Non Labour [France]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Julie Lemesle
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: Ursula Gaemperli, Gudrun Schwilch, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_3164 - France
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Interactive Soil Quality assessment in Europe and China for Agricultural productivity and Environmental Resilience (EU-iSQAPER)1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
Nee
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
C'est travailler le sol sans retournement sur tout ou une partie des parcelles de l'exploitation avec pour objectif l'abandon de la charrue.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
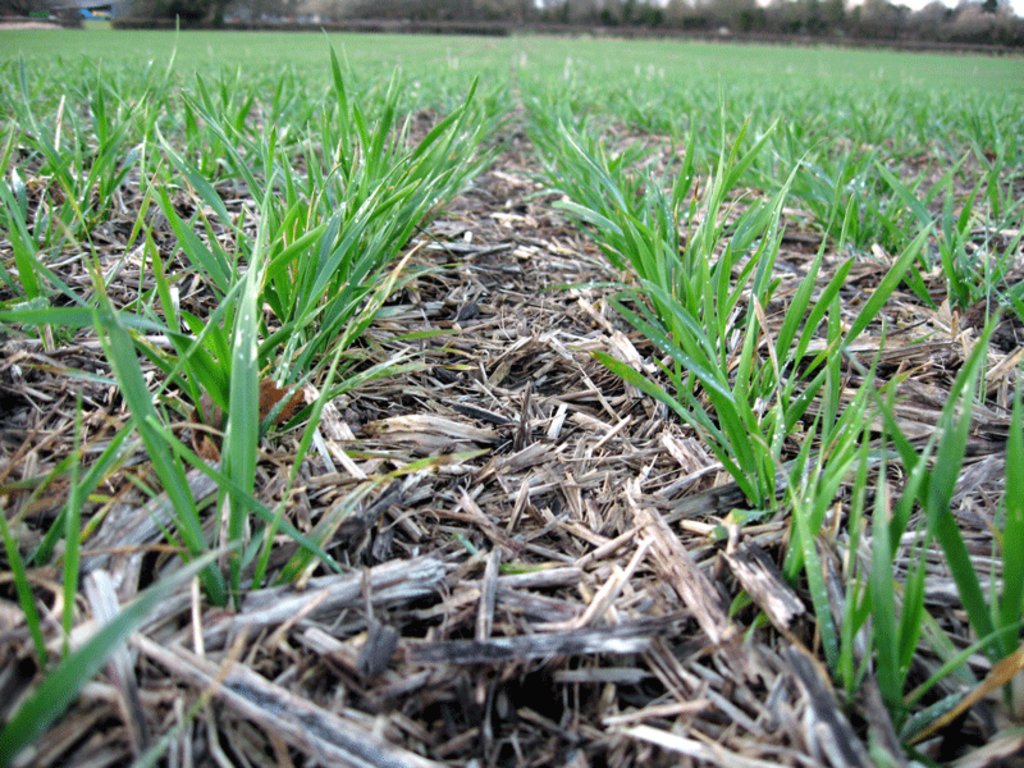
1. Le non-labour est appliqué sur des parcelles cultivés en céréales. climat océanique dans un paysage semi-bocager, sol de qualité bonne à moyenne. Moyens opérationnels agricoles bons et accessibles pour les agriculteurs.
2. Les principales caractéristiques du non-labour sont
- l'absence du passage de la charrue
- la préparation de la terre se faisant par une utilisation d'un désherbant chimique type Glyphosate
3. L'objectif du non-labour est de réduire le travail du sol mécanique et le trafic sur les parcelles.
4. Pour mettre en place une culture sans labour, ici nous allons prendre l'exemple de la culture du maïs, il faut plusieurs étapes:
-Déchaumage
-Désherbage
-travail profond (outils à dents)
-travail superficiel
-semis
Il n'y a donc pas d'étape de labour à la charrue et de décompactage.
5. Les avantages du non labour ainsi que leurs impacts sont:
>Avantage environnemental, amélioration de la valeur agronomique du sol
- réduction de l'érosion
- limitation de la battance
- amélioration de la structure
- augmentation de la porosité et meilleure pénétration de l'eau dans le sol
- amélioration de l'activité biologique
- amélioration de la portance
> Avantage économique
- Gain de temps: l'agriculteur gagne du temps plus qu'il ne passe pas la charrue
- Réduction des charges de mécanisation: moins de temps de travail à l'hectare, donc moins de consommation de fuel
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
France
Region/ State/ Province:
Bretagne/France/Ille et Vilaine
Further specification of location:
Argentré du Plessis
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 1-10 km2
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through land users' innovation
- during experiments/ research
Comments (type of project, etc.):
suite à des travaux de recherches sur le non travail du sol plusieurs groupes d'agriculteurs français se portent vers cette nouvelle technique de culture.
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- create beneficial economic impact
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - maize
- blé
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- minimal soil disturbance
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A1: Vegetation/ soil cover
- A3: Soil surface treatment
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion

physical soil deterioration
- Pc: compaction
- Pk: slaking and crusting
- Ps: subsidence of organic soils, settling of soil
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
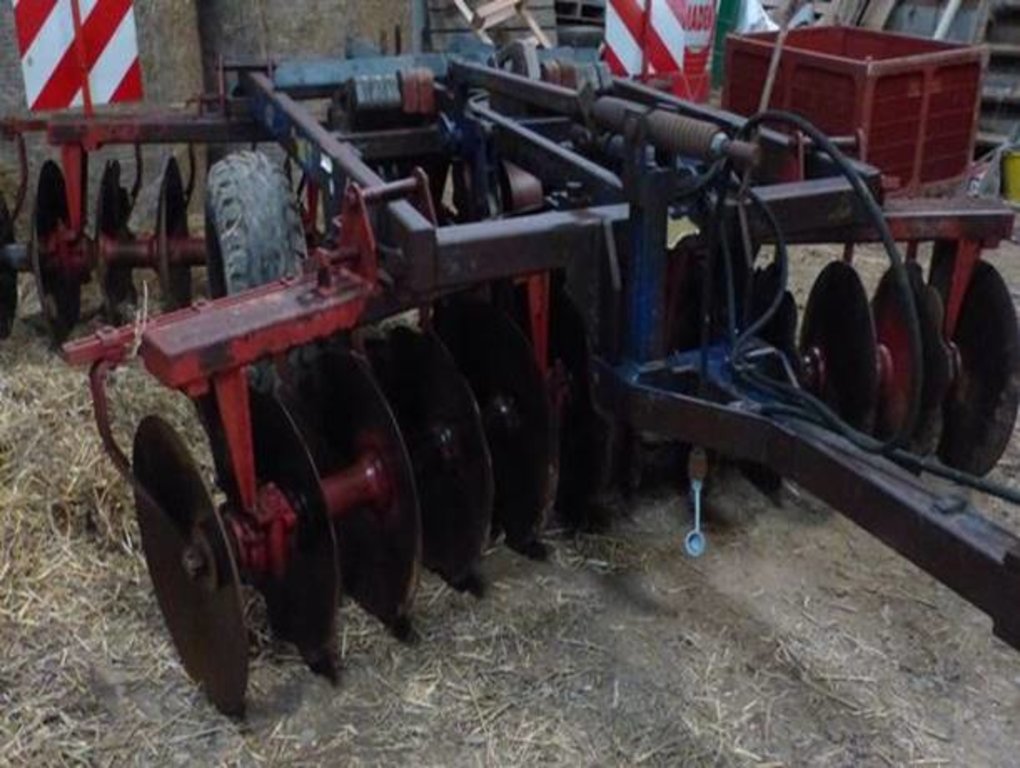
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
Le déchaumeur est utilisé pour détruire les résidus de la culture précédente et pour faire une travail superficiel du sol permettant de nouveau un semis. Il remplace le labour effectué avec une charrue et permet de rester sur un travail en surface en respectant ainsi les différents horizons du sol.
Author:
déchaumeur à disques
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology area
Indicate size and area unit:
1 hectare
other/ national currency (specify):
€
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
115
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | semis direct | 1 X par an |
| 2. | traitement destructif du couvert végétal | 1 x par an |
| 3. | enfouissement superficiel du couvert végétal | 1 X par an |
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
en fonction du "salissement" de la parcelle, nous pouvons être amené à effectué des passages supplémentaires de déchaumeur. chaque passage coute 25€/ha environ
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specify average annual rainfall (if known), in mm:
650.00
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
Climat océanique influé par le Gulf Stream , climat tempéré, avec un hiver doux et un été chaud.
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- not relevant
Comments and further specifications on topography:
climat océanique influencé par le gulf stream hivers doux et été pluvieux
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
on surface
Availability of surface water:
medium
Water quality (untreated):
good drinking water
Is water salinity a problem?
Nee
Is flooding of the area occurring?
Nee
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- medium
Habitat diversity:
- medium
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- mechanized/ motorized
Gender:
- women
- men
Age of land users:
- middle-aged
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- small-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- leased
Water use rights:
- communal (organized)
- individual
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-cultural impacts
conflit lié à l'utilisation du glyphosate dans cette pratique
Ecological impacts
Soil
soil moisture
Comments/ specify:
limitation du dessèchement du sol du fait d'une meilleur couverture
soil cover
Quantity before SLM:
80% sol couvert
Quantity after SLM:
100% sol couvert
soil loss
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
groundwater/ river pollution
Quantity before SLM:
qté glyphosate +
Quantity after SLM:
qté glyphosate ++
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
neutral/ balanced
Long-term returns:
slightly positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
neutral/ balanced
Long-term returns:
slightly positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- 1-10%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
Comments:
cette démarche est liée à l'innovation et la volonté des agriculteurs. elle ne fait pas l'objet d'incitation financière de l'état ou de la PAC.
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
Ja
other (specify):
refus du glyphosate de la part des consommateurs
Specify adaptation of the Technology (design, material/ species, etc.):
privilégier l'enfouissement des couverts végétaux plutot que la destruction par le glyphosate.
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| moins de passage d'outils dans les champs |
| amélioration de la structure et de la vie des sols |
| moins de temps de travail |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| amélioration de la structure et de la vie des sols. |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| utilisation de produits phytosanitaires pour la destruction des couverts | enfouissement des couverts végétaux |
| pas adapté à tous les types de sol | adapter la pratique aux zones pédoclimatiques qui le permettent |
| difficile en agriculture biologique | mener des recherches sur la pratique en bio pour limiter l'impact des adventices et ravageurs des cultures. |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| - | |
| - |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
2
- interviews with land users
2
- compilation from reports and other existing documentation
2
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
18/10/2016
7.3 Links to relevant online information
Title/ description:
Dépliant PDF "Réussir le passage au non-labour"
URL:
http://www.terresinovia.fr/uploads/tx_cetiomlists/depliant_nonlabour_midipyr.pdf
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules