comments/ specify:
ໃນໄລຍະລະດູຝົນເສດພືດຜັກ ແລະ ປຸຍສາມາດເພີ່ມການສະສົມຂອງດິນ.
soil compaction
Comments/ specify:
ລະບົບຮາກທີ່ຂະຫຍາຍຕົວ ແລະ ເລິກຂອງການປູກຫຍ້າປັບປຸງໂຄງສ້າງດິນຢ່າງຈະແຈ້ງ.
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | increase or decrease | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | not known | |
| seasonal temperature | dry season | increase | well |
| annual rainfall | decrease | moderately | |
| seasonal rainfall | wet/ rainy season | decrease | moderately |
| other gradual climate change | increase | not known |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| local rainstorm | moderately |
| local windstorm | moderately |
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| extreme winter conditions | moderately |
| drought | not well |
Biological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| insect/ worm infestation | moderately |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
negative
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly positive
Long-term returns:
positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- single cases/ experimental
If available, quantify (no. of households and/ or area covered):
15
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 91-100%
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
Ja
other (specify):
ຄວາມເປັນເຈົ້າຂອງ ແລະ ອົງການຈັດຕັ້ງ
Specify adaptation of the Technology (design, material/ species, etc.):
ໃນຕົ້ນປີ 2009, ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີກວມເອົາເນື້ອທີ່ບ້ານ 15 ເຮັກຕາ ແລະ ໄດ້ຮັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງຂື້ນ ໂດຍການສະຫນັບສະຫນູນຂອງໂຄງການ ແລະ ຮັກສາໄວ້ໂດຍກຸ່ມລ້ຽງສັດ. ຫຼັງຈາກນັ້ນໃນປີ 2014 - ຫຼັງຈາກຄວາມລົ້ມເຫລວຂອງໂຄງການ ຍ້ອນຄວາມຫຍຸ້ງຍາກໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງ ແລະ ການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ - ຜູ້ໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນຂອງບ້ານ ໄດ້ເຊົ່າດິນຈາກອໍານາດທ້ອງຖິ່ນ ແລະ ນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີດ້ວຍຕົນເອງ.
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| ໃນເບື້ອງຕົ້ນໂຄງການ (ADB) ໄດ້ໃຫ້ອຸປະກອນ, ແກ່ນຫຍ້າ ແລະ ການກະກຽມດິນ |
| ປັບປຸງຄຸນນະພາບການລ້ຽງສັດ |
| ເພີ່ມລາຍຮັບຂອງຄົວເຮືອນຈາກສັດລ້ຽງ |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| ຄຸນະພາບຂອງດີນດີຂື້ນ ຍ້ອນຝຸ່ນສັດ ແລະ ເສດພືດ |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| ນ້ໍາບໍ່ພຽງພໍໃນລະດູແລ້ງ ເຊິ່ງສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ການຜະລິດຫຍ້າ | ຕ້ອງການພື້ນທີ່ເກັບນ້ຳ |
| ຄວາມຫຍຸ້ງຍາກໃນການຄວບຄຸມສັດໃນພື້ນທີ່ຂະຫນາດໃຫຍ່ດັ່ງກ່າວ | ຈໍາກັດພື້ນທີ່ລ້ຽງສັດ |
| ມີຄວາມຫຍຸ້ງຍາກທີ່ຈະເກັບມູນສັດ ເພື່ອໃສ່ຝຸ່ນໃຫ້ດີນ |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
1 ຄັ້ງ
- interviews with land users
2 ຄົນ
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
27/06/2017
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules