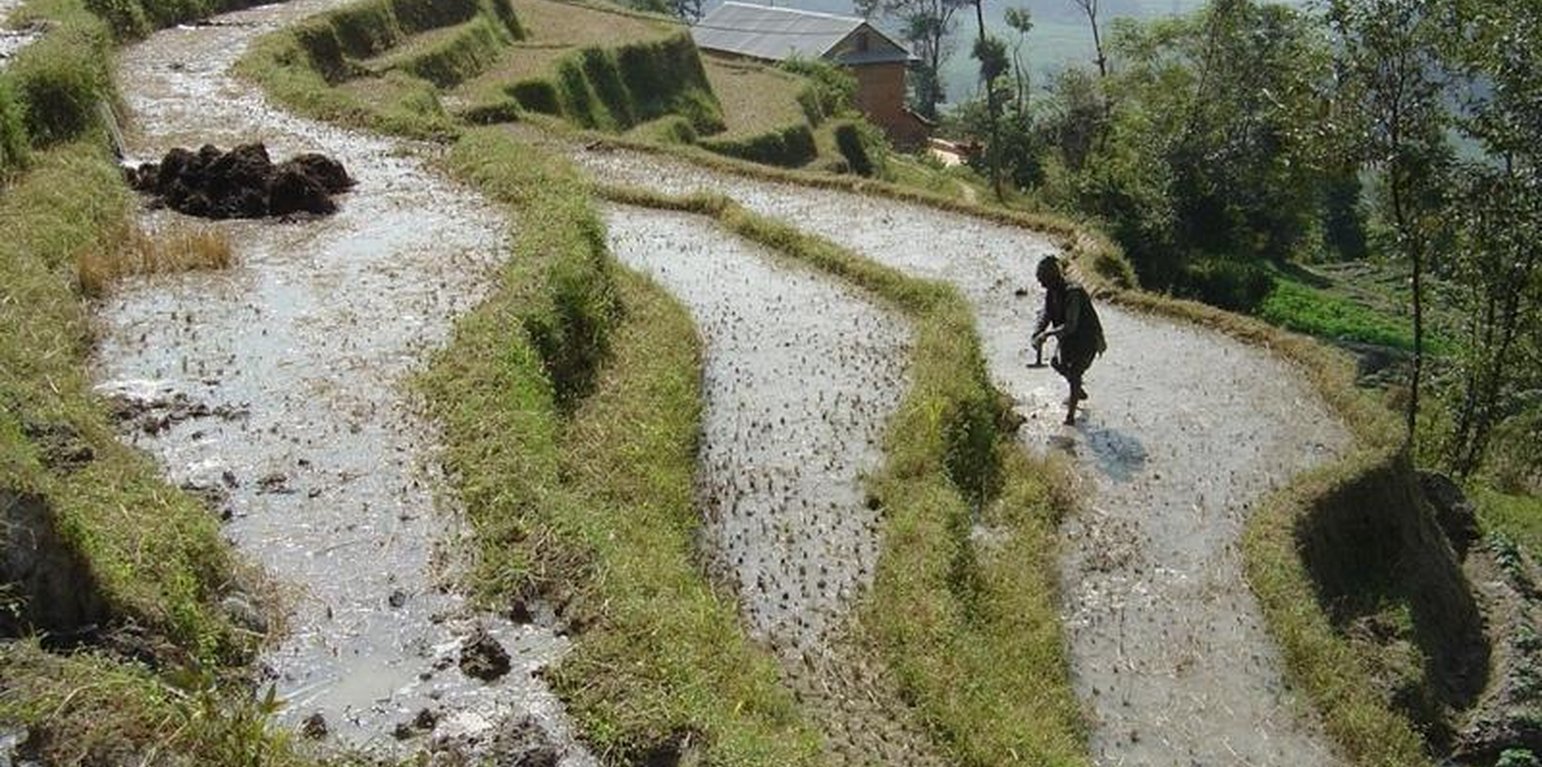




The level bench terrace is a traditional technology that makes irrigated crop production possible on steep, erosion prone slopes. The majority of such terraces in Nepal were constructed by hand many generations ago, but some new land - mostly already under rainfed cultivation on forward sloping terraces - is still being converted into irrigated terraces. The initial costs for the construction of the terraces are extremely high – and annual maintenance costs are considerable also. The climate is humid subtropical, slopes are steep (30%-60%) and soils generally have a sandy loam texture. Terraces are cropped by farmers who mostly have less than 0.5 ha of land each.
Two to three annual crops are grown per year starting with paddy rice during the monsoon, followed by potatoes and/or wheat.
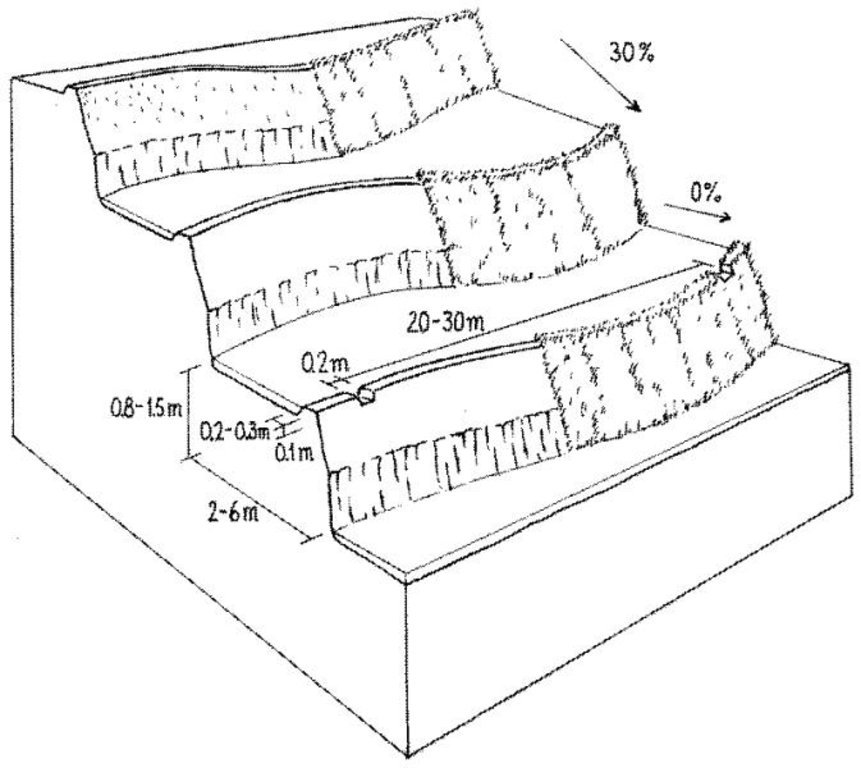
While terrace beds are usually 2–6 m in width, to save labour they are made as wide as they can be without increasing the danger of slips/land slides. Surveying was traditionally done by eye, but now a water-tube level may be used. Risers are 0.8-1.5 m high with a small lip (20-25 cm). The slope of the riser varies from 80 to 160%, depending on the initial gradient of the hill. Stones are incorporated in the risers if available, and grass species such as bermuda grass (Cynodon dactylon) and napier (Pennisetum purpureum) may be planted for stabilisation and as cattle fodder. The risers are compacted (with hoes) to improve ponding conditions for the paddy rice. Twice per year the risers are scraped with a special tool: (1) at the time of land preparation for paddy rice the lower part of riser is sliced, but the upper part is left protected with grasses against the monsoon rains; (2) at the time of wheat planting the whole riser (including the lip) is scraped and spread as green manure on the terrace.
Terraces are flooded with water for paddy rice cultivation: a smaller amount of water is diverted into the fields for other crops. Excess water is drained to the lower terrace by openings in the lip, which are filled with rice straw in order to filter out sediments. The depth of water for rice - when flooded completely - is normally between 10 and 15 cm. Fertility is maintained by addition of farmyard manure, spreading the scraped soil from the riser, and also through sediment carried in the irrigation water. Nowadays, mineral fertilizers are also applied.
الموقع: Manmata subwatershed, Kathmandu, النيبال
عدد مواقع تنفيذ التقنيةالتي تم تحليلها:
انتشار التقنية: منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة (1.0 km²)
في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
تاريخ التنفيذ:
نوع التقديم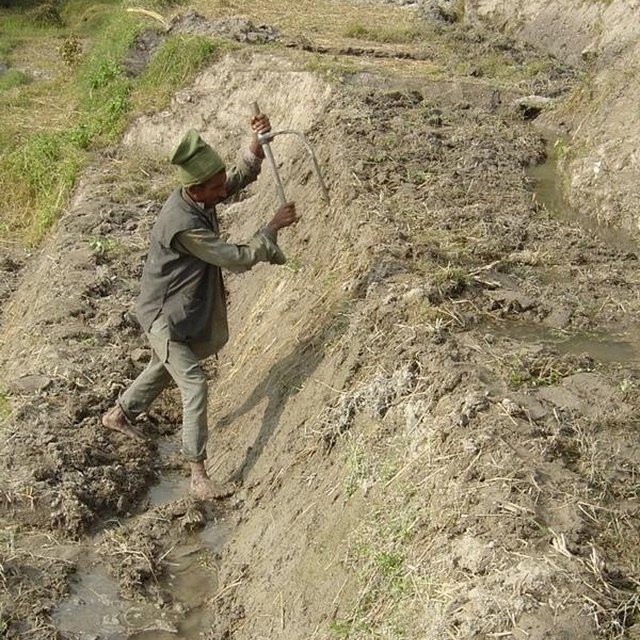





| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة (دولار أمريكي USD) | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل (دولار أمريكي USD) | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي |
| العمالة | |||||
| Labour | ha | 1,0 | 350,0 | 350,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | |||||
| Tools | ha | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | |||||
| Fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 185,0 | 185,0 | 100,0 |
| Compost/manure | ha | 1,0 | 300,0 | 300,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 840.0 | ||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 840.0 | ||||
the technology is a part of a complex farming system
not everyone has access to land for irrigation
when the agreed and scheduled water extraction amounts are exceeded
poor maintenance of topmost terraces may cause landslides
which in turn can cause pipe erosion and riser collapse