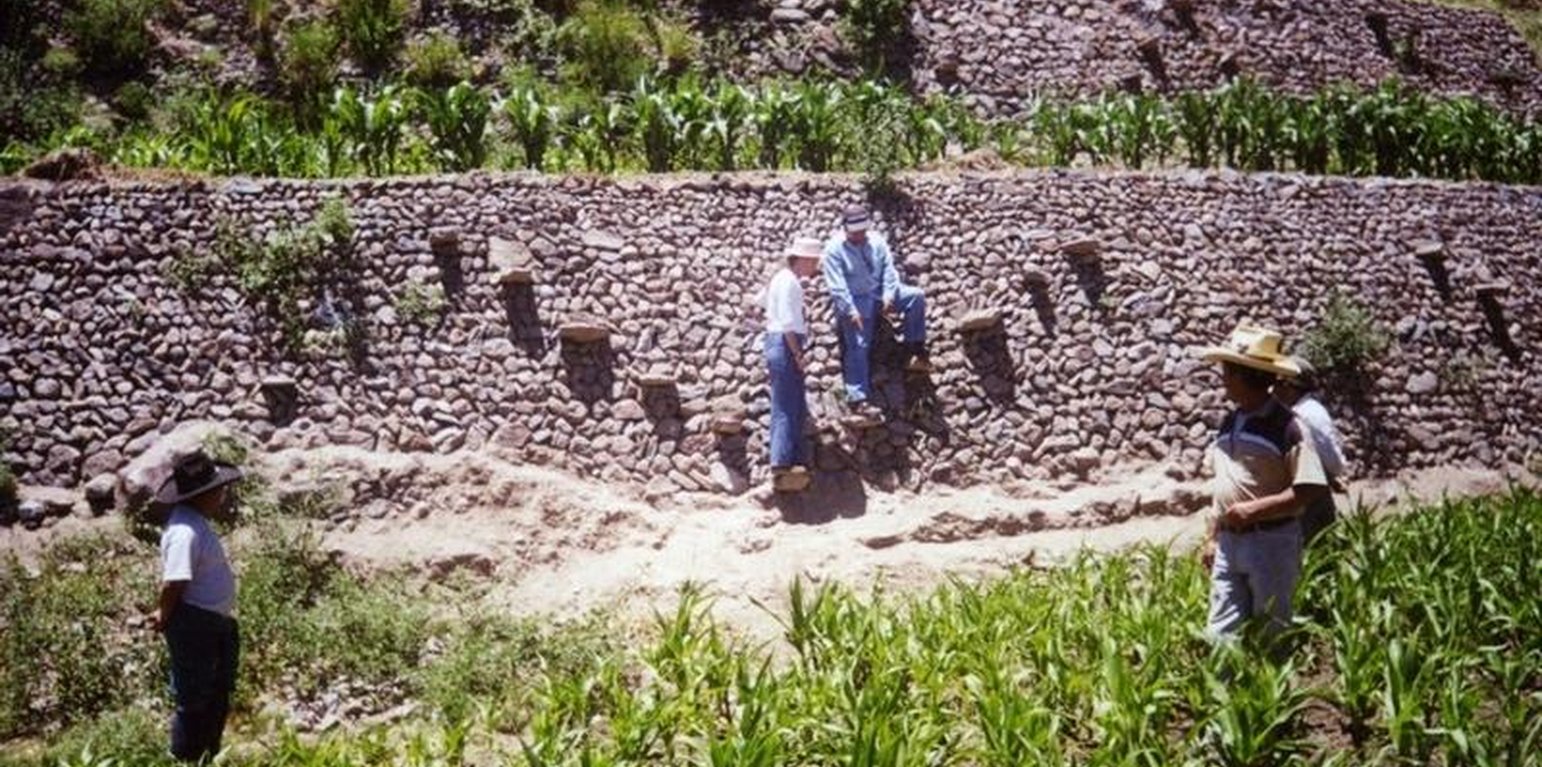
Rehabilitation of ancient terraces
(بيرو)
Andenes / Anchacas / Patapatas
الوصف
Repair of ancient stone wall bench terraces, and of an associated irrigation and drainage system.
The level bench terrace system in the Colca valley of Peru dates back to 600 years AD. Since then the terraces have been continuously used for crop production, but due to lack of maintenance they have deteriorated, and the population has lost its traditional knowledge of repair.
The rehabilitation of the terraces recreates their original structural design. Broken sections are cleared and the various materials - stones, topsoil, subsoil and weeds - are removed and separated. The foundation is re-established, followed by construction of the stone wall (the ‘riser’). Backfilling with subsoil then takes place; this is consolidated and finally covered with topsoil. Simultaneously the complementary irrigation and drainage systems are reconstructed.
The rehabilitated terraces efficiently conserve soil and water on steep slopes, and they create a favourable microclimate for crops, reducing loss of stored heat at night by minimising air movement (preventing frosts) and mitigating dry conditions through moisture conservation. The main economic benefits are from increased yields and crop diversification.
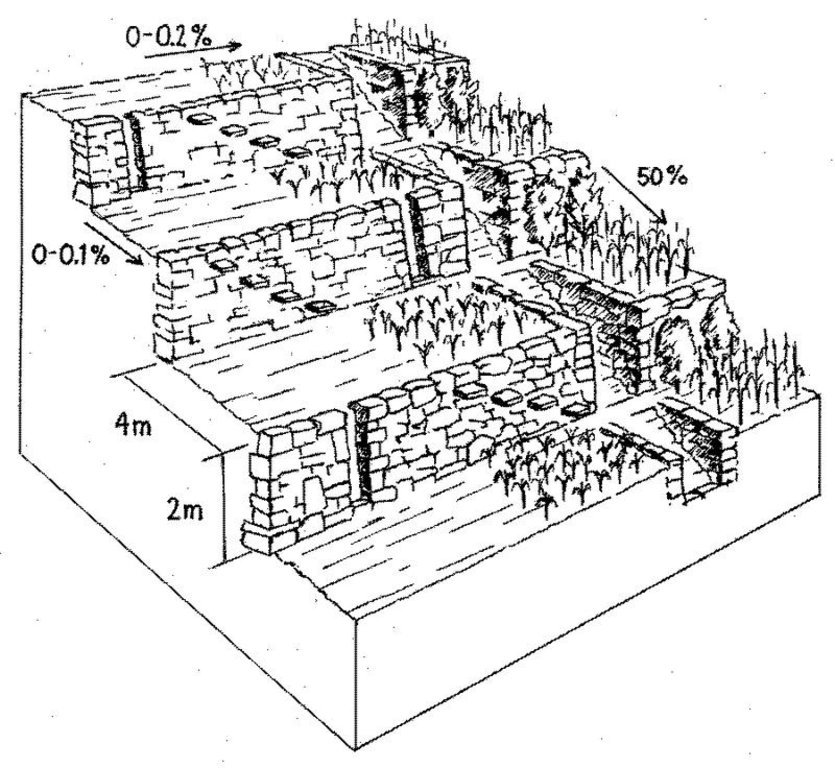
Terraces are spaced and sized according to slope, eg on a 50% slope, terraces are 4 m wide with a 2 m high riser between terrace beds. Stones of ancient terraces had been widely used to build walls for boundary marking after privatisation of land, therefore a large amount of stone had to be provided by splitting rocks and transporting from other locations.
The area is characterised by steep slopes with loamy-sandy, moderately deep soils (on the terrace beds). Most of the annual precipitation (ca. 350 mm) falls within a period of 3 months, which makes irrigation necessary. The farmers in the area own, on average, 1.2 hectares of arable land, divided into around six plots in different agro-ecological zones. Production is mainly for subsistence. Important supportive technologies include agronomic measures such as improved fallow, early tillage, ridging, and intercropping. Tree and shrub planting at the base of terrace walls is an optional measure with the aim of stabilising the walls, diversifying production and again ensuring a good microclimate. On average 250 trees/ha are planted; these are mainly native species such as c’olle (Buddleia spp.), mutuy (Cassia sp.), molle (Schinus molle: the ‘pepper tree’) and various fruit trees including capulí (Prunus salicifolia).
الموقع
الموقع: Río Colca,Caylloma, Arequipa, بيرو
عدد مواقع تنفيذ التقنيةالتي تم تحليلها:
المرجع الجغرافي للمواقع المختارة
انتشار التقنية:
في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
تاريخ التنفيذ:
نوع التقديم
-
من خلال ابتكار مستخدمي الأراضي
-
كجزء من النظام التقليدي (> 50 عامًا)
-
أثناء التجارب/الأبحاث
-
من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
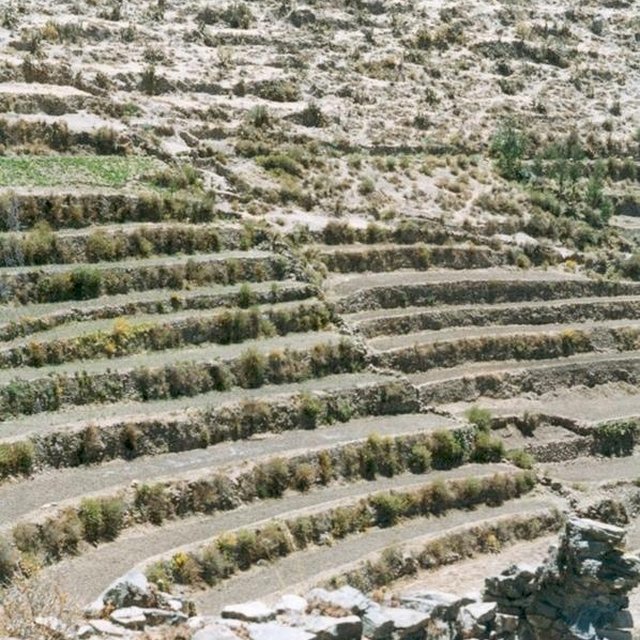

Abandoned terraces in the background clearly contrast with those recently rehabilitated. The agroforestry component (shrub rows along the terrace walls) is an optional supportive measure. (DESCO)
الغرض الرئيسي
-
تحسين الإنتاج
-
الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
-
الحفاظ على النظام البيئي
-
حماية مستجمعات المياه / المناطق الواقعة في اتجاه مجرى النهر - مع تقنيات أخرى
-
الحفاظ على/تحسين التنوع البيولوجي
-
الحد من مخاطر الكوارث
-
التكيف مع تغير المناخ/الظواهر المتطرفة وآثارها
-
التخفيف من تغير المناخ وآثاره
-
خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
-
خلق أثر اجتماعي مفيد
استخدام الأراضي
-
الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية: الحبوب - الذرة, محاصيل الأعلاف - البرسيم (الفصة), الحبوب البقولية والبقول- الفاصوليا, المحاصيل الجذرية/الدرنية - البطاطس
إمدادات المياه
-
بعلية
-
مختلط بعلي-مروي
-
ري كامل
الغرض المتعلق بتدهور الأراضي
-
منع تدهور الأراضي
-
الحد من تدهور الأراضي
-
اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
-
التكيف مع تدهور الأراضي
-
غير قابل للتطبيق
معالجة التدهور
-
تآكل التربة بالمياه - الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح, (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان
-
التدهور الكيميائي للتربة - (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)
-
تدهور المياه - (Ha): التجفيف
مجموعة الإدارة المستدامة للاراضي
-
التدابير المتقاطعة للمنحدرات
-
إدارة الري (بما في ذلك إمدادات المياه والصرف الصحي)
-
تحويل المياه والصرف
تدابير الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
-
التدابير البنيوية - S1: المصاطب المتدرجة
الرسم الفني
المواصفات الفنية
Rehabilitated ancient terraces with high stone risers. Two options for irrigation and drainage of excess water are shown: outlets in the risers (left) and a broad water channel cutting perpendicularly through the terraces (right).
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, increase of infiltration, water harvesting / increase water supply, improvement of microclimate
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, increase in organic matter, increase / maintain water stored in soil, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, improvement of soil structure
Author: Mats Gurtner
التأسيس والصيانة: الأنشطة والمدخلات والتكاليف
حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
- يتم حساب التكاليف:
- العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكلفة: غير متاح
- سعر الصرف (بالدولار الأمريكي): 1 دولار أمريكي = غير متاح
- متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم: غير متاح
أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
غير متاح
أنشطة التأسيس
-
Separation of materials of collapsed wall: subsoil, topsoil, stone, weeds. (التوقيت/الوتيرة: dry period.)
-
Cleaning and re-establishment of the foundation according to originalstructure. (التوقيت/الوتيرة: dry period.)
-
Cutting stones from rocks (blasting and splitting); transporting. (التوقيت/الوتيرة: dry period.)
-
Reconstruction of the stone wall, building on the basis of remainingintact structures of ancient terraces; simultaneous reconstructionof irrigation channels and complementary structures. (التوقيت/الوتيرة: dry period.)
-
Backfilling with subsoil, moistening soil and consolidation with motor (التوقيت/الوتيرة: dry period.)
-
Covering with fertile topsoil. (التوقيت/الوتيرة: dry period.)
-
Levelling of terrace bed and completion of riser edge (lip). (التوقيت/الوتيرة: dry period.)
-
Planting of trees below terrace walls (optional). (التوقيت/الوتيرة: dry period.)
-
Improved fallow, early tillage, ridging, and intercropping (supportivemeasures). (التوقيت/الوتيرة: dry period.)
مدخلات وتكاليف التأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات |
الوحدة |
الكمية |
التكاليف لكل وحدة (غير متاح) |
إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل (غير متاح) |
% من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي |
|
العمالة
|
| Labour |
ha |
1,0 |
560,0 |
560,0 |
40,0 |
| Construction supervisor (days) |
ha |
1,0 |
60,0 |
60,0 |
|
|
معدات
|
| Machine use |
ha |
1,0 |
180,0 |
180,0 |
40,0 |
| Tools |
ha |
1,0 |
300,0 |
300,0 |
40,0 |
|
المواد النباتية
|
| Seedlings |
ha |
1,0 |
100,0 |
100,0 |
|
|
مواد البناء
|
| Stone |
ha |
1,0 |
200,0 |
200,0 |
40,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية |
1'400.0 |
|
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي |
1'400.0 |
|
أنشطة الصيانة
-
Irrigation system cleaning. (التوقيت/الوتيرة: None)
-
Clearing weeds from stone wall (التوقيت/الوتيرة: (dry season)./)
-
Inspection of the stone walls’ stability (التوقيت/الوتيرة: (before sowing)./)
-
Repair structures (التوقيت/الوتيرة: (rainy season)./)
-
Tree and root pruning. (التوقيت/الوتيرة: None)
مدخلات وتكاليف الصيانة
| تحديد المدخلات |
الوحدة |
الكمية |
التكاليف لكل وحدة (غير متاح) |
إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل (غير متاح) |
% من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي |
|
العمالة
|
| Labour |
ha |
1,0 |
25,0 |
25,0 |
100,0 |
|
معدات
|
| Tools |
ha |
1,0 |
100,0 |
100,0 |
100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية |
125.0 |
|
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي |
125.0 |
|
المناخ الطبيعي
متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي
-
< 250 مم
-
251- 500 ملم
-
501 - 750ملم
-
1,000-751 ملم
-
1,500-1,100 ملم
-
2,000-1,500 ملم
-
3,000-2,001 ملم
-
4,000-3,100 ملم
-
> 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
-
رطبة
-
شبه رطبة
-
شبه قاحلة
-
قاحلة
المواصفات الخاصة بالمناخ
غير متاح
المنحدر
-
مسطح (0-2%)
-
بسيط (3-5%)
-
معتدل (6-10%)
-
متدحرج (11-15%)
-
تلال (16-30%)
-
شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
-
فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس
-
هضاب/سهول
-
أثلام مرتفعة
-
المنحدرات الجبلية
-
منحدرات التلال
-
منحدرات في السفوح
-
قاع الوادي
الارتفاع
-
100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
-
500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
-
1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
-
1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
-
2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
-
2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
-
3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
-
4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
-
> 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
يتم تطبيق التقنية في
-
حالات محدبة أو نتؤات
-
حالات مقعرة
-
غير ذات صلة
عمق التربة
-
ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
-
ضحلة (21-50 سم)
-
متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
-
عميقة (81-120 سم)
-
عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية)
-
خشن / خفيف (رملي)
-
متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
-
ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح)
-
خشن / خفيف (رملي)
-
متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
-
ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
محتوى المادة العضوية في التربة السطحية
-
عالية (>3%)
-
متوسطة (1-3%)
-
منخفضة (<1%)
مستوى المياه الجوفية
-
سطحية
-
< 5 م
-
50-5 م
-
> 50 م
توافر المياه السطحية
-
زائدة
-
جيد
-
متوسط
-
ضعيف/ غير متوافر
جودة المياه (غير المعالجة)
-
مياه شرب جيدة
-
مياه الشرب سيئة (تتطلب معالجة)
-
للاستخدام الزراعي فقط (الري)
-
غير صالحة للإستعمال
هل تمثل الملوحة مشكلة؟
حدوث الفيضانات
خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي
-
الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
-
مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
-
تجاري/سوق
الدخل من خارج المزرعة
-
أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
-
10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
-
>50% من إجمالي الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة
-
ضعيف جدا
-
ضعيف
-
متوسط
-
ثري
-
ثري جدا
مستوى المكننة
-
عمل يدوي
-
الجر الحيواني
-
ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
مستقر أو مرتحل
-
غير المترحل
-
شبه مرتحل
-
مرتحل
أفراد أو مجموعات
-
فرد/أسرة معيشية
-
المجموعات/ المجتمع المحلي
-
تعاونية
-
موظف (شركة، حكومة)
العمر
-
أطفال
-
شباب
-
متوسط العمر
-
كبار السن
المساحة المستخدمة لكل أسرة
-
< 0.5 هكتارا
-
0.5 - 1 هكتار
-
1 -2 هكتار
-
2 - 5 هكتار
-
5 - 15 هكتار
-
15 - 50 هكتار
-
50 - 100هكتار
-
500-100 هكتار
-
1,000-500 هكتار
-
10,000-1,000 هكتار
-
> 10,000 هكتار
الحجم
-
على نطاق صغير
-
على نطاق متوسط
-
على نطاق واسع
ملكية الارض
-
دولة
-
شركة
-
مجتمعي/قروي
-
لمجموعة
-
فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
-
فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي
-
وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
-
مجتمعي (منظم)
-
مؤجر
-
فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه
-
وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
-
مجتمعي (منظم)
-
مؤجر
-
فردي
الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الآثار
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
إدارة الأراضي
Careful management required (water and livestock)
عبء العمل
Easier crop management (level bench, alignment of crops). On the other hand increased labour constraints: heavy work, const. Maintenance. Heavy work by establishment
Efficiency
Efficient use of irrigation water and fertilizers
Ccarcity of stones (in some places)
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
Regular crop growth and development
Improved microclimate
Reduced wind; conserving heat
الآثار خارج الموقع
تدفقات مجاري مائية موثوقة ومستقرة في موسم الجفاف (بما في ذلك التدفقات المنخفضة)
الفيضانات في اتجاه مجرى النهر (غير مرغوب فيها)
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
تحليل التكلفة والعائد
العوائد مقارنة بتكاليف التأسيس
العوائد مقارنة بتكاليف الصيانة
التبني والتكيف
نسبة مستخدمي الأراضي في المنطقة الذين تبنوا التقنية
-
حالات فردية/تجريبية
-
1-10%
-
11-50%
-
> 50%
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم منهم فعلوا ذلك دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية؟
-
10-0%
-
11-50%
-
51-90%
-
91-100%
عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحة المغطاة
240
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟
مع أي من الظروف المتغيرة؟
-
تغير المناخ / التطرف
-
الأسواق المتغيرة
-
توفر العمالة (على سبيل المثال بسبب الهجرة)
الاستنتاجات والدروس المستفادة
نقاط القوة: وجهة نظر مستخدم الأرض
-
Facilitation of crop management activities (crop alignment, easier tillage with oxen plough, efficiency of pest control, etc)
How can they be sustained / enhanced? Appropriate crop management (see measures mentioned in description).
-
Improved microclimate facilitates crop growth and crop diversification
How can they be sustained / enhanced? Complete with improved agronomic practices and agroforestry.
-
Increased yields and food security
How can they be sustained / enhanced? Conserve crop diversity and genetic variety.
-
Cultural heritage
How can they be sustained / enhanced? Conservation of traditional practices
-
Facilitation of crop management activities (crop alignment, easier tillage with oxen plough, efficiency of pest control, etc)-->Appropriate crop management (see measures mentioned in description). - Improved microclimate facilitates crop growth and crop diversification-->Complete with improved agronomic practices and agroforestry. - Increased yields and food security-->Conserve crop diversity and genetic variety Cultural heritage-->Conservation of traditional practices.
نقاط القوة: وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات
-
Traditional technology is of great value and adapted to local conditions
How can they be sustained / enhanced? Awareness raising of the local population on maintenance of terraces.
-
Successful implementation is product of evaluation, analysis and documentation
of experiences
How can they be sustained / enhanced? Further appraisal of the technology.
-
Soil maintained on steep slopes, no soil loss due to water erosion
How can they be sustained / enhanced? Continuous maintenance and appropriate management through training.
-
More efficient use of irrigation/rain water, longer storage of soil moisture
How can they be sustained / enhanced? Permanent maintenance of structure.
-
Maintenance of soil fertility
How can they be sustained / enhanced? Recycling of organic matter.
نقاط الضعف / المساوىء / المخاطر: وجهة نظر مستخدم الأرضكيفية التغلب عليها
-
Vulnerability of terraces to damage by grazing animals
Do not allow grazing on short terraces with high stone walls.
-
Land users are not skilled in repair of broken sections in the terrace system
More training on maintenance and conservation.
-
Vulnerability of terraces to damage by grazing animals-->Do not allow grazing on short terraces with high stone walls. - Land users are not skilled in repair of broken sections in the terrace system-->More training on maintenance and conservation. Editors’ comments: Terracing systems on hillsides date back to the beginning of agriculture. Often these feature walls (‘risers’) built of stone, and sometimes they are used for irrigation – as in this case from Peru. While many ancient systems have fallen into disrepair with out-migration of rural populations, this is an example of project-based rehabilitation.
نقاط الضعف / المساوىء / المخاطر: وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلوماتكيفية التغلب عليها
-
Specialised work, not easy to carry out – complex system of different
structures
Promote applied research and extension.
-
High rehabilitation costs; increased by loss of traditional forms of reciprocal
work, and a trend towards individualism
Reactivate and strengthen
traditional labour systems based on reciprocity and mutual help.
-
Limited availability of stones impedes the rehabilitation process
Carry
stones from adjacent or remote places, give training in rock splitting.
-
Not appropriate for use of agricultural machines
Awareness creation.
-
Private properties, but not titled
Promote the legalisation of titles to
facilitate the access to credit and technical assistance.
المراجع
المُراجع
-
Fabian Ottiger
-
Alexandra Gavilano
تاريخ التوثيق: 8 يونيو، 2011
اخر تحديث: 13 يونيو، 2019
الأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات
-
Rodolfo Marquina - متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
الوصف الكامل في قاعدة بيانات WOCAT
بيانات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي المرتبطة
تم تسهيل التوثيق من قِبَل
المؤسسة
- Centro de Estudios y Promoción del Desarrollo (DESCO) - بيرو
المشروع
- Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)
المراجع الرئيسية
-
Mejia Marcacuzco AP Folleto de divulgación: Andenes, construcción y mantenimiento. (undated).:
-
Treacy, JM (undated) LasChacras de Coporaque: Andenes y riego en el valle del Colca. Instituto de Estudios Peruanos. DESCO:












