



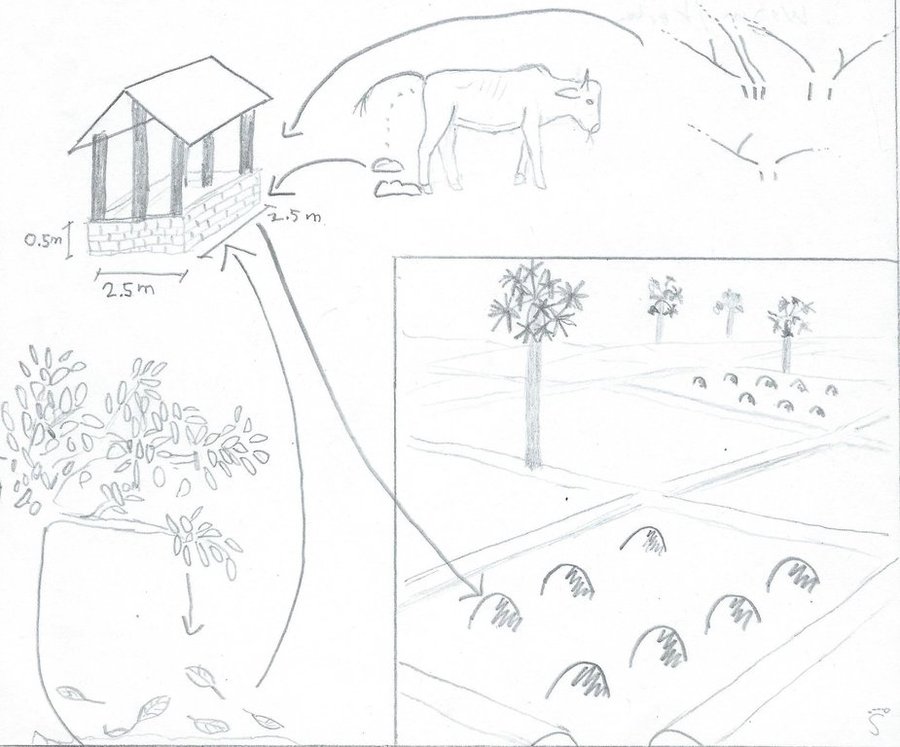
Compost is produced in compost houses and is seen as a good and easy soil amendment. It is produced by mixing organic components (in this case study cow manure, rice straw, different leaves and ash) which are locally available. The ideal mix of ingredients shows an N-to-C ratio of approximately 1 to 25. By adding compost to the topsoil, its humus content is increased, and therefore the soil fertility and water holding capacity are enhanced. Although the technology can be applied with little technological knowledge, the land user’s workload is augmented. This can be detrimental in a human environment with constantly decreasing available labour force.
The purposes of compost production are multifaceted. From the land user’s point of view, the increased yields are certainly one of the most determining factors. This is due to the augmentation of organic matter and nutrients in the topsoil which results in a higher soil fertility. Therefore, the use of chemical fertilizer can be diminished while the yields stay the same. This results in the amelioration of the land user’s livelihood, since he needs to buy less fertilizer. Also, the improved soil structure (according to the land user, the soil is softer and easier to cultivate) and water retention capacity are of importance in this area, since the soils are sandy/loamy, and due to climate change the rainfall is more erratic and droughts more recurrent. Compost also buffers the soil’s pH and prevents acidification. As a consequence, the nutrient availability is increased. Finally, compost adds more biota to the soil.
First, the compost house is built. This can be done either with external inputs such as bricks, cement, and a tin roof (the initial investment is higher, but the recurrent maintenance activities lower), or with locally available, natural inputs such as rice straw and clay for the walls and dried sugar palm leaves for the roof (the initial investment is lower, however there are more recurrent maintenance activities which can be detrimental for the continuation of compost production).
Once the compost house is built, the organic matter (approximately 70 % cow manure, and 30 % rice straw and different leaves, with a small amount of ash) is collected in the surroundings and carried to the compost house. In this case study, compost is produced once during the dry season and once during the wet season. During the dry season, water is added to the organic matter in order to facilitate the composting process. Ideally, the organic matter should be turned in order to guarantee a complete composting process. However, this includes a rather big workload. As a result, turning is not always practiced in the area (high migration rates result in a decrease of available labour force).
When the composting process is completed, the compost is carried to the fields with the use of animal traction. This is done several times: once when the fields are plowed, once when the rice seedlings are transplanted and once while the rice is growing (“top dressing”).
The analyzed area is flat (slope < 2%), with a tropical climate with a (dry and a wet season), and the soils are mostly sandy or loamy. The soils have a low fertility, contain little organic matter, the pH is sinking, the area has been deforested a long time ago and the groundwater table is rather high (1-2 m during the dry season, on the surface during wet season).
Due to climate change, land users notice more erratic rainfalls, temperatures rise and more recurrent droughts. Rice is the predominant crop grown in the area, since it serves as staple food (mix subsistence and commercial activities). Rice is often grown in monocultures and harvested once a year. Once the rice is harvested (dry season), the cattle are released to the paddy fields.
As an addition to rice, most land users grow vegetable and fruits in small home gardens (subsistence) and complement their income by producing handicrafts or through off farm income / remittances from family members working in other places. The increasing migration rate (the young generation leaves the villages to work in the cities, garment industry or abroad) results in a decrease of available labour force in the area. This has detrimental effects on the agricultural activities. Furthermore, the civil war in the 1970s (Khmer Rouge) led to the loss of agricultural knowledge.
الموقع: Rolear Pha-er, Kampong Chhnang, كمبوديا
عدد مواقع تنفيذ التقنيةالتي تم تحليلها:
انتشار التقنية: منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة (approx. 100-10 كم2)
في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
تاريخ التنفيذ: منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
نوع التقديم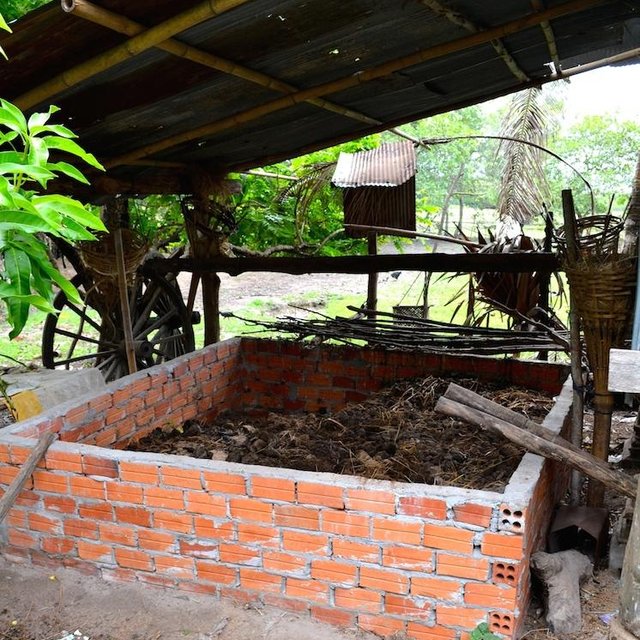





| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة (دولار أمريكي USD) | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل (دولار أمريكي USD) | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي |
| العمالة | |||||
| labour | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 | |
| مواد البناء | |||||
| iron roof | 1,0 | 15,0 | 15,0 | 100,0 | |
| bricks and cement | 1,0 | 31,0 | 31,0 | 100,0 | |
| poles and nails | 5,0 | 1,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 71.0 | ||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 71.0 | ||||
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة (دولار أمريكي USD) | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل (دولار أمريكي USD) | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي |
| العمالة | |||||
| labour | 1,0 | 140,0 | 140,0 | 100,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 140.0 | ||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 140.0 | ||||
The farmer uses less chemical fertilizer. The yields remain the same on the short term.
Less chemical fertilizer used
Due to the use of compost, land users are less dependent on chemical fertilizers. Therefore, the cost of production decreases while the income remains the same.