



Agroforestry is a farming practice that can involve growing of a mixture of woody perennials like trees, shrubs, palms, bamboos, etc. with crops and/or animals, on the same land-management units. Agroforestry systems play an important role in ecological and economical interactions between the different land use components (Lundgren and Raintree, 1982). It represents an interface between agriculture and forestry, and encompasses mixed land-use practices. Agroforestry systems are composed of three attributes:
1. Productivity (improved tree products, yields of associated crops, reduction of cropping system inputs, and increased labor use efficiency);
2. Sustainability (beneficial effects of woody perennials);
3. Adoptability (MoE/Adaptation Fund/UNEP, 2016).
In Cambodia, mungbean grows throughout the whole year almost, depending on the moisture factor. Mungbean is short maturity crop which can be grown both in sloping upland and in lowland areas. In upland areas farmers usually plant their second crop in August and harvest it in October. Mungbean is a crop that can be grown on many soil types, but grows best on alluvial, sandy, and volcanic soils which well drained containing high levels of nutrients (incl. N, P, K, Ca, Mg) and organic matter (MAFF, 2005). Mungbean crop duration depends on the variety, with short-term, medium-term and long-term being harvested between 60-65 days, 65-75 days, and 75-80 days, respectively.
Mungbean residues can make an active contribution to improvement of soil quality through nitrogen fixation and subsequent incorporation of this nitrogen into the soil after root and nodule degeneration by Rhizobium bacteria. The incorporation of the organic root material also improves the soil structure (MAFF, 2005, Chadha, 2010, IRRI-CIMMYT Alliance, 2009). The taproot of the mungbean can penetrate the soil to a depth of 50-60 centimeters. Sometimes, some land users grow mungbean as a green manure crop specifically to improve soil quality (Tauch Ung, 2010).
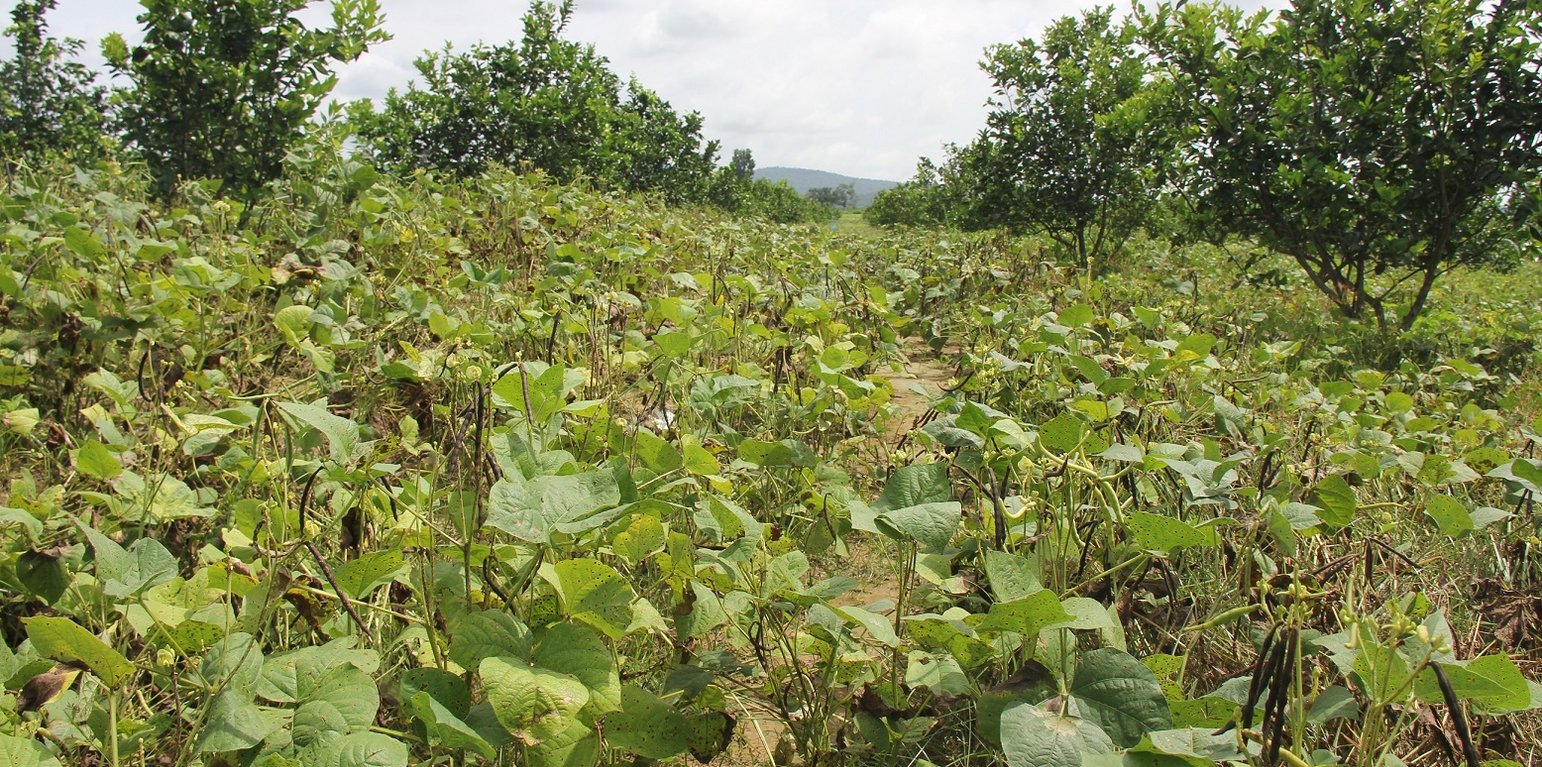
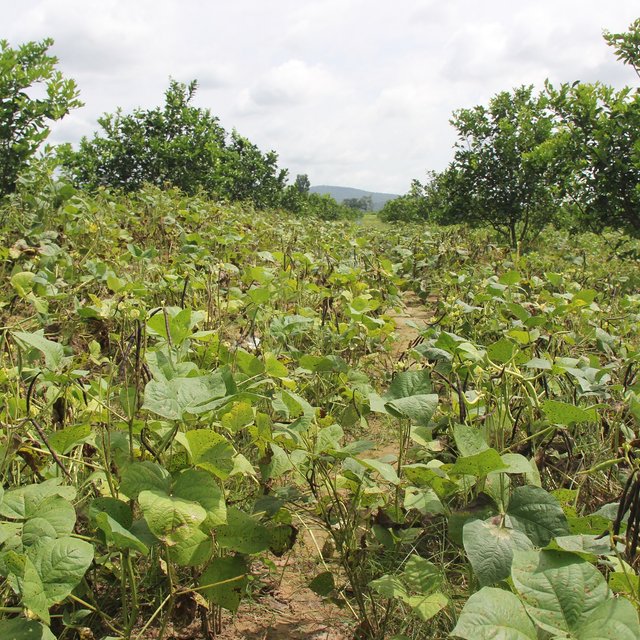
Mr. Chea Sarith is one example of land user who practices intercropping of orange trees with mungbean since 2013. The main purpose is to improve soil fertility, to prevent soil erosion, and to generate income before the orange trees provide fruit. In addition, it eases the weed control. After the harvest the farmer leaves the plant residues on the soil to provide organic matter. With the objective not to harm the roots of the orange trees, he avoids tilling the soil. In general, mungbean grows twice a season depending on the rainfall distribution and soil moisture.
The average yield of direct seeded mungbean as an intercrop between orange trees is about 1,200 kg/ha (harvested 3 times per crop). If mungbean is grown as a single crop the yield is usually ranges from 1,300 to 1,400 kg/ha. The market price for mungbean grain is usually about 4,500 to 5,000 Riel/kg.
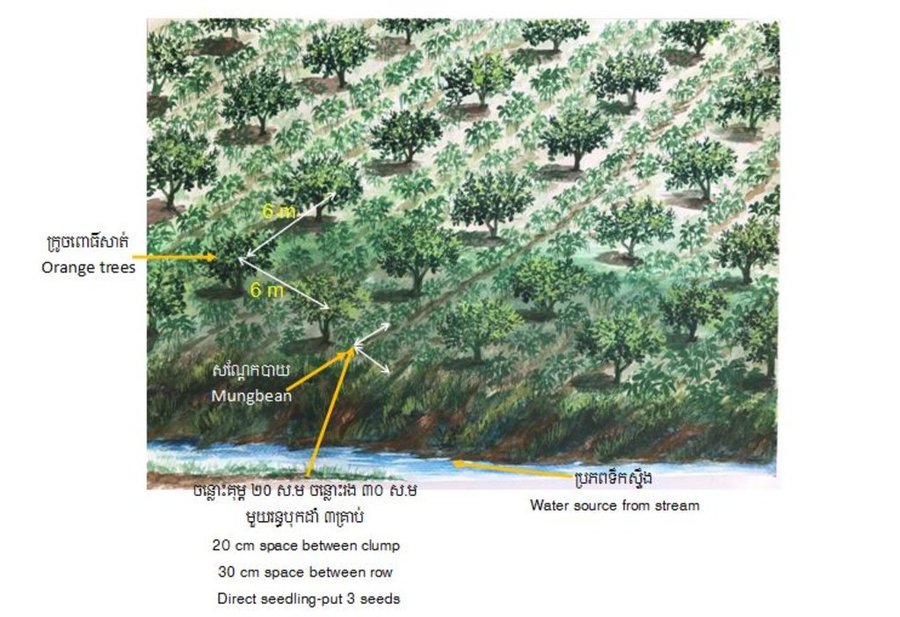
Before planting orange trees the soil requires two turns of ploughing. After first ploughing the soil should dry during 1-2 months, before it can be ploughed again by a wheel harrow. Orange trees then are planted in rows into pits of 1 m x 1 m, with a depth of 70-80 cm. The spacing between the trees, as well as between the rows is usually 6 meters. Before planting, the orange tree seedlings (bought from outside) are usually kept at the farm site for 15 to 20 days, which to allow them to adapt to the conditions of the growing environment. The farmer installed a water pipe in the underground to irrigate the fruit orchard. The nearby stream serves as water source. After the tree plantation, mungbean is sown by direct seeding on the remaining bare soil. This is done by putting 3 to 4 seeds into the seed holes (3 to 4 cm sowing depth at a plant spacing of 20 cm and a row spacing of 30 cm. After harvest the residues of the mungbean plants are squashed by machine and left to rot on the soil surface until is the next mungbean cycle starts by direct seeding.
الموقع: Phnum Kravanh of Cambodia., Ongkrong Village, Samrong Commune, Phnum Kravanh District, Pursat Province., كمبوديا
عدد مواقع تنفيذ التقنيةالتي تم تحليلها: موقع واحد
انتشار التقنية: منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة (approx. < 0.1 كم2 (10 هكتار))
في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
تاريخ التنفيذ: 2013
نوع التقديم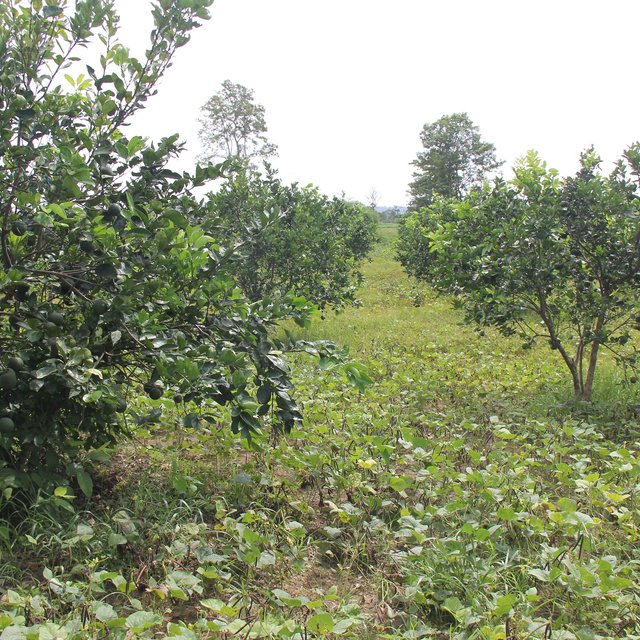








| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة (KHR (Riel)) | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل (KHR (Riel)) | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي |
| العمالة | |||||
| Clear the degraded forest soil | Person-day | 80,0 | 2000,0 | 160000,0 | 100,0 |
| Collect the residue of forest and then burn | Person-day | 60,0 | 20000,0 | 1200000,0 | 100,0 |
| Clear 40 termite mounds in 4 hectares | Person-day | 48,0 | 20000,0 | 960000,0 | 100,0 |
| Hire labor to carry the soil of termite mound to put in the hole of orange tree for planting | Person-day | 180,0 | 20000,0 | 3600000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | |||||
| Grass cutting marchine | piece | 2,0 | 1200000,0 | 2400000,0 | 100,0 |
| Two wheel tractor | piece | 1,0 | 12000000,0 | 12000000,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | |||||
| Orange seedlings | seedling | 1026,0 | 6000,0 | 6156000,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | |||||
| Pumping machine | piece | 1,0 | 1200000,0 | 1200000,0 | 100,0 |
| Irrigation system such as big tube, small tube etc | set | 1,0 | 8000000,0 | 8000000,0 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | |||||
| Planting orange trees | Person-day | 51,0 | 20000,0 | 1020000,0 | 100,0 |
| Pesticide sprayer machine | piece | 3,0 | 600000,0 | 1800000,0 | 100,0 |
| Spraying pesticide hand pump sprayer | piece | 1,0 | 280000,0 | 280000,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 38'776'000.0 | ||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 9'694.0 | ||||
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة (KHR (Riel)) | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل (KHR (Riel)) | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي |
| العمالة | |||||
| Watering the orange trees | Person-day | 11,0 | 20000,0 | 220000,0 | 100,0 |
| Pruning some branches of orange trees | Person-day | 100,0 | 20000,0 | 2000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Hire labor to spray pesticides | Person-day | 8,0 | 20000,0 | 160000,0 | 100,0 |
| Hire labor to harvest mungbean when mature | Person-day | 120,0 | 20000,0 | 2400000,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | |||||
| Mungbean seed (1 hectare need 25 kg of mungbean) seeds) | hectare | 4,0 | 312500,0 | 1250000,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | |||||
| Pesticides for orange trees | bottle | 4,0 | 40000,0 | 160000,0 | 100,0 |
| Chemicals for improving of stem of mungbean | package | 60,0 | 1500,0 | 90000,0 | 100,0 |
| Pesticide to kill worms on mungbean | bottle | 2,0 | 40000,0 | 80000,0 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | |||||
| Direct seeding of mungbean | Person-day | 56,0 | 20000,0 | 1120000,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 7'480'000.0 | ||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 1'870.0 | ||||
The soil fertility was improved, so that the crop production increased steadily. In addition, the farmer now doesn't grow only orange trees, but he also grows mungbean.
The residues of mungbean contain many nutrients, which is suitable for getting good crop quality.
As the farmer plants more than one crop on the plot now, it reduces the production failure. This means that farmer get income from mungbeans before the orange trees provide fruits. The better weed control also reduces insects, which could be harmful to the crop.
There are mungbean and orange trees, now.
Reduced chemical fertilizers on orange trees and mungbean, because after harvesting mungbean residues are kept on the soil which is very good green manure for soil.
The farm income increases considerably due the intercropping system, as both mungbean and orange trees provide yield. In addition, mungbeans provide yield two times per year. Last but not least , mungbean play a key role as green manure which reduces the input of chemical fertilizers and therefore cost.
The mungbean and orange tree cultivation does not consume much of labor force because he doesn't have to spend a lot of time for weeding (as instead of weed mungbeans cover the soil now). On the other hand, the farmer mentioned that the orange plantation is time consuming at the beginning, when the orange trees has to be planted. As well the mungbean need more time at the moment when the plot has to be prepared for first direct seedling. But the technology as a whole entails not a lot of maintenance workload as he uses machinery such as pesticide sprayer machine and mungbean squash machine to facilitate the labor.
The diversification of the crops (oranges and mungbean) has considerably raised the income and therefore strongly prevent food insecurity situations.
The reduction of chemical fertilizer and pesticides provides safer products that improves the health situation. In addition, mungbean and orange fruit deliver many nutrition benefits to human health.
He has joined the orange trees community to sell the orange fruits. Many researches are convinced of his success and the tastiness of his oranges; as for example researchers from the District Office of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Phnum Kravanh, Provincial Department of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Pursat etc.”
By doing the farmer learned that degraded soil can be rehabilitated by the mean of mungbean residues acting as green manure. And from the moment the soil is rehabilitated he can see that this green manure prevents soil degradation at high degree.
Mungbean and orange trees keep the soil moisture, prevent the evaporation to the atmosphere.
Orange trees and mainly the mungbean intercrop cover the soil almost entirely all year around.
The residue of mungbean reduce soil compact by improving the soil structure through providing organic matter to the soil. The increased amount of soil organisms make the sol less compact.
The residues of mungbean left on the soil after harvesting are transformed to organic matter by the process of decay and therefore contribute essentially to increased soil organic matter.
Orange trees and mungbeans are the vegetation cover to avoid bare land, so the sunlight will not come directly to the the soil.
There is more than one crop (orange trees and mungbean).
Now, the soil is somewhat richer in termites, ants, earthworms, crickets ect.
Orange trees and mungbean cultivation promote soil organisms in the habitat.