Cultivos en terrazas [Ecuador]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Pablo Caza
- Editor: Carlos Samaniego
- Reviewers: Giacomo Morelli, Nicole Harari, Johanna Jacobi
Cultivos en terrazas
technologies_3277 - Ecuador
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
land user:
Ecuador
co-compiler:
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Ministerio de Ambiente y Agua Ecuador (MAAE) - EcuadorName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Ministerio de Agricultura y Ganadería Ecuador (MAG) - EcuadorName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Organización de la Naciones Unidas para la Alimentación y la Agricultura Ecuador (FAO Ecuador) - Ecuador1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
20/11/2018
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
Nee
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
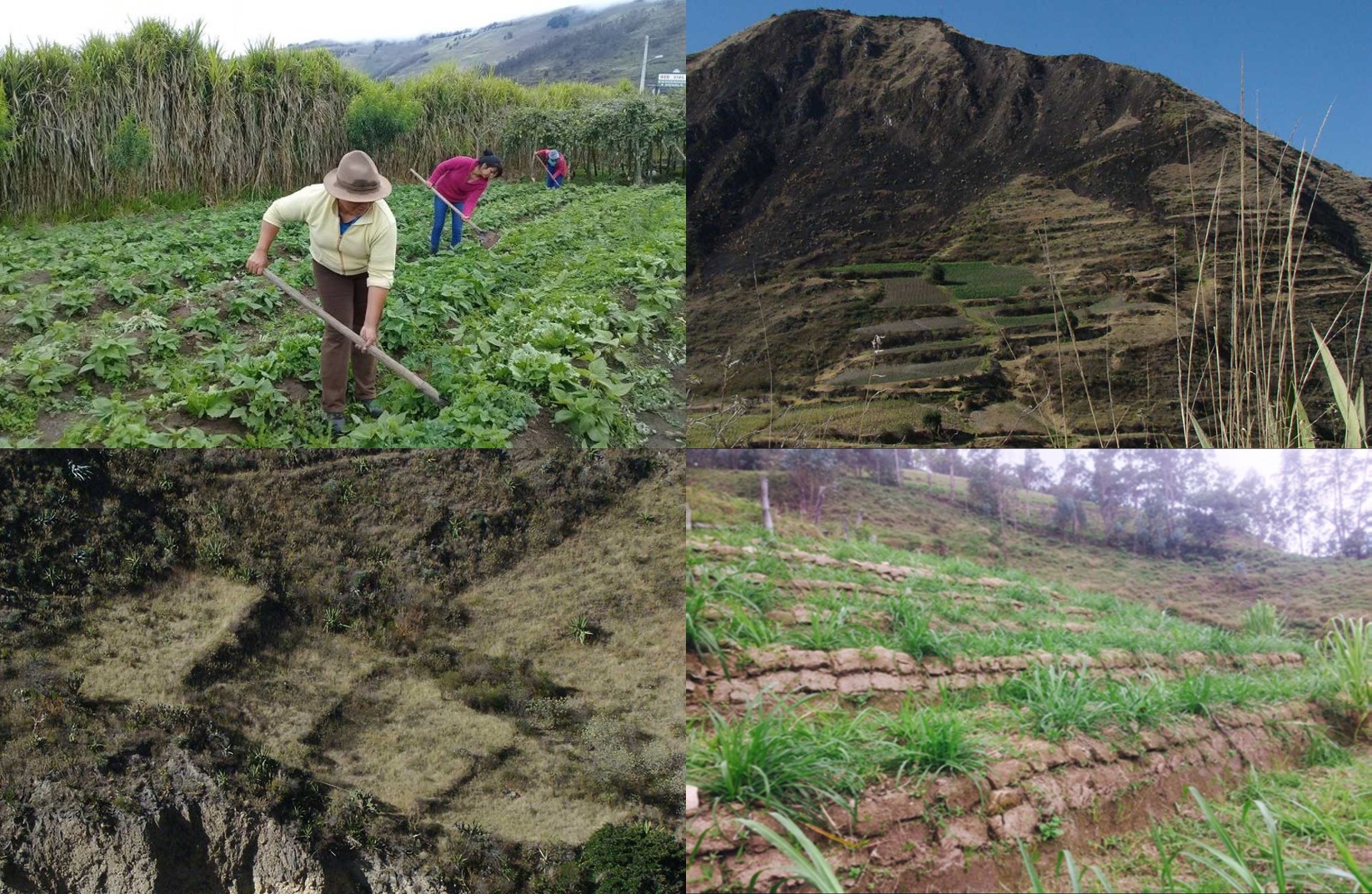
Los cultivos en terrazas son una técnica agrícola de manejo y conservación del suelo originaria de los pueblos andinos. Consiste en cortar el perfil de una pendiente (paisaje montañoso) de manera escalonada para, en el suelo horizontal resultante, sembrar (hortalizas, arbustos o arboles) y cultivar especies agrodiversas que se den en la zona.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
Esta tecnología consiste en la siembra de pastos o arbustos en hileras que tienen la característica de tener las raíces profundas que les permiten sostener la tierra que se desliza por la pendiente y labores culturales que realizan en el terreno, las hileras de pastos o arbustos deben ser sembradas con curvas de nivel con un distanciamiento desde los 5 hasta los 20 m dependiendo de la pendiente. La erosión de los suelos es considerada uno de los problemas ambientales más significativos del sector rural, asimismo, dicha problemática está asociada a una disminución de la productividad y eficiencia de los suelos, provocada por una baja retención tanto del agua como del suelo, cuya tendencia a escurrir se manifiesta en mayor medida en terrenos con pendientes pronunciadas. La incorporación de las técnicas de conservación de aguas y suelos demanda un importante esfuerzo técnico y económico, por lo que los conocimientos referentes a esta temática y los estudios que se han realizado al respecto, son escasos. Este esfuerzo, está dirigido a pequeños propietarios agrícolas y forestales de sectores semiáridos de nuestro país, y que tiene por objetivo el ofrecer nuevas tecnologías de conservación de aguas y suelos, que permitan actuaciones más acordes con el medio ambiente físico y social y que hagan posible acercarse hacia un desarrollo sostenible.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Ecuador
Region/ State/ Province:
Provincia de Chimborazo
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- more than 50 years ago (traditional)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through land users' innovation
- as part of a traditional system (> 50 years)
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- conserve ecosystem
- reduce risk of disasters
- create beneficial economic impact
- create beneficial social impact
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Perennial (non-woody) cropping
- Tree and shrub cropping

Mixed (crops/ grazing/ trees), incl. agroforestry
- Agroforestry
- Agro-pastoralism
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- mixed rainfed-irrigated
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 2
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- agroforestry
- integrated soil fertility management
- irrigation management (incl. water supply, drainage)
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

structural measures
- S1: Terraces
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion
- Wm: mass movements/ landslides
- Wr: riverbank erosion

physical soil deterioration
- Pc: compaction
- Pk: slaking and crusting

biological degradation
- Bq: quantity/ biomass decline
- Bl: loss of soil life
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
- reduce land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
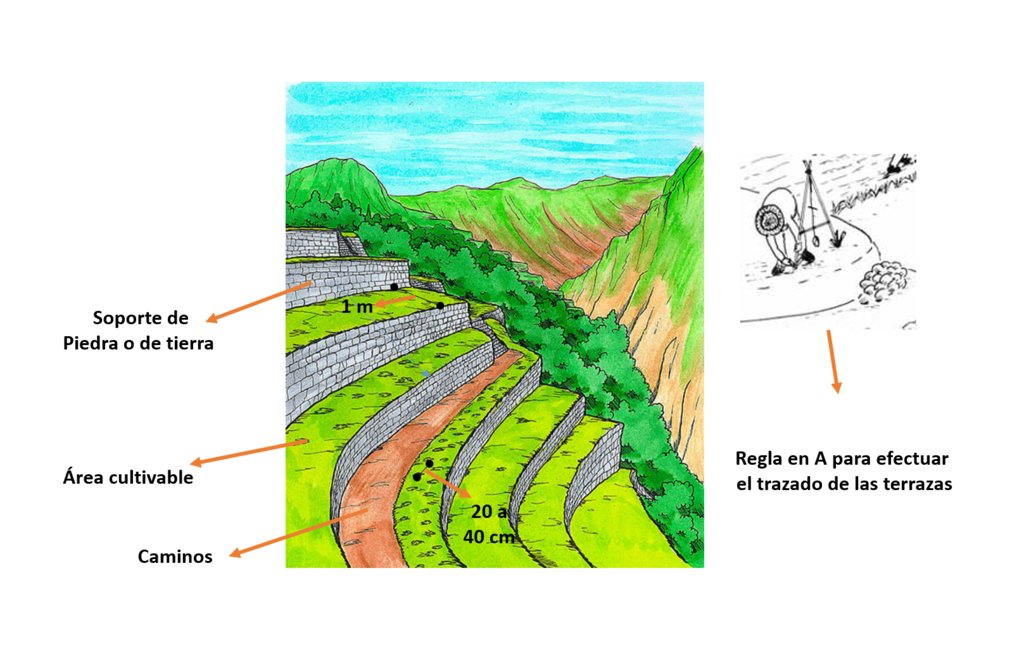
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
Para construir una terraza se la debe mantener a nivel con una regla en A.
Se pueden construir soportes de piedra, o únicamente se lo deja con el talud de tierra.
La distancia entre las terrazas depende, en muchos de los casos, de los cultivos que se van a sembrar. Generalmente tinene 1 metro de ancho y entre cultivos, si son hortalizas, se siembra de 20 a 30 cm entre cada planta.
Las terrazas son una manera excelente de aumentar el área cultivable de un huerto familiar a largo plazo.
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology unit
Specify unit:
cultivos en terrazas
Specify volume, length, etc. (if relevant):
2500 metros cuadrados
Specify currency used for cost calculations:
- US Dollars
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
15
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Limpieza de terreno | Vegetative | inicio |
| 2. | Transporte de materiales | Structural | logistica |
| 3. | Preparación de terreno | Agronomic | implementación |
| 4. | Siembra de pasto o arbustos | Agronomic | implementación |
| 5. | Riego y mantenimiento ( 6 meses) | Management | implementación |
Comments:
Un jornal equivale a un día de trabajo pagado a razón de 15 dólares.
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Limpieza de terreno | jornal | 4.0 | 15.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | Transporte de materiales | jornal | 3.0 | 15.0 | 45.0 | 20.0 |
| Labour | Preparación de terreno | jornal | 40.0 | 15.0 | 600.0 | 50.0 |
| Labour | Siembra de pasto o arbustos | jornal | 3.0 | 15.0 | 45.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Riego y mantenimiento | jornal | 10.0 | 15.0 | 150.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Semilla de pasto | kg | 3.0 | 15.0 | 45.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Pala | unidad | 2.0 | 10.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Barreta | unidad | 2.0 | 10.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Vehiculo | flete | 2.0 | 15.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | Arboles frutales | planta | 25.0 | 3.0 | 75.0 | |
| Plant material | Semillas de hortaliza | kit | 5.0 | 10.0 | 50.0 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 1140.0 | |||||
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Limpieza | Management | mensual |
| 2. | Acondicionamiento de terrazas | Structural | mensual |
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
If possible, break down the costs of maintenance according to the following table, specifying inputs and costs per input. If you are unable to break down the costs, give an estimation of the total costs of maintaining the Technology:
219.0
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Limpieza | Jornal | 6.0 | 15.0 | 90.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | Acondicionamiento de terrazas | jornal | 10.0 | 15.0 | 150.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Machete | machete | 2.0 | 10.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Pala | pala | 2.0 | 10.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 280.0 | |||||
4.8 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
El factor más determinante en esta técnica es la mano de obra.
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- semi-arid
- arid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- concave situations
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- coarse/ light (sandy)
- fine/ heavy (clay)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- coarse/ light (sandy)
- fine/ heavy (clay)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
on surface
Availability of surface water:
medium
Water quality (untreated):
for agricultural use only (irrigation)
Is water salinity a problem?
Nee
Is flooding of the area occurring?
Nee
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- medium
Habitat diversity:
- medium
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- poor
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
Gender:
- women
- men
Age of land users:
- middle-aged
- elderly
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- small-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, not titled
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- leased
- individual
Water use rights:
- leased
- individual
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Comments/ specify:
La producción de los cultivos en terrazas se incrementa debido al uso eficiente del agua.
crop quality
Comments/ specify:
La calidad se incrementa por las condiciones de espacio dispuestas en la ladera, considerando pendiente.
risk of production failure
production area
Income and costs
farm income
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
surface runoff
Climate and disaster risk reduction
landslides/ debris flows
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
water availability
Comments/ specify:
Se realiza infiltración y mejor distribución del agua.
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | Type of climatic change/ extreme | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual rainfall | increase | well |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Hydrological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| landslide | very well |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- single cases/ experimental
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
Nee
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| Las terrazas permiten sostener la tierra que se desliza por la pendiente y labores culturales que realizan en el terreno. |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Deslizamientos | Cálculo adecuado del tamaño del bancal teniendo en cuenta el porcentaje de pendiente. |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Demanda un importante esfuerzo técnico y económico |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
8
- interviews with SLM specialists/ experts
4
7.3 Links to relevant information which is available online
URL:
http://www.fao.org/americas/en/
URL:
http://www.fao.org/americas/en/
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules