



Mushroom cultivation is a preferred and promoted technology by small and medium scale farmers with less land holdings. The technology has the portential to generate considerable nutritional benefits, employment and additional income which, in return, is invested in sustainable land management practices. To date, the demand for mushrooms increases as the result of a fast population growth having less income and food supply. Hence, a growing number of farmers adopt the mushroom production technology.
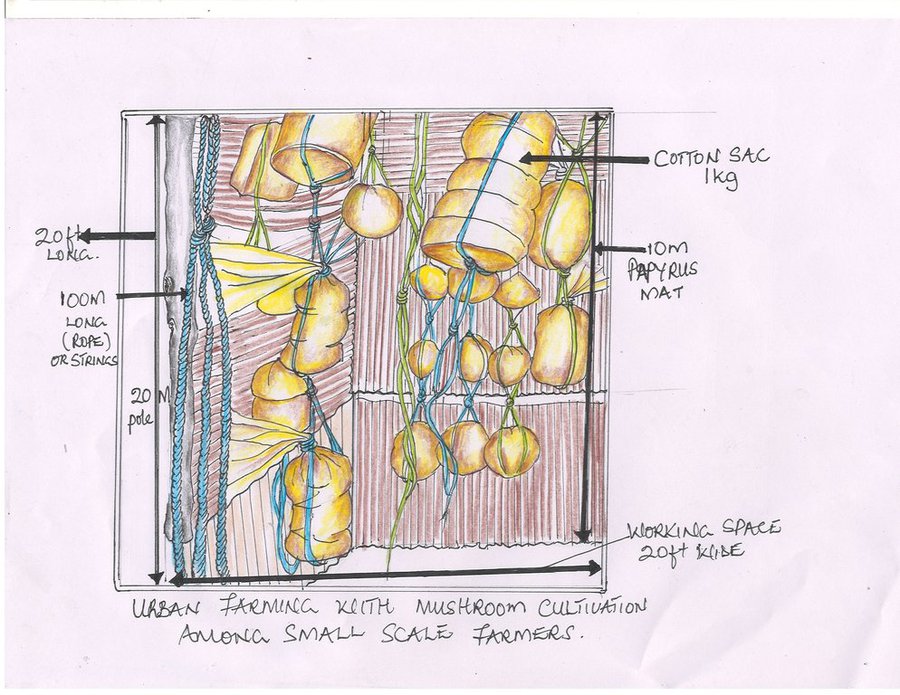
To establish such a technology, materials required include: cotton, a metallic drum (100 litres), a gunny bag of the size of 100kg, water, tarpuline, lime/maize brand, polyethene bags, banana leaf stock, cooking stove, firewood, mushroom seeds, tooth picks/nails and strings of approx. 100m length.
Listed below are the activities / procedures required for the establishment of a mushroom cultivation in a homestead.
-Water-soak the cotton into the drum and cover the drum with a gunny bag
-Remove the water out of the drum. The soaked cotton remains in the drum for around 2 hours
-Remove the soaked cotton on to a taurpline sheet and mix it with cultural lime/rice brand /maze brand that is placed on the taurpline
-Get black polythene bags and pack 1 kg of cotton into each polythene bag
-Place the banana leaf stock at the bottom of the drum and fill it with 20 litres of water
-Cut the gunny bag in the middle and cover the inside part of the drum to prevent burning of the cotton in the polythene bags while boiling
-Place the cotton in polythene bags into the drum and put the drum on the cooking stove to heat. The first line of polythene bags should be bent to prevent boiling water to enter the cotton
-Cover the drum tight with gunny bags
-Steam for around 2 hours
-Remove the firewood to cool until the next day
-Then remove the cooled cotton and place it on the tarpuline
-Buy mushroom seeds, smash the seeds (i.e, one pack of seeds mixes 2 gardens)
-Each kg of cotton mixed containing the mushroom seeds should be squeezed into the black polythene bags in a ball shape and tied on top
-Then get a tooth pick or a nail and pinch down 3 to 4 holes for air to come out
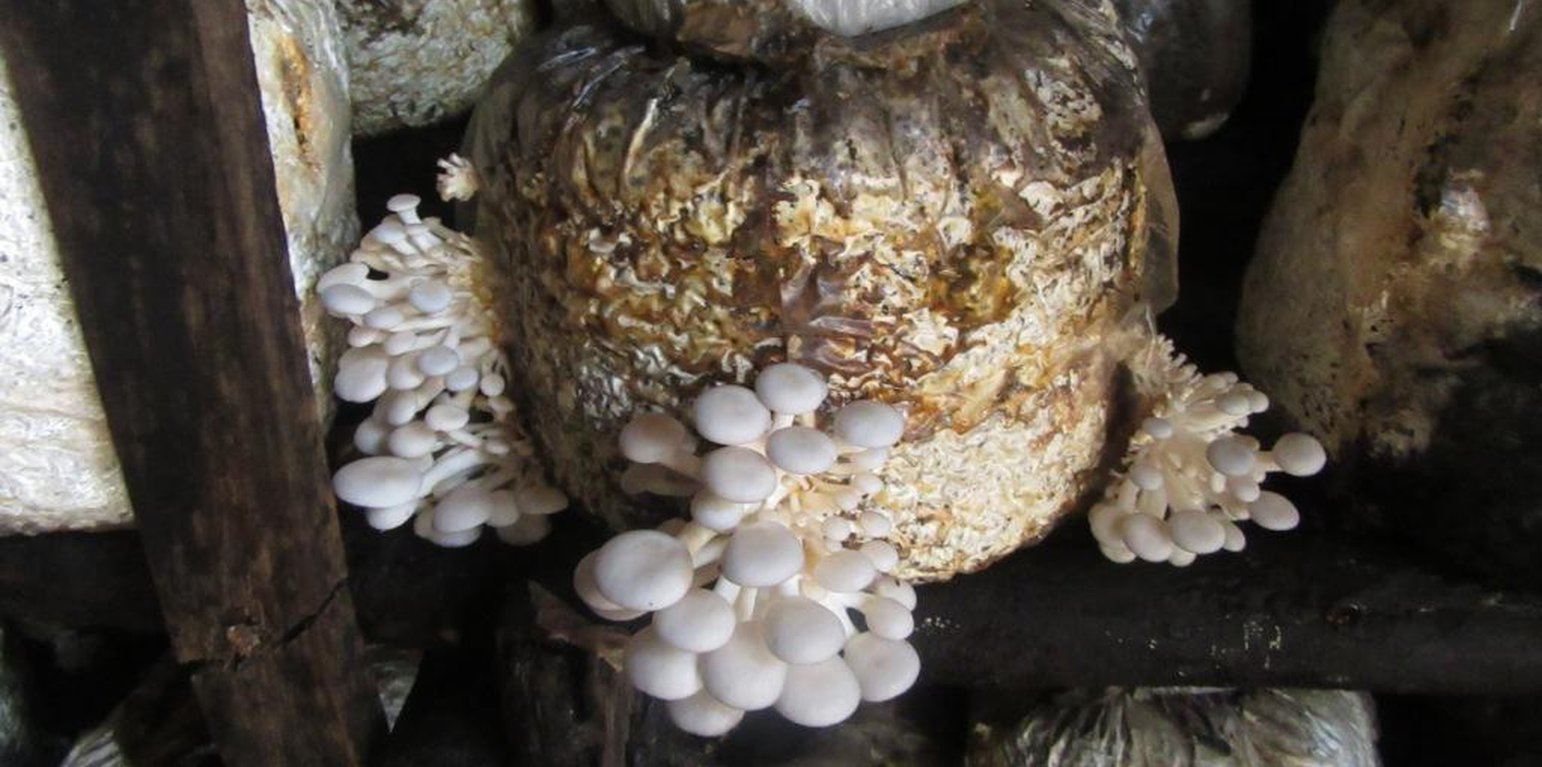
-Tie strings to the packed polythene bags and hang them for 14 days. (Strings enable sprouting on the gardens from all sides). Having moderate light, water needs to be applied twice a day or thrice in case of dry season during a period of 3 weeks
-After 7 days, the mushrooms start sprouting
-Leave the mushroom on the garden for 2-3 days before harvesting
-Once mushrooms are ripe, get a sharp knife and cut the stem carefully
On harvesting, the first week yields 8 Kg every second day, thereafter 3 kg of mushrooms every second day during the second month. Drums can be replaced every after 4 months so that the cost of maintenance is kept relatively low.
Mushrooms are a source of nutrients and proteins (Protein content, 3-7% when fresh and 25- 40% when dry). They are useful in preventing diseases and have medicinal values. Environmentally, the growing of mushrooms reduces pollution through bio-conservation and improves on crop production since harvested manure from the used mushroom ‘garden’ can be recycled as fertilizers for vegetable gardens at homes.
Despite the advantages, the technology faces various challenges: These include lack of a workplace (physical facility), lack of finance and skills on hygiene and sterilization, compost preparation, market challenges that include instability and decrease in sales prices of the products and inputs. Environmental factors like humidity, Ph, light and ventilation if not controlled may influence the growing process. Insects, diseases and animals due to the enclosed environment in which the mushrooms grow are a high risk. This may result in disease infestations like snails infestation.
However, maintenance costs of this technology are cheaper compared to establishment costs with minimum costs required for replacing worn out poles, replacing drums which can be at least every after 5 months.
الموقع: Kamwokya, Kisenyi, Kampala, اوغندا
عدد مواقع تنفيذ التقنيةالتي تم تحليلها: موقع واحد
انتشار التقنية: يتم تطبيقها في نقاط محددة/ تتركز على مساحة صغيرة
تاريخ التنفيذ: منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
نوع التقديم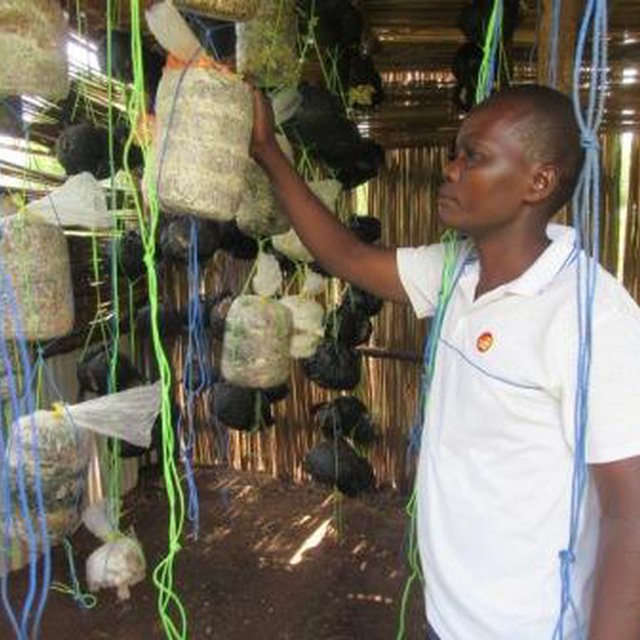



| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة (Uganda shillings) | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل (Uganda shillings) | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي |
| العمالة | |||||
| Making a structure | Man day | 1,0 | 30000,0 | 30000,0 | 100,0 |
| Hanging strings | Man day | 1,0 | 10000,0 | 10000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | |||||
| Drum | piece | 1,0 | 50000,0 | 50000,0 | 100,0 |
| Cotton | piece | 2,0 | 25000,0 | 50000,0 | 100,0 |
| Polythen bags | piece | 2,0 | 3000,0 | 6000,0 | 100,0 |
| Jerricans | piece | 4,0 | 5000,0 | 20000,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | |||||
| Strings | piece | 5,0 | 3000,0 | 15000,0 | 100,0 |
| Poles | piece | 20,0 | 3000,0 | 60000,0 | 100,0 |
| Nails | Kg | 3,0 | 5000,0 | 15000,0 | 100,0 |
| Papyrus mats | piece | 10,0 | 7000,0 | 70000,0 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | |||||
| Tarpuline | piece | 1,0 | 20000,0 | 20000,0 | 100,0 |
| Seed packs | piece | 50,0 | 2000,0 | 100000,0 | 100,0 |
| Maize brand | Kg | 10,0 | 1000,0 | 10000,0 | 100,0 |
| Cultural lime | Kg | 1,0 | 15000,0 | 15000,0 | 100,0 |
| Water | piece | 10,0 | 300,0 | 3000,0 | 100,0 |
| Firewood | piece | 5,0 | 2000,0 | 10000,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 484'000.0 | ||||
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة (Uganda shillings) | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل (Uganda shillings) | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي |
| معدات | |||||
| Replace old poles | piece | 10,0 | 3000,0 | 30000,0 | 100,0 |
| Replace old drums | piece | 50000,0 | 1,0 | 50000,0 | 100,0 |
| Spray snails | man hour | 3000,0 | 1,0 | 3000,0 | 100,0 |
| Cleaning the room in which mushrooms grow on their gardens | man hour | 5000,0 | 1,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 88'000.0 | ||||
She can now be able to pay loans and facilitate home errands.
There are many friendships created through the enterprise.