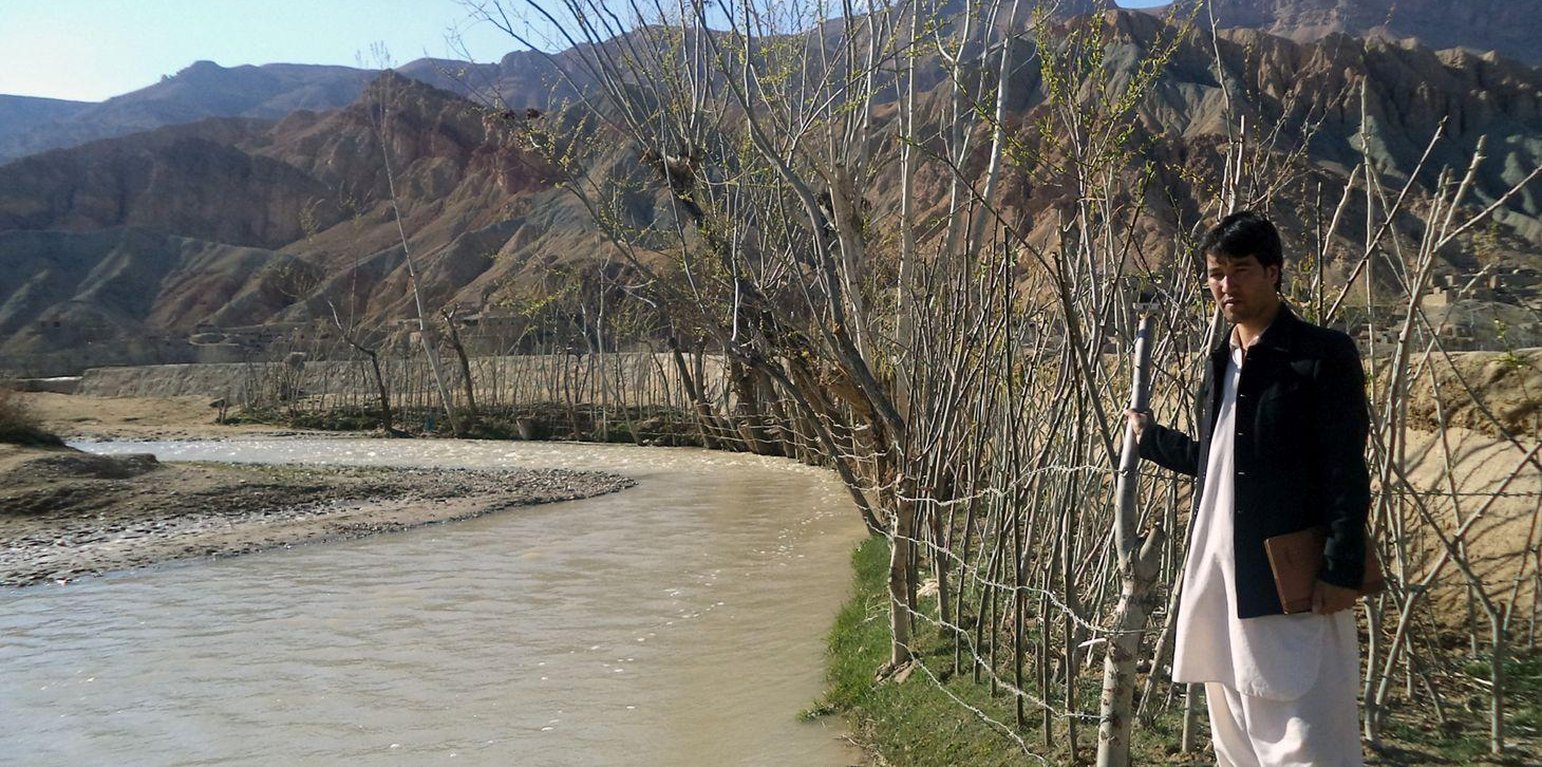




Lack of vegetation coverage in the hills and mountains of Saighan district has become the source of destructive flash floods. Harvest of shrubs and other vegetation for fuel wood and the uncontrolled grazing of animals in upper catchment areas are some of the reasons for the loss of vegetation. Flash floods, that mainly occur during the spring and summer seasons, destroy many hectares of agriculture lands and gardens,damage public infrastructures and sometimes threatens lives.
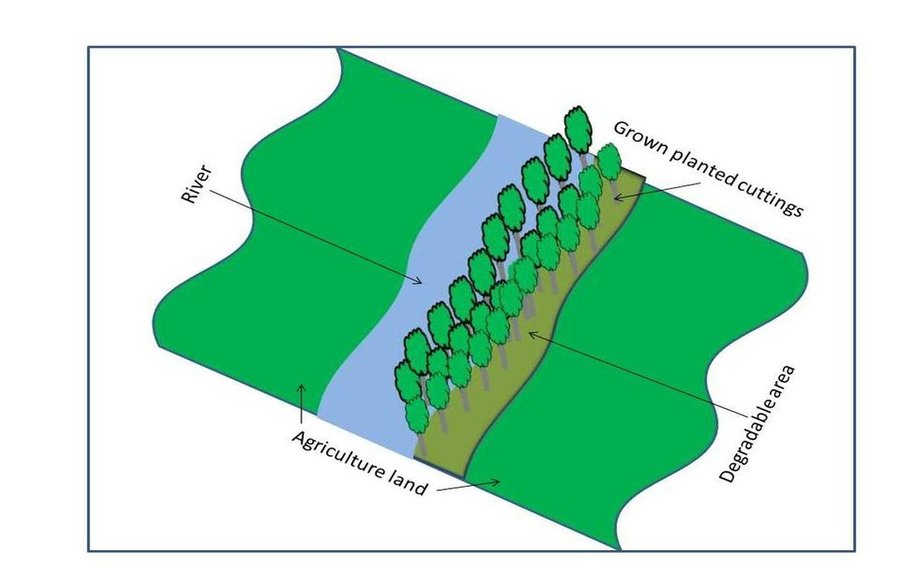
The plantation of long root trees in lower catchment areas is an effective and low-cost technology. Its objective is to prevent flood damage. Trees hold the soil in place with their root structures decreasing land degradation and soil erosion. It is a low cost activity that can be alternative option to protection walls which are more costly, both in terms of establishments and maintenance. Additional benefits of the technology are the increased availability of wood beams for construction, of fuel wood and of fodder. This technology, coupled with information campaigns, may help to provide a strong disincentive against cutting shrubs and grazing in upper catchment areas. In addition, increasing the number of indigenous trees help reduce the negative effects of climate change. The trees also serve as wind breaks.
Having mobilized the community, areas along the watercourse that have been damaged by floods as well as unproductive lands were selected. Based on their ability to adapt well to the local environment, cuttings of Salix (or Willow) and Populus (or Poplar) were selected for planting. Cuttings were provided from the district. Each participating household planted 400 cuttings (2 m long size). The cuttings were planted at a distance of 25 cm and the line to line distance was 100 cm. For the first year, wooden belts, placed along the plating line may protect the new saplings from flood damages, ensuring that the sapling are able to grow. Protection by fencing with barbed wire in two first years also prevents grazing of leaves and new branches by animals.
Interested households should be introduced by the Community Development Council members through a transparent selection process and considering the following criteria:
•the household should be interested to plant long root tree cuttings;
•the household should have enough degraded / riverbank and waste land to plant cuttings;
•Willingness to invest.
The cost of applying riverbank stabilization (plantation of Salix and Populus) is estimated to be 10 AFN/cutting. One person can plant over 500 cuttings per day. In this case, 50% of the cutting cost was contributed by HELVETAS projects and 50% of the cost of the cuttings was contributed by the participating households.
Participating households maintain the plantations. They are responsible for irrigating the cuttings and for protecting them from grazing animals for the first few years. In addition to improved flood protection, participating households increased their understanding riverbank stabilization and energy plantation and managing cuttings (selection, land preparation, fascine and palisade plantation).
Bamyan province is a remote province of Afghanistan with a high poverty rate. It has a semi-arid climate with cold winters and hot and dry summers. During winter, temperatures can drop below -22 degrees. Summer temperatures can reach 34 degrees in the month of July. The average annual rainfall in the area is about 230 mm and some years can be very dry. 90% of the population relies on subsistence agriculture for their livelihoods and off-farm activities are marginal. The growing season in Saighan district is relatively short from April to October and farmers can produce only one crop per year. Farmers with access to irrigation water cultivate cash crops, for example potato and vegetables, in addition to staple crops (wheat) and fodder crops. Those without access to irrigation water cultivate wheat and fodder crops only. Water scarcity during May to September may result to lack of high value crops.
الموقع: Saighan, Bamyan, أفغانستان
عدد مواقع تنفيذ التقنيةالتي تم تحليلها:
انتشار التقنية: منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة (9.85e-05 km²)
في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
تاريخ التنفيذ: منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
نوع التقديم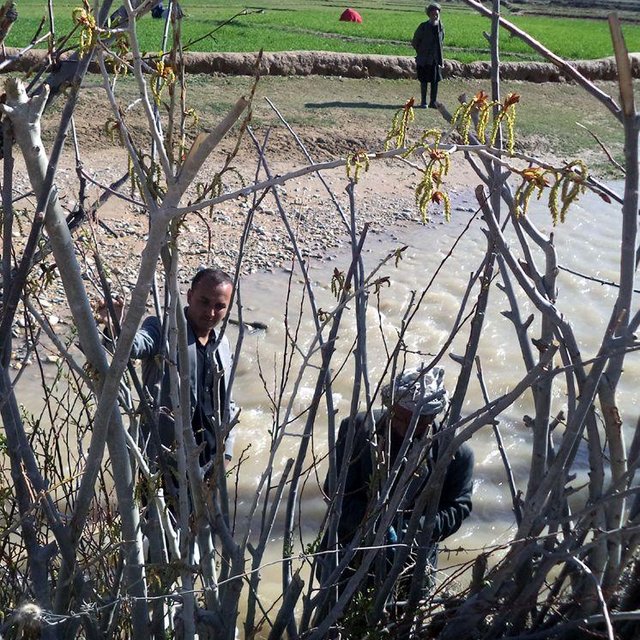





| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة (Afghani) | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل (Afghani) | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي |
| العمالة | |||||
| labour | ha | 1,0 | 54,6 | 54,6 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | |||||
| cutting | ha | 1,0 | 1562,5 | 1562,5 | 50,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 1'617.1 | ||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 25.27 | ||||
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 0
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 19700 kg
The leaves of tree can be more after 5 years, now the saplings are small size
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 0
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 985 pcs
It is going to be increased after some years when the tree saplings groth more sizes
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 0
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 49250 kg
Fuel wood increased
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 0
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 50
The household who applied technology are about sufficient from fuel energy
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 0
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 20%
Houshoulds who applied the technology now they don't pay for providing fuel wood as more as they paid in the past. they provide fuel wood more from their established forest and save their moneys for other needs
People undrestood it is a good technique to control soil erosion and get fuel wood to do not go got mountains for cutting shrubs
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 0
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 30%
Now the boys don't go to the mountains to collect bushes for fuel wood and get education. It has as well contributed the households economically as they do not need to spend money in purchasing fuel wood.
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 0
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 30%
Now the hard wind is not a reason of soil erosion in covered land areas and it get more however the trees grow more and become tall
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 0
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 50%
Protection of area from damage of flood and wind by tree belts decreased soil loss of agriculture lands
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 10
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 50%
Raw materials which accelerate micro organism activities increase in the area
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 10%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 50%
Fallen leaves increased biomass
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 0
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 30%
Wind breaks and protected about more than 3 Hectare agriculture lands
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 0
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 15%
Breaks wave of flood
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 0
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 50%
Decreased damages of wind and frost
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 0
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 50%
Protected the road